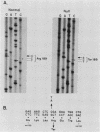
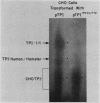
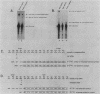
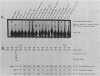
Abstract
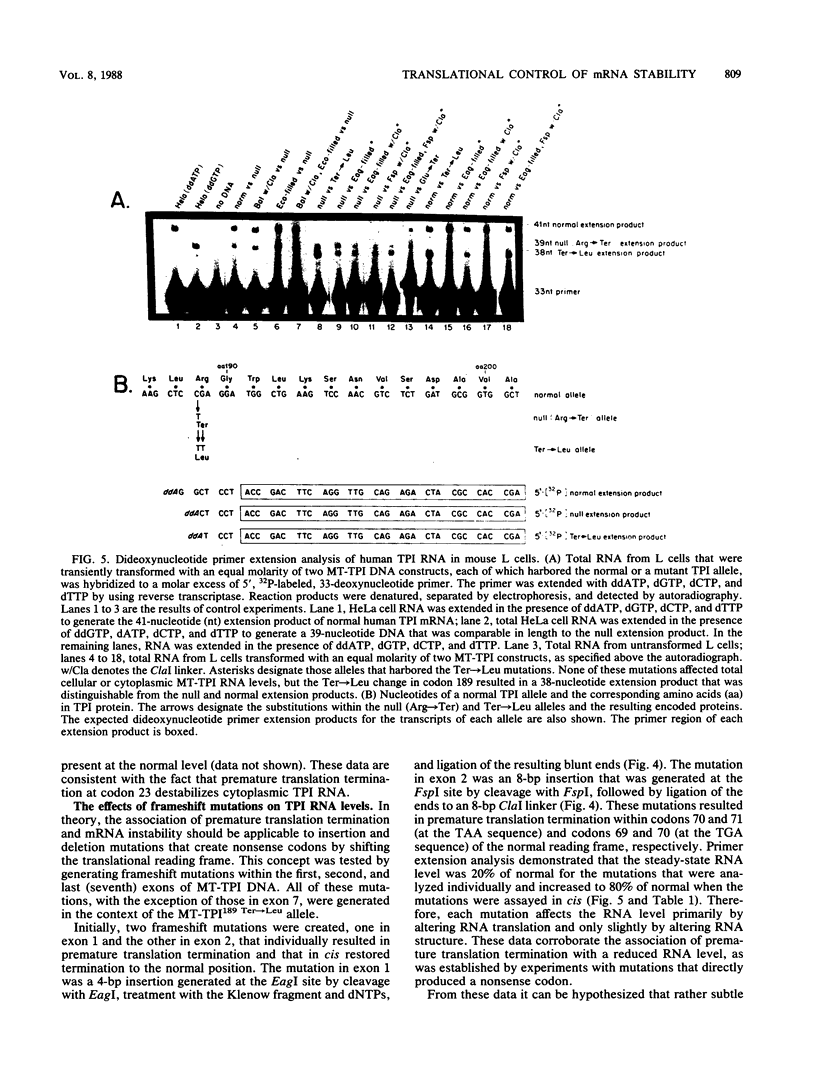
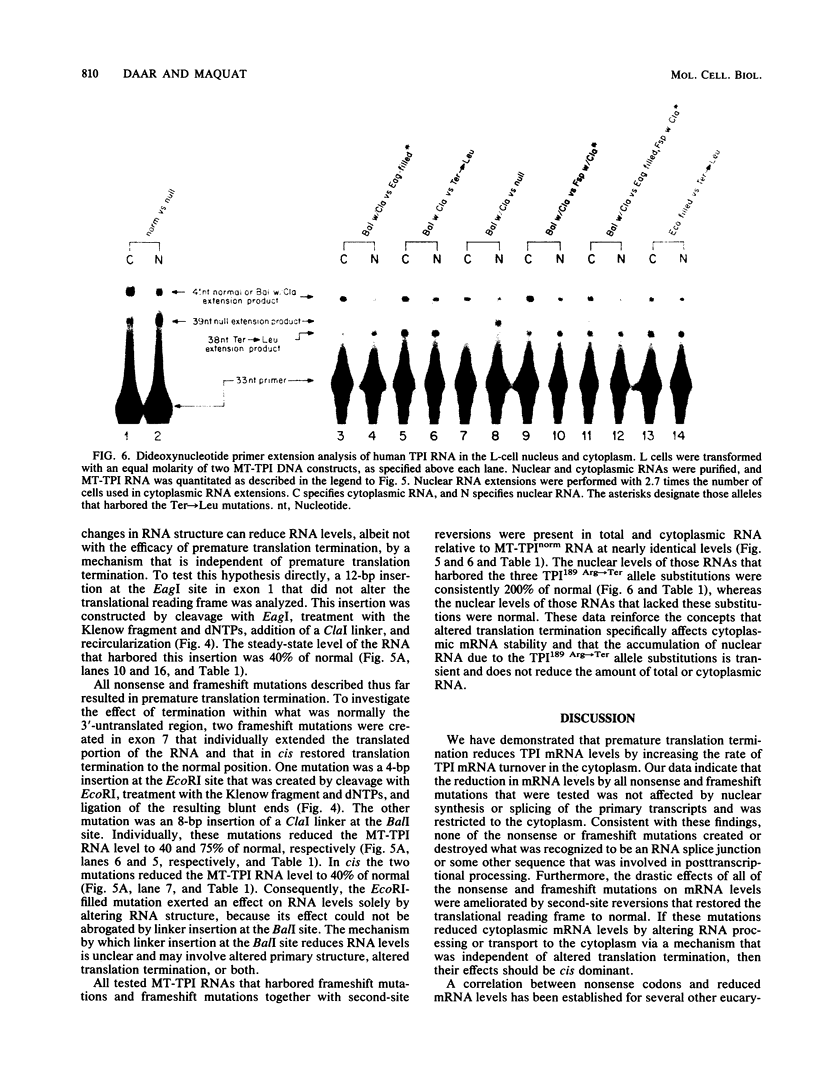
We characterized an anemia-inducing mutation in the human gene for triosephosphate isomerase (TPI) that resulted in the production of prematurely terminated protein and mRNA with a reduced cytoplasmic half-life. The mutation converted a CGA arginine codon to a TGA nonsense codon and generated a protein of 188 amino acids, instead of the usual 248 amino acids. To determine how mRNA primary structure and translation influence mRNA stability, in vitro-mutagenized TPI alleles were introduced into cultured L cells and analyzed for their effect on TPI RNA metabolism. Results indicated that mRNA stability is decreased by all nonsense and frameshift mutations. To determine the relative contribution of the changes in mRNA structure and translation to the altered half-life, the effects of individual mutations were compared with the effects of second-site reversions that restored translation termination to normal. All mutations that resulted in premature translation termination reduced the mRNA half-life solely or mainly by altering the length of the mRNA that was translated. The only mutation that altered translation termination and that reduced the mRNA half-life mainly by affecting the mRNA structure was an insertion that shifted termination to a position downstream of the normal stop codon.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alber T., Banner D. W., Bloomer A. C., Petsko G. A., Phillips D., Rivers P. S., Wilson I. A. On the three-dimensional structure and catalytic mechanism of triose phosphate isomerase. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1981 Jun 26;293(1063):159–171. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1981.0069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alber T., Kawasaki G. Nucleotide sequence of the triose phosphate isomerase gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(5):419–434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Artavanis-Tsakonas S., Harris J. I. Primary structure of triosephosphate isomerase from Bacillus stearothermophilus. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jul;108(2):599–611. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04755.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerji J., Olson L., Schaffner W. A lymphocyte-specific cellular enhancer is located downstream of the joining region in immunoglobulin heavy chain genes. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):729–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D., Schafer M., White R. Restriction sites containing CpG show a higher frequency of polymorphism in human DNA. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):131–138. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90081-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann B., Potash M. J., Köhler G. Consequences of frameshift mutations at the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus of the mouse. EMBO J. 1985 Feb;4(2):351–359. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03636.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bechhofer D. H., Dubnau D. Induced mRNA stability in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(2):498–502. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.2.498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawerman G. Determinants of messenger RNA stability. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):5–6. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90346-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brostrom K. Unstable-haemoglobin haemolytic anaemia. