Abstract
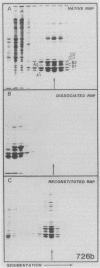
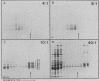
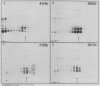
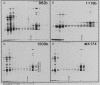
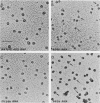
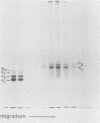
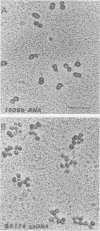
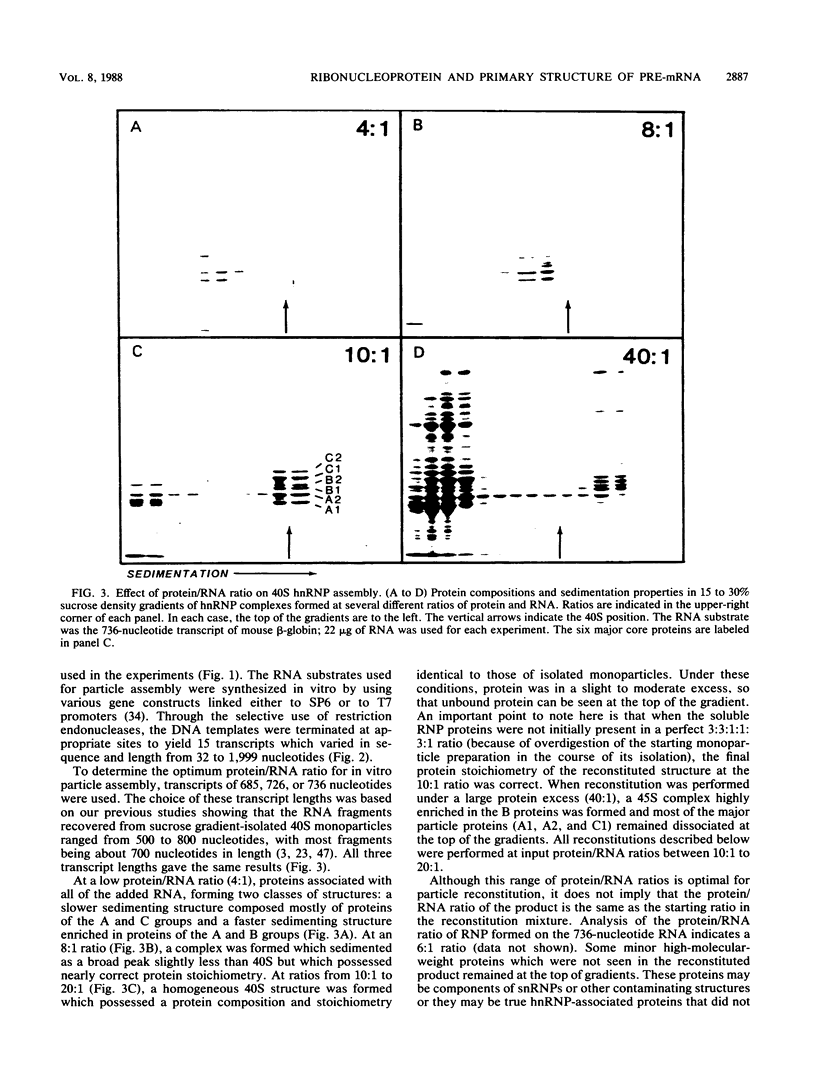
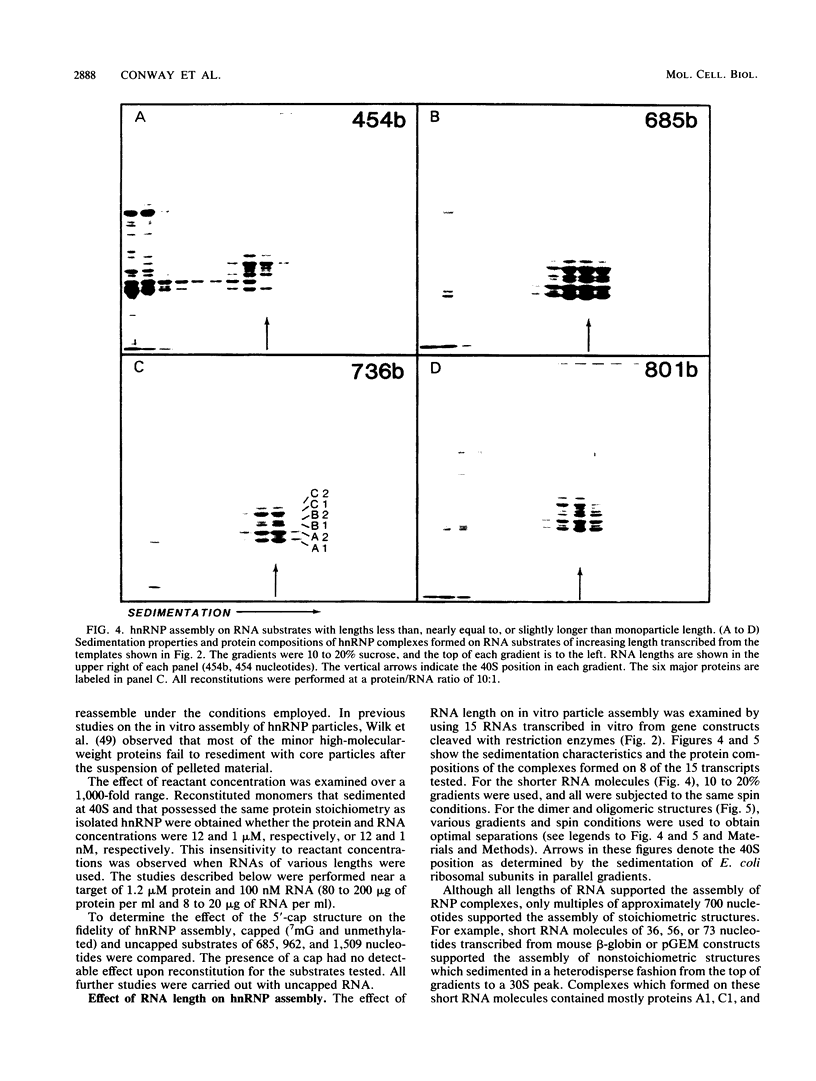
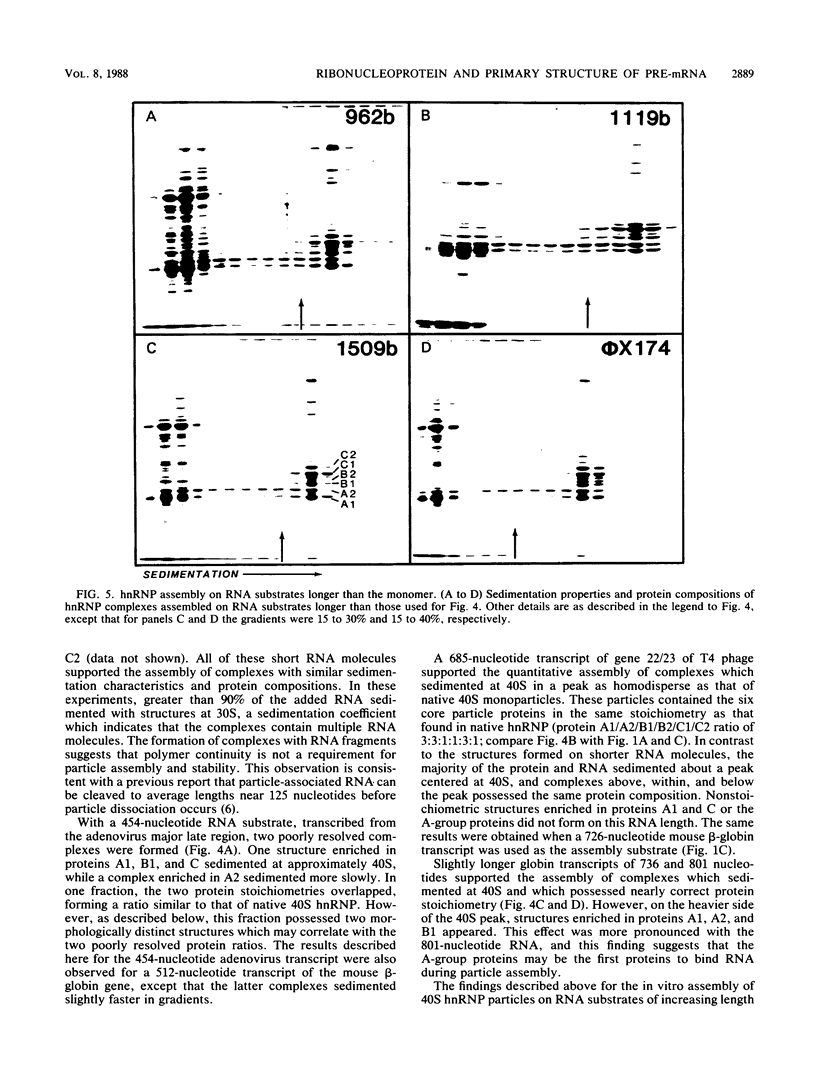
An assay for the in vitro assembly of HeLa cell 40S nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles (hnRNP particles) has been developed. The substrates were single-stranded nucleic acid polymers of defined length and sequence prepared in vitro and the six major core particle proteins from isolated 40S hnRNP. The fidelity of in vitro assembly was evaluated on various physical parameters, including sedimentation, salt dissociation, polypeptide stoichiometry, UV-activated protein-RNA cross-linking, and overall morphology. Correct particle assembly depended on RNA length and on the input protein/RNA ratio but not on the concentration of the reactant mixture nor on the presence or absence of internal RNA processing signals, a 5'-cap structure, a 3'-poly(A) moiety, or ATP as energy source. RNA lengths between 685 and 726 nucleotides supported correct particle assembly. Dimers and oligomeric complexes that possessed the same polypeptide stoichiometry as native hnRNP assembled on RNA chains that were integral multiples of 700 nucleotides. Intermediate-length RNA supported the assembly of nonstoichiometric complexes lacking structural homogeneity. An analysis of these complexes indicates that proteins A1 and A2 may be the first proteins to bind RNA during particle assembly. We conclude that the major proteins of 40S hnRNP particles contain the necessary information for packaging nascent transcripts into a repeating "ribonucleosomal" structure possessing a defined RNA length and protein composition but do not themselves contain the information for modulating packaging that may be required for RNA splicing.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beyer A. L., Bouton A. H., Miller O. L., Jr Correlation of hnRNP structure and nascent transcript cleavage. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(2 Pt 2):155–165. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90299-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyer A. L., Christensen M. E., Walker B. W., LeStourgeon W. M. Identification and characterization of the packaging proteins of core 40S hnRNP particles. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):127–138. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90323-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyer A. L., Miller O. L., Jr, McKnight S. L. Ribonucleoprotein structure in nascent hnRNA is nonrandom and sequence-dependent. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):75–84. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90236-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyer A. Ultrastructural analysis of the ribonucleoprotein structure of nascent hnRNA. Mol Biol Rep. 1983 May;9(1-2):49–58. doi: 10.1007/BF00777473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi Y. D., Dreyfuss G. Isolation of the heterogeneous nuclear RNA-ribonucleoprotein complex (hnRNP): a unique supramolecular assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7471–7475. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi Y. D., Grabowski P. J., Sharp P. A., Dreyfuss G. