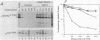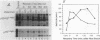Abstract
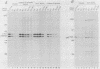
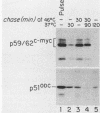
The proteins encoded by both viral and cellular forms of the c-myc oncogene have been previously demonstrated to have exceptionally short in vivo half-lives. In this paper we report a comparative study on the parameters affecting turnover of nuclear oncoproteins c-myc, c-myb, and the rapidly metabolized cytoplasmic enzyme ornithine decarboxylase. The degradation of all three proteins required metabolic energy, did not result in production of cleavage intermediates, and did not involve lysosomes or ubiquitin. A five- to eightfold increase in the half-life of c-myc proteins, and a twofold increase in the half-life of c-myb proteins was detected after heat-shock treatment at 46 degrees C. In contrast, heat shock had no effect on the turnover of ornithine decarboxylase. Heat shock also had the effect of increasing the rate of c-myc protein synthesis twofold, whereas c-myb protein synthesis was decreased nearly fourfold. The increased stability and synthesis of c-myc proteins led to an overall increase in the total level of c-myc proteins in response to heat-shock treatment. Furthermore, treatments which reduced c-myc and c-myb protein turnover, such as heat shock and exposure to inhibitors of metabolic energy production, resulted in reduced detergent solubility of both proteins. The recovery from heat shock, as measured by increased turnover and solubility, was energy dependent and considerably more rapid in thermotolerant cells.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrams H. D., Rohrschneider L. R., Eisenman R. N. Nuclear location of the putative transforming protein of avian myelocytomatosis virus. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):427–439. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90159-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alitalo K., Ramsay G., Bishop J. M., Pfeifer S. O., Colby W. W., Levinson A. D. Identification of nuclear proteins encoded by viral and cellular myc oncogenes. Nature. 1983 Nov 17;306(5940):274–277. doi: 10.1038/306274a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bader J. P., Hausman F. A., Ray D. A. Intranuclear degradation of the transformation-inducing protein encoded by avian MC29 virus. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8303–8308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle W. J., Lipsick J. S., Baluda M. A. Antibodies to the evolutionarily conserved amino-terminal region of the v-myb-encoded protein detect the c-myb protein in widely divergent metazoan species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4685–4689. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson N., Rogers S., Rechsteiner M. Microinjection of ubiquitin: changes in protein degradation in HeLa cells subjected to heat-shock. J Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;104(3):547–555. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.3.547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciechanover A., Finley D., Varshavsky A. The ubiquitin-mediated proteolytic pathway and mechanisms of energy-dependent intracellular protein degradation. J Cell Biochem. 1984;24(1):27–53. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240240104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole M. D. The myc oncogene: its role in transformation and differentiation. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:361–384. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.002045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cory S. Activation of cellular oncogenes in hemopoietic cells by chromosome translocation. Adv Cancer Res. 1986;47:189–234. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60200-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dani C., Blanchard J. M., Piechaczyk M., El Sabouty S., Marty L., Jeanteur P. Extreme instability of myc mRNA in normal and transformed human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7046–7050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donner P., Greiser-Wilke I., Moelling K. Nuclear localization and DNA binding of the transforming gene product of avian myelocytomatosis virus. Nature. 1982 Mar 18;296(5854):262–269. doi: 10.1038/296262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenman R. N., Tachibana C. Y., Abrams H. D., Hann S. R. V-myc- and c-myc-encoded proteins are associated with the nuclear matrix. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):114–126. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenman R. N., Thompson C. B. Oncogenes with potential nuclear function: myc, myb and fos. Cancer Surv. 1986;5(2):309–327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evan G. I., Hancock D. C. Studies on the interaction of the human c-myc protein with cell nuclei: p62c-myc as a member of a discrete subset of nuclear proteins. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):253–261. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90030-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried V. A., Smith H. T., Hildebrandt E., Weiner K. Ubiquitin has intrinsic proteolytic activity: implications for cellular regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3685–3689. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronostajski R. M., Goldberg A. L., Pardee A. B. Energy requirement for degradation of tumor-associated protein p53. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;4(3):442–448. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.3.442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hann S. R., Abrams H. D., Rohrschneider L. R., Eisenman R. N. Proteins encoded by v-myc and c-myc oncogenes: identification and localization in acute leukemia virus transformants and bursal lymphoma cell lines. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):789–798. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90535-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hann S. R., Eisenman R. N. Proteins encoded by the human c-myc oncogene: differential expression in neoplastic cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2486–2497. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hann S. R., King M. W., Bentley D. L., Anderson C. W., Eisenman R. N. A non-AUG translational initiation in c-myc exon 1 generates an N-terminally distinct protein whose synthesis is disrupted in Burkitt's lymphomas. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):185–195. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90507-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle K. J., Karamuz J. E., Leeper D. B. Induction of thermotolerance in Chinese hamster ovary cells by high (45 degrees) or low (40 degrees) hyperthermia. Cancer Res. 1978 Mar;38(3):570–574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershko A., Ciechanover A. Mechanisms of intracellular protein breakdown. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:335–364. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.002003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hölttä E., Pohjanpelto P. Control of ornithine decarboxylase in Chinese hamster ovary cells by polyamines. Translational inhibition of synthesis and acceleration of degradation of the enzyme by putrescine, spermidine, and spermine. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9502–9508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isomaa V. V., Pajunen A. E., Bardin C. W., Jänne O. A. Ornithine decarboxylase in mouse kidney. Purification, characterization, and radioimmunological determination of the enzyme protein. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):6735–6740. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaddurah-Daouk R., Greene J. M., Baldwin A. S., Jr, Kingston R. E. Activation and repression of mammalian gene expression by the c-myc protein. Genes Dev. 1987 Jun;1(4):347–357. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.4.347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley P. M., Schlesinger M. J. The effect of amino acid analogues and heat shock on gene expression in chicken embryo fibroblasts. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1277–1286. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90053-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King M. W., Roberts J. M., Eisenman R. N. Expression of the c-myc proto-oncogene during development of Xenopus laevis. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4499–4508. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempnauer K. H., Bonifer C., Sippel A. E. Identification and characterization of the protein encoded by the human c-myb proto-oncogene. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1903–1911. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04443.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempnauer K. H., Ramsay G., Bishop J. M., Moscovici M. G., Moscovici C., McGrath J. P., Levinson A. D. The product of the retroviral transforming gene v-myb is a truncated version of the protein encoded by the cellular oncogene c-myb. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):345–355. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90416-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist S. The heat-shock response. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1151–1191. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linial M., Gunderson N., Groudine M. Enhanced transcription of c-myc in bursal lymphoma cells requires continuous protein synthesis. Science. 1985 Dec 6;230(4730):1126–1132. doi: 10.1126/science.2999973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro S., Pelham H. R. Use of peptide tagging to detect proteins expressed from cloned genes: deletion mapping functional domains of Drosophila hsp 70. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3087–3093. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02263.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oren M., Maltzman W., Levine A. J. Post-translational regulation of the 54K cellular tumor antigen in normal and transformed cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Feb;1(2):101–110. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.2.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parag H. A., Raboy B., Kulka R. G. Effect of heat shock on protein degradation in mammalian cells: involvement of the ubiquitin system. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):55–61. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04718.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patschinsky T., Walter G., Bister K. Immunological analysis of v-myc gene products using antibodies against a myc-specific synthetic peptide. Virology. 1984 Jul 30;136(2):348–358. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90171-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. Hsp70 accelerates the recovery of nucleolar morphology after heat shock. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3095–3100. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02264.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson H., Hennighausen L., Taub R., DeGrado W., Leder P. Antibodies to human c-myc oncogene product: evidence of an evolutionarily conserved protein induced during cell proliferation. Science. 1984 Aug 17;225(4663):687–693. doi: 10.1126/science.6431612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pontremoli S., Melloni E. Extralysosomal protein degradation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:455–481. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.002323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay G., Evan G. I., Bishop J. M. The protein encoded by the human proto-oncogene c-myc. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7742–7746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos A., Boron W. F. Intracellular pH. Physiol Rev. 1981 Apr;61(2):296–434. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1981.61.2.296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger M. J. Heat shock proteins: the search for functions. J Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;103(2):321–325. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.2.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seglen P. O. Inhibitors of lysosomal function. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:737–764. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96063-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. L., Watt R. A., Sullivan N. F. The v- and c-myc oncogene proteins colocalize in situ with small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles. Oncogene. 1987 Mar;1(1):5–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studzinski G. P., Brelvi Z. S., Feldman S. C., Watt R. A. Participation of c-myc protein in DNA synthesis of human cells. Science. 1986 Oct 24;234(4775):467–470. doi: 10.1126/science.3532322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor C. W., Tabor H. Polyamines. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:749–790. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.003533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Waxman L., Goldberg A. L. Vanadate inhibits the ATP-dependent degradation of proteins in reticulocytes without affecting ubiquitin conjugation. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 10;259(5):2803–2809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods C. M., Lazarides E. Degradation of unassembled alpha- and beta-spectrin by distinct intracellular pathways: regulation of spectrin topogenesis by beta-spectrin degradation. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):959–969. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90356-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]