Abstract
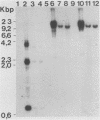
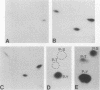
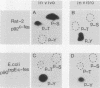
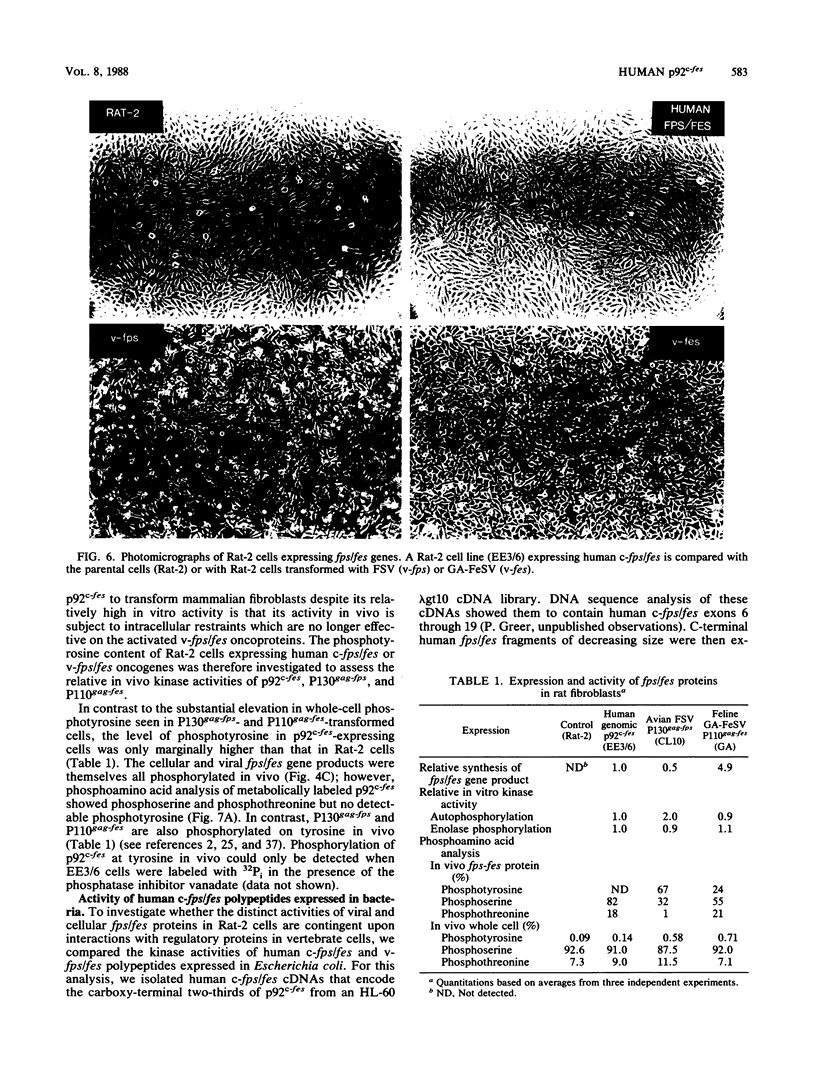
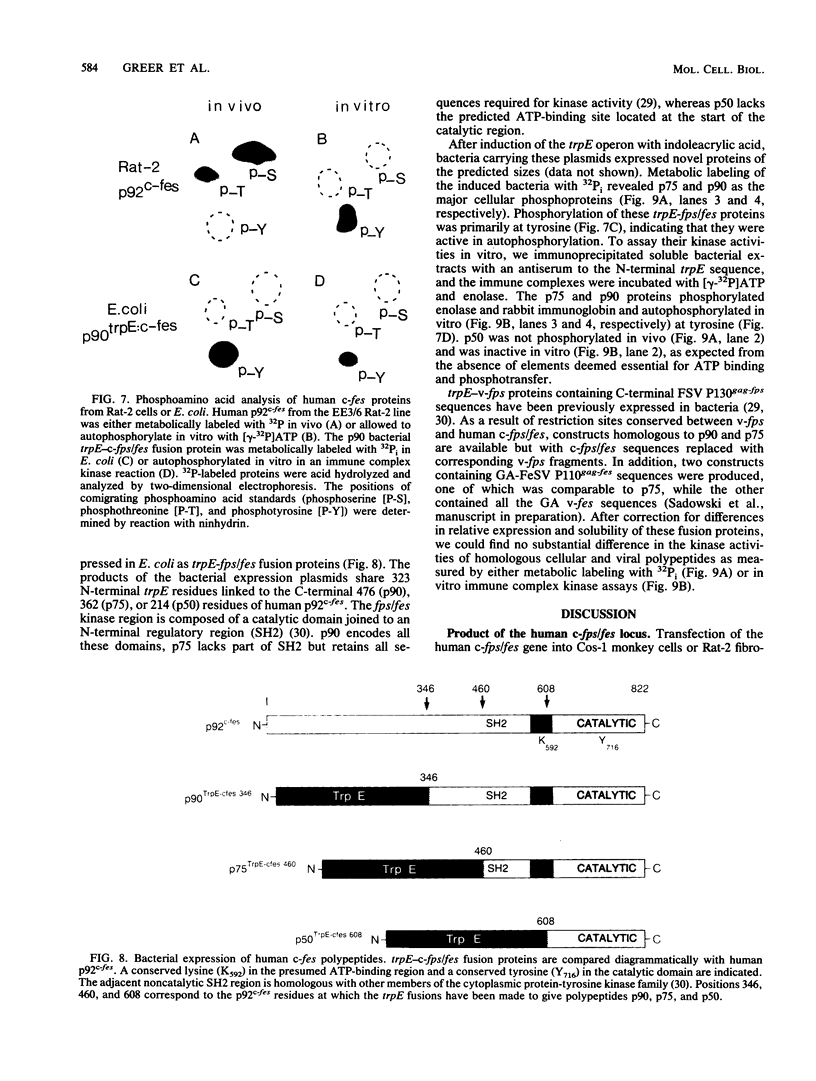
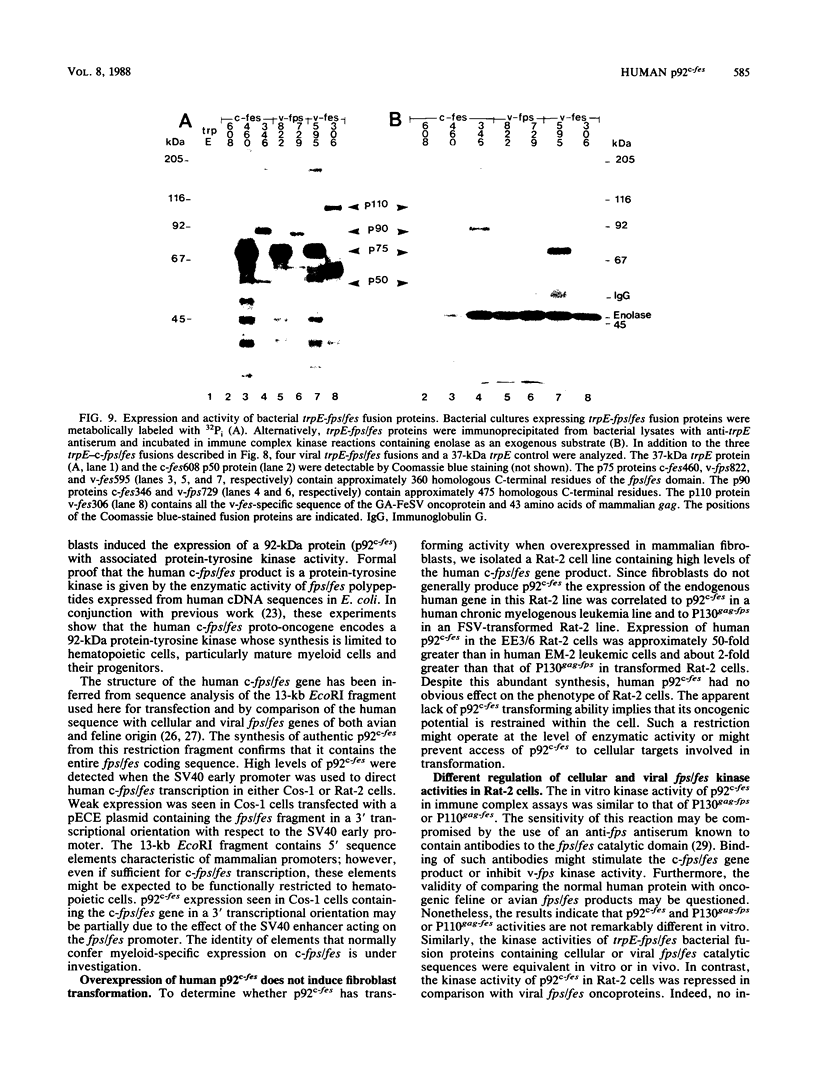
A 13-kilobase EcoRI genomic restriction fragment containing the human c-fps/fes proto-oncogene locus was expressed transiently in Cos-1 monkey cells and stably in Rat-2 fibroblasts. In both cases, human c-fps/fes directed synthesis of a 92-kilodalton protein-tyrosine kinase (p92c-fes) indistinguishable from a tyrosine kinase previously identified with anti-fps antiserum which is specifically expressed in human myeloid cells. Transfected Rat-2 cells containing approximately 50-fold more human p92c-fes than is found in human leukemic cells remained morphologically normal and failed to grow in soft agar. Synthesis of p92c-fes in this phenotypically normal line exceeded that of the P130gag-fps oncoprotein in a v-fps-transformed Rat-2 line. Despite this elevated expression, human p92c-fes induced no substantial increase in cellular phosphotyrosine and was not itself phosphorylated on tyrosine. In contrast, p92c-fes immunoprecipitated from these Rat-2 cells or expressed as an enzymatically active fragment in Escherichia coli from a c-fps/fes cDNA catalyzed tyrosine phosphorylation with an activity similar to that of v-fps/fes polypeptides. Thus, p92c-fes is not transforming when ectopically overexpressed in Rat-2 fibroblasts. This lack of transforming activity correlates with a restriction imposed on the kinase activity of the normal c-fps/fes product in vivo which is apparently lifted for v-fps/fes oncoproteins, suggesting that regulatory interactions within the host cell modify fps/fes protein function and normally restrain its oncogenic potential.
Full text
PDF

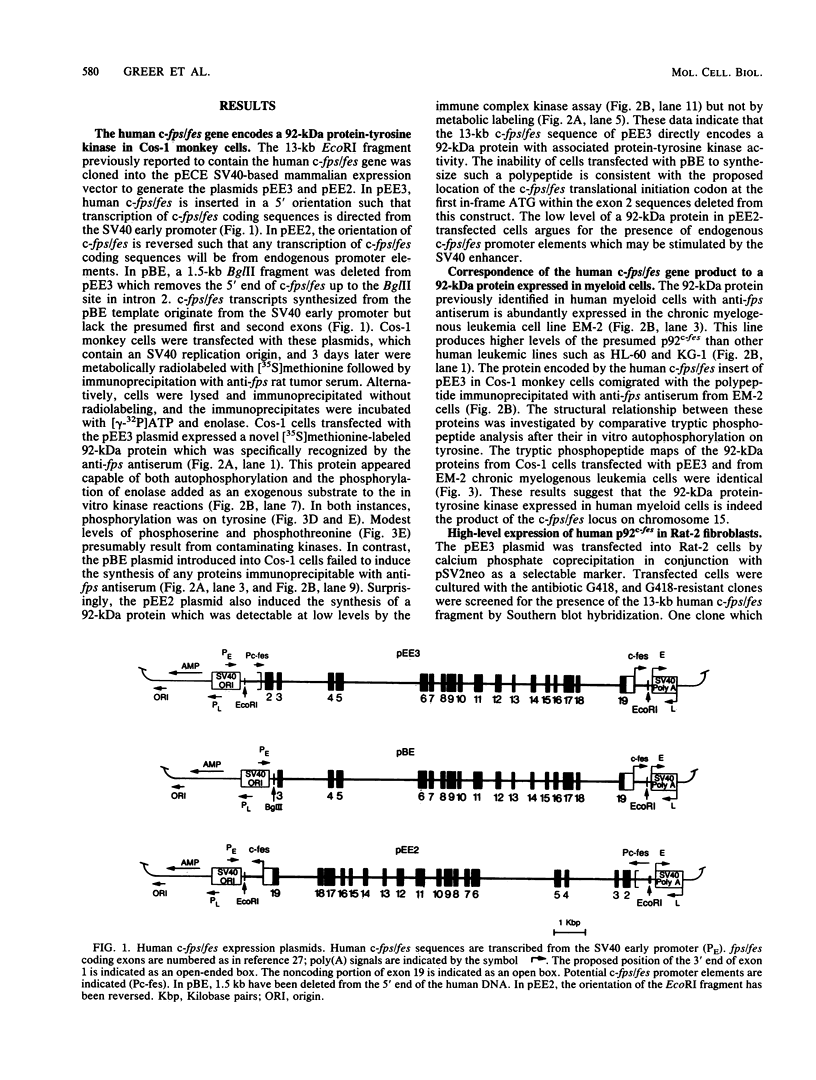


