Abstract
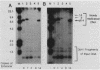
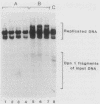
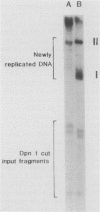
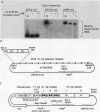
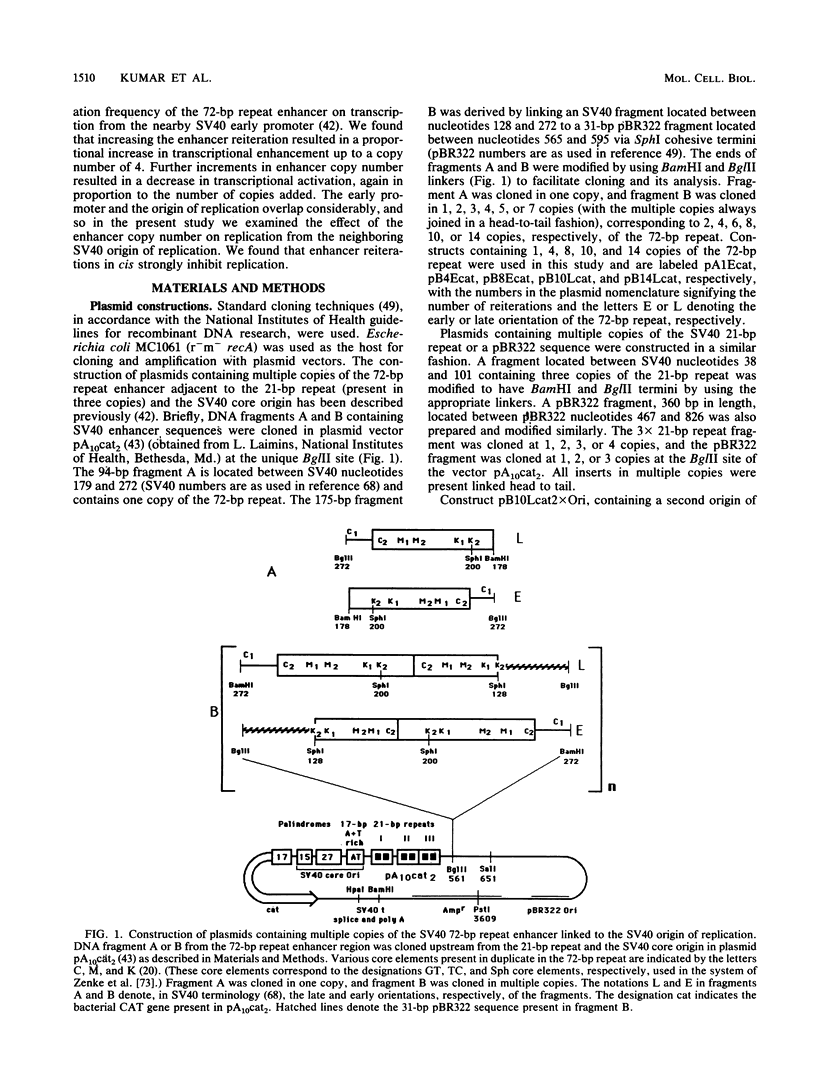
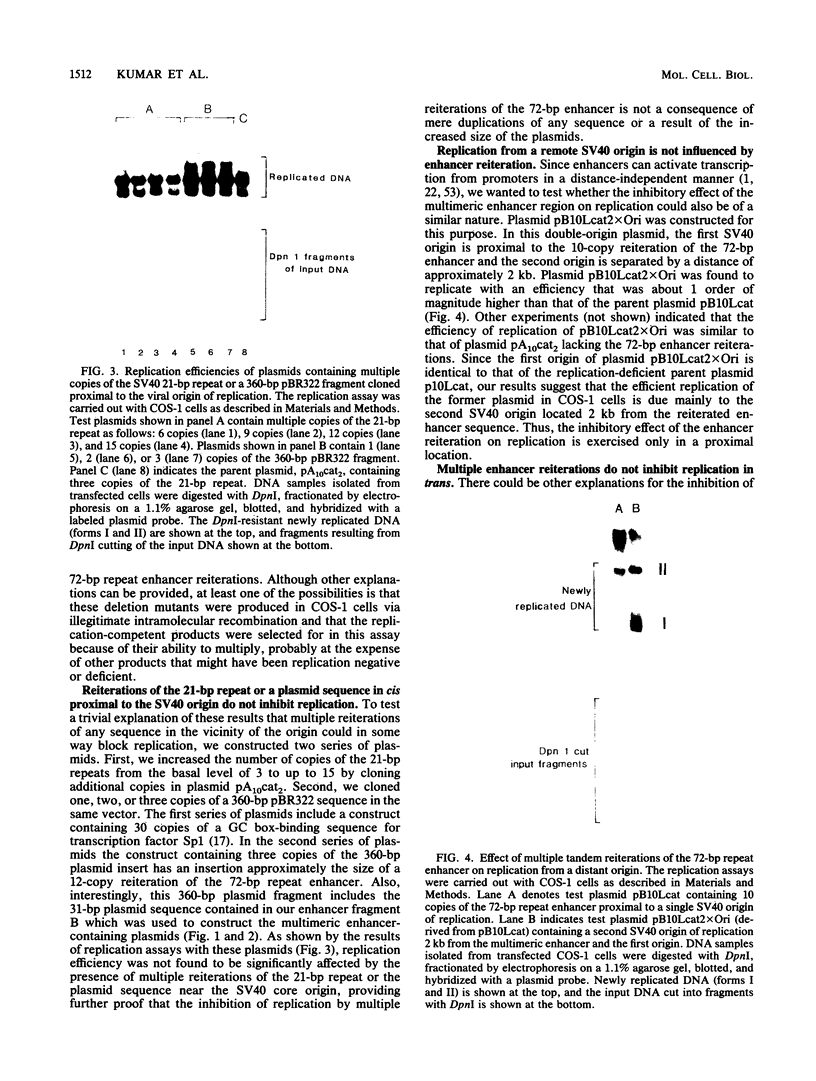
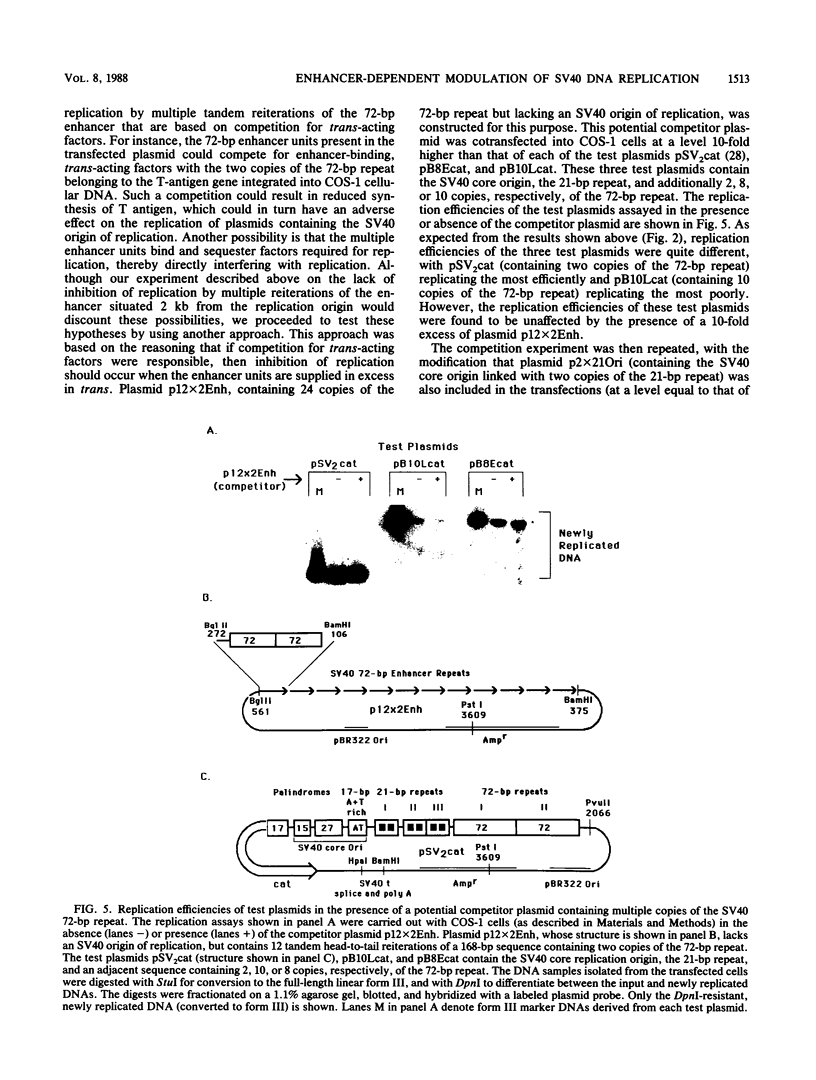
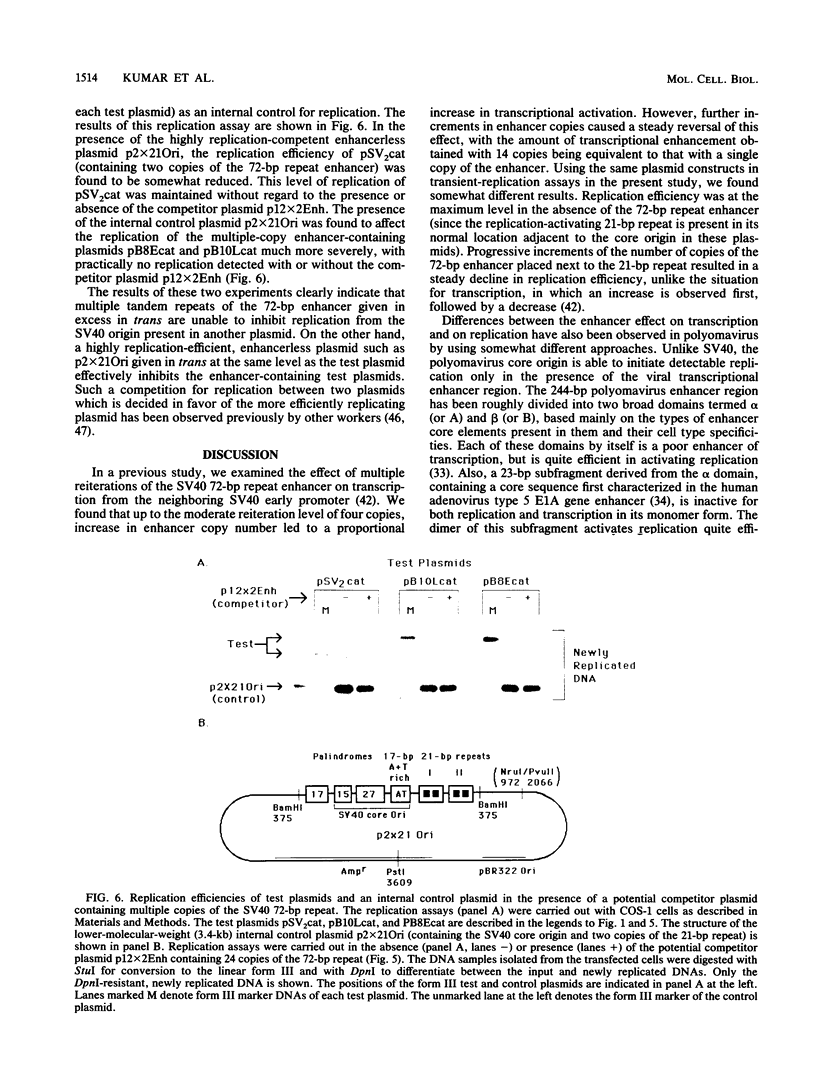
In a previous study in our laboratory, the effect of the reiteration frequency of the simian virus 40 (SV40) 72-base-pair (bp) repeat enhancer on transcription from the proximal SV40 early promoter was investigated (R. Kumar, T. A. Firak, C. T. Schroll, and K. N. Subramanian, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83:3199-3203, 1986). Increasing the enhancer copy number to four increased transcription proportionately; further increments in enhancer copy number reversed this effect, resulting in a decrease in the transcriptional activation. In the present study, the effect of enhancer reiteration on the replication efficiency of plasmids containing the SV40 origin of replication was investigated in transient replication assays in vivo in COS-1 monkey kidney cells producing the SV40 large tumor antigen required for replication. A plasmid containing the SV40 core origin and three copies of the replication-activating, G+C-rich 21-bp repeat promoter element replicated efficiently. Plasmids containing multiple copies of the 72-bp repeat enhancer cloned in head-to-tail linkage adjacent to the 21-bp repeat and the core origin replicated less efficiently; the decrease in replication efficiency could be correlated with the number of copies of the 72-bp repeat; replication was severely curtailed when 10 or more copies of the 72-bp repeat were present. Replication was not significantly inhibited by an increase in the number of copies of the 21-bp repeat to 15 or by the presence of three copies of a 360-bp pBR322 sequence in the immediate vicinity. Multiple copies of the 72-bp enhancer in cis were unable to inhibit replication from a second SV40 origin of replication situated 2 kilobase pairs away from the enhancer reiteration. Replication of four different test plasmids was not inhibited in trans by cotransfection of an excess of a potential competitor plasmid containing a 24-copy reiteration of the 72-bp enhancer. These results indicate that multiple tandem reiterations of the 72-bp enhancer inhibit replication only when they are present in cis adjacent to the origin of replication. Possible explanations for this inhibitory effect, such as an unfavorable local chromatin structure induced by the multimeric enhancer region or reduced or improper communications between factors bound to the multimeric region and the adjacent replication origin, are discussed.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banerji J., Rusconi S., Schaffner W. Expression of a beta-globin gene is enhanced by remote SV40 DNA sequences. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):299–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90413-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., Chambon P. Deletions covering the putative promoter region of early mRNAs of simian virus 40 do not abolish T-antigen expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3865–3869. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., Chambon P. In vivo sequence requirements of the SV40 early promotor region. Nature. 