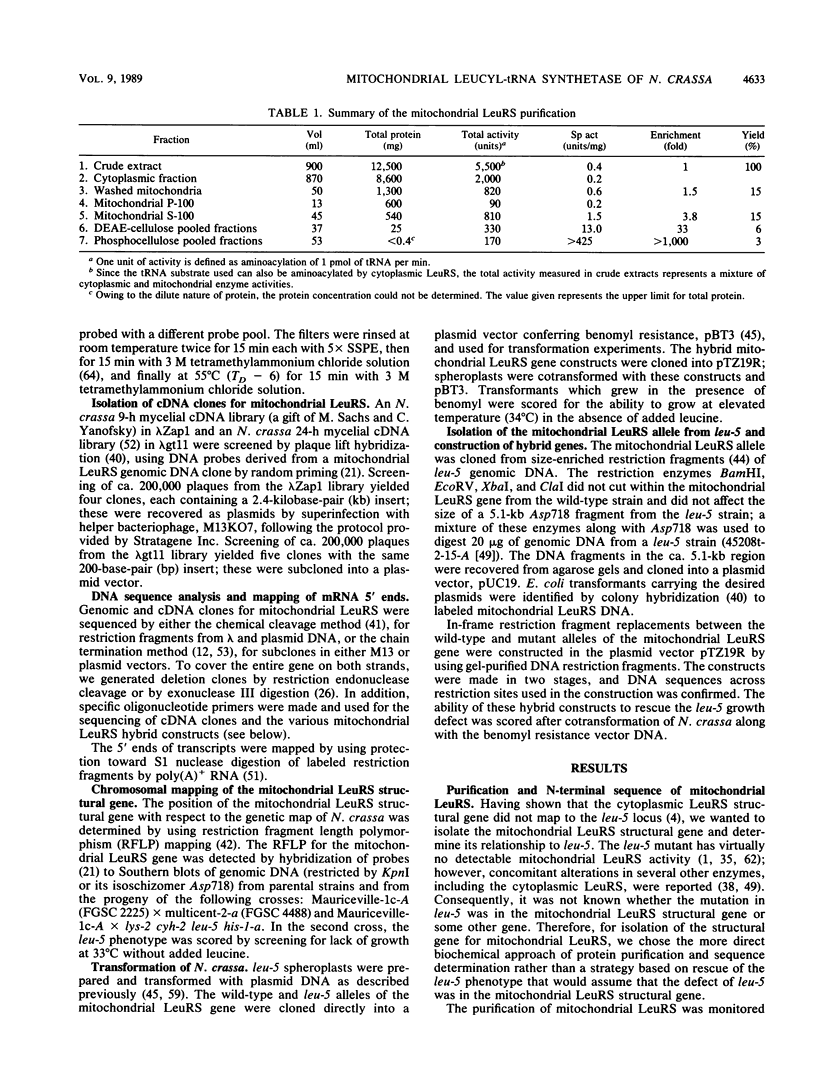
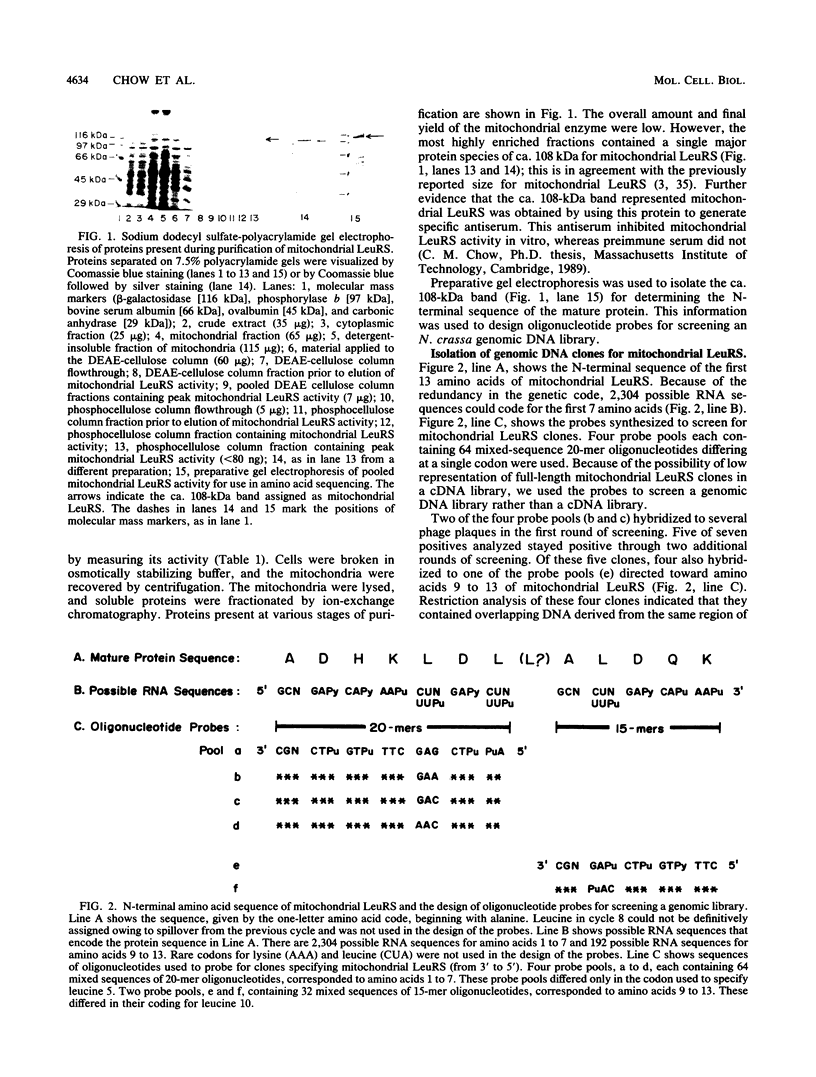
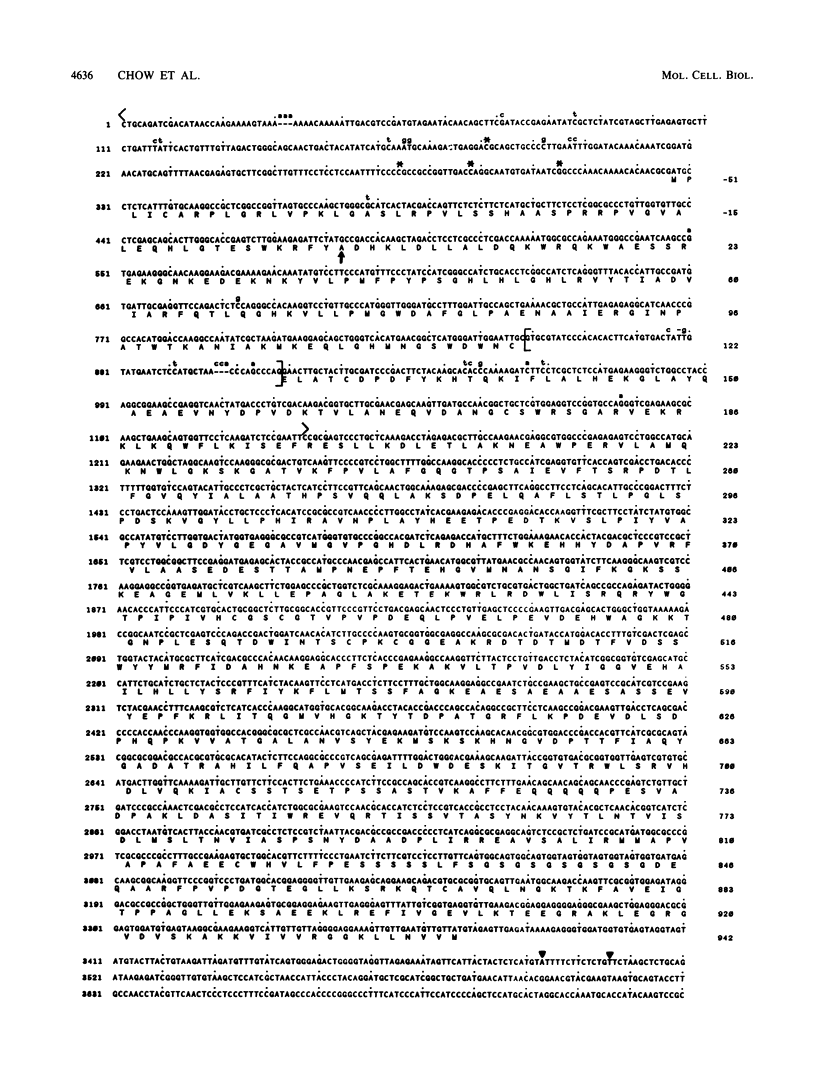
Abstract
We have isolated and characterized the nuclear gene for the mitochondrial leucyl-tRNA synthetase (LeuRS) of Neurospora crassa and have established that a defect in this structural gene is responsible for the leu-5 phenotype. We have purified mitochondrial LeuRS protein, determined its N-terminal sequence, and used this sequence information to identify and isolate a full-length genomic DNA clone. The 3.7-kilobase-pair region representing the structural gene and flanking regions has been sequenced. The 5' ends of the mRNA were mapped by S1 nuclease protection, and the 3' ends were determined from the sequence of cDNA clones. The gene contains a single short intron, 60 base pairs long. The methionine-initiated open reading frame specifies a 52-amino-acid mitochondrial targeting sequence followed by a 942-amino-acid protein. Restriction fragment length polymorphism analyses mapped the mitochondrial LeuRS structural gene to linkage group V, exactly where the leu-5 mutation had been mapped before. We show that the leu-5 strain has a defect in the structural gene for mitochondrial LeuRS by restoring growth under restrictive conditions for this strain after transformation with a wild-type copy of the mitochondrial LeuRS gene. We have cloned the mutant allele present in the leu-5 strain and identified the defect as being due to a Thr-to-Pro change in mitochondrial LeuRS. Finally, we have used immunoblotting to show that despite the apparent lack of mitochondrial LeuRS activity in leu-5 extracts, the leu-5 strain contains levels of mitochondrial LeuRS protein to similar to those of the wild-type strain.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Airas R. K., Schischkoff J., Cramer F. Biochemical comparison of the Neurospora crassa wild-type and the temperature-sensitive leucine-auxotroph mutant leu-5. Detailed kinetic comparison of the leucyl-tRNA synthetases. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Jul 1;158(1):51–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09719.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akins R. A., Lambowitz A. M. A protein required for splicing group I introns in Neurospora mitochondria is mitochondrial tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase or a derivative thereof. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):331–345. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90488-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beauchamp P. M., Horn E. W., Gross S. R. Proposed involvement of an internal promoter in regulation and synthesis of mitochondrial and cytoplasmic leucyl-tRNA synthetases of Neurospora. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1172–1176. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benarous R., Chow C. M., RajBhandary U. L. Cytoplasmic leucyl-tRNA synthetase of Neurospora crassa is not specified by the leu-5 locus. Genetics. 1988 Aug;119(4):805–814. doi: 10.1093/genetics/119.4.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg J. M. Potential metal-binding domains in nucleic acid binding proteins. Science. 