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbacid M., Breitman M. L., Lauver A. V., Long L. K., Vogt P. K. The transformation-specific proteins of avian (Fujinami and PRC-II) and feline (Synder--Theilen and Gardner--Arnstein) sarcoma viruses are immunologically related. Virology. 1981 Apr 30;110(2):411–419. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90071-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbacid M., Lauver A. V., Devare S. G. Biochemical and immunological characterization of polyproteins coded for by the McDonough, Gardner-Arnstein, and Snyder-Theilen strains of feline sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):196–207. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.196-207.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S. J., Gallo R. C., Gallagher R. E. Continuous growth and differentiation of human myeloid leukaemic cells in suspension culture. Nature. 1977 Nov 24;270(5635):347–349. doi: 10.1038/270347a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Esch F. S., Taylor S. S., Hunter T. Phosphorylation sites in enolase and lactate dehydrogenase utilized by tyrosine protein kinases in vivo and in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7835–7841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Gould K. L., Cartwright C. A., Hunter T. Tyr527 is phosphorylated in pp60c-src: implications for regulation. Science. 1986 Mar 21;231(4744):1431–1434. doi: 10.1126/science.2420005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Sefton B. M., Hunter T. Detection and quantification of phosphotyrosine in proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1983;99:387–402. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)99075-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coussens P. M., Cooper J. A., Hunter T., Shalloway D. Restriction of the in vitro and in vivo tyrosine protein kinase activities of pp60c-src relative to pp60v-src. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2753–2763. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis L., Clauser E., Morgan D. O., Edery M., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. Replacement of insulin receptor tyrosine residues 1162 and 1163 compromises insulin-stimulated kinase activity and uptake of 2-deoxyglucose. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90786-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman R. A., Gabrilove J. L., Tam J. P., Moore M. A., Hanafusa H. Specific expression of the human cellular fps/fes-encoded protein NCP92 in normal and leukemic myeloid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2379–2383. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman R. A., Tam J. P., Hanafusa H. Antipeptide antiserum identifies a widely distributed cellular tyrosine kinase related to but distinct from the c-fps/fes-encoded protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1065–1073. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster D. A., Shibuya M., Hanafusa H. Activation of the transformation potential of the cellular fps gene. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):105–115. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80106-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulkes J. G., Chow M., Gorka C., Frackelton A. R., Jr, Baltimore D. Purification and characterization of a protein-tyrosine kinase encoded by the Abelson murine leukemia virus. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 5;260(13):8070–8077. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franchini G., Gelmann E. P., Dalla-Favera R., Gallo R. C., Wong-Staal F. Human gene (c-fes) related to the onc sequences of Snyder-Theilen feline sarcoma virus. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Aug;2(8):1014–1019. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.8.1014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
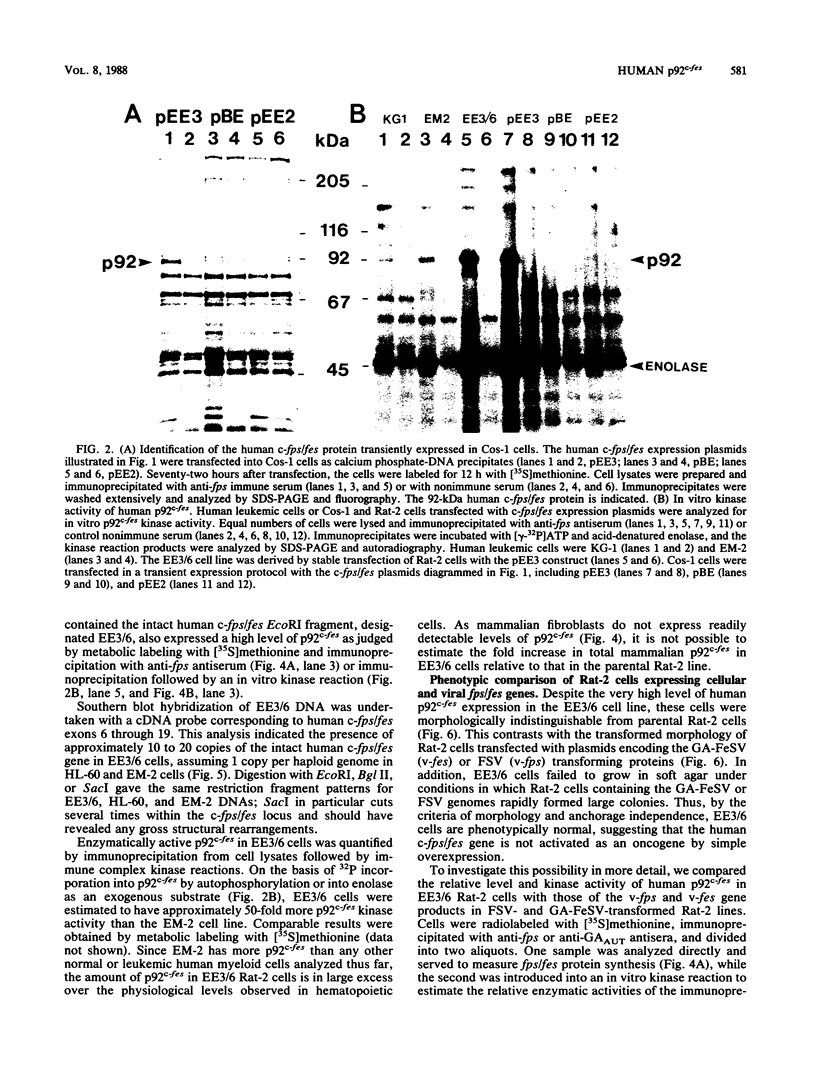
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groffen J., Heisterkamp N., Grosveld F., Van de Ven W., Stephenson J. R. Isolation of human oncogene sequences (v-fes homolog) from a cosmid library. Science. 1982 Jun 4;216(4550):1136–1138. doi: 10.1126/science.6281890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groffen J., Heisterkamp N., Shibuya M., Hanafusa H., Stephenson J. R. Transforming genes of avian (v-fps) and mammalian (v-fes) retroviruses correspond to a common cellular locus. Virology. 1983 Mar;125(2):480–486. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90219-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. C., Hammond C., Bishop J. M. Nucleotide sequence and topography of chicken c-fps. Genesis of a retroviral oncogene encoding a tyrosine-specific protein kinase. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jan 20;181(2):175–186. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90083-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Cooper J. A. Protein-tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:897–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingman-Baker J., Hinze E., Levy J. G., Pawson T. Monoclonal antibodies to the transforming protein of Fujinami avian sarcoma virus discriminate between different fps-encoded proteins. J Virol. 1984 May;50(2):572–578. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.2.572-578.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kmiecik T. E., Shalloway D. Activation and suppression of pp60c-src transforming ability by mutation of its primary sites of tyrosine phosphorylation. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):65–73. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90756-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeffler H. P., Golde D. W. Acute myelogenous leukemia: a human cell line responsive to colony-stimulating activity. Science. 1978 Jun 9;200(4346):1153–1154. doi: 10.1126/science.306682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald I., Levy J., Pawson T. Expression of the mammalian c-fes protein in hematopoietic cells and identification of a distinct fes-related protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2543–2551. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathey-Prevot B., Hanafusa H., Kawai S. A cellular protein is immunologically crossreactive with and functionally homologous to the Fujinami sarcoma virus transforming protein. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):897–906. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90069-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meckling-Hansen K., Nelson R., Branton P., Pawson T. Enzymatic activation of Fujinami sarcoma virus gag-fps transforming proteins by autophosphorylation at tyrosine. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):659–666. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04805.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roebroek A. J., Schalken J. A., Onnekink C., Bloemers H. P., Van de Ven W. J. Structure of the feline c-fes/fps proto-oncogene: genesis of a retroviral oncogene. J Virol. 1987 Jun;61(6):2009–2016. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.6.2009-2016.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roebroek A. J., Schalken J. A., Verbeek J. S., Van den Ouweland A. M., Onnekink C., Bloemers H. P., Van de Ven W. J. The structure of the human c-fes/fps proto-oncogene. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2897–2903. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04020.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roussel M. F., Dull T. J., Rettenmier C. W., Ralph P., Ullrich A., Sherr C. J. Transforming potential of the c-fms proto-oncogene (CSF-1 receptor). Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):549–552. doi: 10.1038/325549a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski I., Pawson T. Catalytic and non-catalytic domains of the Fujinami sarcoma virus P130gag-fps protein-tyrosine kinase distinguished by the expression of v-fps polypeptides in Escherichia coli. Oncogene. 1987 May;1(2):181–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski I., Stone J. C., Pawson T. A noncatalytic domain conserved among cytoplasmic protein-tyrosine kinases modifies the kinase function and transforming activity of Fujinami sarcoma virus P130gag-fps. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4396–4408. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samarut J., Mathey-Prevot B., Hanafusa H. Preferential expression of the c-fps protein in chicken macrophages and granulocytic cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):1067–1072. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.1067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. F., Hare D. L., Cecchini M. A., Weinberg R. A. Construction of a novel oncogene based on synthetic sequences encoding epidermal growth factor. Science. 