Abstract
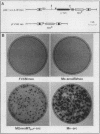
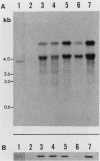
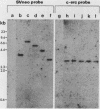
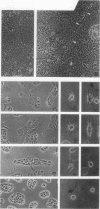
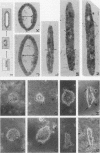
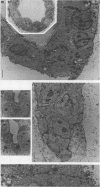
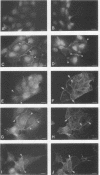
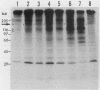
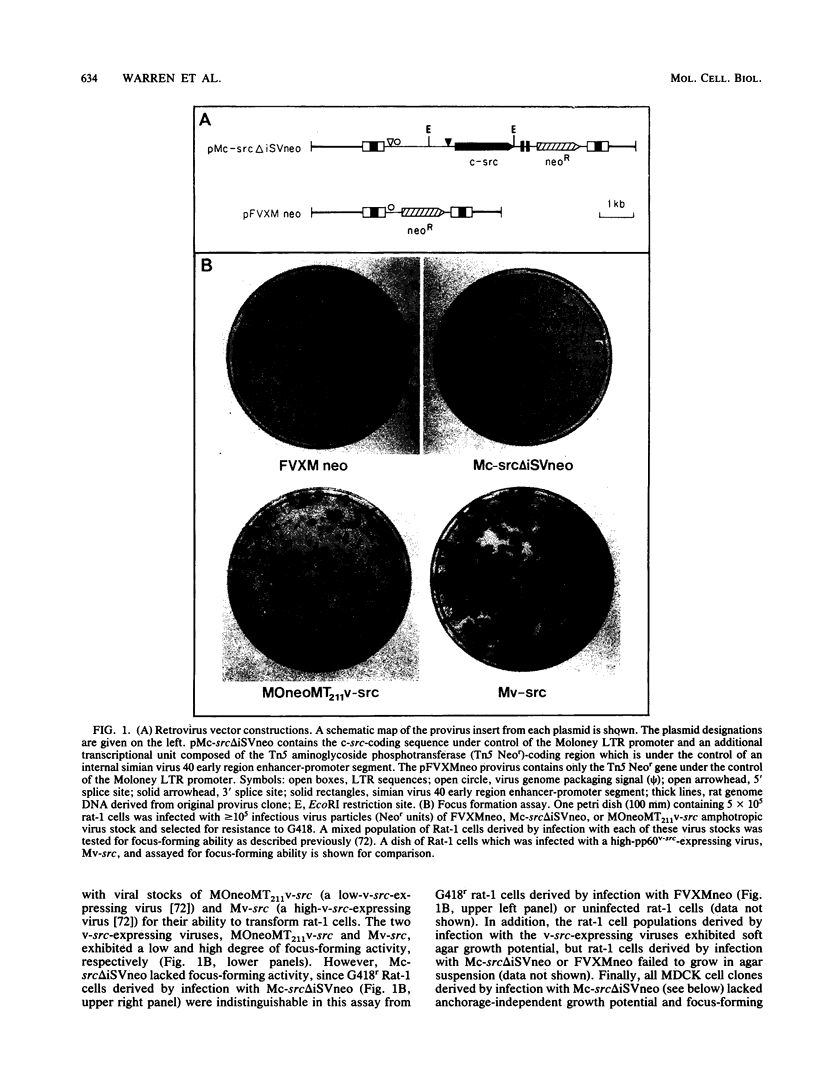
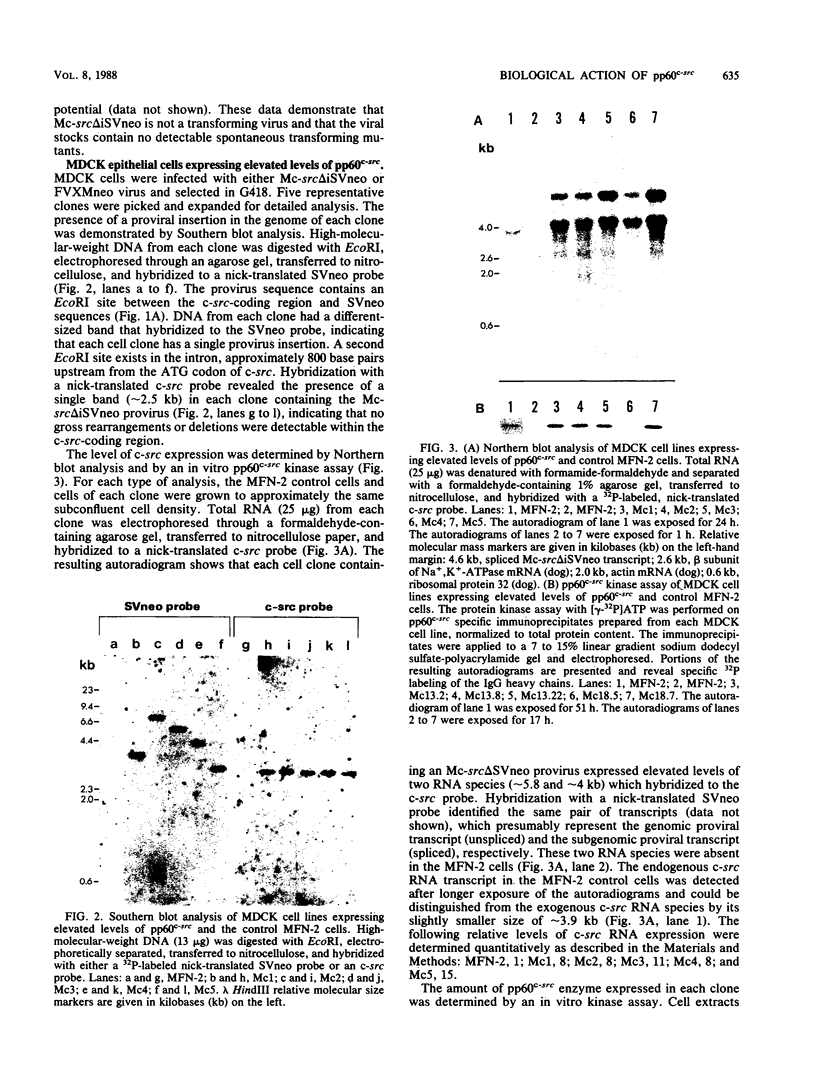
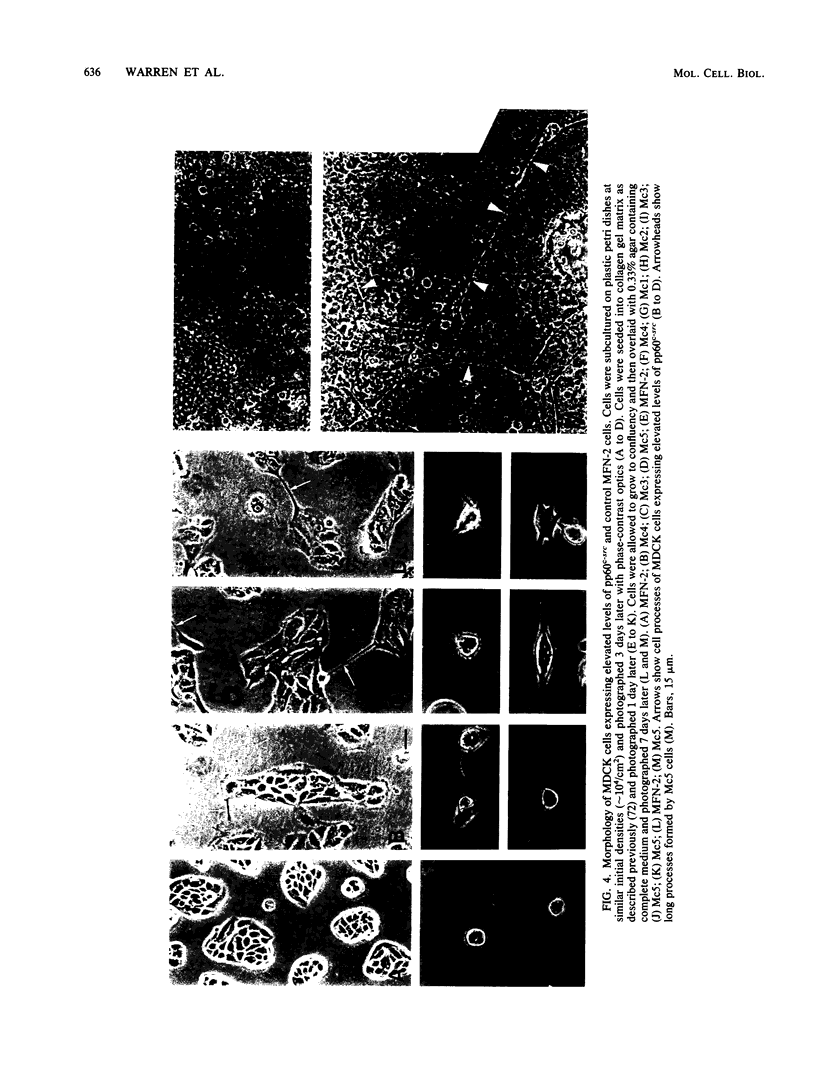
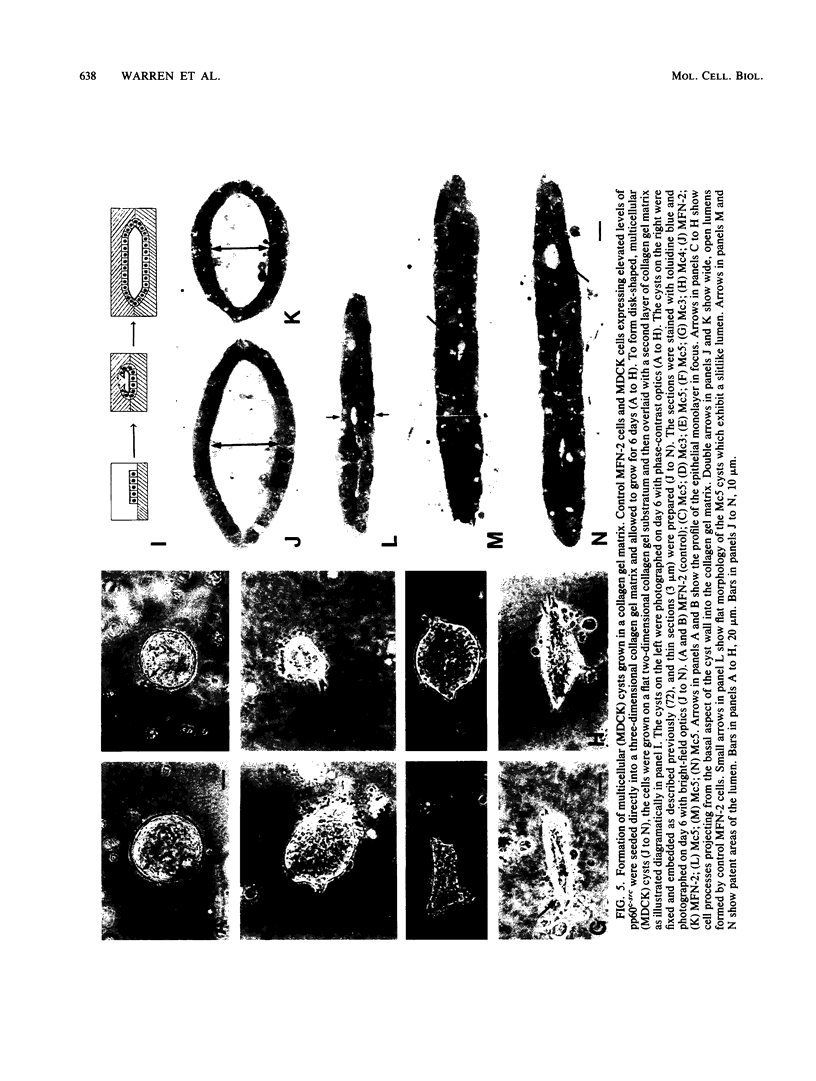
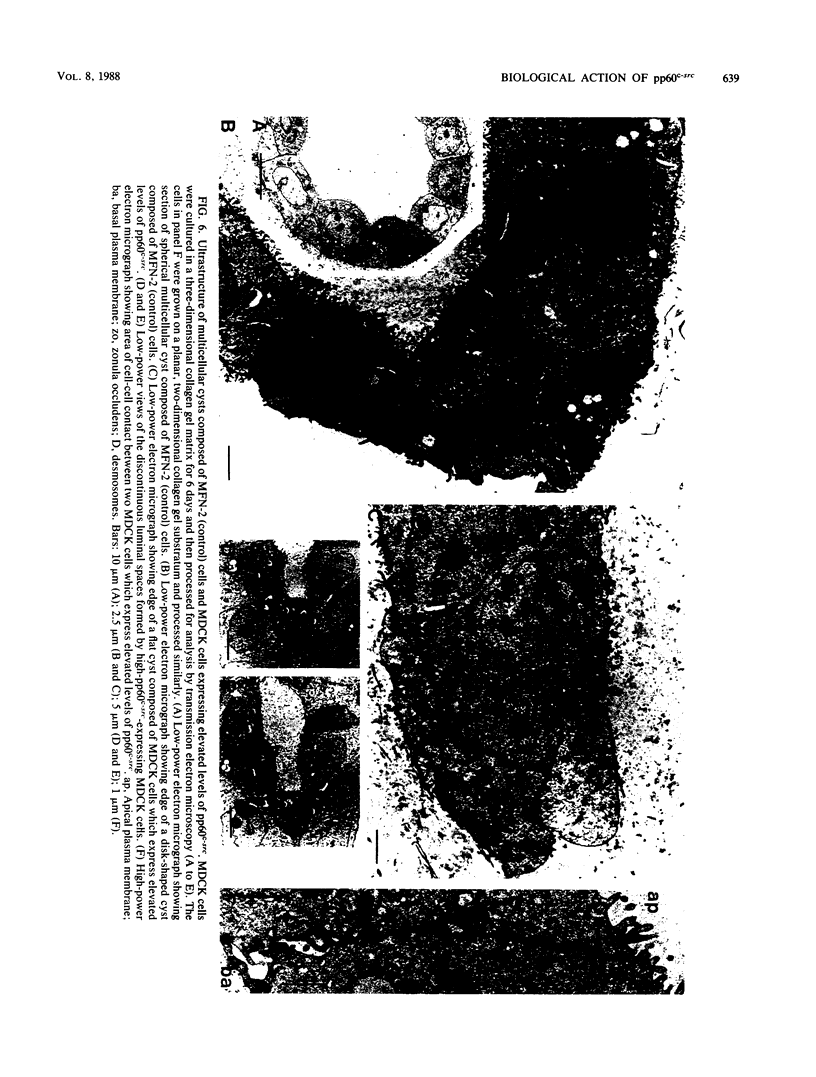
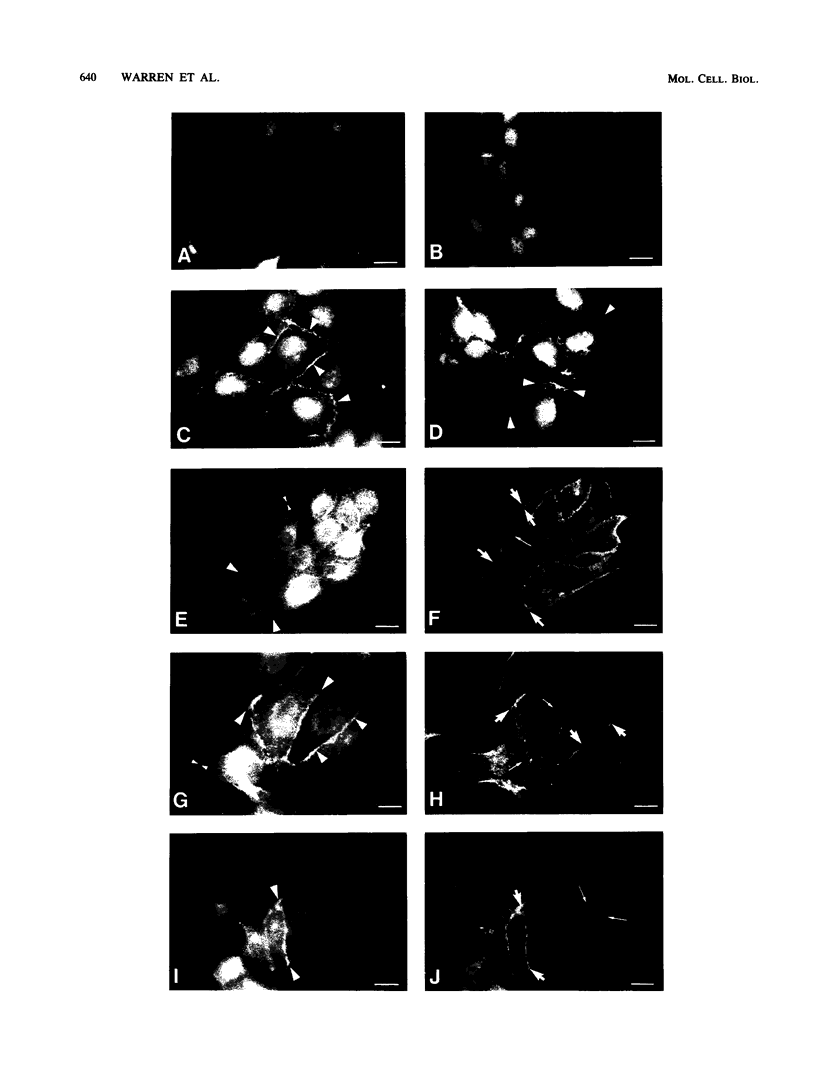
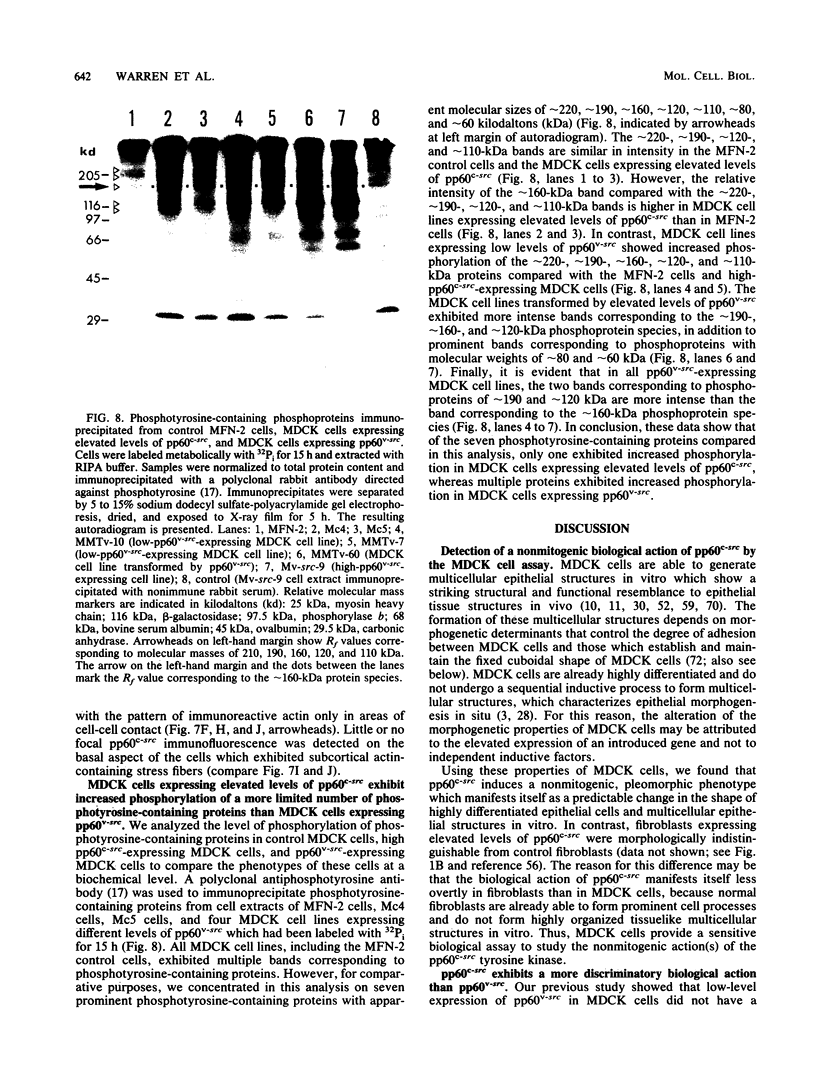
Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cells are highly differentiated and have retained the morphogenetic properties necessary to form polarized, multicellular epithelial structures (cysts) in vitro that resemble epithelial tissues in vivo. We introduced the c-src gene into MDCK cells to elevate the level of the plasma membrane-associated cellular tyrosine kinase, pp60c-src, to levels two- to ninefold higher than that expressed in parent MDCK cells. Our results revealed a highly discriminatory biological action of pp60c-src on the morphogenetic properties of MDCK cells. Elevated expression of pp60c-src conferred on MDCK cells the ability to undergo dramatic changes of cell shape that includes the formation of long cell processes (100 to 200 microns), never observed in control MDCK cells. The morphogenesis of multicellular epithelial cysts was altered by elevated levels of pp60c-src and led to predictable distortions of their three-dimensional architecture. However, these cells established morphologically normal cell polarity, formed adhesive epithelial cell-cell contacts indistinguishable from those of control MDCK cells, and exhibited neither focus-forming ability or anchorage-independent growth potential. Finally, we showed that MDCK cells expressing elevated levels of pp60c-src exhibit increased phosphorylation of a more limited number of phosphotyrosine-containing proteins than MDCK cells expressing pp60v-src. We suggest that a natural function of pp60c-src is to regulate the morphogenetic properties which determine the shape of differentiated cells and multicellular structures.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnekow A., Gessler M. Activation of the pp60c-src kinase during differentiation of monomyelocytic cells in vitro. EMBO J. 1986 Apr;5(4):701–705. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04270.