Abstract
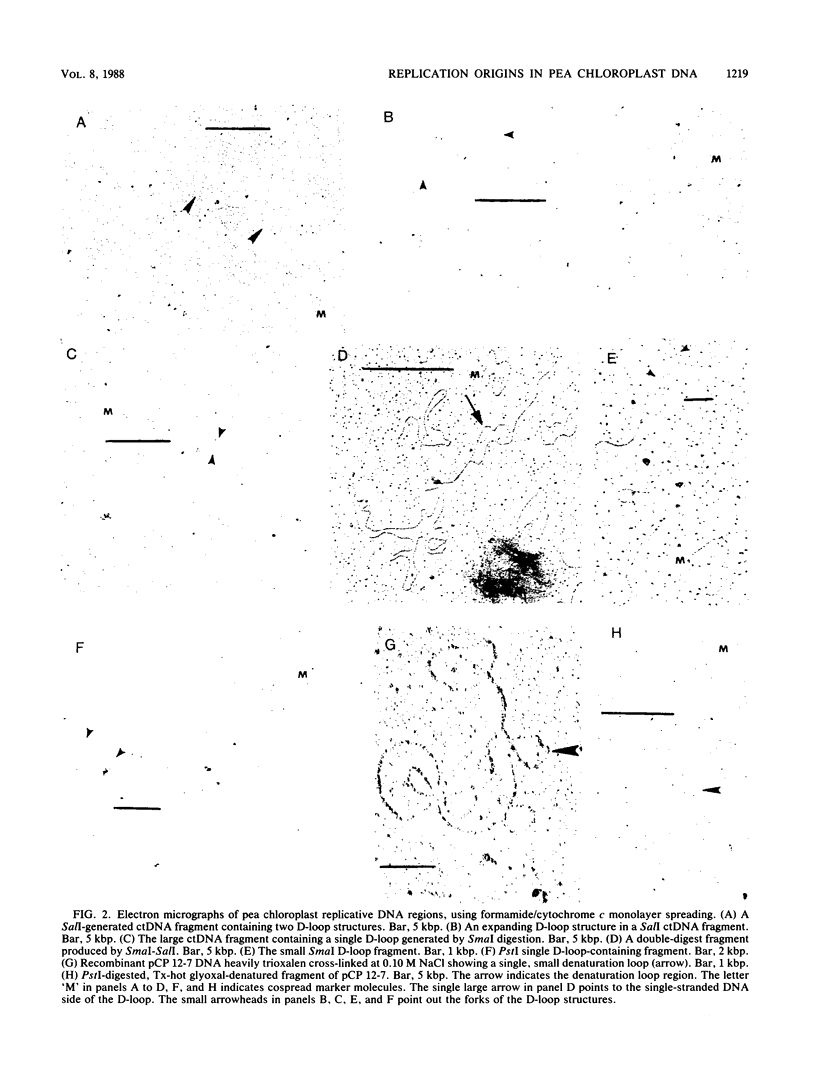
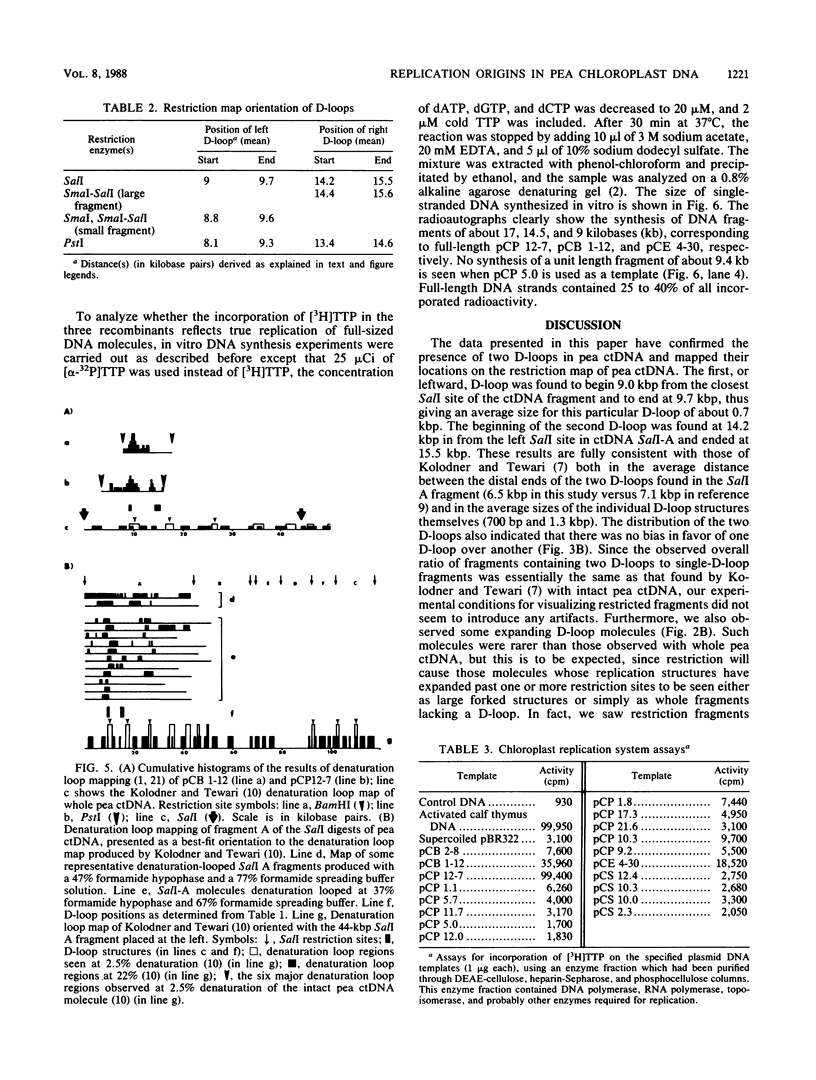
The locations of the two replication origins in pea chloroplast DNA (ctDNA) have been mapped by electron microscopic analysis of restriction digests of supercoiled ctDNA cross-linked with trioxalen. Both origins of replication, identified as displacement loops (D-loops), were present in the 44-kilobase-pair (kbp) SalI A fragment. The first D-loop was located at 9.0 kbp from the closest SalI restriction site. The average size of this D-loop was about 0.7 kbp. The second D-loop started 14.2 kbp in from the same restriction site and ended at about 15.5 kbp, giving it a size of about 1.3 kbp. The orientation of these two D-loops on the restriction map of pea ctDNA was determined by analyzing SmaI, PstI, and SalI-SmaI restriction digests of pea ctDNA. One D-loop has been mapped in the spacer region between the 16S and 23S rRNA genes. The second D-loop was located downstream of the 23S rRNA gene. Denaturation mapping of recombinants pCP 12-7 and pCB 1-12, which contain both D-loops, confirmed the location of the D-loops in the restriction map of pea ctDNA. Denaturation-mapping studies also showed that the two D-loops had different base compositions; the one closest to a SalI restriction site denatured readily compared with the other D-loop. The recombinants pCP 12-7 and pCB 1-12 were found to be highly active in DNA synthesis when used as templates in a partially purified replication system from pea chloroplasts. Analysis of in vitro-synthesized DNA with either of these recombinants showed that full-length template DNA was synthesized. Recombinants from other regions of the pea chloroplast genome showed no significant DNA synthesis activity in vitro.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cech T. R., Pardue M. L. Electron microscopy of DNA crosslinked with trimethylpsoralen: test of the secondary structure of eukaryotic inverted repeat sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2644–2648. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu N. M., Oishi K. K., Tewari K. K. Physical mapping of the pea chloroplast DNA and localization of the ribosomal RNA genes. Plasmid. 1981 Nov;6(3):279–292. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(81)90036-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold B., Carrillo N., Tewari K. K., Bogorad L. Nucleotide sequence of a preferred maize chloroplast genome template for in vitro DNA synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):194–198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koller B., Delius H. Origin of replication in chloroplast DNA of Euglena gracilis located close to the region of variable size. EMBO J. 1982;1(8):995–998. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01283.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolodner R. D., Tewari K. K. Chloroplast DNA from higher plants replicates by both the Cairns and the rolling circle mechanism. Nature. 1975 Aug 28;256(5520):708–711. doi: 10.1038/256708a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolodner R. D., Tewari K. K. Denaturation mapping studies on the circular chloroplast deoxyribonucleic acid from pea leaves. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jul 10;250(13):4888–4895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolodner R., Tewari K. K. Presence of displacement loops in the covalently closed circular chloroplast deoxyribonucleic acid from higher plants. J Biol Chem. 1975 Nov 25;250(22):8840–8847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolodner R., Tewari K. K. The molecular size and conformation of the chloroplast DNA from higher plants. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Sep 1;402(3):372–390. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(75)90273-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKown R. L., Tewari K. K. Purification and properties of a pea chloroplast DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2354–2358. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer J. D. Comparative organization of chloroplast genomes. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:325–354. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.001545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer J. D., Thompson W. F. Rearrangements in the chloroplast genomes of mung bean and pea. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5533–5537. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waddell J., Wang X. M., Wu M. Electron microscopic localization of the chloroplast DNA replicative origins in Chlamydomonas reinhardii. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 11;12(9):3843–3856. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.9.3843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang X. M., Chang C. H., Waddell J., Wu M. Cloning and delimiting one chloroplast DNA replicative origin of Chlamydomonas. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 11;12(9):3857–3872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.9.3857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu M., Lou J. K., Chang D. Y., Chang C. H., Nie Z. Q. Structure and function of a chloroplast DNA replication origin of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6761–6765. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]