1987 Jan 16;235(4786):321–324. doi: 10.1126/science.3492043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone J. C., Atkinson T., Smith M., Pawson T. Identification of functional regions in the transforming protein of Fujinami sarcoma virus by in-phase insertion mutagenesis. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):549–558. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90385-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topp W. C. Normal rat cell lines deficient in nuclear thymidine kinase. Virology. 1981 Aug;113(1):408–411. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90168-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van de Ven W. J., Reynolds F. H., Jr, Stephenson J. R. The nonstructural components of polyproteins encoded by replication-defective mammalian transforming retroviruses are phosphorylated and have associated protein kinase activity. Virology. 1980 Feb;101(1):185–197. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90495-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinmaster G., Hinze E., Pawson T. Mapping of multiple phosphorylation sites within the structural and catalytic domains of the Fujinami avian sarcoma virus transforming protein. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):29–41. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.29-41.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinmaster G., Pawson T. Protein kinase activity of FSV (Fujinami sarcoma virus) P130gag-fps shows a strict specificity for tyrosine residues. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):328–333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinmaster G., Zoller M. J., Smith M., Hinze E., Pawson T. Mutagenesis of Fujinami sarcoma virus: evidence that tyrosine phosphorylation of P130gag-fps modulates its biological activity. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):559–568. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90386-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. C., Martin G. S. Cellular localization of c-fps gene product NCP98. J Virol. 1984 Dec;52(3):913–918. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.3.913-918.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]