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernfield M. R., Wessells N. K. Intra- and extracellular control of epithelial morphogenesis. Symp Soc Dev Biol. 1970;29:195–249. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-395534-0.50014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M. Cellular oncogenes and retroviruses. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:301–354. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.001505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugge J. S., Cotton P. C., Queral A. E., Barrett J. N., Nonner D., Keane R. W. Neurones express high levels of a structurally modified, activated form of pp60c-src. Nature. 1985 Aug 8;316(6028):554–557. doi: 10.1038/316554a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugge J. S., Erikson E., Erikson R. L. Antibody to virion structural proteins in mammals bearing avian sarcoma virus-induced tumors. Virology. 1978 Feb;84(2):429–433. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90259-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugge J. S., Erikson R. L. Identification of a transformation-specific antigen induced by an avian sarcoma virus. Nature. 1977 Sep 22;269(5626):346–348. doi: 10.1038/269346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess D. R. Reactivation of intestinal epithelial cell brush border motility: ATP-dependent contraction via a terminal web contractile ring. J Cell Biol. 1982 Dec;95(3):853–863. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.3.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHN Z. A., BENSON B. THE DIFFERENTIATION OF MONONUCLEAR PHAGOCYTES. MORPHOLOGY, CYTOCHEMISTRY, AND BIOCHEMISTRY. J Exp Med. 1965 Jan 1;121:153–170. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.1.153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright C. A., Eckhart W., Simon S., Kaplan P. L. Cell transformation by pp60c-src mutated in the carboxy-terminal regulatory domain. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):83–91. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90758-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cereijido M., Ehrenfeld J., Meza I., Martínez-Palomo A. Structural and functional membrane polarity in cultured monolayers of MDCK cells. J Membr Biol. 1980;52(2):147–159. doi: 10.1007/BF01869120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cereijido M., Robbins E. S., Dolan W. J., Rotunno C. A., Sabatini D. D. Polarized monolayers formed by epithelial cells on a permeable and translucent support. J Cell Biol. 1978 Jun;77(3):853–880. doi: 10.1083/jcb.77.3.