Abstract
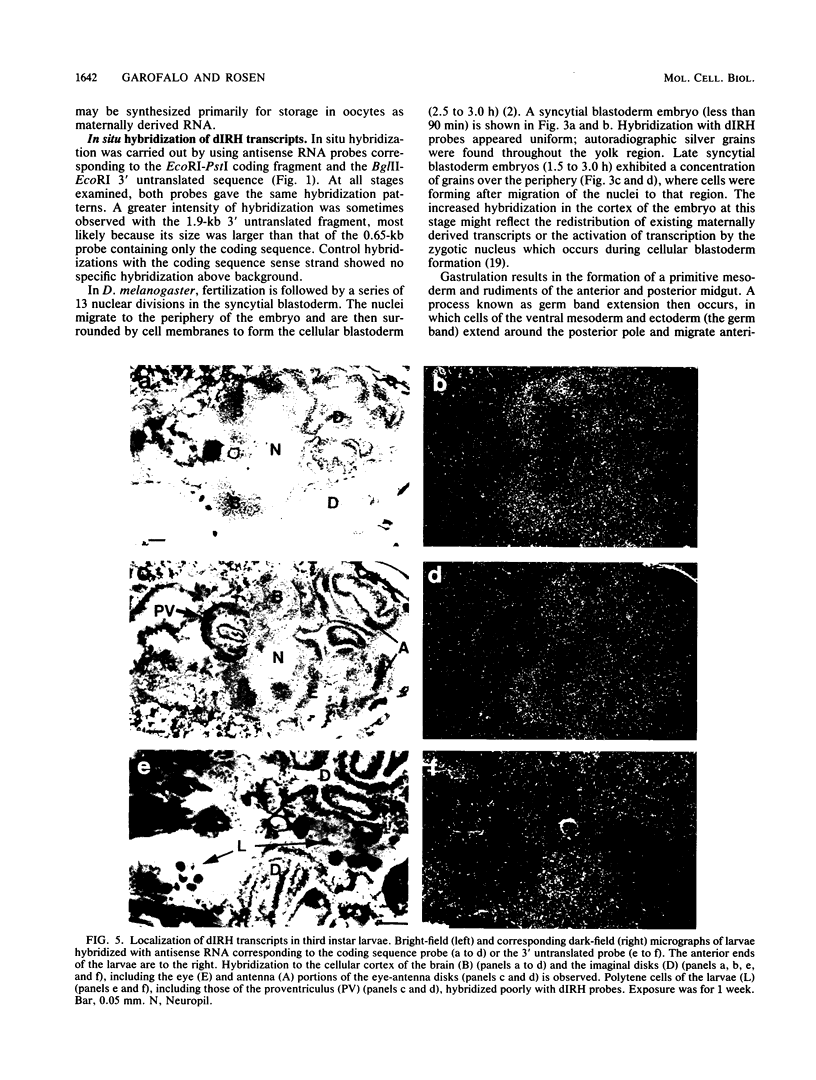
The Drosophila melanogaster insulin receptor (Drosophila insulin receptor homolog [dIRH]) is similar to its mammalian counterpart in deduced amino acid sequence, subunit structure, and ligand-stimulated protein tyrosine kinase activity. The function of this receptor in D. melanogaster is not yet known. However, a role in development is suggested by the observations that levels of insulin-stimulated kinase activity and expression of dIRH mRNA are maximal during Drosophila midembryogenesis. In this study, a 2.9-kilobase (kb) cDNA clone corresponding to both the dIRH tyrosine kinase domain and some of the 3' untranslated sequence was used to determine the tissue distribution of dIRH mRNA during development. Two principal mRNAs of 11 and 8.6 kb hybridized with the dIRH cDNA in Northern (RNA) blot analysis. The abundance of the 8.6-kb mRNA increased transiently in early embryos, whereas the 11-kb species was most abundant during midembryogenesis. A similar pattern of expression was previously determined by Northern analysis, using a dIRH genomic clone (L. Petruzzelli, R. Herrera, R. Arenas-Garcia, R. Fernandez, M. J. Birnbaum, and O. M. Rosen, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83:4710-4714, 1986). In situ hybridization revealed dIRH transcripts in the ovaries of adult flies, in which the transcripts appeared to be synthesized by nurse cells for eventual storage as maternal RNA in the mature oocyte. Throughout embryogenesis, dIRH transcripts were ubiquitously expressed, although after midembryogenesis, higher levels were detected in the developing nervous system. Nervous system expression remained elevated throughout the larval stages and persisted in the adult, in which the cortex of the brain and ganglion cells were among the most prominently labeled tissues. In larvae, the imaginal disk cells exhibited comparatively high levels of dIRH mRNA expression. The broad distribution of dIRH mRNA in embryos and imaginal disks is compatible with a role for dIRH in anabolic processes required for cell growth. The apparently elevated expression of dIRH mRNA in nervous tissue during mid- and late embryogenesis coincides with a period of active neurite outgrowth and suggests that dIRH may be involved in this process.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamson E. D., Meek J. The ontogeny of epidermal growth factor receptors during mouse development. Dev Biol. 1984 May;103(1):62–70. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Pablo F., Roth J., Hernandez E., Pruss R. M. Insulin is present in chicken eggs and early chick embryos. Endocrinology. 1982 Dec;111(6):1909–1916. doi: 10.1210/endo-111-6-1909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duve H., Thorpe A., Lazarus N. R. Isolation of material displaying insulin-like immunological biological activity from the brain of the blowfly Calliphora vomitoria. Biochem J. 1979 Nov 15;184(2):221–227. doi: 10.1042/bj1840221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebina Y., Ellis L., Jarnagin K., Edery M., Graf L., Clauser E., Ou J. H., Masiarz F., Kan Y. W., Goldfine I. D. The human insulin receptor cDNA: the structural basis for hormone-activated transmembrane signalling. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):747–758. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90334-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Almonacid R., Rosen O. M. Structure and ligand specificity of the Drosophila melanogaster insulin receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2718–2727. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory R. J., Kammermeyer K. L., Vincent W. S., 3rd, Wadsworth S. G. Primary sequence and developmental expression of a novel Drosophila melanogaster src gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2119–2127. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havrankova J., Roth J., Brownstein M. Insulin receptors are widely distributed in the central nervous system of the rat. Nature. 1978 Apr 27;272(5656):827–829. doi: 10.1038/272827a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendricks S. A., de Pablo F., Roth J. Early development and tissue-specific patterns of insulin binding in chick embryo. Endocrinology. 1984 Oct;115(4):1315–1323. doi: 10.1210/endo-115-4-1315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. J., Milner R. D. Insulin as a growth factor. Pediatr Res. 1985 Sep;19(9):879–886. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198509000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kammermeyer K. L., Wadsworth S. C. Expression of Drosophila epidermal growth factor receptor homologue in mitotic cell populations. Development. 1987 Jun;100(2):201–210. doi: 10.1242/dev.100.2.201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidd S., Lockett T. J., Young M. W. The Notch locus of Drosophila melanogaster. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):421–433. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90376-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lev Z., Leibovitz N., Segev O., Shilo B. Z. Expression of the src and abl cellular oncogenes during development of Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 May;4(5):982–984. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.5.982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lev Z., Shilo B. Z., Kimchie Z. Developmental changes in expression of the Drosophila melanogaster epidermal growth factor receptor gene. Dev Biol. 1985 Aug;110(2):499–502. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90107-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy B. T., Sorge L. K., Meymandi A., Maness P. F. pp60c-src Kinase is in chick and human embryonic tissues. Dev Biol. 1984 Jul;104(1):9–17. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90031-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livneh E., Glazer L., Segal D., Schlessinger J., Shilo B. Z. The Drosophila EGF receptor gene homolog: conservation of both hormone binding and kinase domains. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):599–607. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90208-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Miller O. L., Jr Ultrastructural patterns of RNA synthesis during early embryogenesis of Drosophila melanogaster. Cell. 1976 Jun;8(2):305–319. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90014-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchison T. J., Sedat J. Localization of antigenic determinants in whole Drosophila embryos. Dev Biol. 1983 Sep;99(1):261–264. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90275-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagasawa H., Kataoka H., Isogai A., Tamura S., Suzuki A., Mizoguchi A., Fujiwara Y., Suzuki A., Takahashi S. Y., Ishizaki H. Amino acid sequence of a prothoracicotropic hormone of the silkworm Bombyx mori. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5840–5843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishida Y., Hata M., Nishizuka Y., Rutter W. J., Ebina Y. Cloning of a Drosophila cDNA encoding a polypeptide similar to the human insulin receptor precursor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Dec 15;141(2):474–481. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80197-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petruzzelli L., Herrera R., Arenas-Garcia R., Fernandez R., Birnbaum M. J., Rosen O. M. Isolation of a Drosophila genomic sequence homologous to the kinase domain of the human insulin receptor and detection of the phosphorylated Drosophila receptor with an anti-peptide antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4710–4714. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petruzzelli L., Herrera R., Garcia-Arenas R., Rosen O. M. Acquisition of insulin-dependent protein tyrosine kinase activity during Drosophila embryogenesis. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 25;260(30):16072–16075. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Recio-Pinto E., Ishii D. N. Effects of insulin, insulin-like growth factor-II and nerve growth factor on neurite outgrowth in cultured human neuroblastoma cells. Brain Res. 1984 Jun 8;302(2):323–334. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90246-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Recio-Pinto E., Rechler M. M., Ishii D. N. Effects of insulin, insulin-like growth factor-II, and nerve growth factor on neurite formation and survival in cultured sympathetic and sensory neurons. J Neurosci. 1986 May;6(5):1211–1219. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-05-01211.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schejter E. D., Segal D., Glazer L., Shilo B. Z. Alternative 5' exons and tissue-specific expression of the Drosophila EGF receptor homolog transcripts. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):1091–1101. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90709-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seecof R. L., Dewhurst S. Insulin is a Drosophila hormone and acts to enhance the differentiation of embryonic Drosophila cells. Cell Differ. 1974 Jun;3(1):63–70. doi: 10.1016/0045-6039(74)90041-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal D., Shilo B. Z. Tissue localization of Drosophila melanogaster ras transcripts during development. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2241–2248. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. A., Drees B., Kornberg T., Bishop J. M. The nucleotide sequence and the tissue-specific expression of Drosophila c-src. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):831–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90279-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tager H. S., Markese J., Kramer K. J., Speirs R. D., Childs C. N. Glucagon-like and insulin-like hormones of the insect neurosecretory system. Biochem J. 1976 Jun 15;156(3):515–520. doi: 10.1042/bj1560515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. B., Bastiani M. J., Bate M., Goodman C. S. From grasshopper to Drosophila: a common plan for neuronal development. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):203–207. doi: 10.1038/310203a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Bell J. R., Chen E. Y., Herrera R., Petruzzelli L. M., Dull T. J., Gray A., Coussens L., Liao Y. C., Tsubokawa M. Human insulin receptor and its relationship to the tyrosine kinase family of oncogenes. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):756–761. doi: 10.1038/313756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Gray A., Tam A. W., Yang-Feng T., Tsubokawa M., Collins C., Henzel W., Le Bon T., Kathuria S., Chen E. Insulin-like growth factor I receptor primary structure: comparison with insulin receptor suggests structural determinants that define functional specificity. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2503–2512. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04528.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadsworth S. C., Madhavan K., Bilodeau-Wentworth D. Maternal inheritance of transcripts from three Drosophila src-related genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 25;13(6):2153–2170. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.6.2153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadsworth S. C., Vincent W. S., 3rd, Bilodeau-Wentworth D. A Drosophila genomic sequence with homology to human epidermal growth factor receptor. Nature. 1985 Mar 14;314(6007):178–180. doi: 10.1038/314178a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]