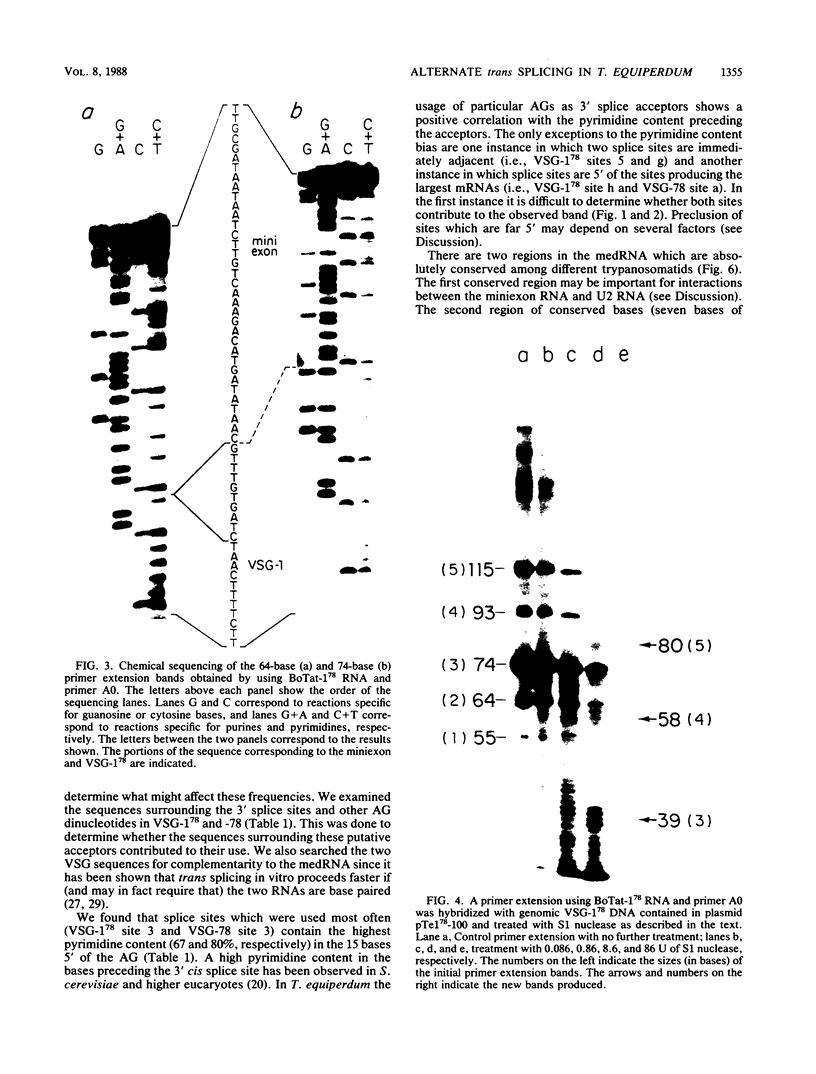
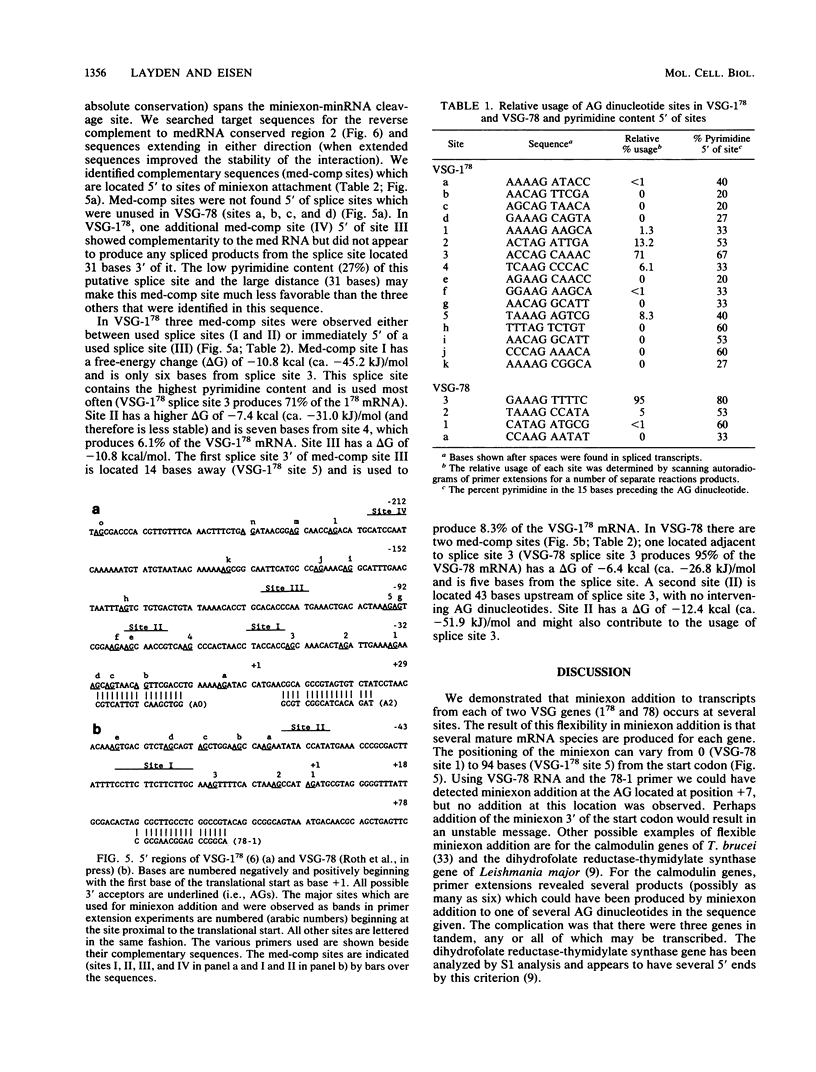
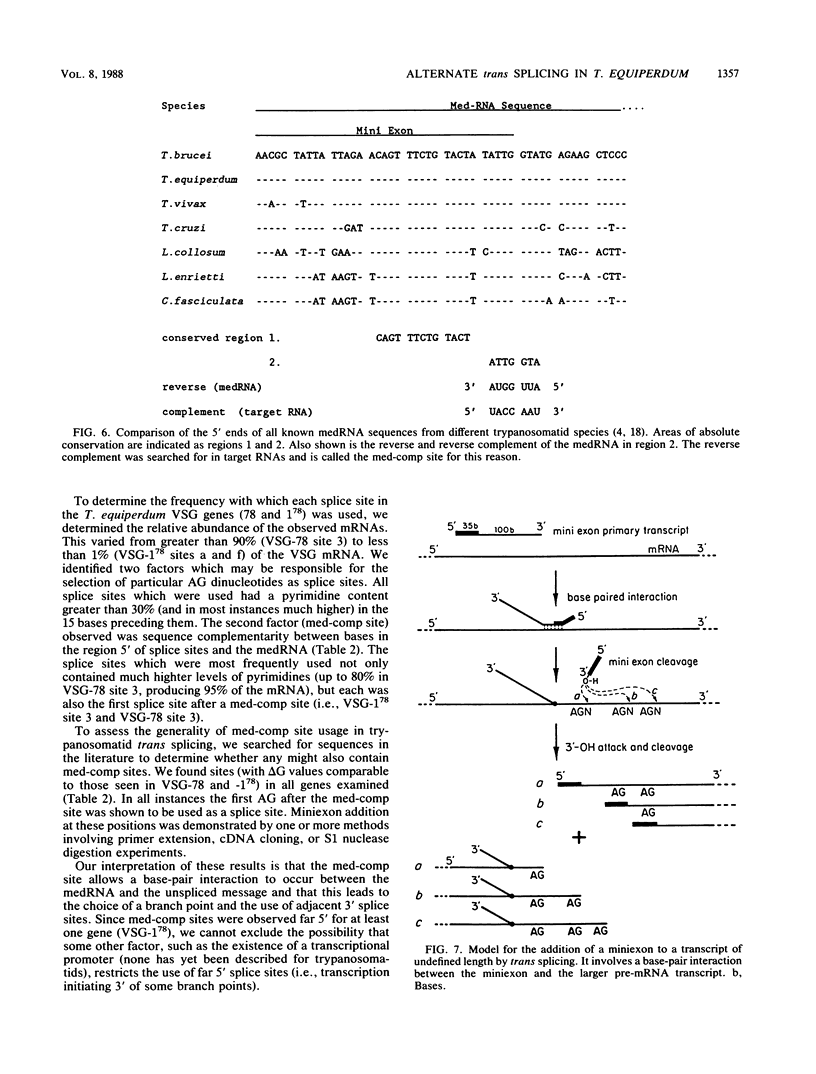
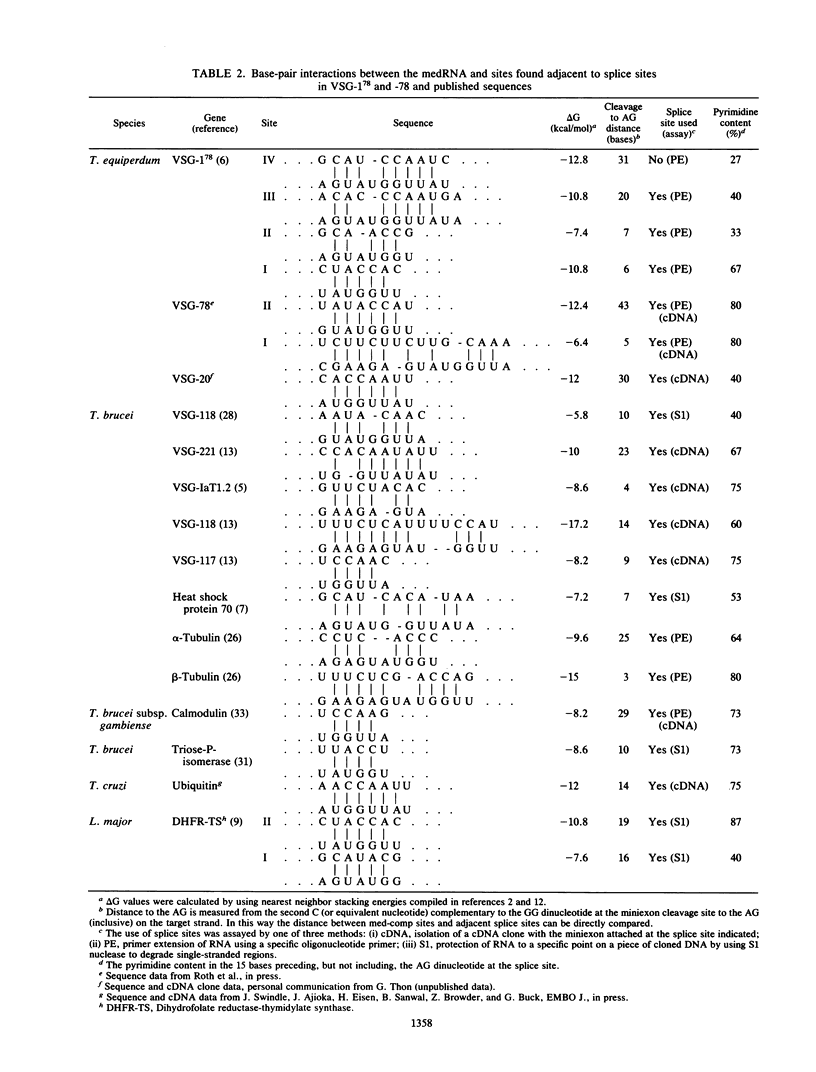
Abstract
We examined the structures of the 5' ends of mRNAs encoding variant surface glycoprotein 78 (VSG-78) and VSG-1(78) in Trypanosoma equiperdum. Several mRNA species were found for each gene, and all contained the 35-base miniexon (or spliced leader) sequence attached at different positions on their 5' ends. Thus, the generation of multiple messages for each VSG occurred by attachment of the miniexon at one of several 3' splice acceptor sites. The frequency with which individual splice sites were used varied from less than 1 to 95% of the RNA produced from a particular gene. We propose that the miniexon RNA and RNA from the VSG genes may interact via base pairing and that this in part specifies the use of particular acceptor sites. Sequences complementary to the miniexon primary transcript, termed the "med-comp site," were found in both genes and in several published sequences. Splice sites were most often used if they were the first site 3' of the med-comp site and contained a high pyrimidine content in the bases preceding the AG acceptor signal.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borer P. N., Dengler B., Tinoco I., Jr, Uhlenbeck O. C. Stability of ribonucleic acid double-stranded helices. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jul 15;86(4):843–853. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90357-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capbern A., Giroud C., Baltz T., Mattern P. Trypanosoma equiperdum: etude des variations antigéniques au cours de la trypanosomose experimentale du lapin. Exp Parasitol. 1977 Jun;42(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(77)90055-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Lange T., Berkvens T. M., Veerman H. J., Frasch A. C., Barry J. D., Borst P. Comparison of the genes coding for the common 5' terminal sequence of messenger RNAs in three trypanosome species. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 11;12(11):4431–4443. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.11.4431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donelson J. E., Murphy W. J., Brentano S. T., Rice-Ficht A. C., Cain G. D. Comparison of the expression-linked extra copy (ELC) and basic copy (BC) genes of a trypanosome surface antigen. J Cell Biochem. 1983;23(1-4):1–12. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240230102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florent I., Baltz T., Raibaud A., Eisen H. On the role of repeated sequences 5' to variant surface glycoprotein genes in African trypanosomes. Gene. 1987;53(1):55–62. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90092-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass D. J., Polvere R. I., Van der Ploeg L. H. Conserved sequences and transcription of the hsp70 gene family in Trypanosoma brucei. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4657–4666. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Sakaki Y. Dideoxy sequencing method using denatured plasmid templates. Anal Biochem. 1986 Feb 1;152(2):232–238. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90403-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapler G. M., Zhang K., Beverley S. M. Sequence and S1 nuclease mapping of the 5' region of the dihydrofolate reductase-thymidylate synthase gene of Leishmania major. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 24;15(8):3369–3383. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.8.3369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller E. B., Noon W. A. Intron splicing: a conserved internal signal in introns of animal pre-mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7417–7420. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird P. W., Zomerdijk J. C., de Korte D., Borst P. In vivo labelling of intermediates in the discontinuous synthesis of mRNAs in Trypanosoma brucei. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):1055–1062. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04858.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu A. Y., Van der Ploeg L. H., Rijsewijk F. A., Borst P. The transposition unit of variant surface glycoprotein gene 118 of Trypanosoma brucei. Presence of repeated elements at its border and absence of promoter-associated sequences. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 15;167(1):57–75. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80034-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertins P., Gallwitz D. Nuclear pre-mRNA splicing in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe strictly requires an intron-contained, conserved sequence element. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1757–1763. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02428.