Abstract
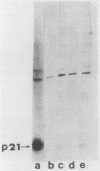
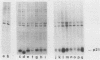
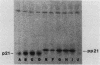
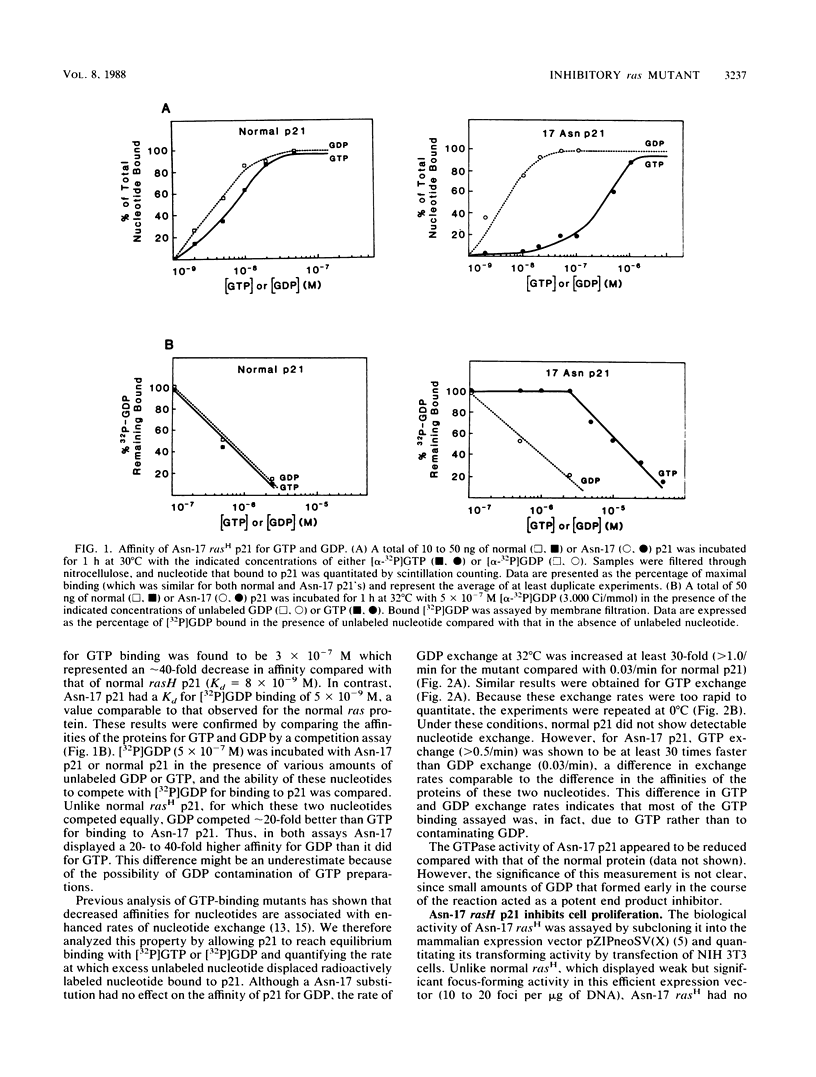
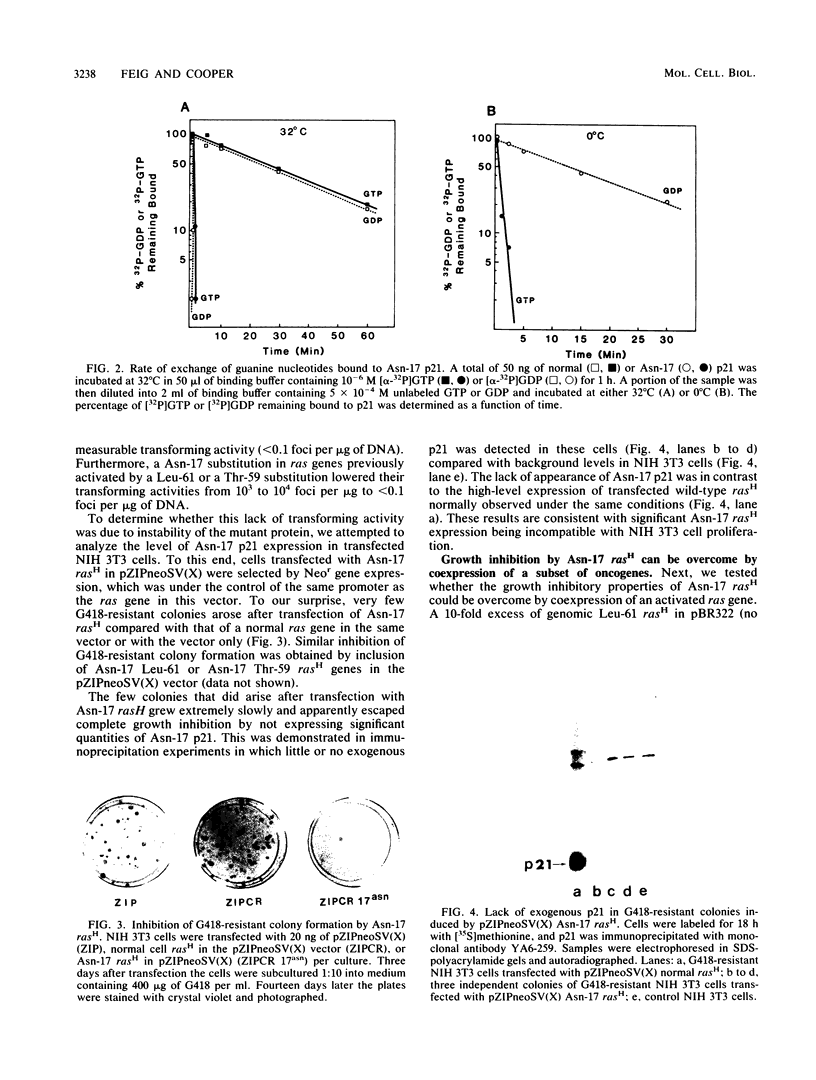
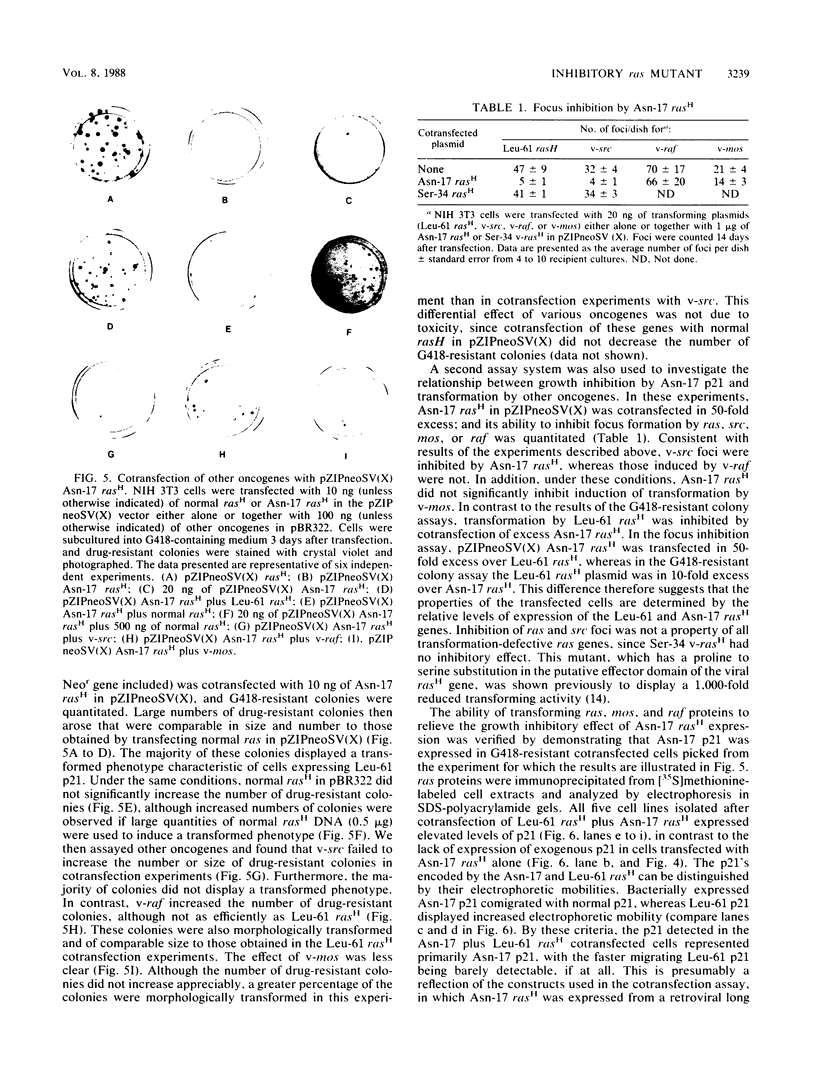
Substitution of asparagine for serine at position 17 decreased the affinity of rasH p21 for GTP 20- to 40-fold without significantly affecting its affinity for GDP. Transfection of NIH 3T3 cells with a mammalian expression vector containing the Asn-17 rasH gene and a Neor gene under the control of the same promoter yielded only a small fraction of the expected number of G418-resistant colonies, indicating that expression of Asn-17 p21 inhibited cell proliferation. The inhibitory effect of Asn-17 p21 required its localization to the plasma membrane and was reversed by coexpression of an activated ras gene, indicating that the mutant p21 blocked the endogenous ras function required for NIH 3T3 cell proliferation. NIH 3T3 cells transformed by v-mos and v-raf, but not v-src, were resistant to inhibition by Asn-17 p21, indicating that the requirement for normal ras function can be bypassed by these cytoplasmic oncogenes. The Asn-17 mutant represents a novel reagent for the study of ras function by virtue of its ability to inhibit cellular ras activity in vivo. Since this phenotype is likely associated with the preferential affinity of the mutant protein for GDP, analogous mutations might also yield inhibitors of other proteins whose activities are regulated by guanine nucleotide binding.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bar-Sagi D., Feramisco J. R. Induction of membrane ruffling and fluid-phase pinocytosis in quiescent fibroblasts by ras proteins. Science. 1986 Sep 5;233(4768):1061–1068. doi: 10.1126/science.3090687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Sagi D., Feramisco J. R. Microinjection of the ras oncogene protein into PC12 cells induces morphological differentiation. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):841–848. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90280-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbacid M. ras genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:779–827. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.004023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair D. G., McClements W. L., Oskarsson M. K., Fischinger P. J., Vande Woude G. F. Biological activity of cloned Moloney sarcoma virus DNA: Terminally redundant sequences may enhance transformation efficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3504–3508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cepko C. L., Roberts B. E., Mulligan R. C. Construction and applications of a highly transmissible murine retrovirus shuttle vector. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1053–1062. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90440-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesa P. G., Rettig W. J., Melamed M. R., Old L. J., Niman H. L. Expression of p21ras in normal and malignant human tissues: lack of association with proliferation and malignancy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3234–3238. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clanton D. J., Hattori S., Shih T. Y. Mutations of the ras gene product p21 that abolish guanine nucleotide binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5076–5080. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clanton D. J., Lu Y. Y., Blair D. G., Shih T. Y. Structural significance of the GTP-binding domain of ras p21 studied by site-directed mutagenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3092–3097. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland N. G., Cooper G. M. Transfection by exogenous and endogenous murine retrovirus DNAs. Cell. 1979 Feb;16(2):347–356. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Der C. J., Cooper G. M. Altered gene products are associated with activation of cellular rasK genes in human lung and colon carcinomas. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):201–208. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90510-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Der C. J., Finkel T., Cooper G. M. Biological and biochemical properties of human rasH genes mutated at codon 61. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):167–176. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90495-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Der C. J., Pan B. T., Cooper G. M. rasH mutants deficient in GTP binding. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;6(9):3291–3294. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.9.3291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feig L. A., Cooper G. M. Relationship among guanine nucleotide exchange, GTP hydrolysis, and transforming potential of mutated ras proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2472–2478. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feig L. A., Corbley M., Pan B. T., Roberts T. M., Cooper G. M. Structure/function analysis of ras using random mutagenesis coupled with functional screening assays. Mol Endocrinol. 1987 Feb;1(2):127–136. doi: 10.1210/mend-1-2-127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feig L. A., Pan B. T., Roberts T. M., Cooper G. M. Isolation of ras GTP-binding mutants using an in situ colony-binding assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4607–4611. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feramisco J. R., Gross M., Kamata T., Rosenberg M., Sweet R. W. Microinjection of the oncogene form of the human H-ras (T-24) protein results in rapid proliferation of quiescent cells. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):109–117. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90531-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field J., Broek D., Kataoka T., Wigler M. Guanine nucleotide activation of, and competition between, RAS proteins from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2128–2133. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischman L. F., Chahwala S. B., Cantley L. ras-transformed cells: altered levels of phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate and catabolites. Science. 1986 Jan 24;231(4736):407–410. doi: 10.1126/science.3001936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furth M. E., Aldrich T. H., Cordon-Cardo C. Expression of ras proto-oncogene proteins in normal human tissues. Oncogene. 1987 Mar;1(1):47–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs J. B., Sigal I. S., Poe M., Scolnick E. M. Intrinsic GTPase activity distinguishes normal and oncogenic ras p21 molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5704–5708. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrero I., Wong H., Pellicer A., Burstein D. E. Activated N-ras gene induces neuronal differentiation of PC12 rat pheochromocytoma cells. J Cell Physiol. 1986 Oct;129(1):71–76. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041290111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagag N., Lacal J. C., Graber M., Aaronson S., Viola M. V. Microinjection of ras p21 induces a rapid rise in intracellular pH. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1984–1988. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashijima T., Ferguson K. M., Sternweis P. C., Smigel M. D., Gilman A. G. Effects of Mg2+ and the beta gamma-subunit complex on the interactions of guanine nucleotides with G proteins. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 15;262(2):762–766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jurnak F. Structure of the GDP domain of EF-Tu and location of the amino acids homologous to ras oncogene proteins. Science. 1985 Oct 4;230(4721):32–36. doi: 10.1126/science.3898365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kataoka T., Powers S., McGill C., Fasano O., Strathern J., Broach J., Wigler M. Genetic analysis of yeast RAS1 and RAS2 genes. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):437–445. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90374-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacal J. C., Aaronson S. A. Activation of ras p21 transforming properties associated with an increase in the release rate of bound guanine nucleotide. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4214–4220. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacal J. C., Moscat J., Aaronson S. A. Novel source of 1,2-diacylglycerol elevated in cells transformed by Ha-ras oncogene. Nature. 1987 Nov 19;330(6145):269–272. doi: 10.1038/330269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manne V., Bekesi E., Kung H. F. Ha-ras proteins exhibit GTPase activity: point mutations that activate Ha-ras gene products result in decreased GTPase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):376–380. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick F., Clark B. F., la Cour T. F., Kjeldgaard M., Norskov-Lauritsen L., Nyborg J. A model for the tertiary structure of p21, the product of the ras oncogene. Science. 1985 Oct 4;230(4721):78–82. doi: 10.1126/science.3898366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath J. P., Capon D. J., Goeddel D. V., Levinson A. D. Comparative biochemical properties of normal and activated human ras p21 protein. Nature. 1984 Aug 23;310(5979):644–649. doi: 10.1038/310644a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulcahy L. S., Smith M. R., Stacey D. W. Requirement for ras proto-oncogene function during serum-stimulated growth of NIH 3T3 cells. Nature. 1985 Jan 17;313(5999):241–243. doi: 10.1038/313241a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papageorge A. G., Willumsen B. M., Johnsen M., Kung H. F., Stacey D. W., Vass W. C., Lowy D. R. A transforming ras gene can provide an essential function ordinarily supplied by an endogenous ras gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1843–1846. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preiss J., Loomis C. R., Bishop W. R., Stein R., Niedel J. E., Bell R. M. Quantitative measurement of sn-1,2-diacylglycerols present in platelets, hepatocytes, and ras- and sis-transformed normal rat kidney cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8597–8600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp U. R., Goldsborough M. D., Mark G. E., Bonner T. I., Groffen J., Reynolds F. H., Jr, Stephenson J. R. Structure and biological activity of v-raf, a unique oncogene transduced by a retrovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4218–4222. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalloway D., Zelenetz A. D., Cooper G. M. Molecular cloning and characterization of the chicken gene homologous to the transforming gene of Rous sarcoma virus. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):531–541. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90344-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih T. Y., Weeks M. O., Gruss P., Dhar R., Oroszlan S., Scolnick E. M. Identification of a precursor in the biosynthesis of the p21 transforming protein of harvey murine sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1982 Apr;42(1):253–261. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.1.253-261.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigal I. S., Gibbs J. B., D'Alonzo J. S., Scolnick E. M. Identification of effector residues and a neutralizing epitope of Ha-ras-encoded p21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4725–4729. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigal I. S., Gibbs J. B., D'Alonzo J. S., Temeles G. L., Wolanski B. S., Socher S. H., Scolnick E. M. Mutant ras-encoded proteins with altered nucleotide binding exert dominant biological effects. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):952–956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. R., DeGudicibus S. J., Stacey D. W. Requirement for c-ras proteins during viral oncogene transformation. Nature. 1986 Apr 10;320(6062):540–543. doi: 10.1038/320540a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stacey D. W., Kung H. F. Transformation of NIH 3T3 cells by microinjection of Ha-ras p21 protein. Nature. 1984 Aug 9;310(5977):508–511. doi: 10.1038/310508a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stacey D. W., Watson T., Kung H. F., Curran T. Microinjection of transforming ras protein induces c-fos expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):523–527. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweet R. W., Yokoyama S., Kamata T., Feramisco J. R., Rosenberg M., Gross M. The product of ras is a GTPase and the T24 oncogenic mutant is deficient in this activity. Nature. 1984 Sep 20;311(5983):273–275. doi: 10.1038/311273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatchell K., Chaleff D. T., DeFeo-Jones D., Scolnick E. M. Requirement of either of a pair of ras-related genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for spore viability. Nature. 1984 Jun 7;309(5968):523–527. doi: 10.1038/309523a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda T., Uno I., Ishikawa T., Powers S., Kataoka T., Broek D., Cameron S., Broach J., Matsumoto K., Wigler M. In yeast, RAS proteins are controlling elements of adenylate cyclase. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):27–36. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90305-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trahey M., McCormick F. A cytoplasmic protein stimulates normal N-ras p21 GTPase, but does not affect oncogenic mutants. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):542–545. doi: 10.1126/science.2821624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakelam M. J., Davies S. A., Houslay M. D., McKay I., Marshall C. J., Hall A. Normal p21N-ras couples bombesin and other growth factor receptors to inositol phosphate production. Nature. 1986 Sep 11;323(6084):173–176. doi: 10.1038/323173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter M., Clark S. G., Levinson A. D. The oncogenic activation of human p21ras by a novel mechanism. Science. 1986 Aug 8;233(4764):649–652. doi: 10.1126/science.3487832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willumsen B. M., Norris K., Papageorge A. G., Hubbert N. L., Lowy D. R. Harvey murine sarcoma virus p21 ras protein: biological and biochemical significance of the cysteine nearest the carboxy terminus. EMBO J. 1984 Nov;3(11):2581–2585. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02177.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willumsen B. M., Papageorge A. G., Kung H. F., Bekesi E., Robins T., Johnsen M., Vass W. C., Lowy D. R. Mutational analysis of a ras catalytic domain. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2646–2654. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]