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S., Erikson R. L. Protein kinase activity associated with the avian sarcoma virus src gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):2021–2024. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.2021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cone R. D., Mulligan R. C. High-efficiency gene transfer into mammalian cells: generation of helper-free recombinant retrovirus with broad mammalian host range. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6349–6353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotton P. C., Brugge J. S. Neural tissues express high levels of the cellular src gene product pp60c-src. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;3(6):1157–1162. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.6.1157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ek B., Heldin C. H. Use of an antiserum against phosphotyrosine for the identification of phosphorylated components in human fibroblasts stimulated by platelet-derived growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 10;259(17):11145–11152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARQUHAR M. G., PALADE G. E. Junctional complexes in various epithelia. J Cell Biol. 1963 May;17:375–412. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.2.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRENCH J. E., MACFARLANE R. G., SANDERS A. G. THE STRUCTURE OF HAEMOSTATIC PLUGS AND EXPERIMENTAL THROMBI IN SMALL ARTERIES. Br J Exp Pathol. 1964 Oct;45:467–474. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUJITA S. ANALYSIS OF NEURON DIFFERENTIATION IN THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM BY TRITIATED THYMIDINE AUTORADIOGRAPHY. J Comp Neurol. 1964 Jun;122:311–327. doi: 10.1002/cne.901220303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fults D. W., Towle A. C., Lauder J. M., Maness P. F. pp60c-src in the developing cerebellum. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):27–32. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gee C. E., Griffin J., Sastre L., Miller L. J., Springer T. A., Piwnica-Worms H., Roberts T. M. Differentiation of myeloid cells is accompanied by increased levels of pp60c-src protein and kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5131–5135. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiger B., Avnur Z., Rinnerthaler G., Hinssen H., Small V. J. Microfilament-organizing centers in areas of cell contact: cytoskeletal interactions during cell attachment and locomotion. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;99(1 Pt 2):83s–91s. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.1.83s. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiger B., Dutton A. H., Tokuyasu K. T., Singer S. J. Immunoelectron microscope studies of membrane-microfilament interactions: distributions of alpha-actinin, tropomyosin, and vinculin in intestinal epithelial brush border and chicken gizzard smooth muscle cells. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 1):614–628. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilead Z., Jeng Y. H., Wold W. S., Sugawara K., Rho H. M., Harter M. L., Green M. Immunological identification of two adenovirus 2-induced early proteins possibly involved in cell transformation. Nature. 1976 Nov 18;264(5583):263–266. doi: 10.1038/264263a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden A., Nemeth S. P., Brugge J. S. Blood platelets express high levels of the pp60c-src-specific tyrosine kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):852–856. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonda T. J., Sheiness D. K., Bishop J. M. Transcripts from the cellular homologs of retroviral oncogenes: distribution among chicken tissues. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Jun;2(6):617–624. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.6.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gumbiner B., Simons K. A functional assay for proteins involved in establishing an epithelial occluding barrier: identification of a uvomorulin-like polypeptide. J Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;102(2):457–468. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.2.457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall H. G., Farson D. A., Bissell M. J. Lumen formation by epithelial cell lines in response to collagen overlay: a morphogenetic model in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4672–4676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath J. P., Dunn G. A. Cell to substratum contacts of chick fibroblasts and their relation to the microfilament system. A correlated interference-reflexion and high-voltage electron-microscope study. J Cell Sci. 1978 Feb;29:197–212. doi: 10.1242/jcs.29.1.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T. A tail of two src's: mutatis mutandis. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90745-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Cooper J. A. Protein-tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:897–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs C., Rübsamen H. Expression of pp60c-src protein kinase in adult and fetal human tissue: high activities in some sarcomas and mammary carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1983 Apr;43(4):1696–1702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. J., Coussens P. M., Danko A. V., Shalloway D. Overexpressed pp60c-src can induce focus formation without complete transformation of NIH 3T3 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):1073–1083. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.1073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karfunkel P. The mechanisms of neural tube formation. Int Rev Cytol. 1974;38(0):245–271. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60927-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller T. C., 3rd, Mooseker M. S. Ca++-calmodulin-dependent phosphorylation of myosin, and its role in brush border contraction in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1982 Dec;95(3):943–959. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.3.943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kmiecik T. E., Shalloway D. Activation and suppression of pp60c-src transforming ability by mutation of its primary sites of tyrosine phosphorylation. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):65–73. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90756-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriegler M., Perez C. F., Hardy C., Botchan M. Transformation mediated by the SV40 T antigens: separation of the overlapping SV40 early genes with a retroviral vector. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):483–491. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90503-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy B. T., Sorge L. K., Meymandi A., Maness P. F. pp60c-src Kinase is in chick and human embryonic tissues. Dev Biol. 1984 Jul;104(1):9–17. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90031-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. B., Iba H., Hanafusa H. Activation of the transforming potential of p60c-src by a single amino acid change. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4228–4232. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsich L. A., Lewis A. J., Brugge J. S. Isolation of monoclonal antibodies that recognize the transforming proteins of avian sarcoma viruses. J Virol. 1983 Nov;48(2):352–360. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.2.352-360.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch S. A., Brugge J. S., Levine J. M. Induction of altered c-src product during neural differentiation of embryonal carcinoma cells. Science. 1986 Nov 14;234(4778):873–876. doi: 10.1126/science.3095923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maness P. F., Sorge L. K., Fults D. W. An early developmental phase of pp60c-src expression in the neural ectoderm. Dev Biol. 1986 Sep;117(1):83–89. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90350-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann R., Mulligan R. C., Baltimore D. Construction of a retrovirus packaging mutant and its use to produce helper-free defective retrovirus. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):153–159. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90344-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchesi V. T. Stabilizing infrastructure of cell membranes. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:531–561. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.002531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misfeldt D. S., Hamamoto S. T., Pitelka D. R. Transepithelial transport in cell culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1212–1216. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mooseker M. S. Organization, chemistry, and assembly of the cytoskeletal apparatus of the intestinal brush border. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:209–241. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.001233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson W. J., Veshnock P. J. Dynamics of membrane-skeleton (fodrin) organization during development of polarity in Madin-Darby canine kidney epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;103(5):1751–1765. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.5.1751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppermann H., Levinson A. D., Varmus H. E., Levintow L., Bishop J. M. Uninfected vertebrate cells contain a protein that is closely related to the product of the avian sarcoma virus transforming gene (src). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1804–1808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R. C., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Expression of v-src and chicken c-src in rat cells demonstrates qualitative differences between pp60v-src and pp60c-src. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):131–139. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90308-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piwnica-Worms H., Saunders K. B., Roberts T. M., Smith A. E., Cheng S. H. Tyrosine phosphorylation regulates the biochemical and biological properties of pp60c-src. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):75–82. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90757-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodewald R., Newman S. B., Karnovsky M. J. Contraction of isolated brush borders from the intestinal epithelium. J Cell Biol. 1976 Sep;70(3):541–554. doi: 10.1083/jcb.70.3.541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr Growth and differentiated properties of a kidney epithelial cell line (MDCK). Am J Physiol. 1981 Mar;240(3):C106–C109. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1981.240.3.C106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schartl M., Barnekow A. The expression in eukaryotes of a tyrosine kinase which is reactive with pp60v-src antibodies. Differentiation. 1982;23(2):109–114. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1982.tb01273.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalloway D., Coussens P. M., Yaciuk P. Overexpression of the c-src protein does not induce transformation of NIH 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7071–7075. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. A., Drees B., Kornberg T., Bishop J. M. The nucleotide sequence and the tissue-specific expression of Drosophila c-src. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):831–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90279-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons K., Fuller S. D. Cell surface polarity in epithelia. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:243–288. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.001331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorge L. K., Levy B. T., Maness P. F. pp60c-src is developmentally regulated in the neural retina. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):249–257. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90218-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spooner B. S., Wessells N. K. An analysis of salivary gland morphogenesis: role of cytoplasmic microfilaments and microtubules. Dev Biol. 1972 Jan;27(1):38–54. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(72)90111-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanstrom R., Parker R. C., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Transduction of a cellular oncogene: the genesis of Rous sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2519–2523. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeya T., Hanafusa H. Structure and sequence of the cellular gene homologous to the RSV src gene and the mechanism for generating the transforming virus. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):881–890. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentich J. D., Tchao R., Leighton J. Hemicyst formation stimulated by cyclic AMP in dog kidney cell line MDCK. J Cell Physiol. 1979 Aug;100(2):291–304. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041000210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vardimon L., Fox L. E., Moscona A. A. Accumulation of c-src mRNA is developmentally regulated in embryonic neural retina. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):4109–4111. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.4109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren S. L., Nelson W. J. Nonmitogenic morphoregulatory action of pp60v-src on multicellular epithelial structures. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1326–1337. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeds A. Actin-binding proteins--regulators of cell architecture and motility. Nature. 1982 Apr 29;296(5860):811–816. doi: 10.1038/296811a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wehland J., Osborn M., Weber K. Cell-to-substratum contacts in living cells: a direct correlation between interference-reflexion and indirect-immunofluorescence microscopy using antibodies against actin and alpha-actinin. J Cell Sci. 1979 Jun;37:257–273. doi: 10.1242/jcs.37.1.257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessells N. K., Spooner B. S., Ash J. F., Bradley M. O., Luduena M. A., Taylor E. L., Wrenn J. T., Yamada K. Microfilaments in cellular and developmental processes. Science. 1971 Jan 15;171(3967):135–143. doi: 10.1126/science.171.3967.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker M. B. The functioning of blood platelets. Sci Am. 1980 Jun;242(6):86–103. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0680-86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuckerman S. H., Douglas S. D. Dynamics of the macrophage plasma membrane. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1979;33:267–307. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.33.100179.001411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]