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins: role in RNA splicing. Science. 1986 Mar 28;231(4745):1534–1539. doi: 10.1126/science.3952495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung S. Y., Wooley J. Set of novel, conserved proteins fold pre-messenger RNA into ribonucleosomes. Proteins. 1986 Nov;1(3):195–210. doi: 10.1002/prot.340010302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daskal Y., Komaromy L., Busch H. Isolation and partial characterization of perichromatin granules. A unique class of nuclear RNP particles. Exp Cell Res. 1980 Mar;126(1):39–46. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(80)90468-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfuss G., Choi Y. D., Adam S. A. Characterization of heterogeneous nuclear RNA-protein complexes in vivo with monoclonal antibodies. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;4(6):1104–1114. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.6.1104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Economidis I. V., Pederson T. Structure of nuclear ribonucleoprotein: heterogeneous nuclear RNA is complexed with a major sextet of proteins in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(6):1599–1602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.6.1599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fakan S., Leser G., Martin T. E. Ultrastructural distribution of nuclear ribonucleoproteins as visualized by immunocytochemistry on thin sections. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;98(1):358–363. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.1.358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glätzer K. H., Kloetzel P. M. Differential chromosomal distribution of ribonucleoprotein antigens in nuclei of Drosophila spermatocytes. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2113–2119. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabowski P. J., Padgett R. A., Sharp P. A. Messenger RNA splicing in vitro: an excised intervening sequence and a potential intermediate. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):415–427. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90372-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabowski P. J., Seiler S. R., Sharp P. A. A multicomponent complex is involved in the splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):345–353. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80130-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R. Pre-mRNA splicing. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:671–708. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.003323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ITZHAKI R. F., GILL D. M. A MICRO-BIURET METHOD FOR ESTIMATING PROTEINS. Anal Biochem. 1964 Dec;9:401–410. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(64)90200-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konarska M. M., Grabowski P. J., Padgett R. A., Sharp P. A. Characterization of the branch site in lariat RNAs produced by splicing of mRNA precursors. Nature. 1985 Feb 14;313(6003):552–557. doi: 10.1038/313552a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konarska M. M., Padgett R. A., Sharp P. A. Recognition of cap structure in splicing in vitro of mRNA precursors. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):731–736. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90268-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar A., Williams K. R., Szer W. Purification and domain structure of core hnRNP proteins A1 and A2 and their relationship to single-stranded DNA-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):11266–11273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeStourgeon W. M., Beyer A. L., Christensen M. E., Walker B. W., Poupore S. M., Daniels L. P. The packaging proteins of core hnRNP particles and the maintenance of proliferative cell states. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 2):885–898. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lothstein L., Arenstorf H. P., Chung S. Y., Walker B. W., Wooley J. C., LeStourgeon W. M. General organization of protein in HeLa 40S nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles. J Cell Biol. 1985 May;100(5):1570–1581. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.5.1570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malcolm D. B., Sommerville J. The structure of chromosome-derived ribonucleoprotein in oocytes of Triturus cristatus carnifex (Laurenti). Chromosoma. 1974;48(2):137–158. doi: 10.1007/BF00283960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malcolm D. B., Sommerville J. The structure of nuclear ribonucleoprotein of amphibian oocytes. J Cell Sci. 1977 Apr;24:143–165. doi: 10.1242/jcs.24.1.143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Reed R. The role of small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles in pre-mRNA splicing. Nature. 1987 Feb 19;325(6106):673–678. doi: 10.1038/325673a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin T., Billings P., Levey A., Ozarslan S., Quinlan T., Swift H., Urbas L. Some properties of RNA:protein complexes from the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:921–932. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin T., Billings P., Pullman J., Stevens B., Kinniburgh A. Substructure of nuclear ribonucleoprotein complexes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 2):899–909. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayrand S., Pederson T. Nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles probed in living cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2208–2212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osheim Y. N., Miller O. L., Jr, Beyer A. L. RNP particles at splice junction sequences on Drosophila chorion transcripts. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):143–151. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osheim Y. N., Miller O. L., Jr Novel amplification and transcriptional activity of chorion genes in Drosophila melanogaster follicle cells. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):543–553. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90435-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pederson T. Nuclear RNA-protein interactions and messenger RNA processing. J Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;97(5 Pt 1):1321–1326. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.5.1321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pederson T. Proteins associated with heterogeneous nuclear RNA in eukaryotic cells. J Mol Biol. 1974 Feb 25;83(2):163–183. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90386-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pullman J. M., Martin T. E. Reconstitution of nucleoprotein complexes with mammalian heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein (hnRNP) core proteins. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;97(1):99–111. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.1.