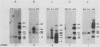Abstract
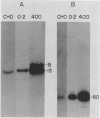
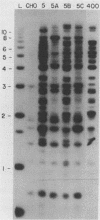
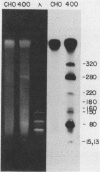
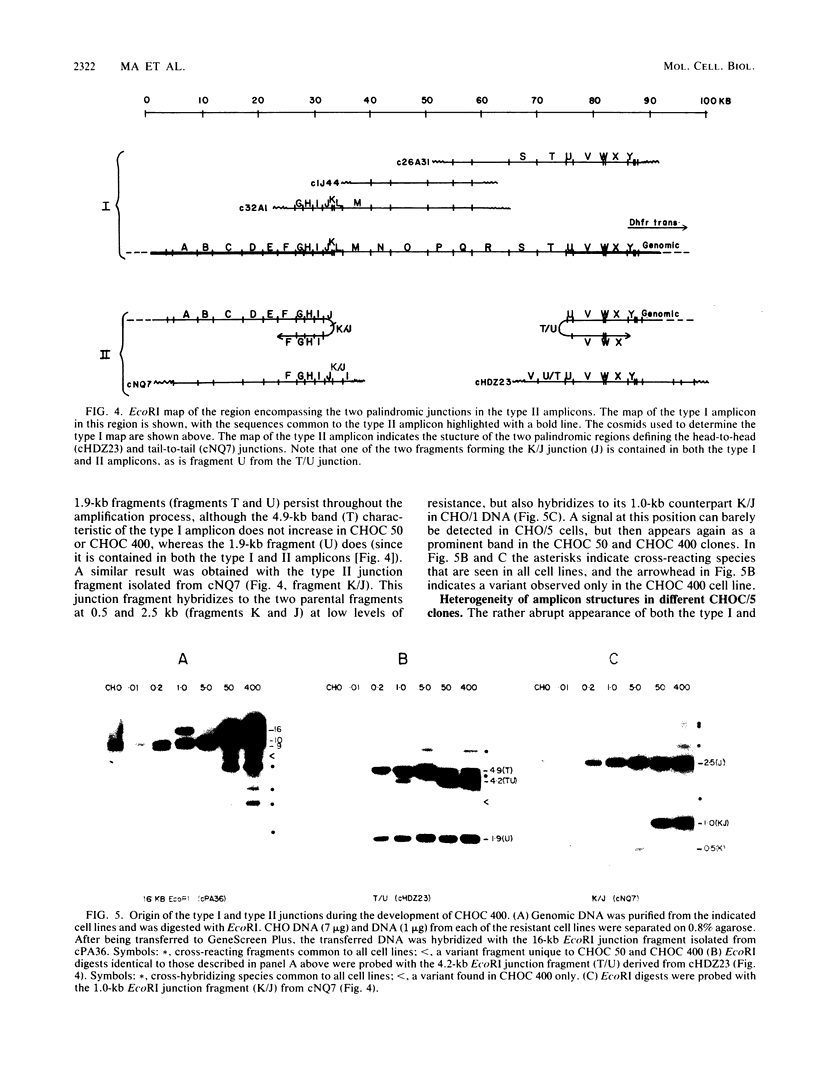
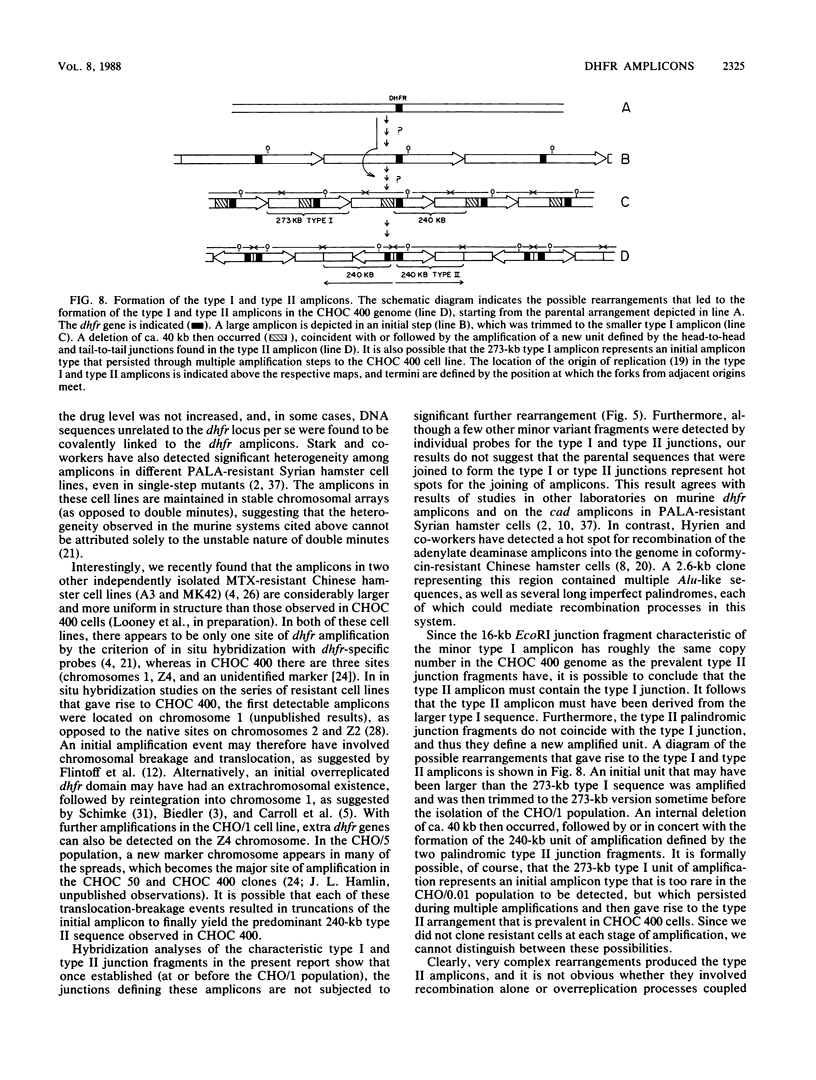
We have recently isolated overlapping recombinant cosmids that represent the equivalent of two complete dihydrofolate reductase (dhfr) amplicon types from the methotrexate-resistant Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cell line CHOC 400. In the work described in this report, we used pulse-field gradient gel electrophoresis to analyze large SfiI restriction fragments arising from the amplified dhfr domains. The junction between the 260-kilobase type I amplicons (which are arranged in head-to-tail configurations in the genome) has been localized, allowing the construction of a linear map of the parental dhfr locus. We also show that the 220-kilobase type II amplicons are arranged as inverted repeat structures in the CHOC 400 genome and arose from the type I sequence relatively early in the amplification process. Our data indicate that there are a number of minor amplicon types in the CHOC 400 cell line that were not detected in previous studies; however, the type II amplicons represent ca. 75% of all the amplicons in the CHOC 400 genome. Both the type I and type II amplicons are shown to be composed entirely of sequences that were present in the parental dhfr locus. Studies of less resistant cell lines show that initial amplicons can be larger than those observed in CHOC 400. Once established, a given amplicon type appears to be relatively stable throughout subsequent amplification steps. We also present a modification of an in-gel renaturation method that gives a relatively complete picture of the size and variability of amplicons in the genome.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alitalo K., Schwab M., Lin C. C., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Homogeneously staining chromosomal regions contain amplified copies of an abundantly expressed cellular oncogene (c-myc) in malignant neuroendocrine cells from a human colon carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(6):1707–1711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.6.1707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ardeshir F., Giulotto E., Zieg J., Brison O., Liao W. S., Stark G. R. Structure of amplified DNA in different Syrian hamster cell lines resistant to N-(phosphonacetyl)-L-aspartate. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;3(11):2076–2088. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.11.2076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biedler J. L., Spengler B. A. A novel chromosome abnormality in human neuroblastoma and antifolate-resistant Chinese hamster cell lives in culture. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1976 Sep;57(3):683–695. doi: 10.1093/jnci/57.3.683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll S. M., Gaudray P., De Rose M. L., Emery J. F., Meinkoth J. L., Nakkim E., Subler M., Von Hoff D. D., Wahl G. M. Characterization of an episome produced in hamster cells that amplify a transfected CAD gene at high frequency: functional evidence for a mammalian replication origin. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1740–1750. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S., Groudine M. Amplification of endogenous myc-related DNA sequences in a human myeloid leukaemia cell line. Nature. 1982 Aug 12;298(5875):679–681. doi: 10.1038/298679a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalla-Favera R., Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C. Onc gene amplification in promyelocytic leukaemia cell line HL-60 and primary leukaemic cells of the same patient. Nature. 1982 Sep 2;299(5878):61–63. doi: 10.1038/299061a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debatisse M., Hyrien O., Petit-Koskas E., de Saint-Vincent B. R., Buttin G. Segregation and rearrangement of coamplified genes in different lineages of mutant cells that overproduce adenylate deaminase. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1776–1781. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Federspiel N. A., Beverley S. M., Schilling J. W., Schimke R. T. Novel DNA rearrangements are associated with dihydrofolate reductase gene amplification. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):9127–9140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flintoff W. F., Livingston E., Duff C., Worton R. G. Moderate-level gene amplification in methotrexate-resistant Chinese hamster ovary cells is accompanied by chromosomal translocations at or near the site of the amplified DHFR gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;4(1):69–76. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.1.69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford M., Fried M. Large inverted duplications are associated with gene amplification. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):425–430. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90328-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner K., Laas W., Patterson D. Fractionation of large mammalian DNA restriction fragments using vertical pulsed-field gradient gel electrophoresis. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1986 Mar;12(2):185–195. doi: 10.1007/BF01560665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giulotto E., Saito I., Stark G. R. Structure of DNA formed in the first step of CAD gene amplification. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2115–2121. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04474.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross-Bellard M., Oudet P., Chambon P. Isolation of high-molecular-weight DNA from mammalian cells. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jul 2;36(1):32–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02881.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamlin J. L., Milbrandt J. D., Heintz N. H., Azizkhan J. C. DNA sequence amplification in mammalian cells. Int Rev Cytol. 1984;90:31–82. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61487-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hand R. Eucaryotic DNA: organization of the genome for replication. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):317–325. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90001-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintz N. H., Milbrandt J. D., Greisen K. S., Hamlin J. L. Cloning of the initiation region of a mammalian chromosomal replicon. 1983 Mar 31-Apr 6Nature. 302(5907):439–441. doi: 10.1038/302439a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyrien O., Debatisse M., Buttin G., de Saint Vincent B. R. A hotspot for novel amplification joints in a mosaic of Alu-like repeats and palindromic A + T-rich DNA. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2401–2408. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02518.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J., Brown P. C., Schimke R. T. Amplified dihydrofolate reductase genes in unstably methotrexate-resistant cells are associated with double minute chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5669–5673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinzler K. W., Zehnbauer B. A., Brodeur G. M., Seeger R. C., Trent J. M., Meltzer P. S., Vogelstein B. Amplification units containing human N-myc and c-myc genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):1031–1035. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.1031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Looney J. E., Hamlin J. L. Isolation of the amplified dihydrofolate reductase domain from methotrexate-resistant Chinese hamster ovary cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):569–577. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milbrandt J. D., Heintz N. H., White W. C., Rothman S. M., Hamlin J. L. Methotrexate-resistant Chinese hamster ovary cells have amplified a 135-kilobase-pair region that includes the dihydrofolate reductase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6043–6047. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montoya-Zavala M., Hamlin J. L. Similar 150-kilobase DNA sequences are amplified in independently derived methotrexate-resistant Chinese hamster cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):619–627. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunberg J. H., Kaufman R. J., Schimke R. T., Urlaub G., Chasin L. A. Amplified dihydrofolate reductase genes are localized to a homogeneously staining region of a single chromosome in a methotrexate-resistant Chinese hamster ovary cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5553–5556. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K. C., Mann D. A. Rapid transfer of DNA from agarose gels to nylon membranes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7207–7221. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts M., Melera P. W., Davide J. P., Hart J. T., Ruddle F. H. Assignment of the native Chinese hamster dihydrofolate reductase gene to chromosome 2. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1983;36(4):599–604. doi: 10.1159/000131982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roninson I. B., Abelson H. T., Housman D. E., Howell N., Varshavsky A. Amplification of specific DNA sequences correlates with multi-drug resistance in Chinese hamster cells. Nature. 1984 Jun 14;309(5969):626–628. doi: 10.1038/309626a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roninson I. B. Detection and mapping of homologous, repeated and amplified DNA sequences by DNA renaturation in agarose gels. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 25;11(16):5413–5431. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.16.5413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimke R. T. Gene amplification in cultured animal cells. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):705–713. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90406-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab M., Alitalo K., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M., George D. A cellular oncogene (c-Ki-ras) is amplified, overexpressed, and located within karyotypic abnormalities in mouse adrenocortical tumour cells. Nature. 1983 Jun 9;303(5917):497–501. doi: 10.1038/303497a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark G. R., Wahl G. M. Gene amplification. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:447–491. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.002311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Bliek A. M., Van der Velde-Koerts T., Ling V., Borst P. Overexpression and amplification of five genes in a multidrug-resistant Chinese hamster ovary cell line. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1671–1678. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Vitto L., Padgett R. A., Stark G. R. Single-copy and amplified CAD genes in Syrian hamster chromosomes localized by a highly sensitive method for in situ hybridization. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Mar;2(3):308–319. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.3.308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeung C. Y., Frayne E. G., Al-Ubaidi M. R., Hook A. G., Ingolia D. E., Wright D. A., Kellems R. E. Amplification and molecular cloning of murine adenosine deaminase gene sequences. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):15179–15185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieg J., Clayton C. E., Ardeshir F., Giulotto E., Swyryd E. A., Stark G. R. Properties of single-step mutants of Syrian hamster cell lines resistant to N-(phosphonacetyl)-L-aspartate. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;3(11):2089–2098. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.11.2089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bruijn M. H., Van der Bliek A. M., Biedler J. L., Borst P. Differential amplification and disproportionate expression of five genes in three multidrug-resistant Chinese hamster lung cell lines. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4717–4722. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]