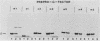Abstract
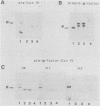
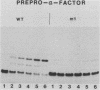
We used a genetic approach to identify point mutations in the signal sequence of a secreted eucaryotic protein, yeast alpha-factor. Signal sequence mutants were obtained by selecting for cells that partially mistargeted into mitochondria a fusion protein consisting of the alpha-factor signal sequence fused to the mature portion of an imported mitochondrial protein (Cox IV). The mutations resulted in replacement of a residue in the hydrophobic core of the signal sequence with either a hydrophilic amino acid or a proline. After reassembly into an intact alpha-factor gene, the substitutions were found to decrease up to 50-fold the rate of translocation of prepro-alpha-factor across microsomal membranes in vitro. Two of three mutants tested produced lower steady-state levels of alpha-factor in intact yeast cells, although the magnitude of the effect was less than that in the cell-free system.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alber T., Kawasaki G. Nucleotide sequence of the triose phosphate isomerase gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(5):419–434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allison D. S., Schatz G. Artificial mitochondrial presequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9011–9015. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ammerer G. Expression of genes in yeast using the ADCI promoter. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:192–201. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson S. A., Hall M. N., Silhavy T. J. Genetic analysis of protein export in Escherichia coli K12. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:101–134. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.000533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blachly-Dyson E., Stevens T. H. Yeast carboxypeptidase Y can be translocated and glycosylated without its amino-terminal signal sequence. J Cell Biol. 1987 May;104(5):1183–1191. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.5.1183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Dobberstein B. Transfer of proteins across membranes. I. Presence of proteolytically processed and unprocessed nascent immunoglobulin light chains on membrane-bound ribosomes of murine myeloma. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):835–851. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs M. S., Cornell D. G., Dluhy R. A., Gierasch L. M. Conformations of signal peptides induced by lipids suggest initial steps in protein export. Science. 1986 Jul 11;233(4760):206–208. doi: 10.1126/science.2941862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs M. S., Gierasch L. M., Zlotnick A., Lear J. D., DeGrado W. F. In vivo function and membrane binding properties are correlated for Escherichia coli lamB signal peptides. Science. 1985 May 31;228(4703):1096–1099. doi: 10.1126/science.3158076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. A., Halvorson H. O., Raney P., Perlman D. Conformational alterations in the proximal portion of the yeast invertase signal peptide do not block secretion. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;197(3):351–357. doi: 10.1007/BF00329928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhni P. C., Daum G., Schatz G. Import of proteins into mitochondria. Partial purification of a matrix-located protease involved in cleavage of mitochondrial precursor polypeptides. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):4937–4943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshaies R. J., Schekman R. A yeast mutant defective at an early stage in import of secretory protein precursors into the endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;105(2):633–645. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.2.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowhan W., Bibus C. R., Schatz G. The cytoplasmically-made subunit IV is necessary for assembly of cytochrome c oxidase in yeast. EMBO J. 1985 Jan;4(1):179–184. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb02334.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emr S. D., Silhavy T. J. Importance of secondary structure in the signal sequence for protein secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4599–4603. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasser S. M., Daum G., Schatz G. Import of proteins into mitochondria. Energy-dependent uptake of precursors by isolated mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):13034–13041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen W., Garcia P. D., Walter P. In vitro protein translocation across the yeast endoplasmic reticulum: ATP-dependent posttranslational translocation of the prepro-alpha-factor. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):397–406. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90325-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurt E. C., Allison D. S., Müller U., Schatz G. Amino-terminal deletions in the presequence of an imported mitochondrial protein block the targeting function and proteolytic cleavage of the presequence at the carboxy terminus. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 25;262(3):1420–1424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurt E. C., Pesold-Hurt B., Schatz G. The amino-terminal region of an imported mitochondrial precursor polypeptide can direct cytoplasmic dihydrofolate reductase into the mitochondrial matrix. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3149–3156. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02272.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurt E. C., Pesold-Hurt B., Suda K., Oppliger W., Schatz G. The first twelve amino acids (less than half of the pre-sequence) of an imported mitochondrial protein can direct mouse cytosolic dihydrofolate reductase into the yeast mitochondrial matrix. EMBO J. 1985 Aug;4(8):2061–2068. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03892.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahimi I., Gentz R. A functional interaction between the signal peptide and the translation apparatus is detected by the use of a single point mutation which blocks translocation across mammalian endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10189–10194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius D., Blair L., Brake A., Sprague G., Thorner J. Yeast alpha factor is processed from a larger precursor polypeptide: the essential role of a membrane-bound dipeptidyl aminopeptidase. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):839–852. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90070-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser C. A., Botstein D. Secretion-defective mutations in the signal sequence for Saccharomyces cerevisiae invertase. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2382–2391. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser C. A., Preuss D., Grisafi P., Botstein D. Many random sequences functionally replace the secretion signal sequence of yeast invertase. Science. 1987 Jan 16;235(4786):312–317. doi: 10.1126/science.3541205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurjan J. Alpha-factor structural gene mutations in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: effects on alpha-factor production and mating. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):787–796. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurjan J., Herskowitz I. Structure of a yeast pheromone gene (MF alpha): a putative alpha-factor precursor contains four tandem copies of mature alpha-factor. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):933–943. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90298-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maarse A. C., Van Loon A. P., Riezman H., Gregor I., Schatz G., Grivell L. A. Subunit IV of yeast cytochrome c oxidase: cloning and nucleotide sequencing of the gene and partial amino acid sequencing of the mature protein. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2831–2837. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02216.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelis S., Beckwith J. Mechanism of incorporation of cell envelope proteins in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1982;36:435–465. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.36.100182.002251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milstein C., Brownlee G. G., Harrison T. M., Mathews M. B. A possible precursor of immunoglobulin light chains. Nat New Biol. 1972 Sep 27;239(91):117–120. doi: 10.1038/newbio239117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Lerman L. S., Maniatis T. A general method for saturation mutagenesis of cloned DNA fragments. Science. 1985 Jul 19;229(4710):242–247. doi: 10.1126/science.2990046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M., Ibrahimi I., Chang C. N., Walter P., Blobel G. A bacterial secretory protein requires signal recognition particle for translocation across mammalian endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):11860–11863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman D., Raney P., Halvorson H. O. Mutations affecting the signal sequence alter synthesis and secretion of yeast invertase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5033–5037. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilgrim D., Young E. T. Primary structure requirements for correct sorting of the yeast mitochondrial protein ADH III to the yeast mitochondrial matrix space. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):294–304. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roise D., Horvath S. J., Tomich J. M., Richards J. H., Schatz G. A chemically synthesized pre-sequence of an imported mitochondrial protein can form an amphiphilic helix and perturb natural and artificial phospholipid bilayers. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1327–1334. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04363.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothblatt J. A., Meyer D. I. Secretion in yeast: reconstitution of the translocation and glycosylation of alpha-factor and invertase in a homologous cell-free system. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):619–628. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90271-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauer I., Emr S., Gross C., Schekman R. Invertase signal and mature sequence substitutions that delay intercompartmental transport of active enzyme. J Cell Biol. 1985 May;100(5):1664–1675. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.5.1664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw K. J., Olson M. V. Effects of altered 5'-flanking sequences on the in vivo expression of a Saccharomyces cerevisiae tRNATyr gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;4(4):657–665. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.4.657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silve S., Monod M., Hinnen A., Haguenauer-Tsapis R. The yeast acid phosphatase can enter the secretory pathway without its N-terminal signal sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3306–3314. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suissa M. Spectrophotometric quantitation of silver grains eluted from autoradiograms. Anal Biochem. 1983 Sep;133(2):511–514. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90117-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talmadge K., Stahl S., Gilbert W. Eukaryotic signal sequence transports insulin antigen in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3369–3373. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Blobel G. Purification of a membrane-associated protein complex required for protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7112–7116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P. Signal recognition. Two receptors act sequentially. 1987 Aug 27-Sep 2Nature. 328(6133):763–764. doi: 10.1038/328763a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters M. G., Blobel G. Secretory protein translocation in a yeast cell-free system can occur posttranslationally and requires ATP hydrolysis. J Cell Biol. 1986 May;102(5):1543–1550. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.5.1543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters M. G., Chirico W. J., Blobel G. Protein translocation across the yeast microsomal membrane is stimulated by a soluble factor. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 2):2629–2636. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner W. The assembly of proteins into biological membranes: The membrane trigger hypothesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:23–45. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.000323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedmann M., Kurzchalia T. V., Hartmann E., Rapoport T. A. A signal sequence receptor in the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. 1987 Aug 27-Sep 2Nature. 328(6133):830–833. doi: 10.1038/328830a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Loon A. P., Young E. T. Intracellular sorting of alcohol dehydrogenase isoenzymes in yeast: a cytosolic location reflects absence of an amino-terminal targeting sequence for the mitochondrion. EMBO J. 1986 Jan;5(1):161–165. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04191.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Signal sequences. The limits of variation. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jul 5;184(1):99–105. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90046-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]