Abstract
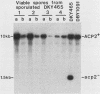
The high-mobility-group (HMG) proteins, a group of nonhistone chromatin-associated proteins, have been extensively characterized in higher eucaryotic cells. To test the biological function of an HMG protein, we have cloned and mutagenized a gene encoding an HMG-like protein from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. A yeast genomic DNA library was screened with an oligonucleotide designed to hybridize to any yeast gene containing an amino acid sequence conserved in several higher eucaryotic HMG proteins. DNA sequencing and Northern (RNA) blot analysis revealed that one gene, called ACP2 (acidic protein 2), synthesizes a poly(A)+ RNA in S. cerevisiae which encodes a 27,000-molecular-weight protein whose amino acid sequence is homologous to those of calf HMG1 and HMG2 and trout HMGT proteins. Standard procedures were used to construct a diploid yeast strain in which one copy of the ACP2 gene was mutated by replacement with the URA3 gene. When this diploid was sporulated and dissected, only half of the spores were viable. About half of the nonviable spores proceeded through two or three cell divisions and then stopped dividing; the rest did not germinate at all. None of the viable spores contained the mutant ACP2 gene, thus proving that the protein encoded by ACP2 is required for cell viability. The results presented here demonstrate that an HMG-like protein has an essential physiological function.
Full text
PDF





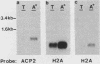
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennetzen J. L., Hall B. D. Codon selection in yeast. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3026–3031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonne-Andrea C., Harper F., Sobczak J., De Recondo A. M. Rat liver HMG1: a physiological nucleosome assembly factor. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1193–1199. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01950.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucci L. R., Brock W. A., Goldknopf I. L., Meistrich M. L. Characterization of high mobility group protein levels during spermatogenesis in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):8840–8846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler A. P., Mardian J. K., Olins D. E. Nonhistone chromosomal protein HMG 1 interactions with DNA. Fluorescence and thermal denaturation studies. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 5;260(19):10613–10620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron J. R., Philippsen P., Davis R. W. Analysis of chromosomal integration and deletions of yeast plasmids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977;4(5):1429–1448. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.5.1429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choe J., Kolodrubetz D., Grunstein M. The two yeast histone H2A genes encode similar protein subtypes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(5):1484–1487. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.5.1484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryer D. R., Eccleshall R., Marmur J. Isolation of yeast DNA. Methods Cell Biol. 1975;12:39–44. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60950-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayhoff M. O., Barker W. C., Hunt L. T. Establishing homologies in protein sequences. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:524–545. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91049-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Dilworth S. M., Black S. J., Kearsey S. E., Cox L. S., Laskey R. A. Nucleoplasmin cDNA sequence reveals polyglutamic acid tracts and a cluster of sequences homologous to putative nuclear localization signals. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):69–74. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04720.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobson M. J., Tuite M. F., Roberts N. A., Kingsman A. J., Kingsman S. M., Perkins R. E., Conroy S. C., Fothergill L. A. Conservation of high efficiency promoter sequences in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Apr 24;10(8):2625–2637. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.8.2625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earnshaw W. C., Sullivan K. F., Machlin P. S., Cooke C. A., Kaiser D. A., Pollard T. D., Rothfield N. F., Cleveland D. W. Molecular cloning of cDNA for CENP-B, the major human centromere autoantigen. J Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;104(4):817–829. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.4.817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finley D., Ozkaynak E., Varshavsky A. The yeast polyubiquitin gene is essential for resistance to high temperatures, starvation, and other stresses. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):1035–1046. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90711-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabrielli F., Hancock R., Faber A. J. Characterisation of a chromatin fraction bearing pulse-labelled RNA. 2. Quantification of histones and high-mobility-group proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Nov;120(2):363–369. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05713.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn S., Hoar E. T., Guarente L. Each of three "TATA elements" specifies a subset of the transcription initiation sites at the CYC-1 promoter of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8562–8566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isackson P. J., Fishback J. L., Bidney D. L., Reeck G. R. Preferential affinity of high molecular weight high mobility group non-histone chromatin proteins for single-stranded DNA. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):5569–5572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson J. B., Pollock J. M., Jr, Rill R. L. Chromatin fractionation procedure that yields nucleosomes containing near-stoichiometric amounts of high mobility group nonhistone chromosomal proteins. Biochemistry. 1979 Aug 21;18(17):3739–3748. doi: 10.1021/bi00584a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. M., Snyder M., Chang L. M., Davis R. W., Campbell J. L. Isolation of the gene encoding yeast DNA polymerase I. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):369–377. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90042-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuehl L., Salmond B., Tran L. Concentrations of high-mobility-group proteins in the nucleus and cytoplasm of several rat tissues. J Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;99(2):648–654. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.2.648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landsman D., Soares N., Gonzalez F. J., Bustin M. Chromosomal protein HMG-17. Complete human cDNA sequence and evidence for a multigene family. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 5;261(16):7479–7484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy W B., Wong N. C., Dixon G. H. Selective association of the trout-specific H6 protein with chromatin regions susceptible to DNase I and DNase II: possible location of HMG-T in the spacer region between core nucleosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2810–2814. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1435–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.2983426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann C., Buhler J. M., Treich I., Sentenac A. RPC40, a unique gene for a subunit shared between yeast RNA polymerases A and C. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):627–637. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90241-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin C. S., Warner J. R., Edmonds M., Nakazato H., Vaughan M. H. Polyadenylic acid sequences in yeast messenger ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1973 Feb 25;248(4):1466–1471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., McLachlan A. D., Klug A. Repetitive zinc-binding domains in the protein transcription factor IIIA from Xenopus oocytes. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1609–1614. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03825.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagawa F., Fink G. R. The relationship between the "TATA" sequence and transcription initiation sites at the HIS4 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8557–8561. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naumovski L., Friedberg E. C. A DNA repair gene required for the incision of damaged DNA is essential for viability in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4818–4821. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrander J., Kempe T., Messing J. Construction of improved M13 vectors using oligodeoxynucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T. Protein-DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:293–321. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pentecost B. T., Wright J. M., Dixon G. H. Isolation and sequence of cDNA clones coding for a member of the family of high mobility group proteins (HMG-T) in trout and analysis of HMG-T-mRNA's in trout tissues. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 11;13(13):4871–4888. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.13.4871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds P., Higgins D. R., Prakash L., Prakash S. The nucleotide sequence of the RAD3 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a potential adenine nucleotide binding amino acid sequence and a nonessential acidic carboxyl terminal region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 11;13(7):2357–2372. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.7.2357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds P., Weber S., Prakash L. RAD6 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae encodes a protein containing a tract of 13 consecutive aspartates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):168–172. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. D., Fink G. R. KAR1, a gene required for function of both intranuclear and extranuclear microtubules in yeast. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):1047–1060. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90712-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M., Grisafi P., Botstein D. Structure and function of the yeast URA3 gene: expression in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1984 Jul-Aug;29(1-2):113–124. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90172-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shastri K., Isackson P. J., Fishback J. L., Land M. D., Reeck G. R. Influence of nonhistone chromatin protein HMG-1 on the enzymatic digestion of purified DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Aug 25;10(16):5059–5072. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.16.5059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shortle D., Haber J. E., Botstein D. Lethal disruption of the yeast actin gene by integrative DNA transformation. Science. 1982 Jul 23;217(4557):371–373. doi: 10.1126/science.7046050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiker S., Mardian J. K., Isenberg I. Chomosomal HMG proteins occur in three eukaryotic kingdoms. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 May 15;82(1):129–135. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90586-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoute J. A., Marzluff W. F. HMG-proteins 1 and 2 are required for transcription of chromatin by endogenous RNA polymerase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Aug 31;107(4):1279–1284. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(82)80136-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teem J. L., Abovich N., Kaufer N. F., Schwindinger W. F., Warner J. R., Levy A., Woolford J., Leer R. J., van Raamsdonk-Duin M. M., Mager W. H. A comparison of yeast ribosomal protein gene DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 26;12(22):8295–8312. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.22.8295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tremethick D. J., Molloy P. L. High mobility group proteins 1 and 2 stimulate transcription in vitro by RNA polymerases II and III. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 25;261(15):6986–6992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. E., Saraste M., Runswick M. J., Gay N. J. Distantly related sequences in the alpha- and beta-subunits of ATP synthase, myosin, kinases and other ATP-requiring enzymes and a common nucleotide binding fold. EMBO J. 1982;1(8):945–951. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01276.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber S., Isenberg I. High mobility group proteins of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochemistry. 1980 May 13;19(10):2236–2240. doi: 10.1021/bi00551a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang R., Lis J., Wu R. Elution of DNA from agarose gels after electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:176–182. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaret K. S., Sherman F. DNA sequence required for efficient transcription termination in yeast. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):563–573. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90211-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zitomer R. S., Hall B. D. Yeast cytochrome c messenger RNA. In vitro translation and specific immunoprecipitation of the CYC1 gene product. J Biol Chem. 1976 Oct 25;251(20):6320–6326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]