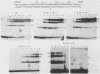
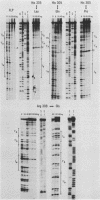
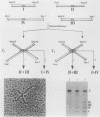
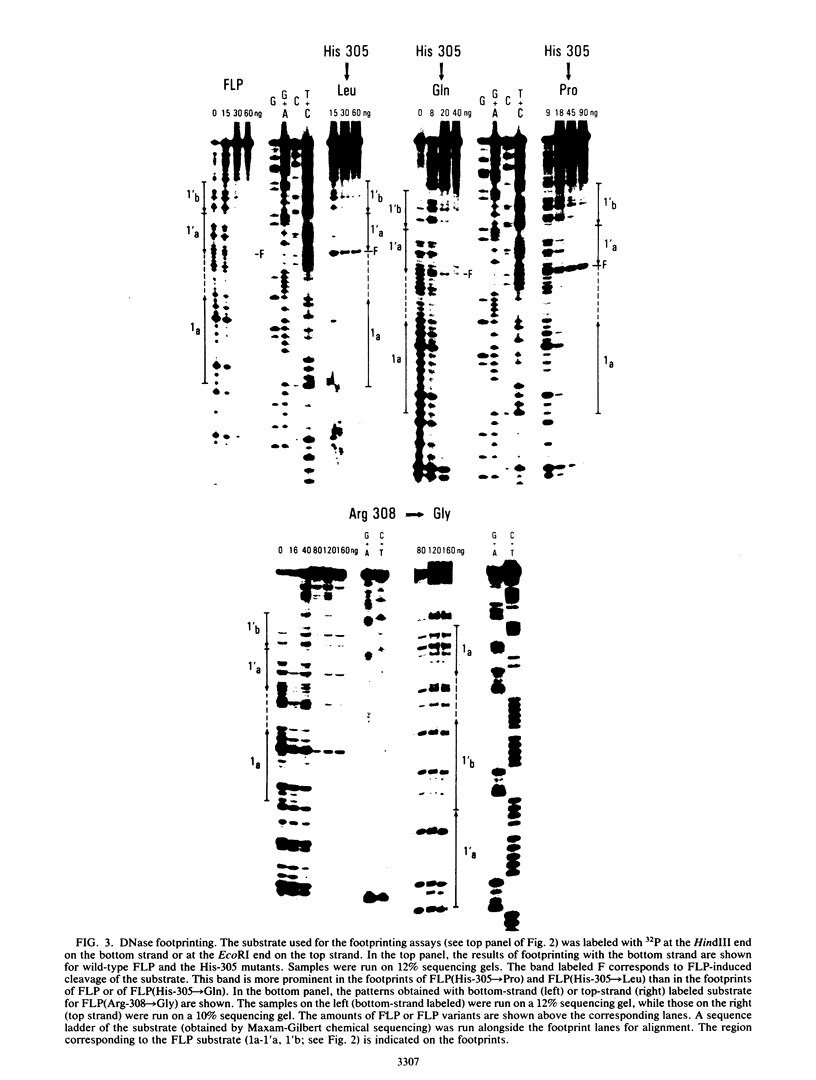
Abstract
The site-specific recombinase (FLP) encoded by the yeast plasmid 2 micron circle belongs to the integrase (of phage lambda) family of recombinases. The sparse homology within the members of this family contrasts with the invariance of three residues, His-396, Arg-399, and Tyr-433 (the numbers correspond to the family alignment positions), among them. We report here results on substrate recognition and catalysis by FLP proteins altered at these residues. Mutations of the conserved His and Tyr that aborted the reaction at specific steps of catalysis permitted genetic dissection of the possible biochemical steps of recombination. We provide indirect evidence that recombination by FLP proceeds through a Holliday junction intermediate.