1981 Mar 26;290(5804):304–310. doi: 10.1038/290304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergsma D. J., Olive D. M., Hartzell S. W., Subramanian K. N. Territorial limits and functional anatomy of the simian virus 40 replication origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):381–385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady J., Loeken M. R., Khoury G. Interaction between two transcriptional control sequences required for tumor-antigen-mediated simian virus 40 late gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7299–7303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady J., Radonovich M., Thoren M., Das G., Salzman N. P. Simian virus 40 major late promoter: an upstream DNA sequence required for efficient in vitro transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;4(1):133–141. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand A. H., Breeden L., Abraham J., Sternglanz R., Nasmyth K. Characterization of a "silencer" in yeast: a DNA sequence with properties opposite to those of a transcriptional enhancer. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):41–48. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90059-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne B. J., Davis M. S., Yamaguchi J., Bergsma D. J., Subramanian K. N. Definition of the simian virus 40 early promoter region and demonstration of a host range bias in the enhancement effect of the simian virus 40 72-base-pair repeat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):721–725. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell B. A., Villarreal L. P. Lymphoid and other tissue-specific phenotypes of polyomavirus enhancer recombinants: positive and negative combinational effects on enhancer specificity and activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2068–2079. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cereghini S., Yaniv M. Assembly of transfected DNA into chromatin: structural changes in the origin-promoter-enhancer region upon replication. EMBO J. 1984 Jun;3(6):1243–1253. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01959.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandrasekharappa S. C., Subramanian K. N. Effects of position and orientation of the 72-base-pair-repeat transcriptional enhancer on replication from the simian virus 40 core origin. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):2973–2980. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.2973-2980.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLucia A. L., Deb S., Partin K., Tegtmeyer P. Functional interactions of the simian virus 40 core origin of replication with flanking regulatory sequences. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):138–144. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.138-144.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deb S., DeLucia A. L., Baur C. P., Koff A., Tegtmeyer P. Domain structure of the simian virus 40 core origin of replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1663–1670. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deb S., DeLucia A. L., Koff A., Tsui S., Tegtmeyer P. The adenine-thymine domain of the simian virus 40 core origin directs DNA bending and coordinately regulates DNA replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4578–4584. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMaio D., Nathans D. Regulatory mutants of simian virus 40. Effect of mutations at a T antigen binding site on DNA replication and expression of viral genes. J Mol Biol. 1982 Apr 15;156(3):531–548. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90265-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. The promoter-specific transcription factor Sp1 binds to upstream sequences in the SV40 early promoter. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90210-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernoult-Lange M., May P., Moreau P., May E. Simian virus 40 late promoter region able to initiate simian virus 40 early gene transcription in the absence of the simian virus 40 origin sequence. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):163–173. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.163-173.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D., Baty D., Chambon P. The repeated GC-rich motifs upstream from the TATA box are important elements of the SV40 early promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2447–2464. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firak T. A., Subramanian K. N. Minimal transcriptional enhancer of simian virus 40 is a 74-base-pair sequence that has interacting domains. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3667–3676. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm M., Berg P. Deletion mapping of DNA regions required for SV40 early region promoter function in vivo. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(5):457–481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm M., Berg P. Simian virus 40 early- and late-region promoter functions are enhanced by the 72-base-pair repeat inserted at distant locations and inverted orientations. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;3(6):991–999. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.6.991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerard R. D., Montelone B. A., Walter C. F., Innis J. W., Scott W. A. Role of specific simian virus 40 sequences in the nuclease-sensitive structure in viral chromatin. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):52–58. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerard R., Gluzman Y. Functional analysis of the role of the A + T-rich region and upstream flanking sequences in simian virus 40 DNA replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4570–4577. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gheysen D., van de Voorde A., Contreras R., Vanderheyden J., Duerinck F., Fiers W. Simian virus 40 mutants carrying extensive deletions in the 72-base-pair repeat region. J Virol. 1983 Jul;47(1):1–14. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.1.1-14.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh P. K., Lebowitz P. Simian virus 40 early mRNA's contain multiple 5' termini upstream and downstream from a Hogness-Goldberg sequence; a shift in 5' termini during the lytic cycle is mediated by large T antigen. J Virol. 1981 Oct;40(1):224–240. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.1.224-240.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruss P., Dhar R., Khoury G. Simian virus 40 tandem repeated sequences as an element of the early promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):943–947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen U., Sharp P. A. Sequences controlling in vitro transcription of SV40 promoters. EMBO J. 1983;2(12):2293–2303. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01737.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartzell S. W., Byrne B. J., Subramanian K. N. Mapping of the late promoter of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):23–27. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartzell S. W., Byrne B. J., Subramanian K. N. The simian virus 40 minimal origin and the 72-base-pair repeat are required simultaneously for efficient induction of late gene expression with large tumor antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6335–6339. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearing P., Shenk T. The adenovirus type 5 E1A transcriptional control region contains a duplicated enhancer element. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):695–703. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W., Gluzman Y. Duplications of a mutated simian virus 40 enhancer restore its activity. Nature. 1985 Feb 21;313(6004):711–714. doi: 10.1038/313711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertz G. Z., Mertz J. E. Bidirectional promoter elements of simian virus 40 are required for efficient replication of the viral DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3513–3522. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imagawa M., Chiu R., Karin M. Transcription factor AP-2 mediates induction by two different signal-transduction pathways: protein kinase C and cAMP. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90152-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jongstra J., Reudelhuber T. L., Oudet P., Benoist C., Chae C. B., Jeltsch J. M., Mathis D. J., Chambon P. Induction of altered chromatin structures by simian virus 40 enhancer and promoter elements. Nature. 1984 Feb 23;307(5953):708–714. doi: 10.1038/307708a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller J. M., Alwine J. C. Analysis of an activatable promoter: sequences in the simian virus 40 late promoter required for T-antigen-mediated trans activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1859–1869. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhl D., de la Fuente J., Chaturvedi M., Parimoo S., Ryals J., Meyer F., Weissmann C. Reversible silencing of enhancers by sequences derived from the human IFN-alpha promoter. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1057–1069. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90172-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar R., Firak T. A., Schroll C. T., Subramanian K. N. Activation of gene expression is adversely affected at high multiplicities of linked simian virus 40 enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3199–3203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L. A., Khoury G., Gorman C., Howard B., Gruss P. Host-specific activation of transcription by tandem repeats from simian virus 40 and Moloney murine sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6453–6457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L. A., Tsichlis P., Khoury G. Multiple enhancer domains in the 3' terminus of the Prague strain of Rous sarcoma virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Aug 24;12(16):6427–6442. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.16.6427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W., Mitchell P., Tjian R. Purified transcription factor AP-1 interacts with TPA-inducible enhancer elements. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):741–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90612-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. J., Peden K. W., Dixon R. A., Kelly T. Functional organization of the simian virus 40 origin of DNA replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1117–1128. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luthman H., Nilsson M. G., Magnusson G. Non-contiguous segments of the polyoma genome required in cis for DNA replication. J Mol Biol. 1982 Nov 15;161(4):533–550. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90406-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercola M., Goverman J., Mirell C., Calame K. Immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer requires one or more tissue-specific factors. Science. 1985 Jan 18;227(4684):266–270. doi: 10.1126/science.3917575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertz J. E., Berg P. Defective simian virus 40 genomes: isolation and growth of individual clones. Virology. 1974 Nov;62(1):112–124. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90307-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreau P., Hen R., Wasylyk B., Everett R., Gaub M. P., Chambon P. The SV40 72 base repair repeat has a striking effect on gene expression both in SV40 and other chimeric recombinants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):6047–6068. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.6047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller W. J., Mueller C. R., Mes A. M., Hassell J. A. Polyomavirus origin for DNA replication comprises multiple genetic elements. J Virol. 1983 Sep;47(3):586–599. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.3.586-599.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Tjian R. Construction and analysis of simian virus 40 origins defective in tumor antigen binding and DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6491–6495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ondek B., Shepard A., Herr W. Discrete elements within the SV40 enhancer region display different cell-specific enhancer activities. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):1017–1025. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04854.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peden K. W., Pipas J. M., Pearson-White S., Nathans D. Isolation of mutants of an animal virus in bacteria. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1392–1396. doi: 10.1126/science.6251547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld P. J., Kelly T. J. Purification of nuclear factor I by DNA recognition site affinity chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):1398–1408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schirm S., Jiricny J., Schaffner W. The SV40 enhancer can be dissected into multiple segments, each with a different cell type specificity. Genes Dev. 1987 Mar;1(1):65–74. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.1.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöler H. R., Gruss P. Specific interaction between enhancer-containing molecules and cellular components. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):403–411. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90233-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalloway D., Kleinberger T., Livingston D. M. Mapping of SV40 DNA replication origin region binding sites for the SV40 T antigen by protection against exonuclease III digestion. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):411–422. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90627-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Tjian R. T-antigen-DNA polymerase alpha complex implicated in simian virus 40 DNA replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):4077–4087. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.4077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stillman B., Gerard R. D., Guggenheimer R. A., Gluzman Y. T antigen and template requirements for SV40 DNA replication in vitro. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2933–2939. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04026.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Vigneron M., Matthes H., Wildeman A., Zenke M., Chambon P. Requirement of stereospecific alignments for initiation from the simian virus 40 early promoter. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):121–126. doi: 10.1038/319121a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P., Lewton B. A., DeLucia A. L., Wilson V. G., Ryder K. Topography of simian virus 40 A protein-DNA complexes: arrangement of protein bound to the origin of replication. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):151–161. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.151-161.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P. Simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis: the viral replicon. J Virol. 1972 Oct;10(4):591–598. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.4.591-598.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R. Protein-DNA interactions at the origin of simian virus 40 DNA replication. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):655–661. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyndall C., La Mantia G., Thacker C. M., Favaloro J., Kamen R. A region of the polyoma virus genome between the replication origin and late protein coding sequences is required in cis for both early gene expression and viral DNA replication. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6231–6250. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veldman G. M., Lupton S., Kamen R. Polyomavirus enhancer contains multiple redundant sequence elements that activate both DNA replication and gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):649–658. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Wasylyk C., Chambon P. Short and long range activation by the SV40 enhancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5589–5608. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiher H., König M., Gruss P. Multiple point mutations affecting the simian virus 40 enhancer. Science. 1983 Feb 11;219(4585):626–631. doi: 10.1126/science.6297005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenke M., Grundström T., Matthes H., Wintzerith M., Schatz C., Wildeman A., Chambon P. Multiple sequence motifs are involved in SV40 enhancer function. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):387–397. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04224.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Villiers J., Schaffner W., Tyndall C., Lupton S., Kamen R. Polyoma virus DNA replication requires an enhancer. Nature. 1984 Nov 15;312(5991):242–246. doi: 10.1038/312242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]