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1976 May;65(3):397–400. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1976.tb04904.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. R., Daar I. O., Krug J. R., Maquat L. E. Characterization of the functional gene and several processed pseudogenes in the human triosephosphate isomerase gene family. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1694–1706. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunn H. F., Schmidt G. J., Haney D. N., Dluhy R. G. Hemoglobin Cranston, an unstable variant having an elongated beta chain due to nonhomologous crossover between two normal beta chain genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3609–3613. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang J. C., Kan Y. W. beta 0 thalassemia, a nonsense mutation in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2886–2889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clay S. A., Shore N. A., Landing B. H. Triosephosphate isomerase deficiency. A case report with neuropathological findings. Am J Dis Child. 1982 Sep;136(9):800–802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corran P. H., Waley S. G. The amino acid sequence of rabbit muscle triose phosphate isomerase. Biochem J. 1975 Feb;145(2):335–344. doi: 10.1042/bj1450335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daar I. O., Artymiuk P. J., Phillips D. C., Maquat L. E. Human triose-phosphate isomerase deficiency: a single amino acid substitution results in a thermolabile enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7903–7907. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubnau D. Translational attenuation: the regulation of bacterial resistance to the macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin B antibiotics. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1984;16(2):103–132. doi: 10.3109/10409238409102300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fallon A. M., Jinks C. S., Strycharz G. D., Nomura M. Regulation of ribosomal protein synthesis in Escherichia coli by selective mRNA inactivation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3411–3415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furth A. J., Milman J. D., Priddle J. D., Offord R. E. Studies on the subunit structure and amino acid sequence of trisoe phosphate isomerase from chicken breast muscle. Biochem J. 1974 Apr;139(1):11–22. doi: 10.1042/bj1390011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glanville N., Durnam D. M., Palmiter R. D. Structure of mouse metallothionein-I gene and its mRNA. Nature. 1981 Jul 16;292(5820):267–269. doi: 10.1038/292267a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves R. A., Pandey N. B., Chodchoy N., Marzluff W. F. Translation is required for regulation of histone mRNA degradation. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):615–626. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90240-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gritz L., Davies J. Plasmid-encoded hygromycin B resistance: the sequence of hygromycin B phosphotransferase gene and its expression in Escherichia coli and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):179–188. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90223-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta R. S., Schlessinger D. Coupling of rates of transcription, translation, and messenger ribonucleic acid degradation in streptomycin-dependent mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jan;125(1):84–93. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.1.84-93.