Full text
PDF



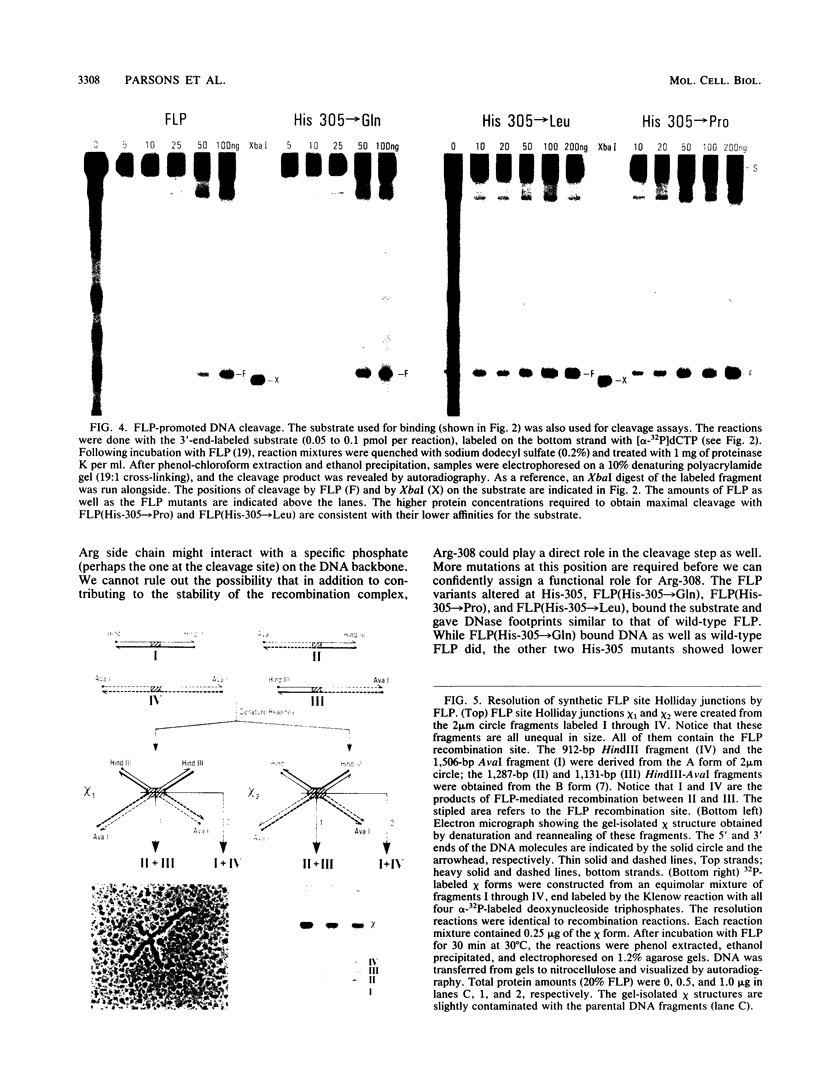
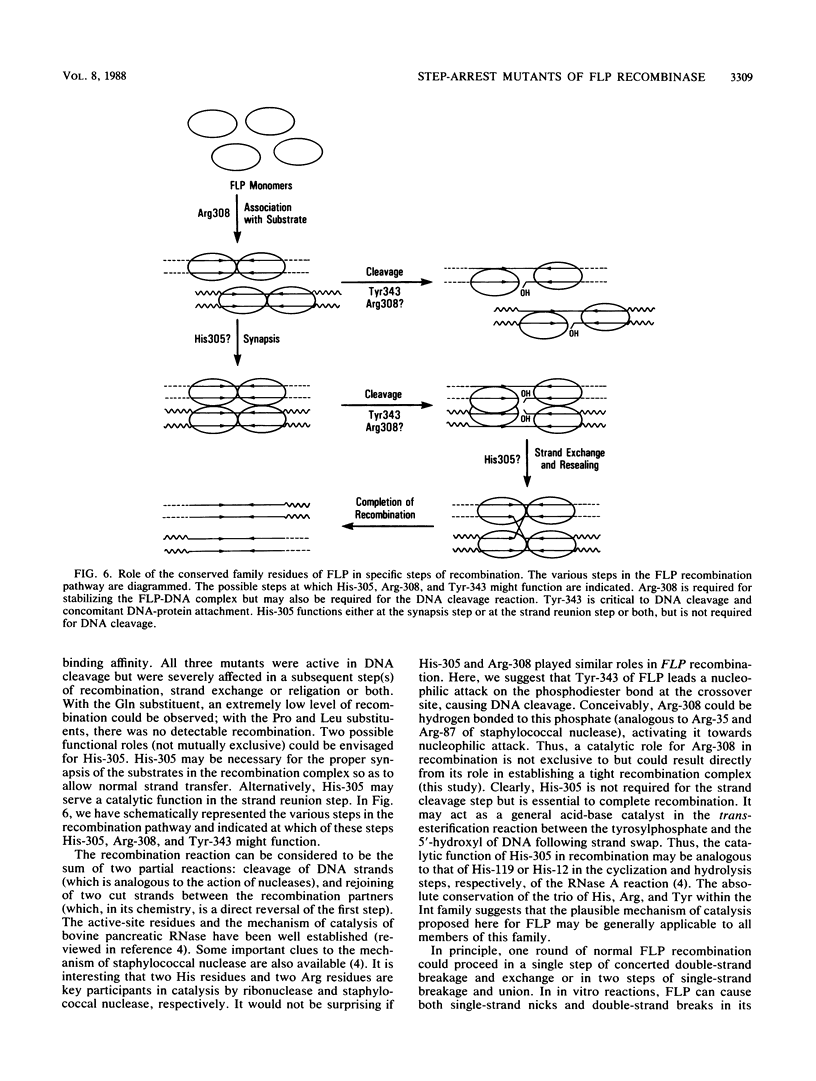

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews B. J., Beatty L. G., Sadowski P. D. Isolation of intermediates in the binding of the FLP recombinase of the yeast plasmid 2-micron circle to its target sequence. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jan 20;193(2):345–358. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90223-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews B. J., Proteau G. A., Beatty L. G., Sadowski P. D. The FLP recombinase of the 2 micron circle DNA of yeast: interaction with its target sequences. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):795–803. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90339-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argos P., Landy A., Abremski K., Egan J. B., Haggard-Ljungquist E., Hoess R. H., Kahn M. L., Kalionis B., Narayana S. V., Pierson L. S., 3rd The integrase family of site-specific recombinases: regional similarities and global diversity. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):433–440. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04229.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell L., Byers B. Occurrence of crossed strand-exchange forms in yeast DNA during meiosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3445–3449. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M. G., Crothers D. M. CAP and RNA polymerase interactions with the lac promoter: binding stoichiometry and long range effects. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 11;11(1):141–158. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.1.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronostajski R. M., Sadowski P. D. The FLP recombinase of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae 2 microns plasmid attaches covalently to DNA via a phosphotyrosyl linkage. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):3274–3279. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.3274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. L., Donelson J. E. Nucleotide sequence of the yeast plasmid. Nature. 1980 Aug 28;286(5776):860–865. doi: 10.1038/286860a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoess R. H., Abremski K. Mechanism of strand cleavage and exchange in the Cre-lox site-specific recombination system. J Mol Biol. 1985 Feb 5;181(3):351–362. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90224-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoess R., Wierzbicki A., Abremski K. Isolation and characterization of intermediates in site-specific recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6840–6844. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu P. L., Landy A. Resolution of synthetic att-site Holliday structures by the integrase protein of bacteriophage lambda. Nature. 1984 Oct 25;311(5988):721–726. doi: 10.1038/311721a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayaram M. Two-micrometer circle site-specific recombination: the minimal substrate and the possible role of flanking sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5875–5879. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitts P. A., Nash H. A. Homology-dependent interactions in phage lambda site-specific recombination. Nature. 1987 Sep 24;329(6137):346–348. doi: 10.1038/329346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell A., Gellert M. Mechanistic aspects of DNA topoisomerases. Adv Protein Chem. 1986;38:69–107. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60526-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuuchi K., Weisberg R., Enquist L., Mizuuchi M., Buraczynska M., Foeller C., Hsu P. L., Ross W., Landy A. Structure and function of the phage lambda att site: size, int-binding sites, and location of the crossover point. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 1):429–437. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash H. A., Bauer C. E., Gardner J. F. Role of homology in site-specific recombination of bacteriophage lambda: evidence against joining of cohesive ends. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4049–4053. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norris K., Norris F., Christiansen L., Fiil N. Efficient site-directed mutagenesis by simultaneous use of two primers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 11;11(15):5103–5112. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.15.5103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunes-Düby S. E., Matsumoto L., Landy A. Site-specific recombination intermediates trapped with suicide substrates. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):779–788. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90336-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prasad P. V., Young L. J., Jayaram M. Mutations in the 2-microns circle site-specific recombinase that abolish recombination without affecting substrate recognition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2189–2193. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senecoff J. F., Bruckner R. C., Cox M. M. The FLP recombinase of the yeast 2-micron plasmid: characterization of its recombination site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7270–7274. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]