1986 Apr 25;232(4749):485–487. doi: 10.1126/science.2421409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blow D. M., Bhat T. N., Metcalfe A., Risler J. L., Brunie S., Zelwer C. Structural homology in the amino-terminal domains of two aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases. J Mol Biol. 1983 Dec 25;171(4):571–576. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90044-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatton B., Walter P., Ebel J. P., Lacroute F., Fasiolo F. The yeast VAS1 gene encodes both mitochondrial and cytoplasmic valyl-tRNA synthetases. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):52–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatton B., Winsor B., Boulanger Y., Fasiolo F. Cloning and characterization of the yeast methionyl-tRNA synthetase mutation mes1. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 5;262(31):15094–15097. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke N. D., Lien D. C., Schimmel P. Evidence from cassette mutagenesis for a structure-function motif in a protein of unknown structure. Science. 1988 Apr 22;240(4851):521–523. doi: 10.1126/science.3282306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cramer C. L., Ristow J. L., Paulus T. J., Davis R. H. Methods for mycelial breakage and isolation of mitochondria and vacuoles of Neurospora. Anal Biochem. 1983 Feb 1;128(2):384–392. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90390-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Moreno M. R., Smith J. F., Smith R. V. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels: increased sensitivity through a combined Coomassie blue-silver stain procedure. Anal Biochem. 1985 Dec;151(2):466–470. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90206-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dihanich M. E., Najarian D., Clark R., Gillman E. C., Martin N. C., Hopper A. K. Isolation and characterization of MOD5, a gene required for isopentenylation of cytoplasmic and mitochondrial tRNAs of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):177–184. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn A., Bollekens J., Staub A., Benoist C., Mathis D. A multiplicity of CCAAT box-binding proteins. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):863–872. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90513-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis S. R., Morales M. J., Li J. M., Hopper A. K., Martin N. C. Isolation and characterization of the TRM1 locus, a gene essential for the N2,N2-dimethylguanosine modification of both mitochondrial and cytoplasmic tRNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):9703–9709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germann U. A., Müller G., Hunziker P. E., Lerch K. Characterization of two allelic forms of Neurospora crassa laccase. Amino- and carboxyl-terminal processing of a precursor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 15;263(2):885–896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heck J. D., Hatfield G. W. Valyl-tRNA synthetase gene of Escherichia coli K12. Primary structure and homology within a family of aminoacyl-TRNA synthetases. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 15;263(2):868–877. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert C. J., Labouesse M., Dujardin G., Slonimski P. P. The NAM2 proteins from S. cerevisiae and S. douglasii are mitochondrial leucyl-tRNA synthetases, and are involved in mRNA splicing. EMBO J. 1988 Feb;7(2):473–483. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02835.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewick R. M., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E., Dreyer W. J. A gas-liquid solid phase peptide and protein sequenator. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7990–7997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopper A. K., Furukawa A. H., Pham H. D., Martin N. C. Defects in modification of cytoplasmic and mitochondrial transfer RNAs are caused by single nuclear mutations. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):543–550. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90209-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houlahan M. B., Beadle G. W., Calhoun H. G. Linkage Studies with Biochemical Mutants of Neurospora Crassa. Genetics. 1949 Sep;34(5):493–507. doi: 10.1093/genetics/34.5.493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hountondji C., Blanquet S., Lederer F. Methionyl-tRNA synthetase from Escherichia coli: primary structure at the binding site for the 3'-end of tRNAfMet. Biochemistry. 1985 Feb 26;24(5):1175–1180. doi: 10.1021/bi00326a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hountondji C., Dessen P., Blanquet S. Sequence similarities among the family of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases. Biochimie. 1986 Sep;68(9):1071–1078. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(86)80181-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Härtlein M., Madern D. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of the gene for Escherichia coli leucyl-tRNA synthetase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 23;15(24):10199–10210. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.24.10199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koerner T. J., Myers A. M., Lee S., Tzagoloff A. Isolation and characterization of the yeast gene coding for the alpha subunit of mitochondrial phenylalanyl-tRNA synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3690–3696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. The scanning model for translation: an update. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):229–241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunugi S., Uehara-Kunugi Y., von der Haar F., Schischkoff J., Freist W., Englisch U., Cramer F. Biochemical comparison of the Neurospora crassa wild type and the temperature-sensitive and leucine-auxotroph mutant leu-5. Purification of the cytoplasmic and mitochondrial leucyl-tRNA synthetases and comparison of the enzymatic activities and the degradation patterns. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Jul 1;158(1):43–49. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09718.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labouesse M., Herbert C. J., Dujardin G., Slonimski P. P. Three suppressor mutations which cure a mitochondrial RNA maturase deficiency occur at the same codon in the open reading frame of the nuclear NAM2 gene. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):713–721. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04812.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis C. M., Holliday R. Mistranslation and ageing in Neurospora. Nature. 1970 Nov 28;228(5274):877–880. doi: 10.1038/228877a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo K. M., Jones S. S., Hackett N. R., Khorana H. G. Specific amino acid substitutions in bacterioopsin: Replacement of a restriction fragment in the structural gene by synthetic DNA fragments containing altered codons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2285–2289. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