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riva S., Morandi C., Tsoulfas P., Pandolfo M., Biamonti G., Merrill B., Williams K. R., Multhaup G., Beyreuther K., Werr H. Mammalian single-stranded DNA binding protein UP I is derived from the hnRNP core protein A1. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2267–2273. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04494.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samarina O. P., Lukanidin E. M., Molnar J., Georgiev G. P. Structural organization of nuclear complexes containing DNA-like RNA. J Mol Biol. 1968 Apr 14;33(1):251–263. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90292-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A. Splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Science. 1987 Feb 13;235(4790):766–771. doi: 10.1126/science.3544217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sierakowska H., Szer W., Furdon P. J., Kole R. Antibodies to hnRNP core proteins inhibit in vitro splicing of human beta-globin pre-mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 11;14(13):5241–5254. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.13.5241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. O., Glowacka S. K., Szer W. Structure of complexes between a major protein of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles and polyribonucleotides. J Mol Biol. 1983 Dec 25;171(4):439–455. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90039-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsanev R. G., Djondjurov L. P. Ultrastructure of free ribonucleoprotein complexes in spread mammalian nuclei. J Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;94(3):662–666. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.3.662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker B. W., Lothstein L., Baker C. L., LeStourgeon W. M. The release of 40S hnRNP particles by brief digestion of HeLa nuclei with micrococcal nuclease. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Aug 25;8(16):3639–3657. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.16.3639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieringa B., Hofer E., Weissmann C. A minimal intron length but no specific internal sequence is required for splicing the large rabbit beta-globin intron. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):915–925. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90426-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilk H. E., Angeli G., Schäfer K. P. In vitro reconstitution of 35S ribonucleoprotein complexes. Biochemistry. 1983 Sep 13;22(19):4592–4600. doi: 10.1021/bi00288a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. C. Use of polylysine for adsorption of nuclei acids and enzymes to electron microscope specimen films. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2311–2315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wooley J., Chung S. Y., Wall J., Lestourgeon W. Architecture of pre-messenger, nuclear ribonucleoprotein monoparticles. Biophys J. 1986 Jan;49(1):17–19. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83575-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Eekelen C. A., Riemen T., van Venrooij W. J. Specificity in the interaction of hnRNA and mRNA with proteins as revealed by in vivo cross linking. FEBS Lett. 1981 Aug 3;130(2):223–226. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)81125-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]