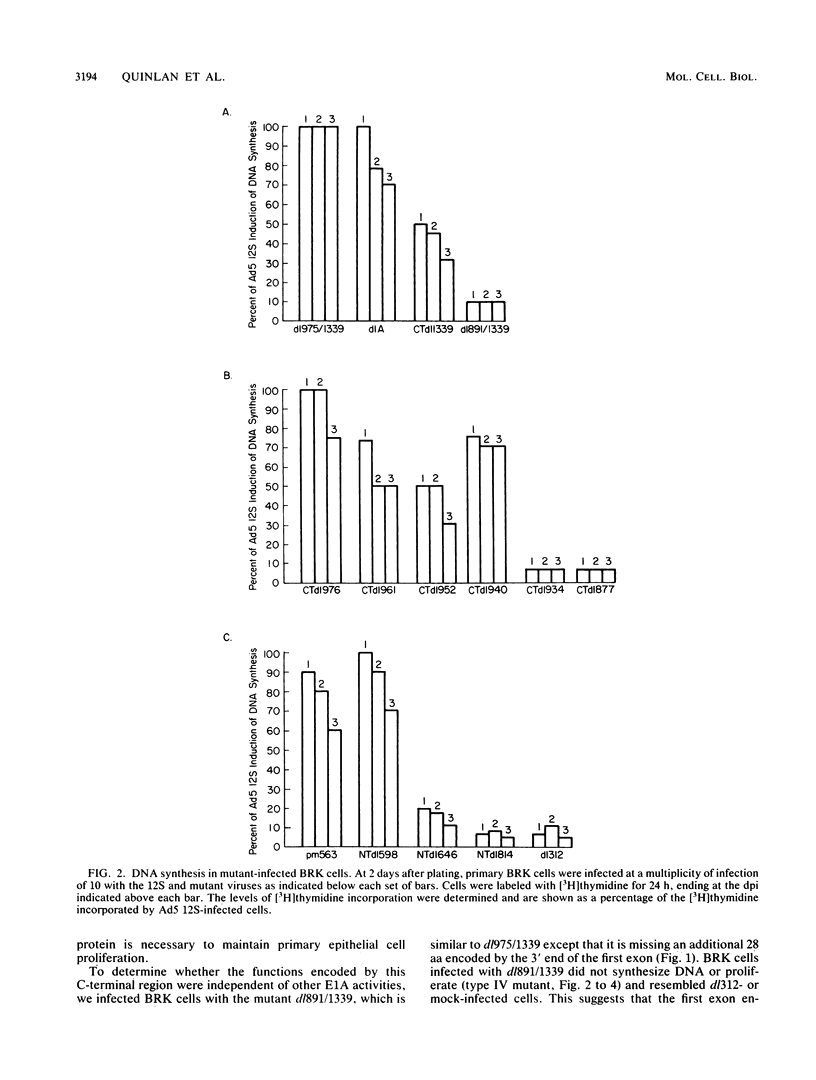
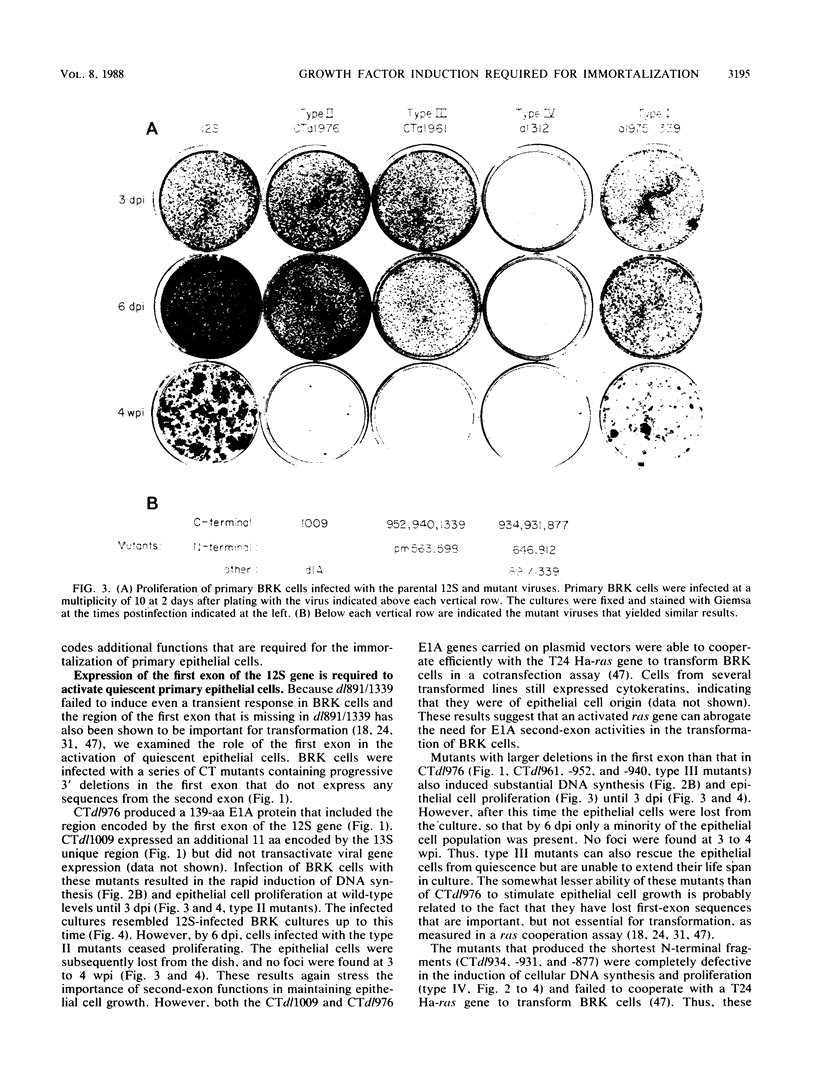
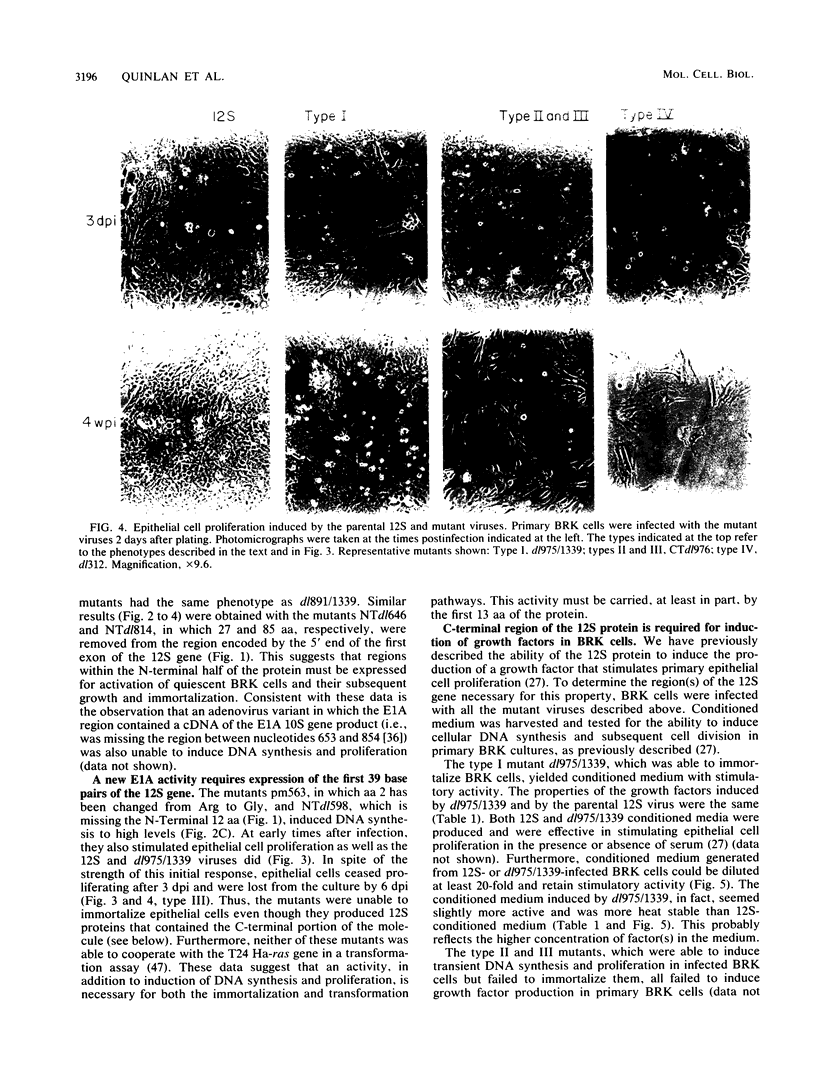
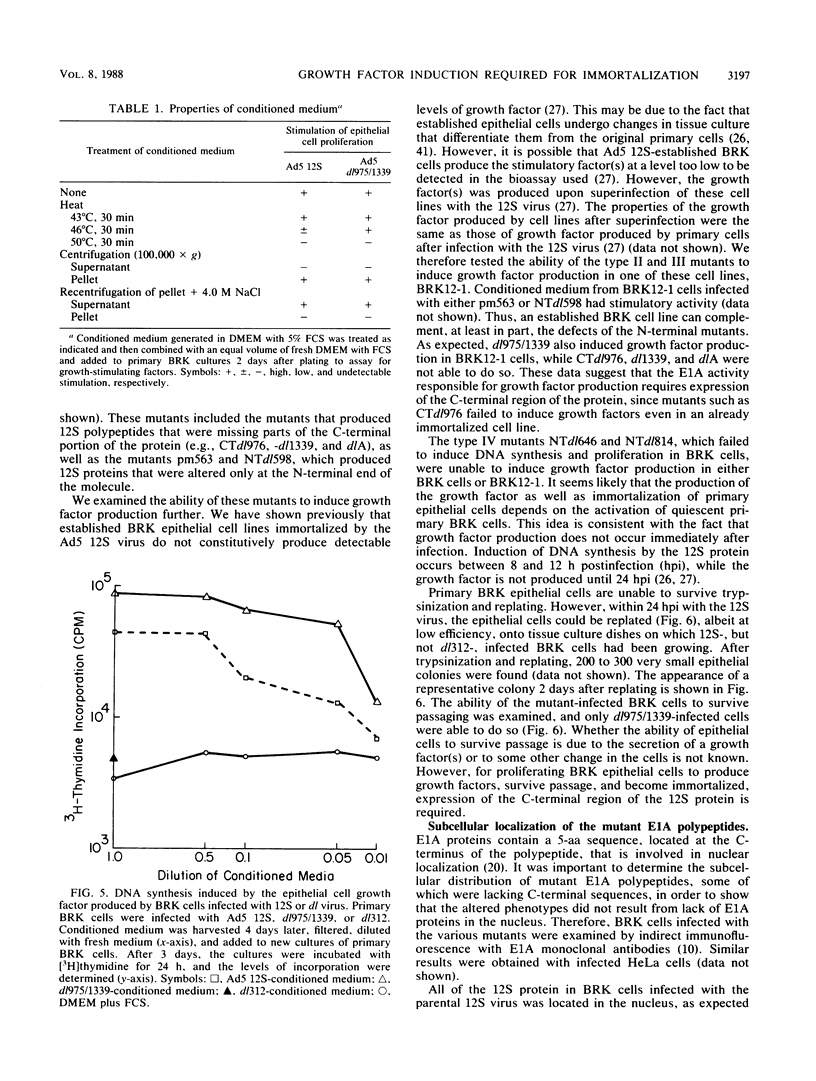
Abstract
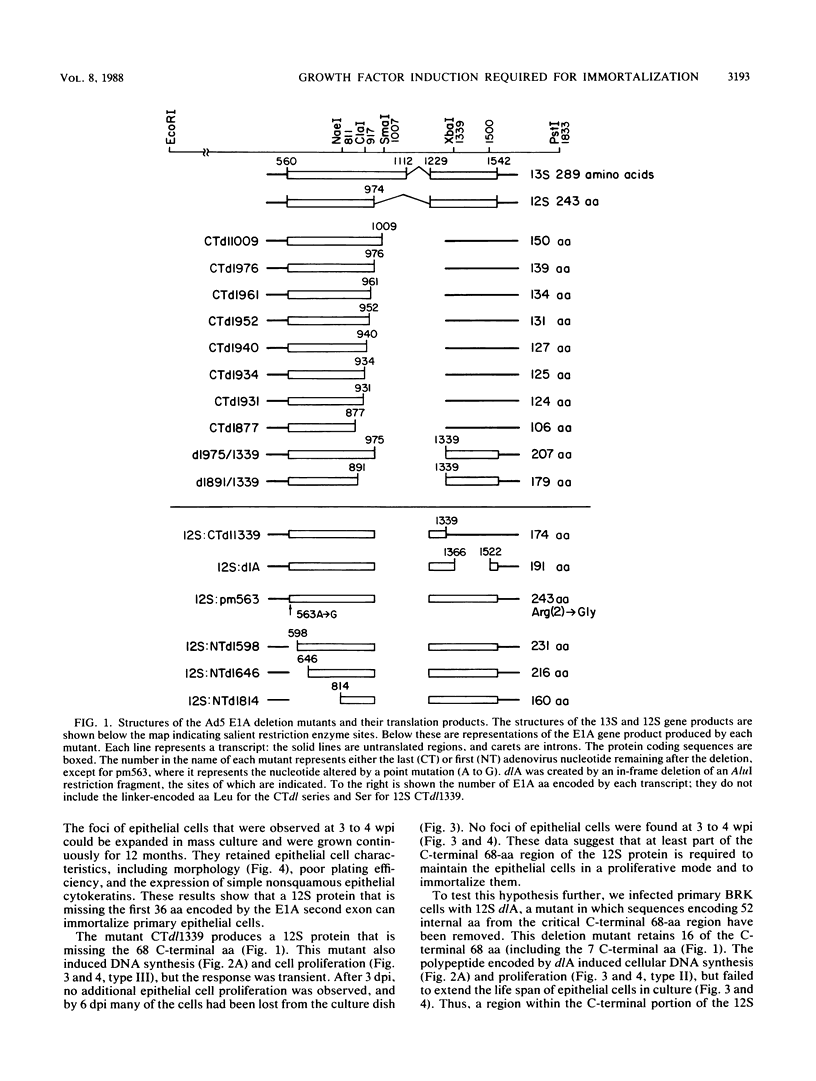
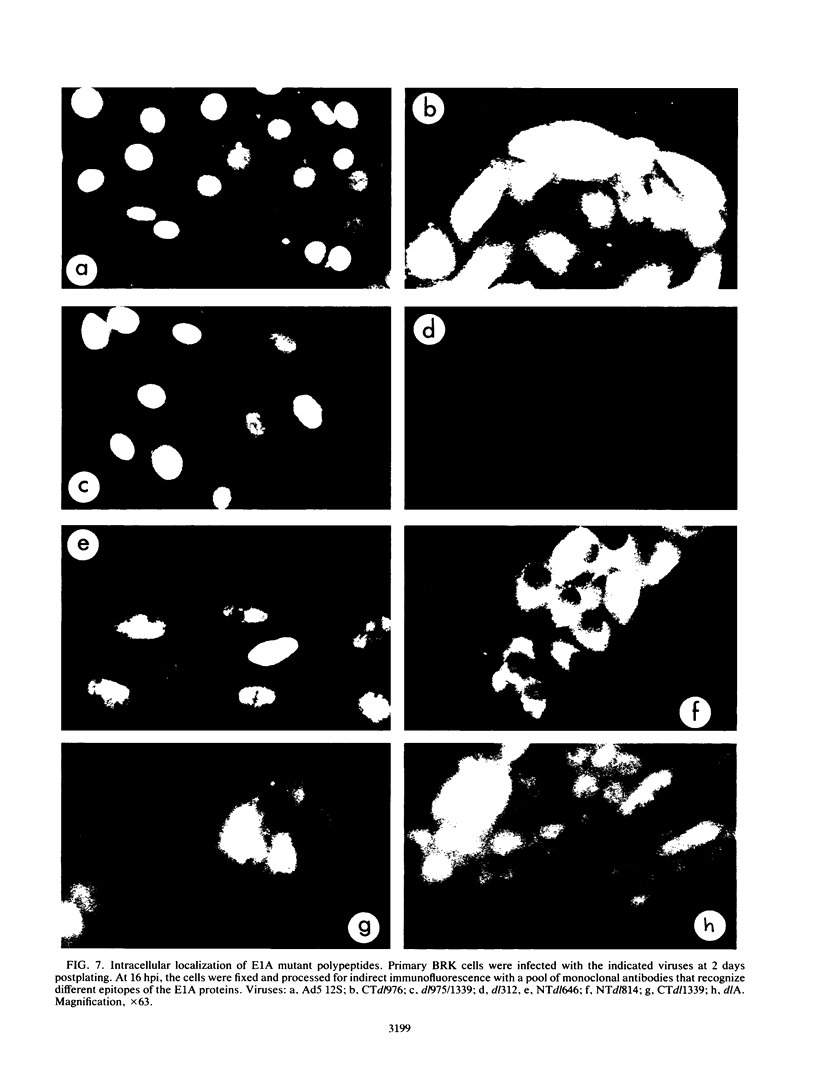
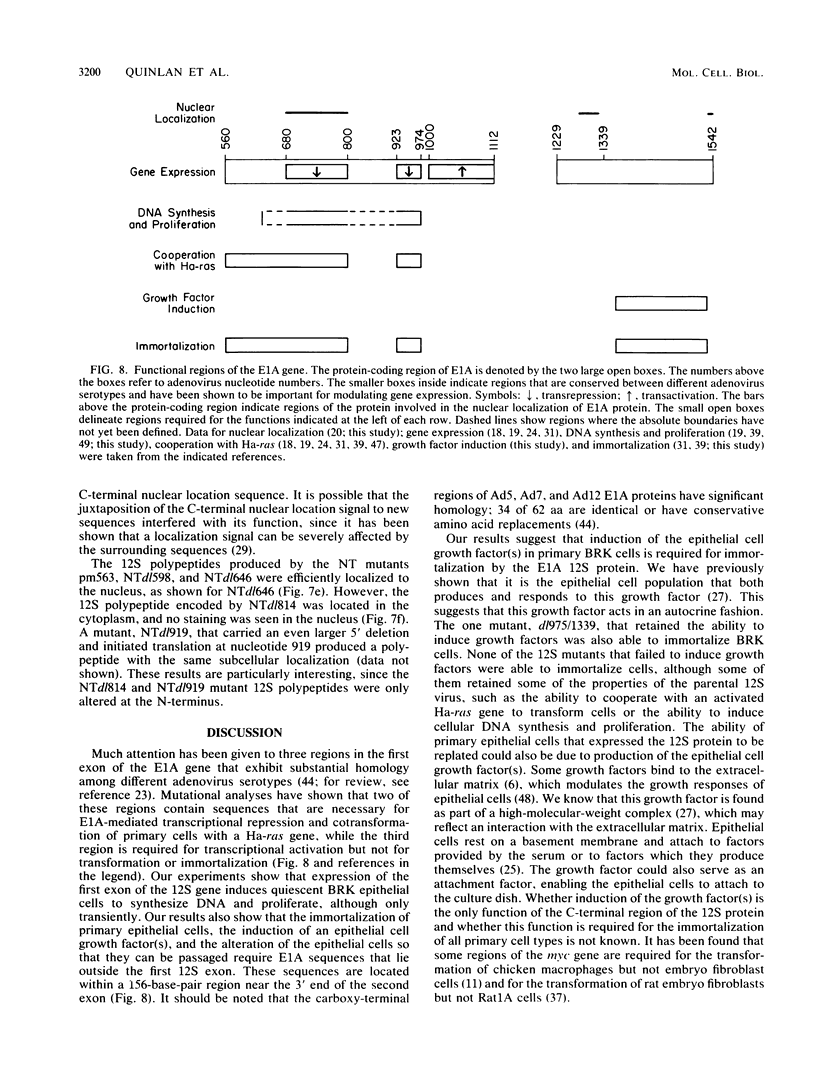
The 12S protein encoded by the adenovirus E1A region induces cellular DNA synthesis in and proliferation and immortalization of primary rat epithelial cells in the presence or absence of serum. It also induces the production of a growth factor(s) that stimulates epithelial cell proliferation. We have undertaken a mutational analysis of the 12S gene to determine the sequences required for these functions. We found that a region near the C-terminus of the 12S protein was required for growth factor induction. No activities have been defined previously for this region. Furthermore, we show that growth factor production was necessary for epithelial cells to survive past their normal life span in culture and to become immortalized. The ability to induce growth factor production required prior expression of E1A activities encoded by the N-terminus of the 12S protein, including activation of quiescent cells into the cell cycle, and an unknown activity that required expression of the first 13 amino acids of the gene. In addition, examination of the subcellular localization of mutant 12S polypeptides suggested new regions that affect the nuclear localization of E1A proteins.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bellett A. J., Li P., David E. T., Mackey E. J., Braithwaite A. W., Cutt J. R. Control functions of adenovirus transformation region E1A gene products in rat and human cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1933–1939. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bürglin T. R., De Robertis E. M. The nuclear migration signal of Xenopus laevis nucleoplasmin. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2617–2625. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02552.