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoekema A., Kastelein R. A., Vasser M., de Boer H. A. Codon replacement in the PGK1 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: experimental approach to study the role of biased codon usage in gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2914–2924. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries R. K., Ley T. J., Anagnou N. P., Baur A. W., Nienhuis A. W. Beta O-39 thalassemia gene: a premature termination codon causes beta-mRNA deficiency without affecting cytoplasmic beta-mRNA stability. Blood. 1984 Jul;64(1):23–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinniburgh A. J., Maquat L. E., Schedl T., Rachmilewitz E., Ross J. mRNA-deficient beta o-thalassemia results from a single nucleotide deletion. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Sep 25;10(18):5421–5427. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.18.5421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb E., Harris J. I., Bridgen J. Triose phosphate isomerase from the coelacanth. An approach to the rapid determination of an amino acid sequence with small amounts of material. Biochem J. 1974 Feb;137(2):185–197. doi: 10.1042/bj1370185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Influence of mRNA secondary structure on binding and migration of 40S ribosomal subunits. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):79–90. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90390-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krisch H. M., Allet B. Nucleotide sequences involved in bacteriophage T4 gene 32 translational self-regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):4937–4941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.4937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Losson R., Lacroute F. Interference of nonsense mutations with eukaryotic messenger RNA stability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5134–5137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu H. S., Yuan P. M., Gracy R. W. Primary structure of human triosephosphate isomerase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):11958–11968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maquat L. E., Chilcote R., Ryan P. M. Human triosephosphate isomerase cDNA and protein structure. Studies of triosephosphate isomerase deficiency in man. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3748–3753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maquat L. E., Kinniburgh A. J., Rachmilewitz E. A., Ross J. Unstable beta-globin mRNA in mRNA-deficient beta o thalassemia. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):543–553. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90396-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchionni M., Gilbert W. The triosephosphate isomerase gene from maize: introns antedate the plant-animal divergence. Cell. 1986 Jul 4;46(1):133–141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90867-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight G. L., O'Hara P. J., Parker M. L. Nucleotide sequence of the triosephosphate isomerase gene from Aspergillus nidulans: implications for a differential loss of introns. Cell. 1986 Jul 4;46(1):143–147. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90868-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moschonas N., de Boer E., Grosveld F. G., Dahl H. H., Wright S., Shewmaker C. K., Flavell R. A. Structure and expression of a cloned beta o thalassaemic globin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Sep 11;9(17):4391–4401. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.17.4391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. Definition and mapping of adenovirus 2 nuclear transcription. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):768–785. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65072-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H., Goff S. C. Nonsense and frameshift mutations in beta 0-thalassemia detected in cloned beta-globin genes. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 10;256(19):9782–9784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. C., Rivers P. S., Sternberg M. J., Thornton J. M., Wilson I. A. An analysis of the three-dimensional structure of chicken triose phosphate isomerase. Biochem Soc Trans. 1977;5(3):642–647. doi: 10.1042/bst0050642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pichersky E., Gottlieb L. D., Hess J. F. Nucleotide sequence of the triose phosphate isomerase gene of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;195(1-2):314–320. doi: 10.1007/BF00332765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirastu M., Saglio G., Chang J. C., Cao A., Kan Y. W. Initiation codon mutation as a cause of alpha thalassemia. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 25;259(20):12315–12317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross J. A precursor of globin messenger RNA. J Mol Biol. 1976 Sep 15;106(2):403–420. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90093-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross J., Peltz S. W., Kobs G., Brewer G. Histone mRNA degradation in vivo: the first detectable step occurs at or near the 3' terminus. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4362–4371. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross J., Pizarro A. Human beta and delta globin messenger RNAs turn over at different rates. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jul 5;167(3):607–617. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80101-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider E., Blundell M., Kennell D. Translation and mRNA decay. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Apr 6;160(2):121–129. doi: 10.1007/BF00267473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinski M. F., Roehr T. J. Activation of the major immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus by cis-acting elements in the promoter-regulatory sequence and by virus-specific trans-acting components. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):431–441. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.431-441.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straus D., Gilbert W. Chicken triosephosphate isomerase complements an Escherichia coli deficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):2014–2018. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.2014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeshita K., Forget B. G., Scarpa A., Benz E. J., Jr Intranuclear defect in beta-globin mRNA accumulation due to a premature translation termination codon. Blood. 1984 Jul;64(1):13–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trecartin R. F., Liebhaber S. A., Chang J. C., Lee K. Y., Kan Y. W., Furbetta M., Angius A., Cao A. beta zero thalassemia in Sardinia is caused by a nonsense mutation. J Clin Invest. 1981 Oct;68(4):1012–1017. doi: 10.1172/JCI110323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weatherall D. J., Clegg J. B. Thalassemia revisited. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):7–9. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90084-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambetti G., Stein J., Stein G. Targeting of a chimeric human histone fusion mRNA to membrane-bound polysomes in HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2683–2687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis of DNA fragments cloned into M13 vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:468–500. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00074-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]