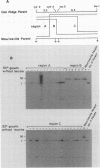
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzenberg R. L., Stevens J. N., Selker E. U., Morzycka-Wroblewska E. Identification and chromosomal distribution of 5S rRNA genes in Neurospora crassa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):2067–2071. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.2067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natsoulis G., Hilger F., Fink G. R. The HTS1 gene encodes both the cytoplasmic and mitochondrial histidine tRNA synthetases of S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):235–243. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90740-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls R. D., Hill A. V., Clegg J. B., Higgs D. R. Direct cloning of specific genomic DNA sequences in plasmid libraries following fragment enrichment. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 11;13(21):7569–7578. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.21.7569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orbach M. J., Porro E. B., Yanofsky C. Cloning and characterization of the gene for beta-tubulin from a benomyl-resistant mutant of Neurospora crassa and its use as a dominant selectable marker. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2452–2461. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paluh J. L., Orbach M. J., Legerton T. L., Yanofsky C. The cross-pathway control gene of Neurospora crassa, cpc-1, encodes a protein similar to GCN4 of yeast and the DNA-binding domain of the oncogene v-jun-encoded protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3728–3732. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pape L. K., Koerner T. J., Tzagoloff A. Characterization of a yeast nuclear gene (MST1) coding for the mitochondrial threonyl-tRNA1 synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15362–15370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins D. D., Radford A., Newmeyer D., Björkman M. Chromosomal loci of Neurospora crassa. Microbiol Rev. 1982 Dec;46(4):426–570. doi: 10.1128/mr.46.4.426-570.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Printz D. B., Gross S. R. An apparent relationship between mistranslation and an altered leucyl-tRNA synthetase in a conditional lethal mutant of Neurospora crassa. Genetics. 1967 Mar;55(3):451–467. doi: 10.1093/genetics/55.3.451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roise D., Theiler F., Horvath S. J., Tomich J. M., Richards J. H., Allison D. S., Schatz G. Amphiphilicity is essential for mitochondrial presequence function. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):649–653. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02859.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs M. S., Bertrand H., Metzenberg R. L., RajBhandary U. L. Cytochrome oxidase subunit V gene of Neurospora crassa: DNA sequences, chromosomal mapping, and evidence that the cya-4 locus specifies the structural gene for subunit V. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):566–577. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs M. S., David M., Werner S., RajBhandary U. L. Nuclear genes for cytochrome c oxidase subunits of Neurospora crassa. Isolation and characterization of cDNA clones for subunits IV, V, VI, and possibly VII. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):869–873. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimmel P. R., Söll D. Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases: general features and recognition of transfer RNAs. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:601–648. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.003125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimmel P. Aminoacyl tRNA synthetases: general scheme of structure-function relationships in the polypeptides and recognition of transfer RNAs. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:125–158. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.001013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M., Green H. Participation of membrane-associated proteins in the formation of the cross-linked envelope of the keratinocyte. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):827–834. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90032-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starzyk R. M., Webster T. A., Schimmel P. Evidence for dispensable sequences inserted into a nucleotide fold. Science. 1987 Sep 25;237(4822):1614–1618. doi: 10.1126/science.3306924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzagoloff A., Akai A., Kurkulos M., Repetto B. Homology of yeast mitochondrial leucyl-tRNA synthetase and isoleucyl- and methionyl-tRNA synthetases of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 15;263(2):850–856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vollmer S. J., Yanofsky C. Efficient cloning of genes of Neurospora crassa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4869–4873. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster T., Tsai H., Kula M., Mackie G. A., Schimmel P. Specific sequence homology and three-dimensional structure of an aminoacyl transfer RNA synthetase. Science. 1984 Dec 14;226(4680):1315–1317. doi: 10.1126/science.6390679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks C. O., Gross S. R. Mutation and "reversion" at the leu-5 locus of neurospora and its effect on the cytoplasmic and mitochondrial leucyl-tRNA synthetases. Biochem Genet. 1971 Dec;5(6):505–516. doi: 10.1007/BF00485668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessel D., Flügge U. I. A method for the quantitative recovery of protein in dilute solution in the presence of detergents and lipids. Anal Biochem. 1984 Apr;138(1):141–143. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90782-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. I., Gitschier J., Lasky L. A., Lawn R. M. Base composition-independent hybridization in tetramethylammonium chloride: a method for oligonucleotide screening of highly complex gene libraries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1585–1588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Mitochondrial targeting sequences may form amphiphilic helices. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1335–1342. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04364.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]