Abstract
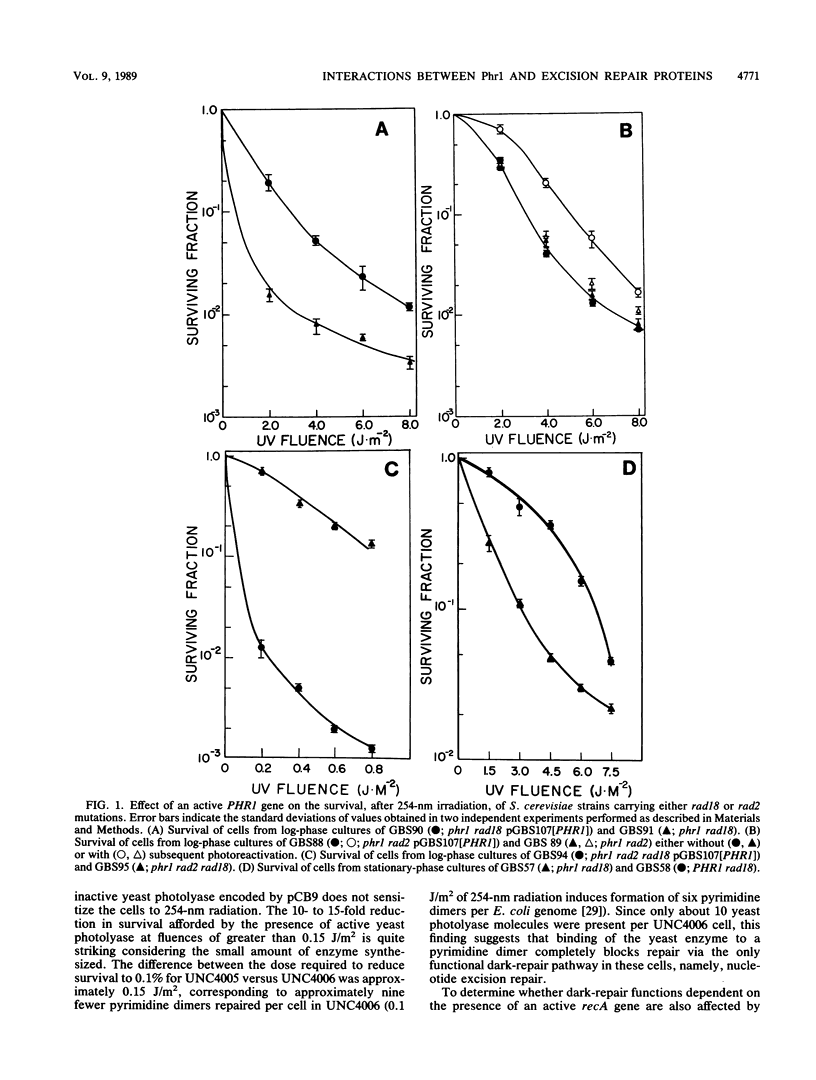
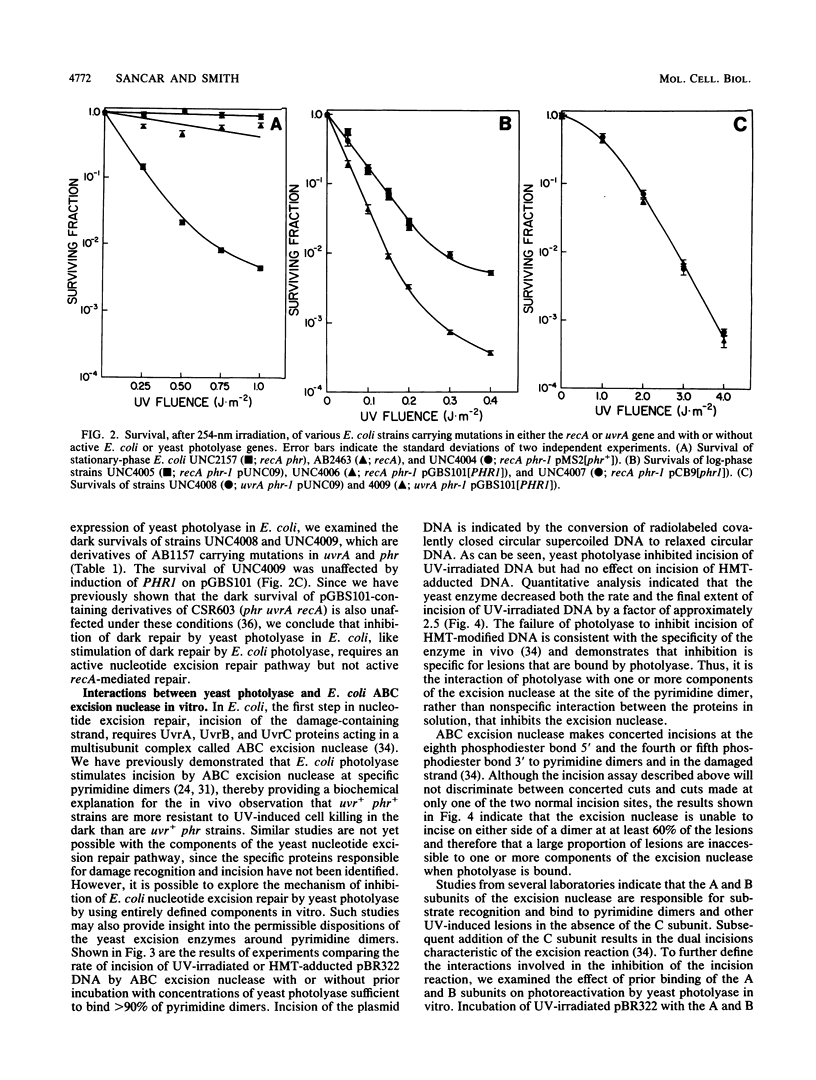
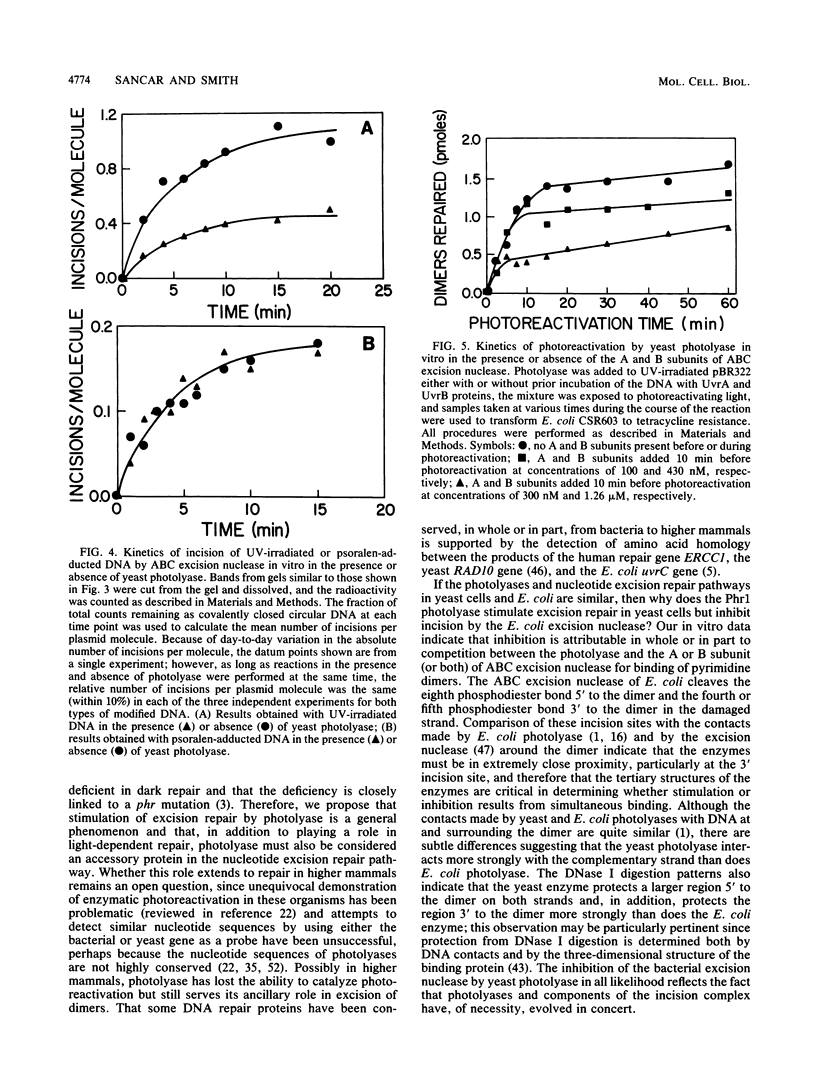
The PHR1 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae encodes a DNA photolyase that catalyzes the light-dependent repair of pyrimidine dimers. In the absence of photoreactivating light, this enzyme binds to pyrimidine dimers but is unable to repair them. We have assessed the effect of bound photolyase on the dark survival of yeast cells carrying mutations in genes that eliminate either nucleotide excision repair (RAD2) or mutagenic repair (RAD18). We found that a functional PHR1 gene enhanced dark survival in a rad18 background but failed to do so in a rad2 or rad2 rad18 background and therefore conclude that photolyase stimulates specifically nucleotide excision repair of dimers in S. cerevisiae. This effect is similar to the effect of Escherichia coli photolyase on excision repair in the bacterium. However, despite the functional and structural similarities between yeast photolyase and the E. coli enzyme and complementation of the photoreactivation deficiency of E. coli phr mutants by PHR1, yeast photolyase failed to enhance excision repair in the bacterium. Instead, Phr1 was found to be a potent inhibitor of dark repair in recA strains but had no effect in uvrA strains. The results of in vitro experiments indicate that inhibition of nucleotide excision repair results from competition between yeast photolyase and ABC excision nuclease for binding at pyrimidine dimers. In addition, the A and B subunits of the excision nuclease, when allowed to bind to dimers before photolyase, suppressed photoreactivation by Phr1. We propose that enhancement of nucleotide excision repair by photolyases is a general phenomenon and that photolyase should be considered an accessory protein in this pathway.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baer M., Sancar G. B. Photolyases from Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Escherichia coli recognize common binding determinants in DNA containing pyrimidine dimers. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4777–4788. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bochner B. R., Huang H. C., Schieven G. L., Ames B. N. Positive selection for loss of tetracycline resistance. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):926–933. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.926-933.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd J. B., Harris P. V. Isolation and characterization of a photorepair-deficient mutant in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1987 Jun;116(2):233–239. doi: 10.1093/genetics/116.2.233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewitt S K, Adelberg E A. The Occurrence of a Genetic Transposition in a Strain of Escherichia Coli. Genetics. 1962 May;47(5):577–585. doi: 10.1093/genetics/47.5.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F., Johnson M. S., Husain I., Van Houten B., Thomas D. C., Sancar A. Domainal evolution of a prokaryotic DNA repair protein and its relationship to active-transport proteins. Nature. 1986 Oct 2;323(6087):451–453. doi: 10.1038/323451a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson L. R., Cox B. S. Excision of bases accompanying the excision of dimers from DNA of UV-irradiated yeast. Mol Gen Genet. 1974;135(1):87–90. doi: 10.1007/BF00433904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedberg E. C. Deoxyribonucleic acid repair in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Mar;52(1):70–102. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.1.70-102.