Abstract
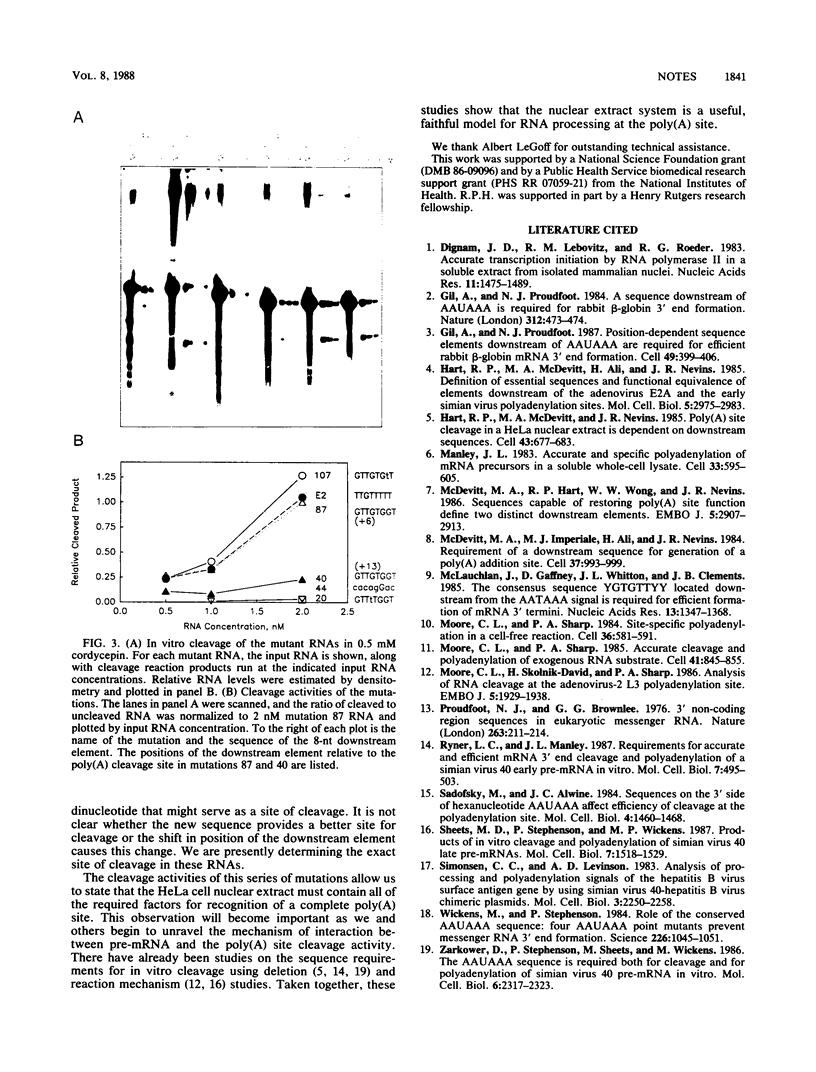
Previous studies have shown that a sequence element downstream of the poly(A) addition site is required for efficient cleavage in vivo. We tested a group of downstream element point mutations in an in vitro reaction using HeLa cell nuclear extract as a source of cleavage activity. In close agreement with earlier studies (M. A. McDevitt, R. P. Hart, W. W. Wong, and J. R. Nevins, EMBO J. 5:2907-2913, 1986), a downstream element from the adenovirus E2a gene directed a higher level of cleavage activity than one from the simian virus 40 early gene. Furthermore, a single-base change in the downstream element could result in a decrease in cleavage activity of about 50-fold. That these mutations have similar effects in vivo and in vitro indicates that the HeLa cell nuclear extract system contains all of the factors required to study the mechanism of sequence recognition.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gil A., Proudfoot N. J. A sequence downstream of AAUAAA is required for rabbit beta-globin mRNA 3'-end formation. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):473–474. doi: 10.1038/312473a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gil A., Proudfoot N. J. Position-dependent sequence elements downstream of AAUAAA are required for efficient rabbit beta-globin mRNA 3' end formation. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):399–406. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90292-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart R. P., McDevitt M. A., Ali H., Nevins J. R. Definition of essential sequences and functional equivalence of elements downstream of the adenovirus E2A and the early simian virus 40 polyadenylation sites. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):2975–2983. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.2975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart R. P., McDevitt M. A., Nevins J. R. Poly(A) site cleavage in a HeLa nuclear extract is dependent on downstream sequences. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):677–683. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90240-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L. Accurate and specific polyadenylation of mRNA precursors in a soluble whole-cell lysate. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):595–605. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90440-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDevitt M. A., Hart R. P., Wong W. W., Nevins J. R. Sequences capable of restoring poly(A) site function define two distinct downstream elements. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2907–2913. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04586.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDevitt M. A., Imperiale M. J., Ali H., Nevins J. R. Requirement of a downstream sequence for generation of a poly(A) addition site. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):993–999. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90433-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLauchlan J., Gaffney D., Whitton J. L., Clements J. B. The consensus sequence YGTGTTYY located downstream from the AATAAA signal is required for efficient formation of mRNA 3' termini. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 25;13(4):1347–1368. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.4.1347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore C. L., Sharp P. A. Accurate cleavage and polyadenylation of exogenous RNA substrate. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):845–855. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80065-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore C. L., Sharp P. A. Site-specific polyadenylation in a cell-free reaction. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):581–591. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90337-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore C. L., Skolnik-David H., Sharp P. A. Analysis of RNA cleavage at the adenovirus-2 L3 polyadenylation site. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1929–1938. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04446.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Brownlee G. G. 3' non-coding region sequences in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):211–214. doi: 10.1038/263211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryner L. C., Manley J. L. Requirements for accurate and efficient mRNA 3' end cleavage and polyadenylation of a simian virus 40 early pre-RNA in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):495–503. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadofsky M., Alwine J. C. Sequences on the 3' side of hexanucleotide AAUAAA affect efficiency of cleavage at the polyadenylation site. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1460–1468. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheets M. D., Stephenson P., Wickens M. P. Products of in vitro cleavage and polyadenylation of simian virus 40 late pre-mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1518–1529. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonsen C. C., Levinson A. D. Analysis of processing and polyadenylation signals of the hepatitis B virus surface antigen gene by using simian virus 40-hepatitis B virus chimeric plasmids. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;3(12):2250–2258. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.12.2250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickens M., Stephenson P. Role of the conserved AAUAAA sequence: four AAUAAA point mutants prevent messenger RNA 3' end formation. Science. 1984 Nov 30;226(4678):1045–1051. doi: 10.1126/science.6208611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarkower D., Stephenson P., Sheets M., Wickens M. The AAUAAA sequence is required both for cleavage and for polyadenylation of simian virus 40 pre-mRNA in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2317–2323. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]