Abstract
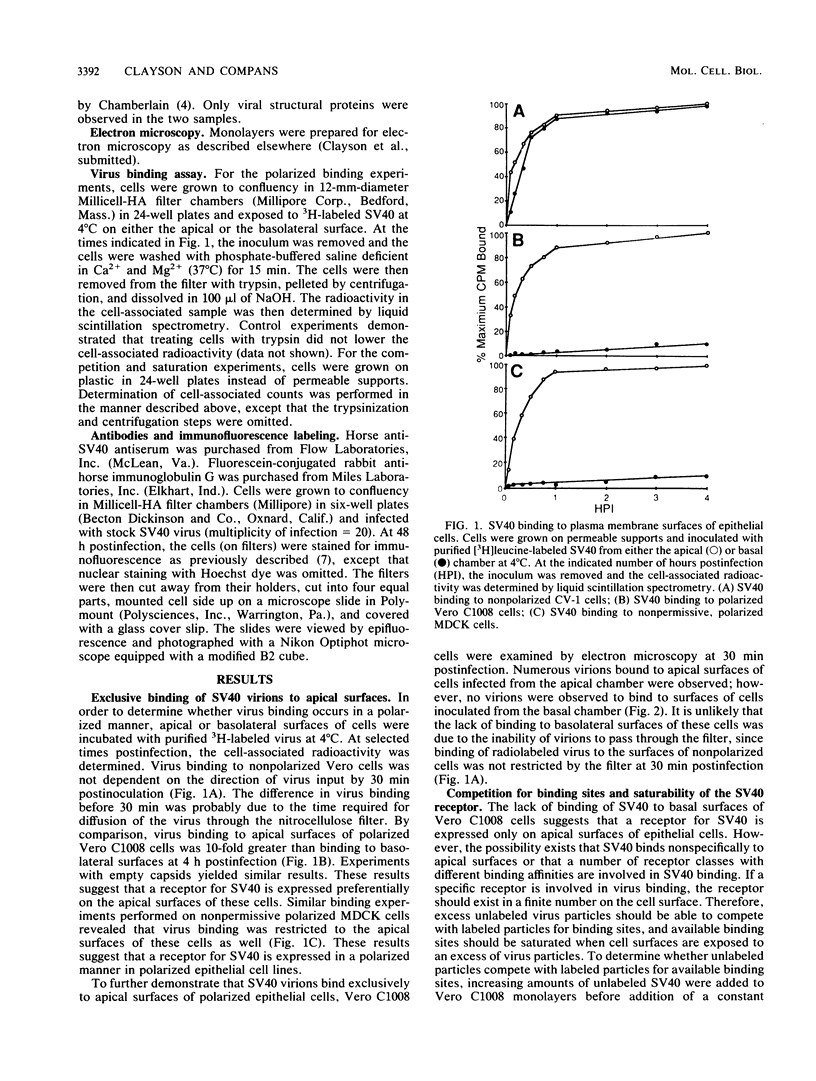
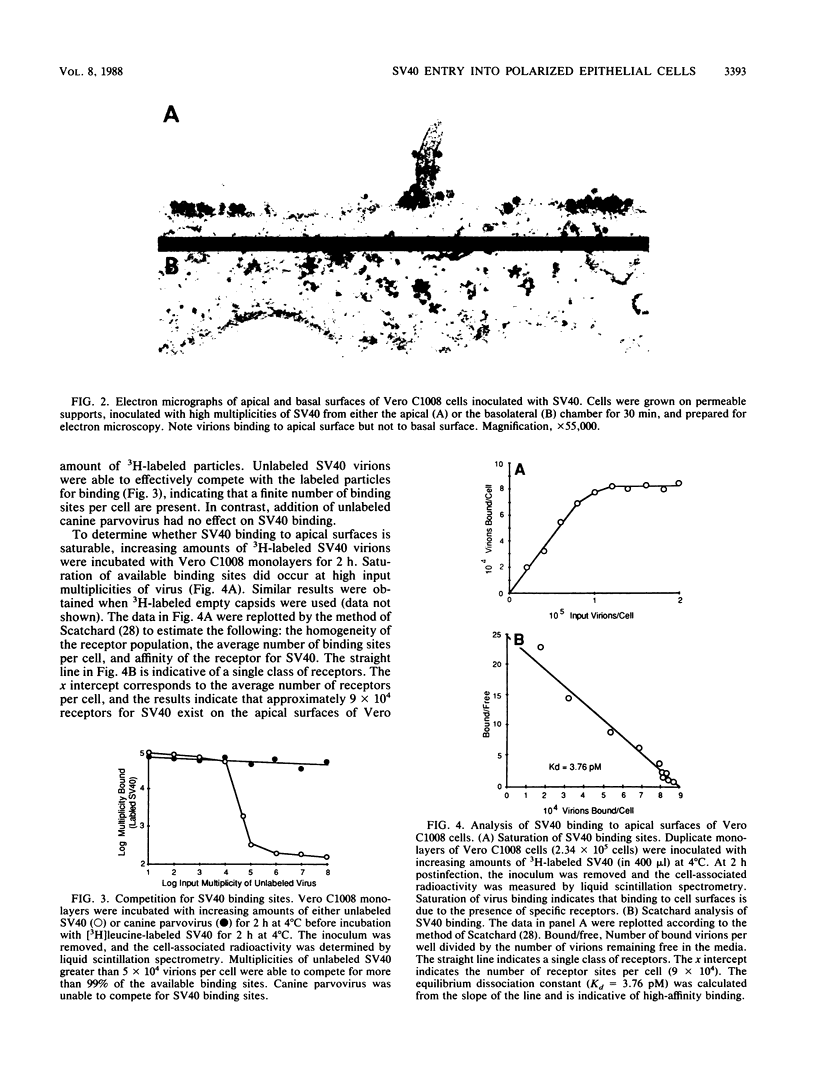
The uptake of simian virus 40 (SV40) by polarized epithelial cells was investigated by growth of cells on permeable supports and inoculation on either the apical or the basolateral surface. Binding of radiolabeled SV40 occurred on the apical but not the basolateral surfaces of permissive polarized Vero C1008 cells and nonpermissive polarized MDCK cells. When similar experiments were performed on nonpolarized Vero or CV-1 cells, virus binding occurred regardless of the direction of virus input. Electron micrographs of Vero C1008 cells infected at high multiplicities revealed virions lining the surfaces of apically infected cells, while the surfaces of basolaterally infected cells were devoid of virus particles. Analysis of the binding data revealed a single class of virus receptors (9 x 10(4) per cell) with a high affinity for SV40 (Kd = 3.76 pM) on the apical surfaces of Vero C 1008 cells. Indirect immunofluorescence studies revealed that synthesis of viral capsid proteins in Vero C1008 cells occurred only when input virions had access to the apical surface. Virus yields from apically infected Vero C1008 cells were 10(5) PFU per cell, while yields obtained from basolaterally infected cells were less than one PFU per cell. These results indicate that a specific receptor for SV40 is expressed exclusively on the apical surfaces of polarized Vero C1008 cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASHKENAZI A., MELNICK J. L. Induced latent infection of monkeys with vacuolating SV-40 Papova virus. Virus in kidneys and urine. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 Nov;111:367–372. doi: 10.3181/00379727-111-27794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbanti-Brodano G., Swetly P., Koprowski H. Early events in the infection of permissive cells with simian virus 40: adsorption, penetration, and uncoating. J Virol. 1970 Jul;6(1):78–86. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.1.78-86.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolen J. B., Consigli R. A. Differential adsorption of polyoma virions and capsids to mouse kidney cells and guinea pig erythrocytes. J Virol. 1979 Nov;32(2):679–683. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.2.679-683.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain J. P. Fluorographic detection of radioactivity in polyacrylamide gels with the water-soluble fluor, sodium salicylate. Anal Biochem. 1979 Sep 15;98(1):132–135. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90716-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dales S. Early events in cell-animal virus interactions. Bacteriol Rev. 1973 Jun;37(2):103–135. doi: 10.1128/br.37.2.103-135.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried H., Cahan L. D., Paulson J. C. Polyoma virus recognizes specific sialyligosaccharide receptors on host cells. Virology. 1981 Feb;109(1):188–192. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90485-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller S. D., von Bonsdorff C. H., Simons K. Cell surface influenza haemagglutinin can mediate infection by other animal viruses. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2475–2485. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03959.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller S., von Bonsdorff C. H., Simons K. Vesicular stomatitis virus infects and matures only through the basolateral surface of the polarized epithelial cell line, MDCK. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):65–77. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90527-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith G. R., Marriott S. J., Rintoul D. A., Consigli R. A. Early events in polyomavirus infection: fusion of monopinocytotic vesicles containing virions with mouse kidney cell nuclei. Virus Res. 1988 Apr;10(1):41–51. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(88)90056-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill A. V. The Combinations of Haemoglobin with Oxygen and with Carbon Monoxide. I. Biochem J. 1913 Oct;7(5):471–480. doi: 10.1042/bj0070471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hummeler K., Tomassini N., Sokol F. Morphological aspects of the uptake of simian virus 40 by permissive cells. J Virol. 1970 Jul;6(1):87–93. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.1.87-93.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kielian M., Helenius A. pH-induced alterations in the fusogenic spike protein of Semliki Forest virus. J Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;101(6):2284–2291. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.6.2284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenard J., Miller D. K. Uncoating of enveloped viruses. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):5–6. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90368-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEYER H. M., Jr, HOPPS H. E., ROGERS N. G., BROOKS B. E., BERNHEIM B. C., JONES W. P., NISALAK A., DOUGLAS R. D. Studies on simian virus 40. J Immunol. 1962 Jun;88:796–806. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay R. L., Consigli R. A. Early events in polyoma virus infection: attachment, penetration, and nuclear entry. J Virol. 1976 Aug;19(2):620–636. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.2.620-636.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marriott S. J., Griffith G. R., Consigli R. A. Octyl-beta-D-glucopyranoside extracts polyomavirus receptor moieties from the surfaces of mouse kidney cells. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):375–382. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.375-382.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M., Griffiths G., Dean G. E., Mellman I., Helenius A. Three-dimensional structure of endosomes in BHK-21 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2899–2903. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M. The entry of enveloped viruses into cells by endocytosis. Biochem J. 1984 Feb 15;218(1):1–10. doi: 10.1042/bj2180001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M., Wellsteed J., Kern H., Harms E., Helenius A. Monensin inhibits Semliki Forest virus penetration into culture cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5297–5301. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maul G. G., Rovera G., Vorbrodt A., Abramczuk J. Membrane fusion as a mechanism of simian virus 40 entry into different cellular compartments. J Virol. 1978 Dec;28(3):936–944. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.3.936-944.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellman I., Fuchs R., Helenius A. Acidification of the endocytic and exocytic pathways. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:663–700. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäntyjärvi R. A., Arstila P. P., Meurman O. H. Hemagglutination by BK virus, a tentative new member of the papovavirus group. Infect Immun. 1972 Nov;6(5):824–828. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.5.824-828.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura T., Kawai N., Kawai M., Notake K., Ichihara I. Fusion of SV40-induced endocytotic vacuoles with the nuclear membrane. Cell Struct Funct. 1986 Jun;11(2):135–141. doi: 10.1247/csf.11.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norkin L. C., Einck K. H. Cell killing by Simian virus 40: protective effect of chloroquine. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Dec;14(6):930–932. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.6.930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett B. L., Rogers C. M., Walker D. L. JC virus, a human polyomavirus associated with progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: additional biological characteristics and antigenic relationships. Infect Immun. 1977 Feb;15(2):656–662. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.2.656-662.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez Boulan E., Sabatini D. D. Asymmetric budding of viruses in epithelial monlayers: a model system for study of epithelial polarity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):5071–5075. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.5071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin D. H. Reovirus serotype 1 binds to the basolateral membrane of intestinal epithelial cells. Microb Pathog. 1987 Sep;3(3):215–219. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90098-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimura H., Umeno Y., Kimura G. Effects of inhibitors of the cytoplasmic structures and functions on the early phase of infection of cultured cells with simian virus 40. Virology. 1987 May;158(1):34–43. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90235-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons K., Fuller S. D. Cell surface polarity in epithelia. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:243–288. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.001331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upcroft P. Simian virus 40 infection is not mediated by lysosomal activation. J Gen Virol. 1987 Sep;68(Pt 9):2477–2480. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-9-2477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]