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Game J. C., Cox B. S. Synergistic interactions between rad mutations in yeast. Mutat Res. 1973 Oct;20(1):35–44. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(73)90095-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green G., MacQuillan A. M. Photorepair of ultraviolet-induced petite mutational damage in Saccharomyces cerevisiae requires the product of the PHR1 gene. J Bacteriol. 1980 Nov;144(2):826–829. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.2.826-829.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. D., Mount D. W. Mechanisms of DNA replication and mutagenesis in ultraviolet-irradiated bacteria and mammalian cells. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1981;25:53–126. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60483-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hays J. B., Martin S. J., Bhatia K. Repair of nonreplicating UV-irradiated DNA: cooperative dark repair by Escherichia coli uvr and phr functions. J Bacteriol. 1985 Feb;161(2):602–608. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.2.602-608.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnen A., Hicks J. B., Fink G. R. Transformation of yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1929–1933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard-Flanders P., Theriot L. Mutants of Escherichia coli K-12 defective in DNA repair and in genetic recombination. Genetics. 1966 Jun;53(6):1137–1150. doi: 10.1093/genetics/53.6.1137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husain I., Sancar G. B., Holbrook S. R., Sancar A. Mechanism of damage recognition by Escherichia coli DNA photolyase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 25;262(27):13188–13197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonczyk P., Fijalkowska I., Ciesla Z. Overproduction of the epsilon subunit of DNA polymerase III counteracts the SOS mutagenic response of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9124–9127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence C. W., Christensen R. UV mutagenesis in radiation-sensitive strains of yeast. Genetics. 1976 Feb;82(2):207–232. doi: 10.1093/genetics/82.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorence M. C., Rupert C. S. Convenient construction of recA deletion derivatives of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Oct;156(1):458–459. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.1.458-459.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacQuillan A. M., Herman A., Coberly J. S., Green G. A second photoreactivation-deficient mutation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Photochem Photobiol. 1981 Dec;34(6):673–677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maloy S. R., Nunn W. D. Selection for loss of tetracycline resistance by Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):1110–1111. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.1110-1111.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meechan P. J., Milam K. M., Cleaver J. E. Evaluation of homology between cloned Escherichia coli and yeast DNA photolyase genes and higher eukaryotic genomes. Mutat Res. 1986 Sep;166(2):143–147. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(86)90012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myles G. M., Van Houten B., Sancar A. Utilization of DNA photolyase, pyrimidine dimer endonucleases, and alkali hydrolysis in the analysis of aberrant ABC excinuclease incisions adjacent to UV-induced DNA photoproducts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 11;15(3):1227–1243. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.3.1227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prakash L. Characterization of postreplication repair in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and effects of rad6, rad18, rev3 and rad52 mutations. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184(3):471–478. doi: 10.1007/BF00352525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUPERT C. S. Photoenzymatic repair of ultraviolet damage in DNA. II. Formation of an enzyme-substrate complex. J Gen Physiol. 1962 Mar;45:725–741. doi: 10.1085/jgp.45.4.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick M. A. A photoreactivationless mutant of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Photochem Photobiol. 1969 Apr;9(4):307–312. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1969.tb07294.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rupp W. D., Howard-Flanders P. Discontinuities in the DNA synthesized in an excision-defective strain of Escherichia coli following ultraviolet irradiation. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jan 28;31(2):291–304. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90445-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rupp W. D., Wilde C. E., 3rd, Reno D. L., Howard-Flanders P. Exchanges between DNA strands in ultraviolet-irradiated Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1971 Oct 14;61(1):25–44. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90204-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Franklin K. A., Sancar G. B. Escherichia coli DNA photolyase stimulates uvrABC excision nuclease in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7397–7401. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Hack A. M., Rupp W. D. Simple method for identification of plasmid-coded proteins. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):692–693. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.692-693.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Rupert C. S. Determination of plasmid molecular weights from ultraviolet sensitivities. Nature. 1978 Mar 30;272(5652):471–472. doi: 10.1038/272471a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Sancar G. B. DNA repair enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:29–67. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.000333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar G. B. Expression of a Saccharomyces cerevisiae photolyase gene in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Feb;161(2):769–771. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.2.769-771.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar G. B. Sequence of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae PHR1 gene and homology of the PHR1 photolyase to E. coli photolyase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 25;13(22):8231–8246. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.22.8231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar G. B., Smith F. W. Construction of plasmids which lead to overproduction of yeast PHR1 photolyase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Escherichia coli. Gene. 1988 Apr 15;64(1):87–96. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90483-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar G. B., Smith F. W., Heelis P. F. Purification of the yeast PHR1 photolyase from an Escherichia coli overproducing strain and characterization of the intrinsic chromophores of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15457–15465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar G. B., Smith F. W., Lorence M. C., Rupert C. S., Sancar A. Sequences of the Escherichia coli photolyase gene and protein. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):6033–6038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar G. B., Smith F. W., Sancar A. Binding of Escherichia coli DNA photolyase to UV-irradiated DNA. Biochemistry. 1985 Apr 9;24(8):1849–1855. doi: 10.1021/bi00329a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar G. B., Smith F. W., Sancar A. Identification and amplification of the E. coli phr gene product. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Oct 11;11(19):6667–6678. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.19.6667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suck D., Oefner C. Structure of DNase I at 2.0 A resolution suggests a mechanism for binding to and cutting DNA. Nature. 1986 Jun 5;321(6070):620–625. doi: 10.1038/321620a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. C., Levy M., Sancar A. Amplification and purification of UvrA, UvrB, and UvrC proteins of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 15;260(17):9875–9883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unrau P., Wheatcroft R., Cox B. S. The excision of pyrimidine dimers from DNA of ultraviolet irradiated yeast. Mol Gen Genet. 1971;113(4):359–362. doi: 10.1007/BF00272336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Houten B., Gamper H., Sancar A., Hearst J. E. DNase I footprint of ABC excinuclease. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 25;262(27):13180–13187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker G. C. Mutagenesis and inducible responses to deoxyribonucleic acid damage in Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Mar;48(1):60–93. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.1.60-93.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox D. R., Prakash L. Incision and postincision steps of pyrimidine dimer removal in excision-defective mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1981 Nov;148(2):618–623. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.2.618-623.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K., Fujiwara Y., Shinagawa H. Evidence that the phr+ gene enhances the ultraviolet resistance of Escherichia coli recA strains in the dark. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;192(1-2):282–284. doi: 10.1007/BF00327679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K., Satake M., Shinagawa H. A multicopy phr-plasmid increases the ultraviolet resistance of a recA strain of Escherichia coli. Mutat Res. 1984 Jan;131(1):11–18. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(84)90042-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasui A., Langeveld S. A. Homology between the photoreactivation genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Escherichia coli. Gene. 1985;36(3):349–355. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90190-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasui A., Laskowski W. Determination of the number of photoreactivating enzyme molecules per haploid Saccharomyces cells. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1975 Dec;28(6):511–518. doi: 10.1080/09553007514551371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Duin M., de Wit J., Odijk H., Westerveld A., Yasui A., Koken M. H., Hoeijmakers J. H., Bootsma D. Molecular characterization of the human excision repair gene ERCC-1: cDNA cloning and amino acid homology with the yeast DNA repair gene RAD10. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):913–923. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90014-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



