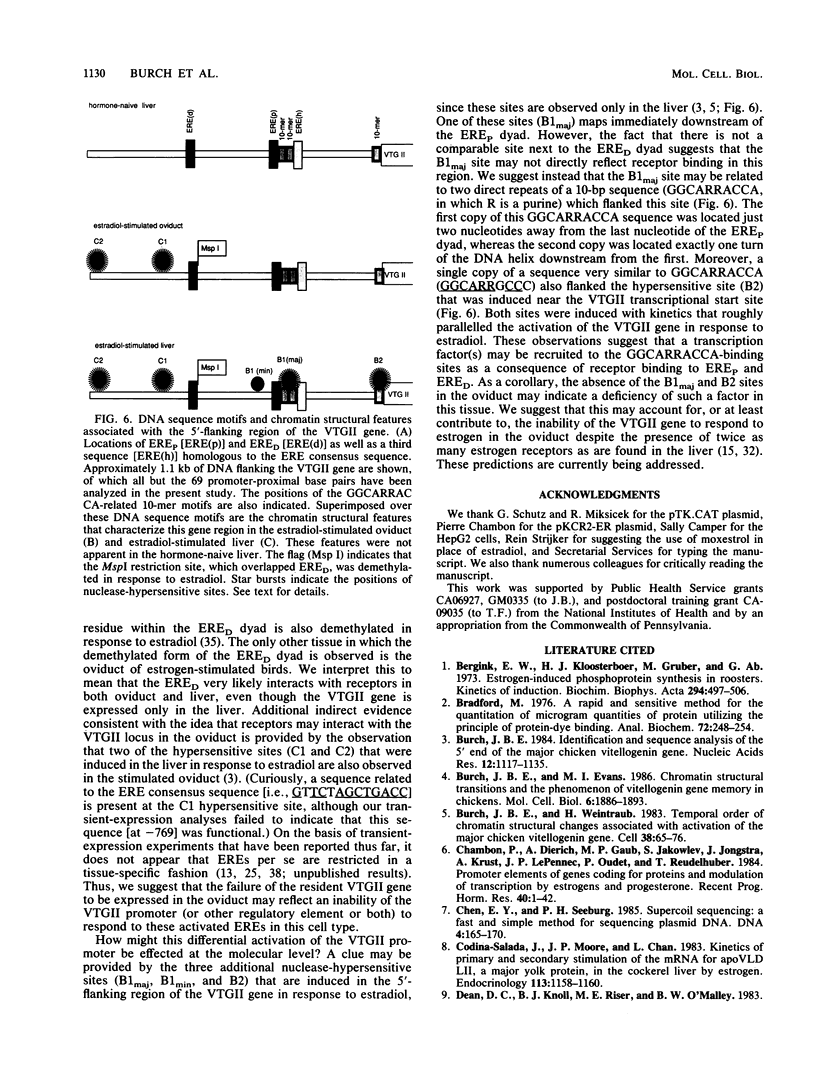
Abstract
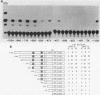
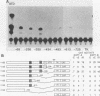
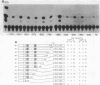
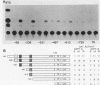
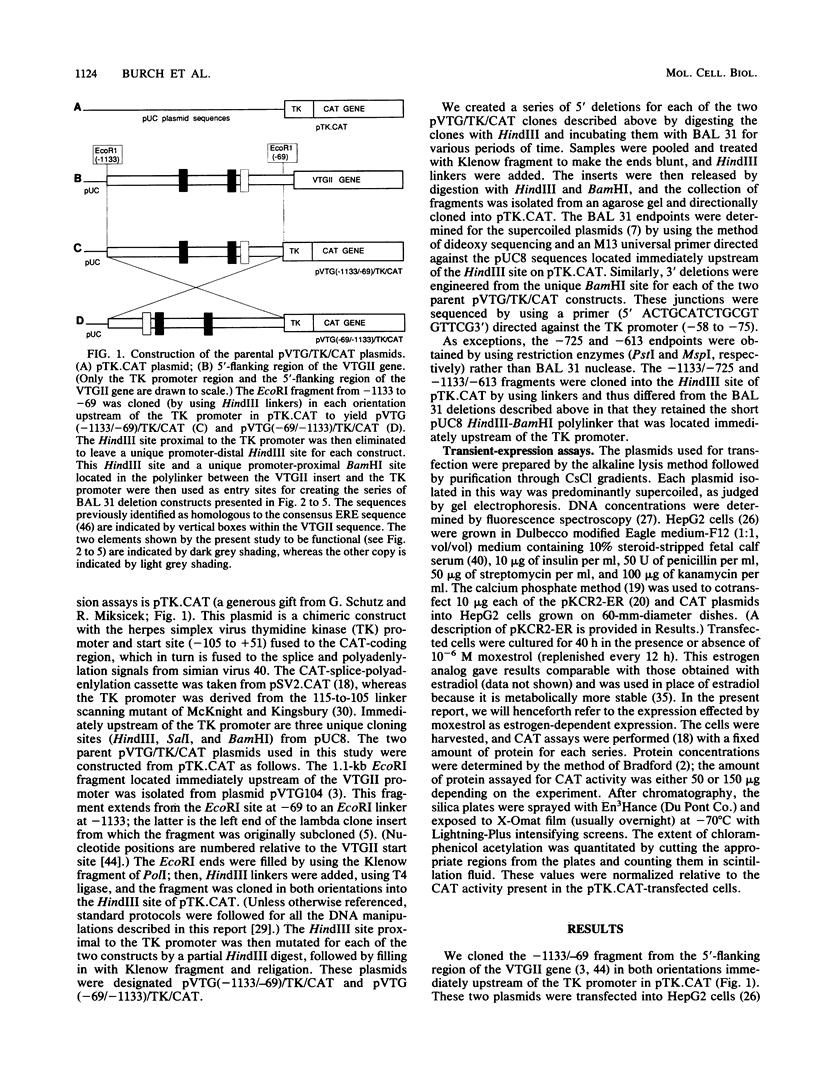
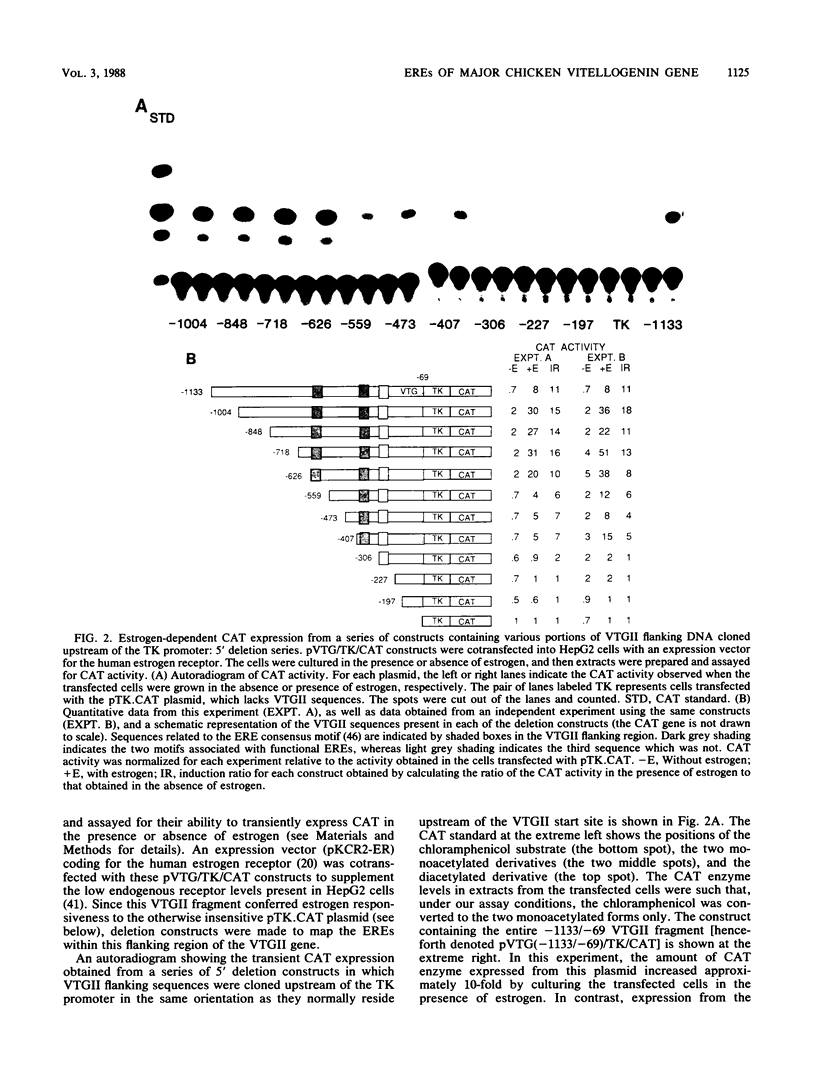
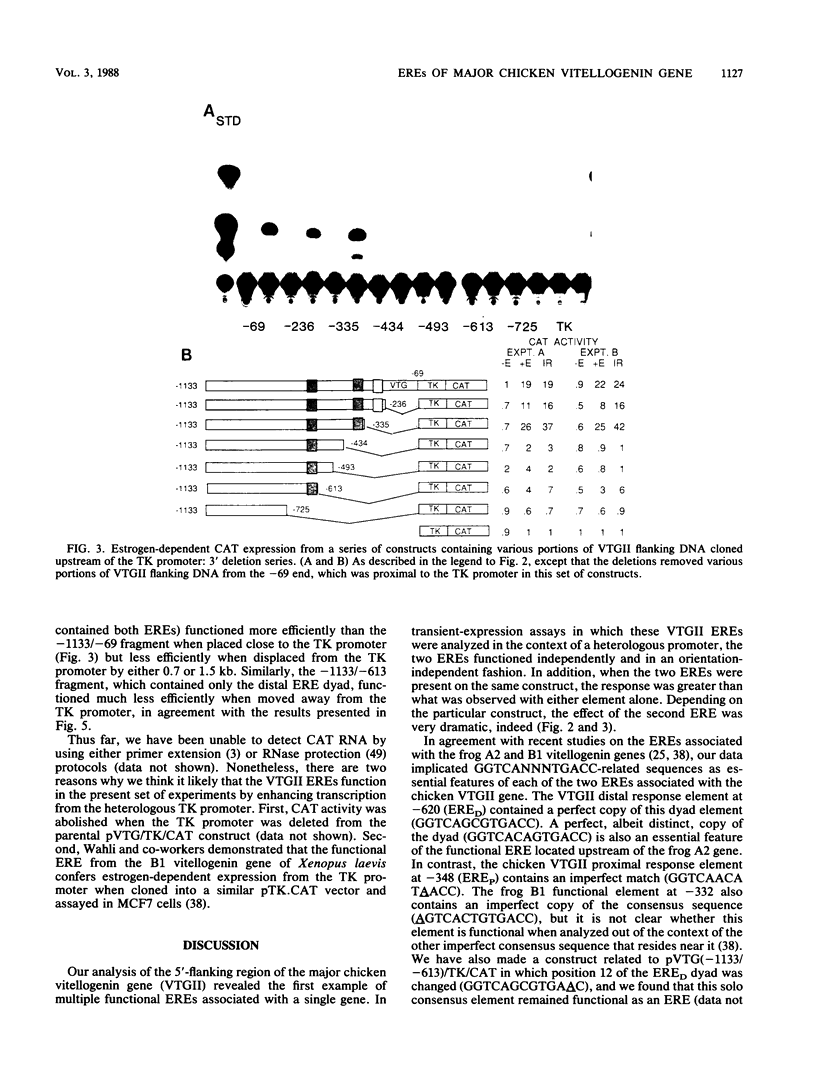
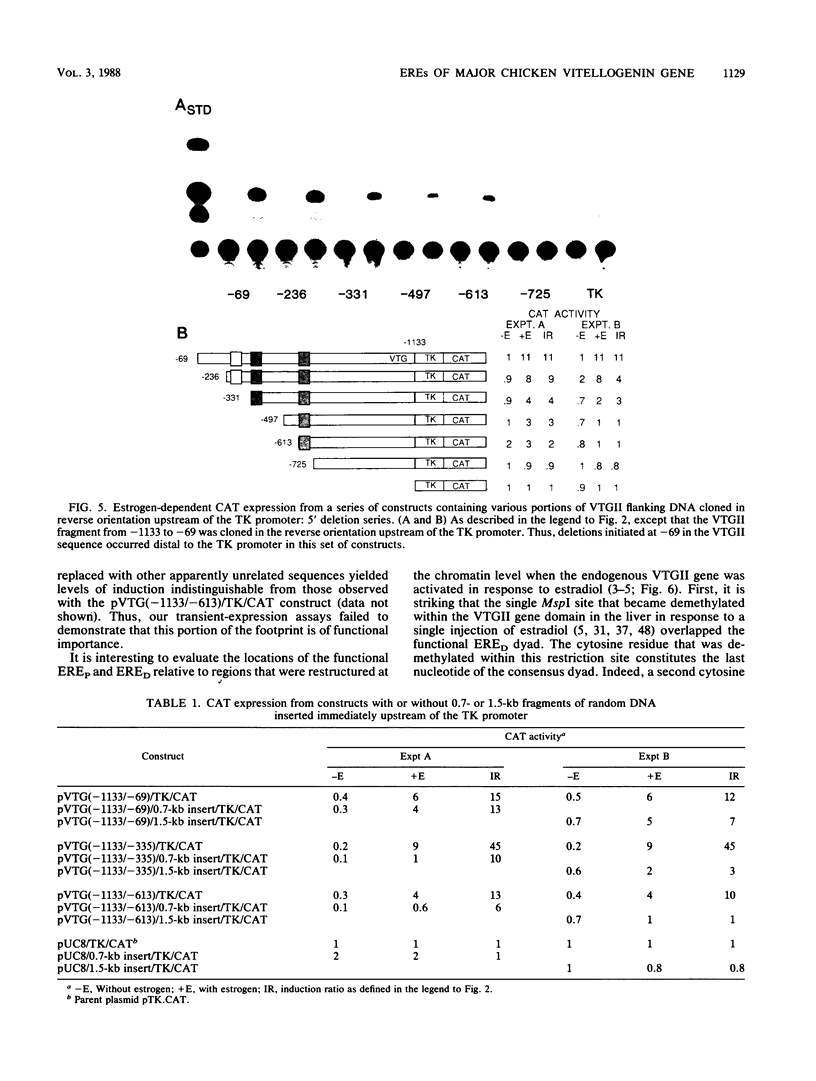
We used a transient-expression assay to identify two estrogen response elements (EREs) associated with the major chicken vitellogenin gene (VTGII). Each element was characterized by its ability to confer estrogen responsiveness when cloned in either orientation next to a chimeric reporter gene consisting of the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase promoter and the chloramphenicol acetyl transferase-coding region. Deletion analyses indicated that sequences necessary for the distal ERE resided within the region from -626 to -613 (nucleotide positions relative to the VTGII start site) whereas those necessary for the proximal ERE were within the region from -358 to -335. These distal and proximal elements contain, respectively, a perfect copy and an imperfect copy of the 13-base-pair sequence that is an essential feature of the EREs associated with two frog vitellogenin genes. These chicken VTGII EREs mapped near regions that were restructured at the chromatin level when the endogenous VTGII gene was expressed in the liver in response to estradiol. These data suggest a model for the tissue-specific expression of this estrogen-responsive gene.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergink E. W., Kloosterboer H. J., Gruber M., Ab G. Estrogen-induced phosphoprotein synthesis in roosters. Kinetics of induction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 4;294(1):497–506. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90105-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch J. B., Evans M. I. Chromatin structural transitions and the phenomenon of vitellogenin gene memory in chickens. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):1886–1893. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.1886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch J. B. Identification and sequence analysis of the 5' end of the major chicken vitellogenin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):1117–1135. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.1117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch J. B., Weintraub H. Temporal order of chromatin structural changes associated with activation of the major chicken vitellogenin gene. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):65–76. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90335-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambon P., Dierich A., Gaub M. P., Jakowlev S., Jongstra J., Krust A., LePennec J. P., Oudet P., Reudelhuber T. Promoter elements of genes coding for proteins and modulation of transcription by estrogens and progesterone. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1984;40:1–42. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571140-1.50005-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Codina-Salada J., Moore J. P., Chan L. Kinetics of primary and secondary stimulation of the mRNA for APOVLDL-II, a major yolk protein, in the cockerel liver by estrogen. Endocrinology. 1983 Sep;113(3):1158–1160. doi: 10.1210/endo-113-3-1158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean D. C., Knoll B. J., Riser M. E., O'Malley B. W. A 5'-flanking sequence essential for progesterone regulation of an ovalbumin fusion gene. Nature. 1983 Oct 6;305(5934):551–554. doi: 10.1038/305551a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deeley R. G., Tam S. P., Archer T. K. The effects of estrogen on apolipoprotein synthesis. Can J Biochem Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;63(8):882–889. doi: 10.1139/o85-109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deeley R. G., Udell D. S., Burns A. T., Gordon J. I., Goldberger R. F. Kinetics of avian vitellogenin messenger RNA induction. Comparison between primary and secondary response to estrogen. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 25;252(22):7913–7915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dierich A., Gaub M. P., LePennec J. P., Astinotti D., Chambon P. Cell-specificity of the chicken ovalbumin and conalbumin promoters. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2305–2312. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02505.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Druege P. M., Klein-Hitpass L., Green S., Stack G., Chambon P., Ryffel G. U. Introduction of estrogen-responsiveness into mammalian cell lines. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Dec 9;14(23):9329–9337. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.23.9329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elbrecht A., Lazier C. B., Protter A. A., Williams D. L. Independent developmental programs for two estrogen-regulated genes. Science. 1984 Aug 10;225(4662):639–641. doi: 10.1126/science.6740331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. I., O'Malley P. J., Krust A., Burch J. B. Developmental regulation of the estrogen receptor and the estrogen responsiveness of five yolk protein genes in the avian liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8493–8497. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. I., Silva R., Burch J. B. Isolation of chicken vitellogenin I and III cDNAs and the developmental regulation of five estrogen-responsive genes in the embryonic liver. Genes Dev. 1988 Jan;2(1):116–124. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.1.116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaub M. P., Dierich A., Astinotti D., Touitou I., Chambon P. The chicken ovalbumin promoter is under negative control which is relieved by steroid hormones. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2313–2320. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02506.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S., Walter P., Kumar V., Krust A., Bornert J. M., Argos P., Chambon P. Human oestrogen receptor cDNA: sequence, expression and homology to v-erb-A. Nature. 1986 Mar 13;320(6058):134–139. doi: 10.1038/320134a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruber M., Bos E. S., Ab G. Hormonal control of vitellogenin synthesis in avian liver. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1976 Jun-Jul;5(1-2):41–50. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(76)90069-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes N. E., Groner B., Sippel A. E., Jeep S., Wurtz T., Nguyen-Huu M. C., Giesecke K., Schütz G. Control of cellular content of chicken egg white protein specific RNA during estrogen administration and withdrawal. Biochemistry. 1979 Feb 20;18(4):616–624. doi: 10.1021/bi00571a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jost J. P., Ohno T., Panyim S., Schuerch A. R. Appearance of vitellogenin mRNA sequences and rate of vitellogenin synthesis in chicken liver following primary and secondary stimulation by 17 beta-estradiol. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Mar 15;84(2):355–361. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12175.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jost J. P., Seldran M., Geiser M. Preferential binding of estrogen-receptor complex to a region containing the estrogen-dependent hypomethylation site preceding the chicken vitellogenin II gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):429–433. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein-Hitpass L., Schorpp M., Wagner U., Ryffel G. U. An estrogen-responsive element derived from the 5' flanking region of the Xenopus vitellogenin A2 gene functions in transfected human cells. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):1053–1061. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90705-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles B. B., Howe C. C., Aden D. P. Human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines secrete the major plasma proteins and hepatitis B surface antigen. Science. 1980 Jul 25;209(4455):497–499. doi: 10.1126/science.6248960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labarca C., Paigen K. A simple, rapid, and sensitive DNA assay procedure. Anal Biochem. 1980 Mar 1;102(2):344–352. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90165-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai E. C., Riser M. E., O'Malley B. W. Regulated expression of the chicken ovalbumin gene in a human estrogen-responsive cell line. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12693–12701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Kingsbury R. Transcriptional control signals of a eukaryotic protein-coding gene. Science. 1982 Jul 23;217(4557):316–324. doi: 10.1126/science.6283634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijlink F. C., Philipsen J. N., Gruber M., Ab G. Methylation of the chicken vitellogenin gene: influence of estradiol administration. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1361–1373. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulvihill E. R., Palmiter R. D. Relationship of nuclear estrogen receptor levels to induction of ovalbumin and conalbumin mRNA in chick oviduct. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 25;252(6):2060–2068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley B. W., McGuire W. L., Kohler P. O., Korenman S. G. Studies on the mechanism of steroid hormone regulation of synthesis of specific proteins. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1969;25:105–160. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571125-8.50006-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Mulvihill E. R., Shepherd J. H., McKnight G. S. Steroid hormone regulation of ovalbumin and conalbumin gene transcription. A model based upon multiple regulatory sites and intermediary proteins. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7910–7916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raynaud J. P., Bouton M. M., Gallet-Bourquin D., Philibert D., Tournemine C., Azadian-Baulanger G. Comparative study of estrogen action. Mol Pharmacol. 1973 Jul;9(4):520–533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renkawitz R., Schütz G., von der Ahe D., Beato M. Sequences in the promoter region of the chicken lysozyme gene required for steroid regulation and receptor binding. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):503–510. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90380-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saluz H. P., Jiricny J., Jost J. P. Genomic sequencing reveals a positive correlation between the kinetics of strand-specific DNA demethylation of the overlapping estradiol/glucocorticoid-receptor binding sites and the rate of avian vitellogenin mRNA synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7167–7171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiler-Tuyns A., Walker P., Martinez E., Mérillat A. M., Givel F., Wahli W. Identification of estrogen-responsive DNA sequences by transient expression experiments in a human breast cancer cell line. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 25;14(22):8755–8770. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.22.8755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro D. Steroid hormone regulation of vitellogenin gene expression. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1982 Mar;12(3):187–203. doi: 10.3109/10409238209108706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley E. R., Palmer R. E., Sohn U. Development of methods for the quantitative in vitro analysis of androgen-dependent and autonomous Shionogi carcinoma 115 cells. Cell. 1977 Jan;10(1):35–44. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90137-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tam S. P., Archer T. K., Deeley R. G. Effects of estrogen on apolipoprotein secretion by the human hepatocarcinoma cell line, HepG2. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1670–1675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tata J. R. Coordinated assembly of the developing egg. Bioessays. 1986 May;4(5):197–201. doi: 10.1002/bies.950040503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker P., Germond J. E., Brown-Luedi M., Givel F., Wahli W. Sequence homologies in the region preceding the transcription initiation site of the liver estrogen-responsive vitellogenin and apo-VLDLII genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 26;12(22):8611–8626. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.22.8611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilks A. F., Cozens P. J., Mattaj I. W., Jost J. P. Estrogen induces a demethylation at the 5' end region of the chicken vitellogenin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4252–4255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinn K., DiMaio D., Maniatis T. Identification of two distinct regulatory regions adjacent to the human beta-interferon gene. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):865–879. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90544-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ten Heggeler-Bordier B., Hipskind R., Seiler-Tuyns A., Martinez E., Corthésy B., Wahli W. Electron microscopic visualization of protein-DNA interactions at the estrogen responsive element and in the first intron of the Xenopus laevis vitellogenin gene. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1715–1720. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02422.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van het Schip F., Strijker R., Samallo J., Gruber M., Geert A. B. Conserved sequence motifs upstream from the co-ordinately expressed vitellogenin and apoVLDLII genes of chicken. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 11;14(21):8669–8680. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.21.8669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]