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlock L. R., Jones N. C. Transformation-defective mutant of adenovirus type 5 containing a single altered E1a mRNA species. J Virol. 1981 Dec;40(3):657–664. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.3.657-664.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Sharnick S. V., Laskey R. A. A polypeptide domain that specifies migration of nucleoplasmin into the nucleus. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):449–458. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90242-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallimore P. H. Viral DNA in transformed cells. II. A study of the sequences of adenovirus 2 DNA IN NINE LINES OF TRANSFORMED RAT CELLS USING SPECIFIC FRAGMENTS OF THE VIRAL GENOME;. J Mol Biol. 1974 Oct 15;89(1):49–72. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90162-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon P. B., Conn G., Hatcher V. B. Glycosaminoglycan production in cultures of early and late passage human endothelial cells: the influence of an anionic endothelial cell growth factor and the extracellular matrix. J Cell Physiol. 1985 Dec;125(3):596–607. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041250332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., Abrahams P. J., Mulder C., Heijneker H. L., Warnaar S. O., De Vries F. A., Fiers W., Van Der Eb A. J. Studies on in vitro transformation by DNA and DNA fragments of human adenoviruses and simian virus 40. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):637–650. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haley K. P., Overhauser J., Babiss L. E., Ginsberg H. S., Jones N. C. Transformation properties of type 5 adenovirus mutants that differentially express the E1A gene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5734–5738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlow E., Franza B. R., Jr, Schley C. Monoclonal antibodies specific for adenovirus early region 1A proteins: extensive heterogeneity in early region 1A products. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):533–546. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.533-546.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heaney M. L., Pierce J., Parsons J. T. Site-directed mutagenesis of the gag-myc gene of avian myelocytomatosis virus 29: biological activity and intracellular localization of structurally altered proteins. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):167–176. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.167-176.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldin C. H., Westermark B. Growth factors: mechanism of action and relation to oncogenes. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):9–20. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90296-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houweling A., van den Elsen P. J., van der Eb A. J. Partial transformation of primary rat cells by the leftmost 4.5% fragment of adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1980 Sep;105(2):537–550. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90054-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Cooper J. A. Protein-tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:897–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N., Shenk T. Isolation of adenovirus type 5 host range deletion mutants defective for transformation of rat embryo cells. Cell. 1979 Jul;17(3):683–689. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90275-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalderon D., Roberts B. L., Richardson W. D., Smith A. E. A short amino acid sequence able to specify nuclear location. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):499–509. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90457-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillie J. W., Green M., Green M. R. An adenovirus E1a protein region required for transformation and transcriptional repression. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):1043–1051. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90704-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillie J. W., Loewenstein P. M., Green M. R., Green M. Functional domains of adenovirus type 5 E1a proteins. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1091–1100. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90175-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons R. H., Ferguson B. Q., Rosenberg M. Pentapeptide nuclear localization signal in adenovirus E1a. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2451–2456. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montell C., Courtois G., Eng C., Berk A. Complete transformation by adenovirus 2 requires both E1A proteins. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):951–961. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90045-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran E., Grodzicker T., Roberts R. J., Mathews M. B., Zerler B. Lytic and transforming functions of individual products of the adenovirus E1A gene. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):765–775. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.765-775.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran E., Mathews M. B. Multiple functional domains in the adenovirus E1A gene. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):177–178. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90418-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran E., Zerler B., Harrison T. M., Mathews M. B. Identification of separate domains in the adenovirus E1A gene for immortalization activity and the activation of virus early genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3470–3480. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orly J., Sato G. Fibronectin mediates cytokinesis and growth of rat follicular cells in serum-free medium. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):295–305. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90155-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinlan M. P., Grodzicker T. Adenovirus E1A 12S protein induces DNA synthesis and proliferation in primary epithelial cells in both the presence and absence of serum. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):673–682. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.673-682.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinlan M. P., Sullivan N., Grodzicker T. Growth factor(s) produced during infection with an adenovirus variant stimulates proliferation of nonestablished epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3283–3287. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson W. D., Roberts B. L., Smith A. E. Nuclear location signals in polyoma virus large-T. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):77–85. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90486-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts B. L., Richardson W. D., Smith A. E. The effect of protein context on nuclear location signal function. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):465–475. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90500-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruley H. E. Adenovirus early region 1A enables viral and cellular transforming genes to transform primary cells in culture. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):602–606. doi: 10.1038/304602a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider J. F., Fisher F., Goding C. R., Jones N. C. Mutational analysis of the adenovirus E1a gene: the role of transcriptional regulation in transformation. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):2053–2060. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02470.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spindler K. R., Eng C. Y., Berk A. J. An adenovirus early region 1A protein is required for maximal viral DNA replication in growth-arrested human cells. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):742–750. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.742-750.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B. Autocrine growth factors and cancer. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):745–747. doi: 10.1038/313745a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stabel S., Argos P., Philipson L. The release of growth arrest by microinjection of adenovirus E1A DNA. EMBO J. 1985 Sep;4(9):2329–2336. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03934.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens C., Harlow E. Differential splicing yields novel adenovirus 5 E1A mRNAs that encode 30 kd and 35 kd proteins. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):2027–2035. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02467.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone J., de Lange T., Ramsay G., Jakobovits E., Bishop J. M., Varmus H., Lee W. Definition of regions in human c-myc that are involved in transformation and nuclear localization. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1697–1709. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D. Cloning of a DNA fragment from the left-hand terminus of the adenovirus type 2 genome and its use in site-directed mutagenesis. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):171–180. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.171-180.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian T., Kuppuswamy M., Nasr R. J., Chinnadurai G. An N-terminal region of adenovirus E1a essential for cell transformation and induction of an epithelial cell growth factor. Oncogene. 1988 Feb;2(2):105–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe T., Nukada T., Nishikawa Y., Sugimoto K., Suzuki H., Takahashi H., Noda M., Haga T., Ichiyama A., Kangawa K. Primary structure of the alpha-subunit of transducin and its relationship to ras proteins. Nature. 1985 May 16;315(6016):242–245. doi: 10.1038/315242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakelam M. J., Davies S. A., Houslay M. D., McKay I., Marshall C. J., Hall A. Normal p21N-ras couples bombesin and other growth factor receptors to inositol phosphate production. Nature. 1986 Sep 11;323(6084):173–176. doi: 10.1038/323173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittaker J. L., Byrd P. J., Grand R. J., Gallimore P. H. Isolation and characterization of four adenovirus type 12-transformed human embryo kidney cell lines. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;4(1):110–116. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.1.110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whyte P., Ruley H. E., Harlow E. Two regions of the adenovirus early region 1A proteins are required for transformation. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):257–265. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.257-265.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright T. C., Jr, Johnstone T. V., Castellot J. J., Karnovsky M. J. Inhibition of rat cervical epithelial cell growth by heparin and its reversal by EGF. J Cell Physiol. 1985 Dec;125(3):499–506. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041250320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerler B., Roberts R. J., Mathews M. B., Moran E. Different functional domains of the adenovirus E1A gene are involved in regulation of host cell cycle products. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):821–829. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Ormondt H., Maat J., Dijkema R. Comparison of nucleotide sequences of the early E1a regions for subgroups A, B and C of human adenoviruses. Gene. 1980 Dec;12(1-2):63–76. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90016-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Elsen P. J., Houweling A., van der Eb A. J. Morphological transformation of human adenoviruses is determined to a large extent by gene products of region E1a. Virology. 1983 Nov;131(1):242–246. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90549-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]