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milhausen M., Nelson R. G., Sather S., Selkirk M., Agabian N. Identification of a small RNA containing the trypanosome spliced leader: a donor of shared 5' sequences of trypanosomatid mRNAs? Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):721–729. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90267-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muhich M. L., Hughes D. E., Simpson A. M., Simpson L. The monogenetic kinetoplastid protozoan, Crithidia fasciculata, contains a transcriptionally active, multicopy mini-exon sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 10;15(7):3141–3153. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.7.3141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy W. J., Watkins K. P., Agabian N. Identification of a novel Y branch structure as an intermediate in trypanosome mRNA processing: evidence for trans splicing. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):517–525. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90616-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Grabowski P. J., Konarska M. M., Seiler S., Sharp P. A. Splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1119–1150. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Konarska M. M., Grabowski P. J., Hardy S. F., Sharp P. A. Lariat RNA's as intermediates and products in the splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Science. 1984 Aug 31;225(4665):898–903. doi: 10.1126/science.6206566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R., Siliciano P. G., Guthrie C. Recognition of the TACTAAC box during mRNA splicing in yeast involves base pairing to the U2-like snRNA. Cell. 1987 Apr 24;49(2):229–239. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90564-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raibaud A., Buck G., Baltz T., Eisen H. Cloning and characterization of a variant surface glycoprotein expression site from Trypanosoma equiperdum. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2950–2956. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez J. R., Pikielny C. W., Rosbash M. In vivo characterization of yeast mRNA processing intermediates. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90467-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin B., Krainer A. R., Maniatis T., Green M. R. Excision of an intact intron as a novel lariat structure during pre-mRNA splicing in vitro. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):317–331. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90553-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sather S., Agabian N. A 5' spliced leader is added in trans to both alpha- and beta-tubulin transcripts in Trypanosoma brucei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5695–5699. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A. Trans splicing: variation on a familiar theme? Cell. 1987 Jul 17;50(2):147–148. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90207-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shea C., Lee M. G., Van der Ploeg L. H. VSG gene 118 is transcribed from a cotransposed pol I-like promoter. Cell. 1987 Aug 14;50(4):603–612. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90033-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solnick D. Does trans splicing in vitro require base pairing between RNAs? Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):211–211. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90752-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton R. E., Boothroyd J. C. Evidence for trans splicing in trypanosomes. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):527–535. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90617-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swinkels B. W., Gibson W. C., Osinga K. A., Kramer R., Veeneman G. H., van Boom J. H., Borst P. Characterization of the gene for the microbody (glycosomal) triosephosphate isomerase of Trypanosoma brucei. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1291–1298. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04358.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschudi C., Richards F. F., Ullu E. The U2 RNA analogue of Trypanosoma brucei gambiense: implications for a splicing mechanism in trypanosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 25;14(22):8893–8903. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.22.8893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschudi C., Young A. S., Ruben L., Patton C. L., Richards F. F. Calmodulin genes in trypanosomes are tandemly repeated and produce multiple mRNAs with a common 5' leader sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):3998–4002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.3998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace J. C., Edmonds M. Polyadenylylated nuclear RNA contains branches. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):950–954. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







