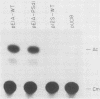
Abstract
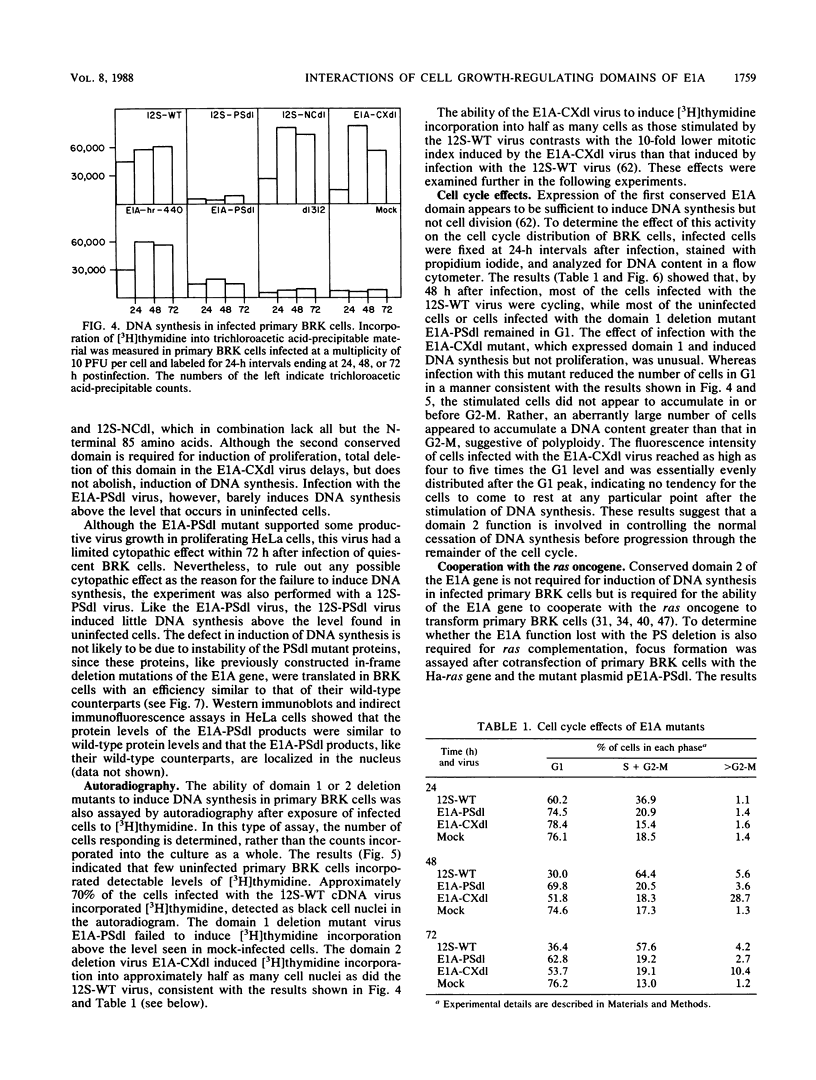
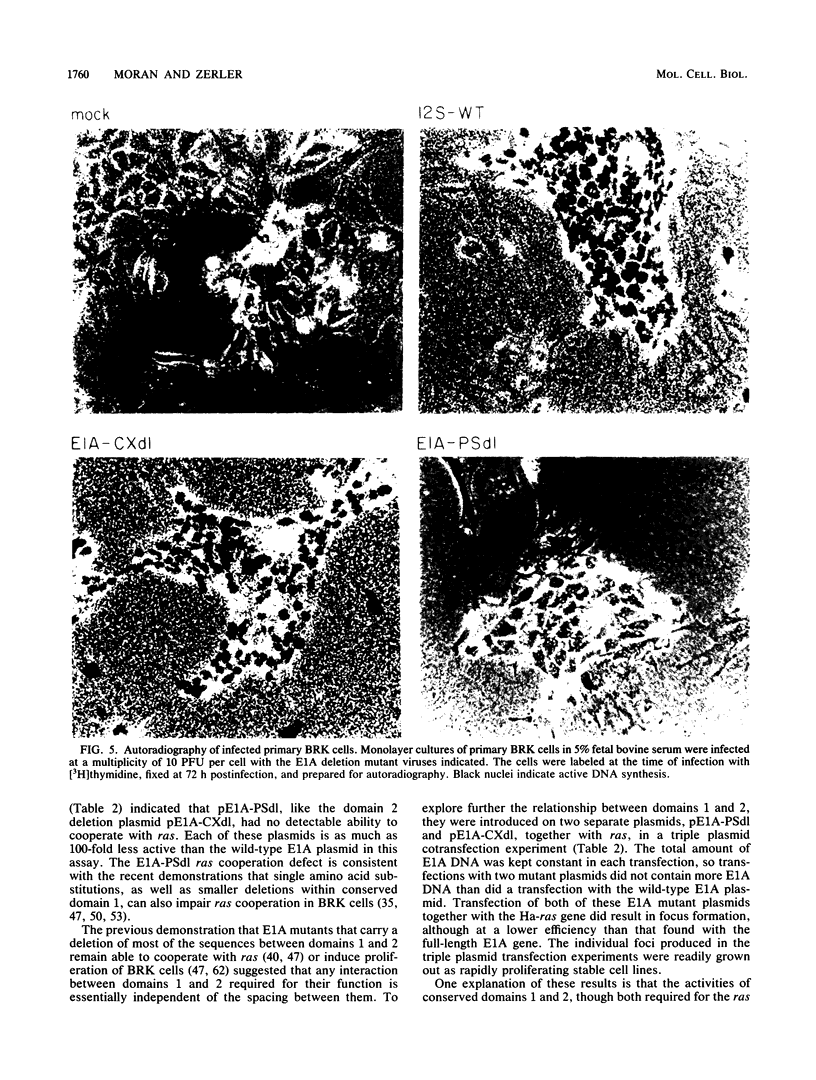
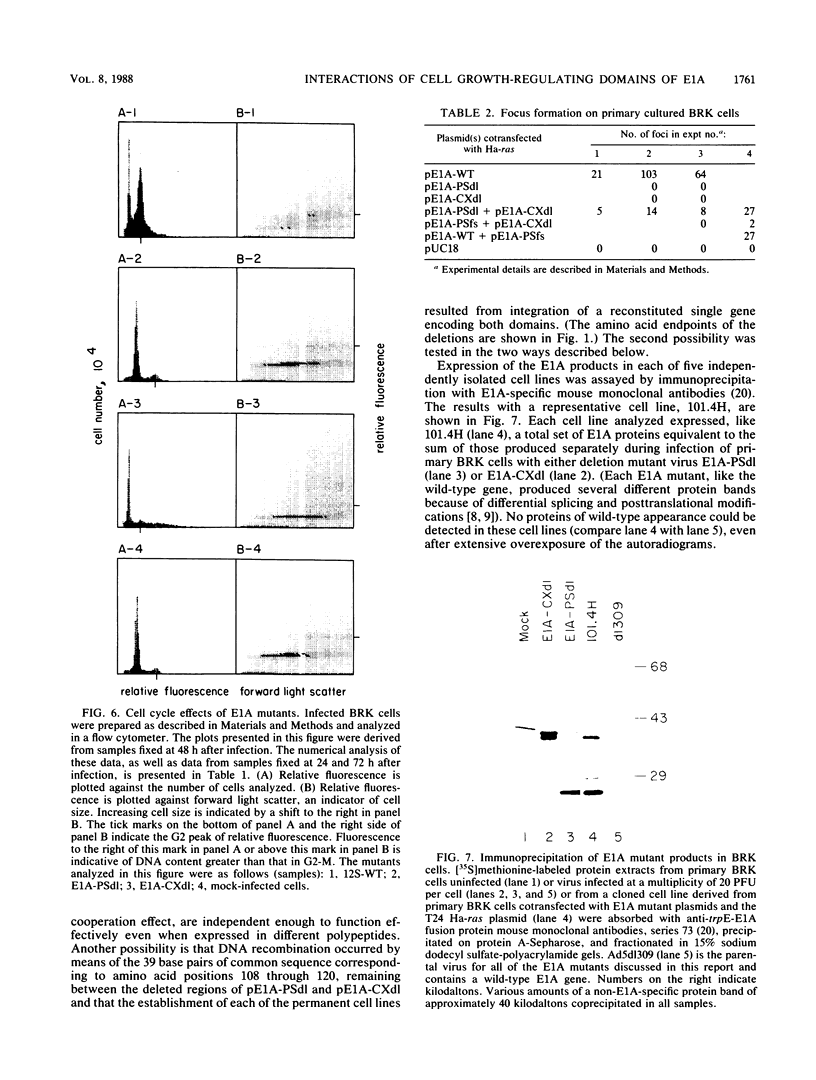
Among the various biological activities expressed by the products of the adenovirus E1A gene are the abilities to induce cellular DNA synthesis and proliferation in quiescent primary baby rat kidney cells. The functional sites for these activities lie principally within two regions of the E1A proteins: an N-terminal region and a small second region of approximately 20 amino acids further downstream. To study the biological functions of the first domain, we constructed an in-frame deletion of amino acid positions 23 through 107 of the E1A products. This deletion did not impede the ability of the E1A products to transactivate the adenovirus early region 3 promoter in a transient-expression assay in HeLa cells. The ability to induce DNA synthesis in quiescent baby rat kidney cells was, however, lost in the absence of these sequences. Deletion of the small second region induced a form of S phase in which DNA synthesis occurred in the apparent absence of controls required for the cessation of DNA synthesis and progression through the remainder of the cell cycle. These cells did not appear to accumulate in or before G2, and many appeared to have a DNA content greater than that in G2. The functions of both domains are required for production of transformed foci in a ras cooperation assay. Focus formation occurred, however, even when the two domains were introduced on two separate plasmids. This complementation effect appeared to require expression of both of the mutant proteins and did not appear to result merely from recombination at the DNA level.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adlakha R. C., Wright D. A., Sahasrabuddhe C. G., Davis F. M., Prashad N., Bigo H., Rao P. N. Partial purification and characterization of mitotic factors from HeLa cells. Exp Cell Res. 1985 Oct;160(2):471–482. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(85)90194-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Lee F., Harrison T., Williams J., Sharp P. A. Pre-early adenovirus 5 gene product regulates synthesis of early viral messenger RNAs. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):935–944. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90333-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Structure of the adenovirus 2 early mRNAs. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):695–711. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90252-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borrelli E., Hen R., Chambon P. Adenovirus-2 E1A products repress enhancer-induced stimulation of transcription. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):608–612. doi: 10.1038/312608a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlock L. R., Jones N. C. Transformation-defective mutant of adenovirus type 5 containing a single altered E1a mRNA species. J Virol. 1981 Dec;40(3):657–664. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.3.657-664.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinnadurai G. Adenovirus 2 Ip+ locus codes for a 19 kd tumor antigen that plays an essential role in cell transformation. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):759–766. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90018-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow L. T., Broker T. R., Lewis J. B. Complex splicing patterns of RNAs from the early regions of adenovirus-2. J Mol Biol. 1979 Oct 25;134(2):265–303. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90036-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downey J. F., Evelegh C. M., Branton P. E., Bayley S. T. Peptide maps and N-terminal sequences of polypeptides from early region 1A of human adenovirus 5. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):30–37. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.30-37.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esche H., Mathews M. B., Lewis J. B. Proteins and messenger RNAs of the transforming region of wild-type and mutant adenoviruses. J Mol Biol. 1980 Sep 25;142(3):399–417. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90279-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fasano O., Taparowsky E., Fiddes J., Wigler M., Goldfarb M. Sequence and structure of the coding region of the human H-ras-1 gene from T24 bladder carcinoma cells. J Mol Appl Genet. 1983;2(2):173–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson B., Krippl B., Andrisani O., Jones N., Westphal H., Rosenberg M. E1A 13S and 12S mRNA products made in Escherichia coli both function as nucleus-localized transcription activators but do not directly bind DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2653–2661. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franza B. R., Jr, Maruyama K., Garrels J. I., Ruley H. E. In vitro establishment is not a sufficient prerequisite for transformation by activated ras oncogenes. Cell. 1986 Feb 14;44(3):409–418. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90462-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallimore P. H. Viral DNA in transformed cells. II. A study of the sequences of adenovirus 2 DNA IN NINE LINES OF TRANSFORMED RAT CELLS USING SPECIFIC FRAGMENTS OF THE VIRAL GENOME;. J Mol Biol. 1974 Oct 15;89(1):49–72. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90162-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenn G. M., Ricciardi R. P. Adenovirus 5 early region 1A host range mutants hr3, hr4, and hr5 contain point mutations which generate single amino acid substitutions. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):66–74. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.66-74.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfarb M., Shimizu K., Perucho M., Wigler M. Isolation and preliminary characterization of a human transforming gene from T24 bladder carcinoma cells. Nature. 1982 Apr 1;296(5856):404–409. doi: 10.1038/296404a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., Harrison T., Williams J. Defective transforming capacity of adenovirus type 5 host-range mutants. Virology. 1978 May 1;86(1):10–21. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haley K. P., Overhauser J., Babiss L. E., Ginsberg H. S., Jones N. C. Transformation properties of type 5 adenovirus mutants that differentially express the E1A gene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5734–5738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlow E., Franza B. R., Jr, Schley C. Monoclonal antibodies specific for adenovirus early region 1A proteins: extensive heterogeneity in early region 1A products. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):533–546. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.533-546.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlow E., Whyte P., Franza B. R., Jr, Schley C. Association of adenovirus early-region 1A proteins with cellular polypeptides. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1579–1589. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hen R., Borrelli E., Chambon P. Repression of the immunoglobulin heavy chain enhancer by the adenovirus-2 E1A products. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1391–1394. doi: 10.1126/science.2999984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hen R., Borrelli E., Fromental C., Sassone-Corsi P., Chambon P. A mutated polyoma virus enhancer which is active in undifferentiated embryonal carcinoma cells is not repressed by adenovirus-2 E1A products. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):249–251. doi: 10.1038/321249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houweling A., van den Elsen P. J., van der Eb A. J. Partial transformation of primary rat cells by the leftmost 4.5% fragment of adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1980 Sep;105(2):537–550. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90054-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N., Shenk T. An adenovirus type 5 early gene function regulates expression of other early viral genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3665–3669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N., Shenk T. Isolation of adenovirus type 5 host range deletion mutants defective for transformation of rat embryo cells. Cell. 1979 Jul;17(3):683–689. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90275-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaczmarek L., Ferguson B., Rosenberg M., Baserga R. Induction of cellular DNA synthesis by purified adenovirus E1A proteins. Virology. 1986 Jul 15;152(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90366-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitchingman G. R., Westphal H. The structure of adenovirus 2 early nuclear and cytoplasmic RNAs. J Mol Biol. 1980 Feb 15;137(1):23–48. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90155-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuppuswamy M. N., Chinnadurai G. Relationship between the transforming and transcriptional regulatory functions of adenovirus 2 E1a oncogene. Virology. 1987 Jul;159(1):31–38. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90344-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land H., Parada L. F., Weinberg R. A. Tumorigenic conversion of primary embryo fibroblasts requires at least two cooperating oncogenes. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):596–602. doi: 10.1038/304596a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. B., Mathews M. B. Control of adenovirus early gene expression: a class of immediate early products. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):303–313. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90138-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillie J. W., Green M., Green M. R. An adenovirus E1a protein region required for transformation and transcriptional repression. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):1043–1051. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90704-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillie J. W., Loewenstein P. M., Green M. R., Green M. Functional domains of adenovirus type 5 E1a proteins. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1091–1100. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90175-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montano X., Lane D. P. The adenovirus Ela gene induces differentiation of F9 teratocarcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1782–1790. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montell C., Courtois G., Eng C., Berk A. Complete transformation by adenovirus 2 requires both E1A proteins. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):951–961. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90045-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran E., Grodzicker T., Roberts R. J., Mathews M. B., Zerler B. Lytic and transforming functions of individual products of the adenovirus E1A gene. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):765–775. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.765-775.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran E., Mathews M. B. Multiple functional domains in the adenovirus E1A gene. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):177–178. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90418-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran E., Zerler B., Harrison T. M., Mathews M. B. Identification of separate domains in the adenovirus E1A gene for immortalization activity and the activation of virus early genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3470–3480. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. Mechanism of activation of early viral transcription by the adenovirus E1A gene product. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(2 Pt 2):213–220. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90304-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perricaudet M., Akusjärvi G., Virtanen A., Pettersson U. Structure of two spliced mRNAs from the transforming region of human subgroup C adenoviruses. Nature. 1979 Oct 25;281(5733):694–696. doi: 10.1038/281694a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinlan M. P., Grodzicker T. Adenovirus E1A 12S protein induces DNA synthesis and proliferation in primary epithelial cells in both the presence and absence of serum. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):673–682. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.673-682.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruley H. E. Adenovirus early region 1A enables viral and cellular transforming genes to transform primary cells in culture. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):602–606. doi: 10.1038/304602a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P., Nurse P. Schizosaccharomyces pombe and Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a look at yeasts divided. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):781–782. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90550-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider J. F., Fisher F., Goding C. R., Jones N. C. Mutational analysis of the adenovirus E1a gene: the role of transcriptional regulation in transformation. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):2053–2060. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02470.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solnick D., Anderson M. A. Transformation-deficient adenovirus mutant defective in expression of region 1A but not region 1B. J Virol. 1982 Apr;42(1):106–113. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.1.106-113.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stabel S., Argos P., Philipson L. The release of growth arrest by microinjection of adenovirus E1A DNA. EMBO J. 1985 Sep;4(9):2329–2336. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03934.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens C., Harlow E. Differential splicing yields novel adenovirus 5 E1A mRNAs that encode 30 kd and 35 kd proteins. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):2027–2035. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02467.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svensson C., Akusjärvi G. Adenovirus 2 early region 1A stimulates expression of both viral and cellular genes. EMBO J. 1984 Apr;3(4):789–794. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01886.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokunaga O., Yaegashi T., Lowe J., Dobbs L., Padmanabhan R. Sequence analysis in the E1 region of adenovirus type 4 DNA. Virology. 1986 Dec;155(2):418–433. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90204-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulfendahl P. J., Linder S., Kreivi J. P., Nordqvist K., Sevensson C., Hultberg H., Akusjärvi G. A novel adenovirus-2 E1A mRNA encoding a protein with transcription activation properties. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):2037–2044. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02468.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Eb A. J., Mulder C., Graham F. L., Houweling A. Transformation with specific fragments of adenovirus DNAs. I. Isolation of specific fragments with transforming activity of adenovirus 2 and 5 DNA. Gene. 1977;2(3-4):115–132. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(77)90012-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velcich A., Kern F. G., Basilico C., Ziff E. B. Adenovirus E1a proteins repress expression from polyomavirus early and late promoters. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):4019–4025. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.4019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velcich A., Ziff E. Adenovirus E1a proteins repress transcription from the SV40 early promoter. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90219-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks D. L., Jones N. C. E1A control of gene expression is mediated by sequences 5' to the transcriptional starts of the early viral genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;3(7):1222–1234. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.7.1222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R., Urlaub G., Chasin L. DNA-mediated transfer of the adenine phosphoribosyltransferase locus into mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1373–1376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu B. J., Hurst H. C., Jones N. C., Morimoto R. I. The E1A 13S product of adenovirus 5 activates transcription of the cellular human HSP70 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2994–2999. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee S. P., Branton P. E. Detection of cellular proteins associated with human adenovirus type 5 early region 1A polypeptides. Virology. 1985 Nov;147(1):142–153. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90234-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerler B., Moran B., Maruyama K., Moomaw J., Grodzicker T., Ruley H. E. Adenovirus E1A coding sequences that enable ras and pmt oncogenes to transform cultured primary cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;6(3):887–899. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.3.887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerler B., Roberts R. J., Mathews M. B., Moran E. Different functional domains of the adenovirus E1A gene are involved in regulation of host cell cycle products. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):821–829. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]