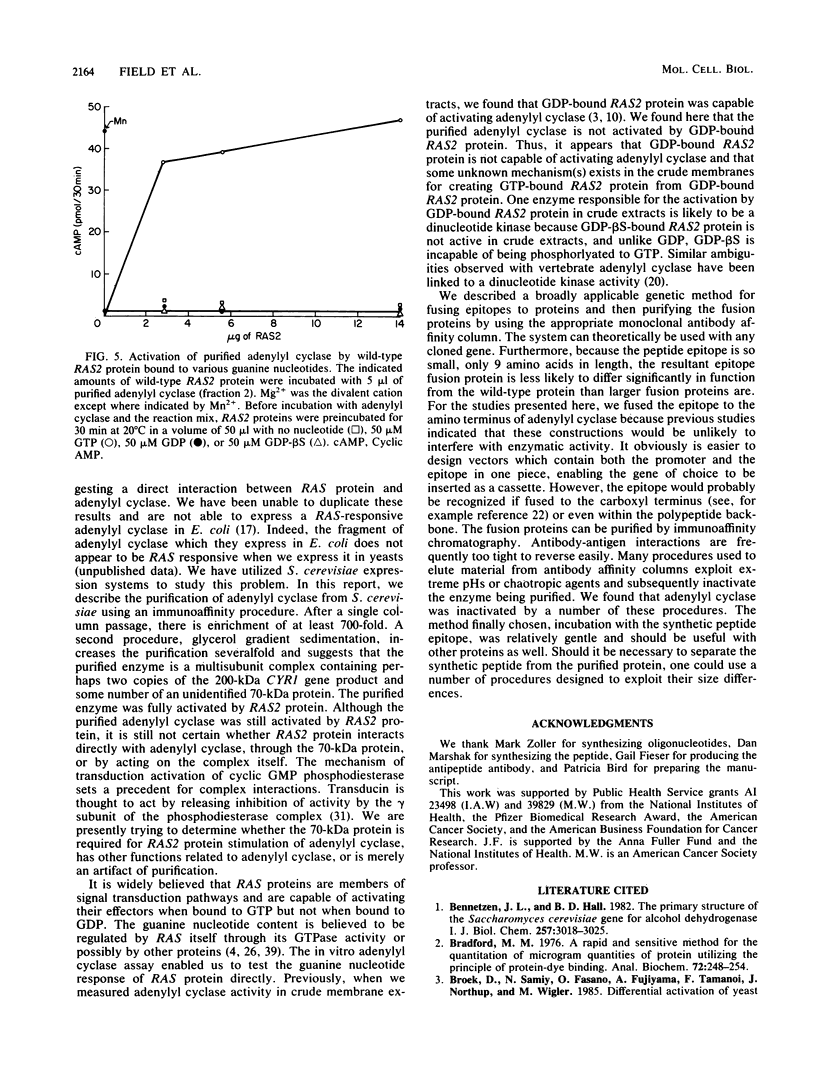
Abstract
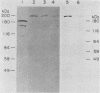
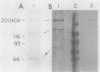
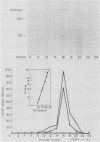
We developed a method for immunoaffinity purification of Saccharomyces cerevisiae adenylyl cyclase based on creating a fusion with a small peptide epitope. Using oligonucleotide technology to encode the peptide epitope we constructed a plasmid that expressed the fusion protein from the S. cerevisiae alcohol dehydrogenase promoter ADH1. A monoclonal antibody previously raised against the peptide was used to purify adenylyl cyclase by affinity chromatography. The purified enzyme appeared to be a multisubunit complex consisting of the 200-kilodalton adenylyl cyclase fusion protein and an unidentified 70-kilodalton protein. The purified protein could be activated by RAS proteins. Activation had an absolute requirement for a guanine nucleoside triphosphate.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennetzen J. L., Hall B. D. The primary structure of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene for alcohol dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3018–3025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broek D., Toda T., Michaeli T., Levin L., Birchmeier C., Zoller M., Powers S., Wigler M. The S. cerevisiae CDC25 gene product regulates the RAS/adenylate cyclase pathway. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):789–799. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90076-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casperson G. F., Walker N., Brasier A. R., Bourne H. R. A guanine nucleotide-sensitive adenylate cyclase in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):7911–7914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S. G., McGrath J. P., Levinson A. D. Expression of normal and activated human Ha-ras cDNAs in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2746–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Vendittis E., Vitelli A., Zahn R., Fasano O. Suppression of defective RAS1 and RAS2 functions in yeast by an adenylate cyclase activated by a single amino acid change. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3657–3663. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04696.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFeo-Jones D., Scolnick E. M., Koller R., Dhar R. ras-Related gene sequences identified and isolated from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nature. 1983 Dec 15;306(5944):707–709. doi: 10.1038/306707a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFeo-Jones D., Tatchell K., Robinson L. C., Sigal I. S., Vass W. C., Lowy D. R., Scolnick E. M. Mammalian and yeast ras gene products: biological function in their heterologous systems. Science. 1985 Apr 12;228(4696):179–184. doi: 10.1126/science.3883495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field J., Broek D., Kataoka T., Wigler M. Guanine nucleotide activation of, and competition between, RAS proteins from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2128–2133. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiyama A., Tamanoi F. Processing and fatty acid acylation of RAS1 and RAS2 proteins in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1266–1270. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs J. B., Sigal I. S., Poe M., Scolnick E. M. Intrinsic GTPase activity distinguishes normal and oncogenic ras p21 molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5704–5708. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins and dual control of adenylate cyclase. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):577–579. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90336-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N., Alexander H., Olson A., Alexander S., Shinnick T. M., Sutcliffe J. G., Lerner R. A. Immunogenic structure of the influenza virus hemagglutinin. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):477–487. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90202-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heideman W., Casperson G. F., Bourne H. R. Adenylyl cyclase in yeast. Hydrodynamic properties and activation by trypsin. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 25;262(15):7087–7091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. E., Cameron S., Toda T., Wigler M., Zoller M. J. Expression in Escherichia coli of BCY1, the regulatory subunit of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8636–8642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kataoka T., Broek D., Wigler M. DNA sequence and characterization of the S. cerevisiae gene encoding adenylate cyclase. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):493–505. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90179-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kataoka T., Powers S., Cameron S., Fasano O., Goldfarb M., Broach J., Wigler M. Functional homology of mammalian and yeast RAS genes. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):19–26. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90304-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kataoka T., Powers S., McGill C., Fasano O., Strathern J., Broach J., Wigler M. Genetic analysis of yeast RAS1 and RAS2 genes. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):437–445. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90374-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura N., Shimada N. GDP does not mediate but rather inhibits hormonal signal to adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2278–2283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath J. P., Capon D. J., Goeddel D. V., Levinson A. D. Comparative biochemical properties of normal and activated human ras p21 protein. Nature. 1984 Aug 23;310(5979):644–649. doi: 10.1038/310644a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro S., Pelham H. R. Use of peptide tagging to detect proteins expressed from cloned genes: deletion mapping functional domains of Drosophila hsp 70. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3087–3093. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02263.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niman H. L., Houghten R. A., Walker L. E., Reisfeld R. A., Wilson I. A., Hogle J. M., Lerner R. A. Generation of protein-reactive antibodies by short peptides is an event of high frequency: implications for the structural basis of immune recognition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):4949–4953. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.4949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers S., Kataoka T., Fasano O., Goldfarb M., Strathern J., Broach J., Wigler M. Genes in S. cerevisiae encoding proteins with domains homologous to the mammalian ras proteins. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):607–612. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90340-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers S., Michaelis S., Broek D., Santa Anna S., Field J., Herskowitz I., Wigler M. RAM, a gene of yeast required for a functional modification of RAS proteins and for production of mating pheromone a-factor. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):413–422. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90598-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson L. C., Gibbs J. B., Marshall M. S., Sigal I. S., Tatchell K. CDC25: a component of the RAS-adenylate cyclase pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Science. 1987 Mar 6;235(4793):1218–1221. doi: 10.1126/science.3547648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon Y., Londos C., Rodbell M. A highly sensitive adenylate cyclase assay. Anal Biochem. 1974 Apr;58(2):541–548. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90222-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner W., Weissmann C. A rapid, sensitive, and specific method for the determination of protein in dilute solution. Anal Biochem. 1973 Dec;56(2):502–514. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90217-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scolnick E. M., Papageorge A. G., Shih T. Y. Guanine nucleotide-binding activity as an assay for src protein of rat-derived murine sarcoma viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5355–5359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih T. Y., Weeks M. O., Gruss P., Dhar R., Oroszlan S., Scolnick E. M. Identification of a precursor in the biosynthesis of the p21 transforming protein of harvey murine sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1982 Apr;42(1):253–261. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.1.253-261.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryer L. Transducin and the cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase: amplifier proteins in vision. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;48(Pt 2):841–852. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.048.01.087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweet R. W., Yokoyama S., Kamata T., Feramisco J. R., Rosenberg M., Gross M. The product of ras is a GTPase and the T24 oncogenic mutant is deficient in this activity. Nature. 1984 Sep 20;311(5983):273–275. doi: 10.1038/311273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamanoi F., Walsh M., Kataoka T., Wigler M. A product of yeast RAS2 gene is a guanine nucleotide binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):6924–6928. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.6924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatchell K., Chaleff D. T., DeFeo-Jones D., Scolnick E. M. Requirement of either of a pair of ras-related genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for spore viability. Nature. 1984 Jun 7;309(5968):523–527. doi: 10.1038/309523a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temeles G. L., Gibbs J. B., D'Alonzo J. S., Sigal I. S., Scolnick E. M. Yeast and mammalian ras proteins have conserved biochemical properties. Nature. 1985 Feb 21;313(6004):700–703. doi: 10.1038/313700a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda T., Cameron S., Sass P., Zoller M., Wigler M. Three different genes in S. cerevisiae encode the catalytic subunits of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Cell. 1987 Jul 17;50(2):277–287. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90223-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda T., Uno I., Ishikawa T., Powers S., Kataoka T., Broek D., Cameron S., Broach J., Matsumoto K., Wigler M. In yeast, RAS proteins are controlling elements of adenylate cyclase. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):27–36. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90305-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trahey M., McCormick F. A cytoplasmic protein stimulates normal N-ras p21 GTPase, but does not affect oncogenic mutants. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):542–545. doi: 10.1126/science.2821624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uno I., Mitsuzawa H., Matsumoto K., Tanaka K., Oshima T., Ishikawa T. Reconstitution of the GTP-dependent adenylate cyclase from products of the yeast CYR1 and RAS2 genes in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7855–7859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varimo K., Londesborough J. Solubilization and other studies on adenylate cyclase of baker's yeast. Biochem J. 1976 Nov;159(2):363–370. doi: 10.1042/bj1590363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willingham M. C., Pastan I., Shih T. Y., Scolnick E. M. Localization of the src gene product of the Harvey strain of MSV to plasma membrane of transformed cells by electron microscopic immunocytochemistry. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):1005–1014. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90091-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson I. A., Niman H. L., Houghten R. A., Cherenson A. R., Connolly M. L., Lerner R. A. The structure of an antigenic determinant in a protein. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):767–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90412-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]