Abstract
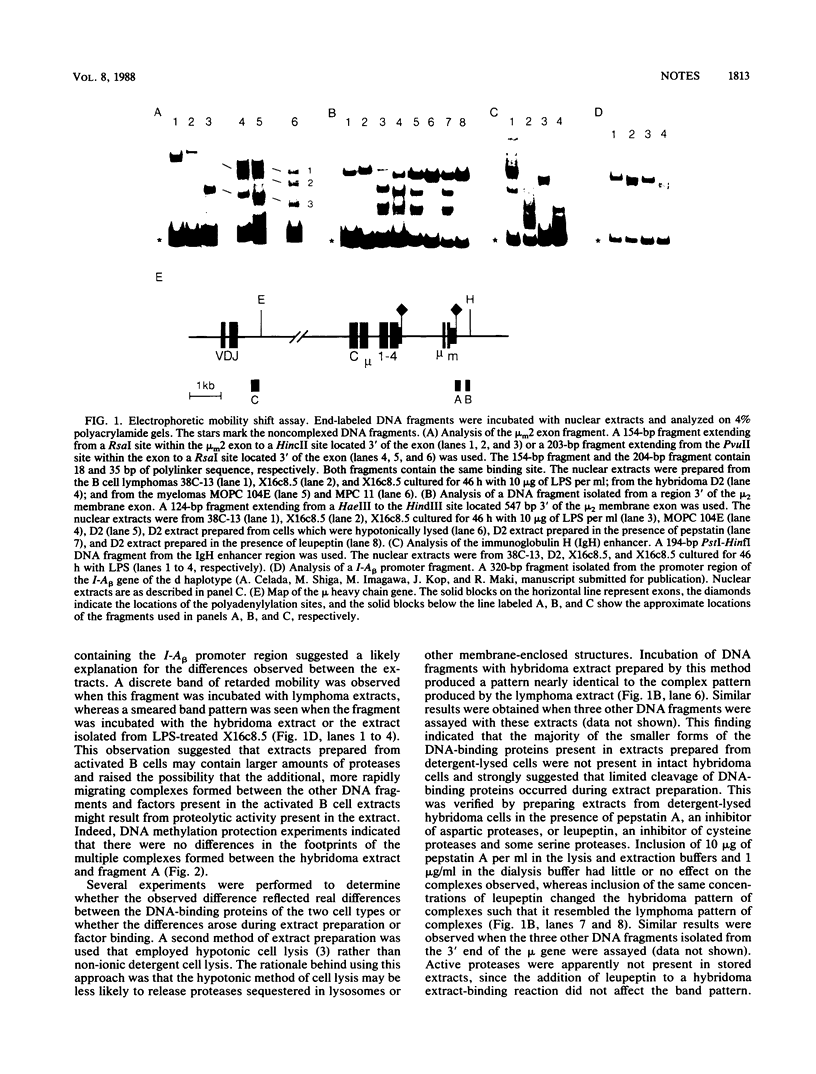
DNA-binding proteins that interact with the 3' end of the mouse mu immunoglobulin heavy chain gene were identified by the electrophoretic mobility shift assay. Complexes of distinctly different mobilities were formed by extracts prepared from B lymphoid lines representing different stages of maturation. The apparent stage-specific differences are shown to be due to proteolytic events that occurred during extract preparation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballard D. W., Bothwell A. Mutational analysis of the immunoglobulin heavy chain promoter region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9626–9630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brent R., Ptashne M. A bacterial repressor protein or a yeast transcriptional terminator can block upstream activation of a yeast gene. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):612–615. doi: 10.1038/312612a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerster T., Matthias P., Thali M., Jiricny J., Schaffner W. Cell type-specificity elements of the immunoglobulin heavy chain gene enhancer. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1323–1330. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02371.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S., Chambon P. Oestradiol induction of a glucocorticoid-responsive gene by a chimaeric receptor. Nature. 1987 Jan 1;325(6099):75–78. doi: 10.1038/325075a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Rosenbauer H., Niedermeyer I., Maier U., Ohrlein A. A repeated 18 bp sequence motif in the mouse rDNA spacer mediates binding of a nuclear factor and transcription termination. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):837–846. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90558-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hromas R., Van Ness B. Nuclear factors bind to regulatory regions of the mouse kappa immunoglobulin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 25;14(12):4837–4848. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.12.4837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keegan L., Gill G., Ptashne M. Separation of DNA binding from the transcription-activating function of a eukaryotic regulatory protein. Science. 1986 Feb 14;231(4739):699–704. doi: 10.1126/science.3080805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley D. E., Perry R. P. Transcriptional and posttranscriptional control of immunoglobulin mRNA production during B lymphocyte development. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 11;14(13):5431–5447. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.13.5431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. J., Evans C. B., Fowlkes B. J., Leiserson W. M., Asofsky R. The effect of the in vivo passage on sIg expression of BALB/c B-cell lines. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;399:122–130. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb25668.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishi H., Miki Y., Kikutani H., Yamamura Y., Kishimoto T. Sequential induction of phospholipid methylation and serine esterase activation in a B cell differentiation factor (BCDF)-stimulated human B cell line. J Immunol. 1983 Oct;131(4):1961–1965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T., Kikutani H., Nishizawa Y., Sakaguchi N., Yamamura Y. Involvement of anti-Ig-activated serine protease in the generation of cytoplasmic factor(s) that are responsible for the transmission of Ig-receptor-mediated signals. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1504–1510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ku G. S., Quigley J. P., Sultzer B. M. The inhibition of the mitogenic stimulation of B lymphocytes by a serine protease inhibitor: commitment to proliferation correlates with an enhanced expression of a cell-associated arginine-specific serine enzyme. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2494–2499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landolfi N. F., Capra J. D., Tucker P. W. Interaction of cell-type-specific nuclear proteins with immunoglobulin VH promoter region sequences. Nature. 1986 Oct 9;323(6088):548–551. doi: 10.1038/323548a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landolfi N. F., Capra J. D., Tucker P. W. Protein-nucleotide contacts in the immunoglobulin heavy-chain promoter region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3851–3855. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda H., Kitamura D., Kudo A., Araki K., Watanabe T. Trans-acting nuclear protein responsible for induction of rearranged human immunoglobulin heavy chain gene. Cell. 1986 Apr 11;45(1):25–33. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90534-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mather E. L., Nelson K. J., Haimovich J., Perry R. P. Mode of regulation of immunoglobulin mu- and delta-chain expression varies during B-lymphocyte maturation. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):329–338. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90226-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson C. L., Orth K., Calame K. L. Binding in vitro of multiple cellular proteins to immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4168–4178. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Inducibility of kappa immunoglobulin enhancer-binding protein Nf-kappa B by a posttranslational mechanism. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):921–928. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90807-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90346-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., Sen R., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. A nuclear factor that binds to a conserved sequence motif in transcriptional control elements of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):154–158. doi: 10.1038/319154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staudt L. M., Singh H., Sen R., Wirth T., Sharp P. A., Baltimore D. A lymphoid-specific protein binding to the octamer motif of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Oct 16;323(6089):640–643. doi: 10.1038/323640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Identification of a protein-binding site that mediates transcriptional response of the c-fos gene to serum factors. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):567–574. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90882-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger J., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. Distinct factors bind to apparently homologous sequences in the immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer. 1986 Aug 28-Sep 3Nature. 322(6082):846–848. doi: 10.1038/322846a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]