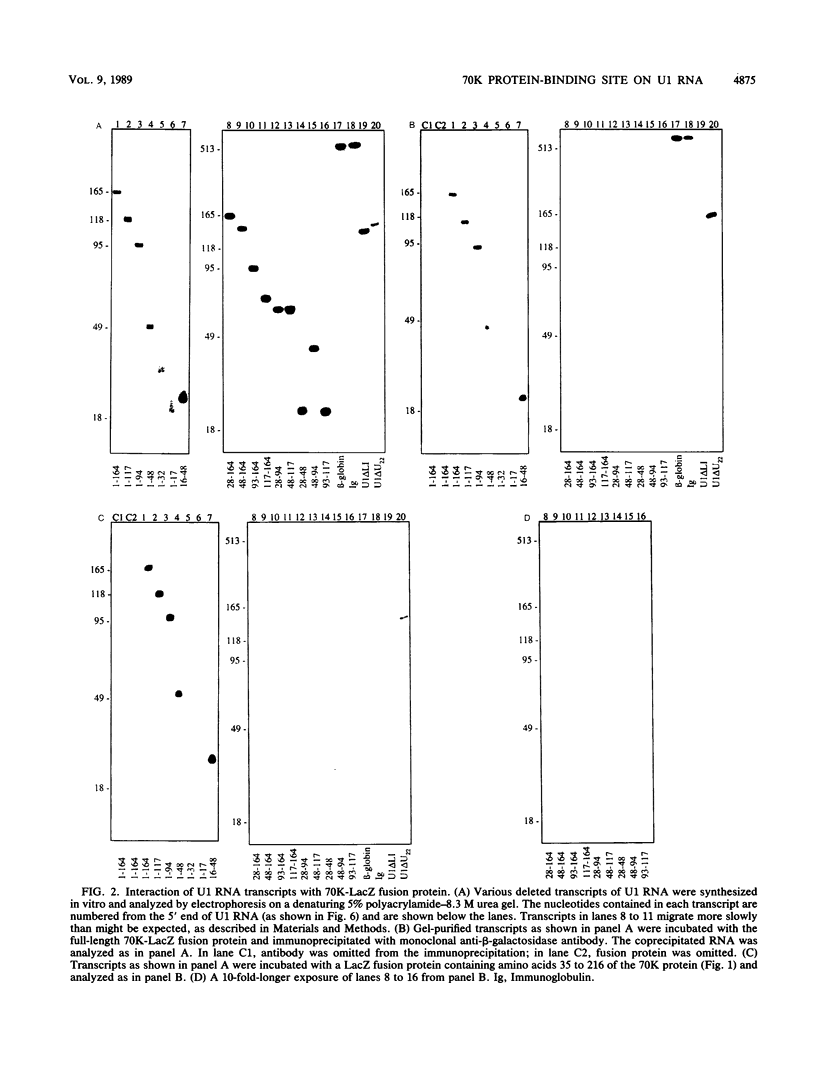
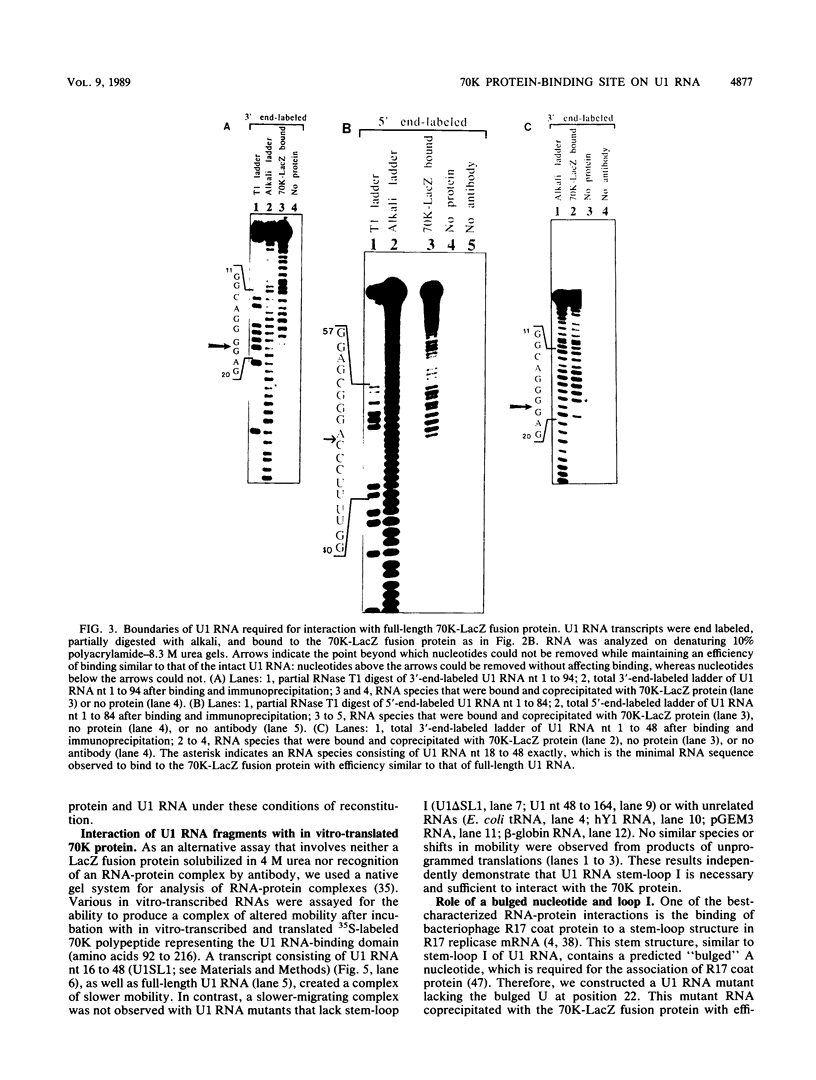
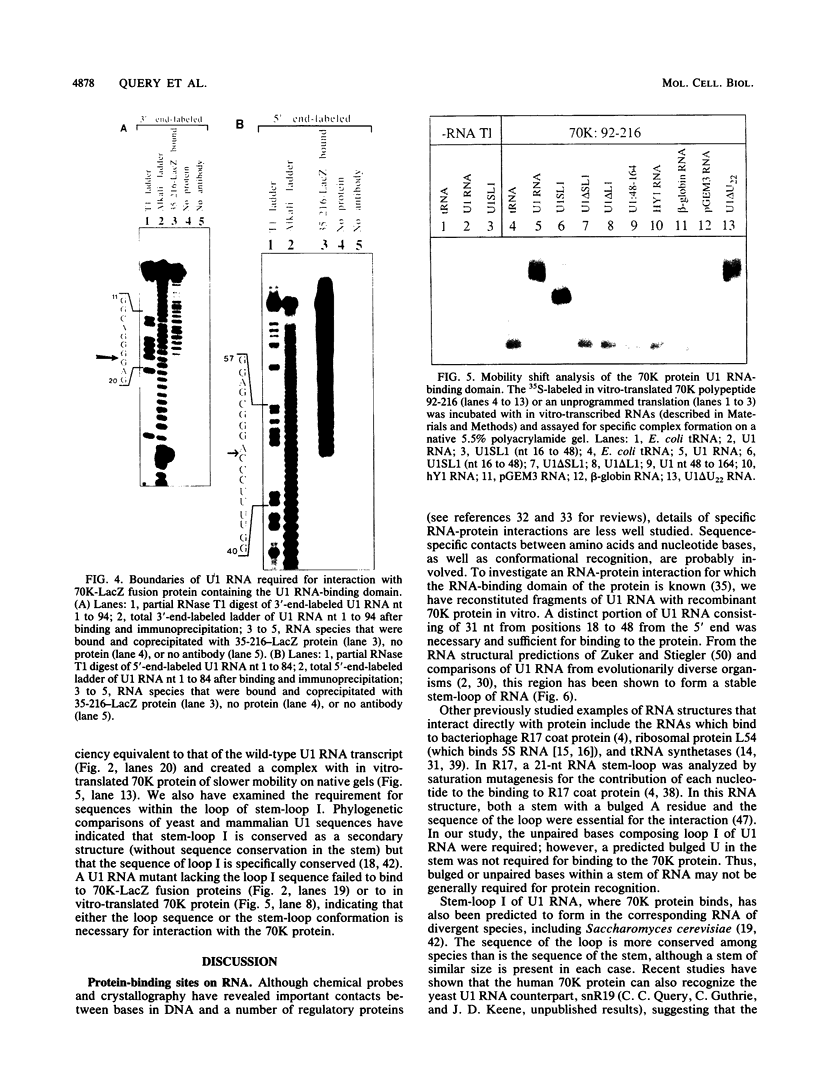
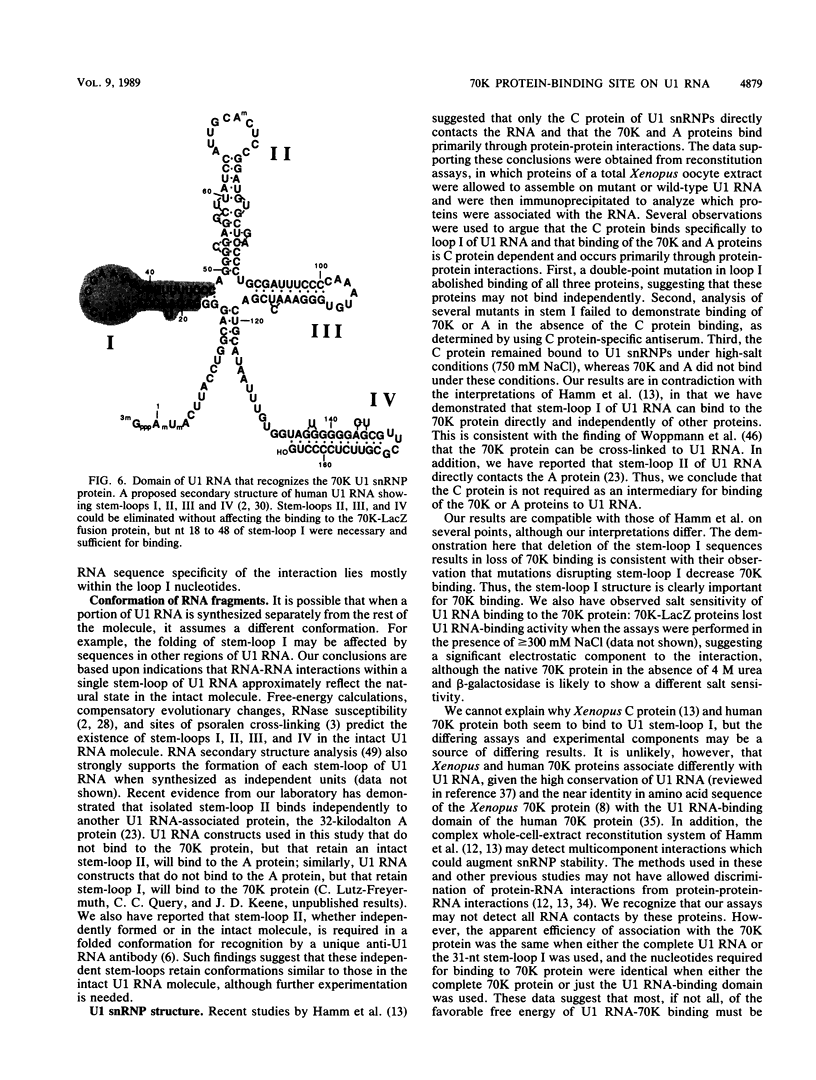
Abstract
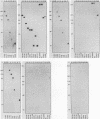
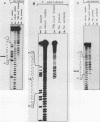
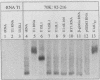
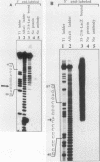
We have defined the nucleotide sequence of a protein-binding domain within U1 RNA that specifically recognizes and binds both to a U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein component (the 70K protein) and to the previously defined RNA-binding domain of the 70K protein. We have investigated direct interactions between purified U1 RNA and 70K protein by reconstitution in vitro. Thirty-one nucleotides of U1 RNA, corresponding to stem-loop I, were required for this interaction. Nucleotides at the 5' end of U1 RNA that are involved in base pairing with the 5' splice site of pre-mRNA were not required for binding. In contrast to other reports, these findings demonstrate that a specific domain of U1 RNA can bind directly to the 70K protein independently of any other snRNP-associated proteins.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Black D. L., Chabot B., Steitz J. A. U2 as well as U1 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins are involved in premessenger RNA splicing. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):737–750. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90270-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branlant C., Krol A., Ebel J. P., Gallinaro H., Lazar E., Jacob M. The conformation of chicken, rat and human U1A RNAs in solution. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Feb 25;9(4):841–858. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.4.841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvet J. P., Myers J. A. In-vivo secondary structure analysis of the small nuclear RNA U1 using psoralen cross-linking. J Mol Biol. 1987 Oct 5;197(3):543–553. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90563-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey J., Cameron V., de Haseth P. L., Uhlenbeck O. C. Sequence-specific interaction of R17 coat protein with its ribonucleic acid binding site. Biochemistry. 1983 May 24;22(11):2601–2610. doi: 10.1021/bi00280a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabot B., Steitz J. A. Multiple interactions between the splicing substrate and small nuclear ribonucleoproteins in spliceosomes. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):281–293. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutscher S. L., Keene J. D. A sequence-specific conformational epitope on U1 RNA is recognized by a unique autoantibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3299–3303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etzerodt M., Vignali R., Ciliberto G., Scherly D., Mattaj I. W., Philipson L. Structure and expression of a Xenopus gene encoding an snRNP protein (U1 70K). EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4311–4321. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03330.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher D. E., Reeves W. H., Conner G. E., Blobel G., Kunkel H. G. Pulse labeling of small nuclear ribonucleoproteins in vivo reveals distinct patterns of antigen recognition by human autoimmune antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):3185–3189. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.3185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freier S. M., Kierzek R., Jaeger J. A., Sugimoto N., Caruthers M. H., Neilson T., Turner D. H. Improved free-energy parameters for predictions of RNA duplex stability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9373–9377. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guthrie C., Patterson B. Spliceosomal snRNAs. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:387–419. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.002131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamm J., Kazmaier M., Mattaj I. W. In vitro assembly of U1 snRNPs. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3479–3485. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02672.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamm J., van Santen V. L., Spritz R. A., Mattaj I. W. Loop I of U1 small nuclear RNA is the only essential RNA sequence for binding of specific U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4787–4791. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hou Y. M., Schimmel P. A simple structural feature is a major determinant of the identity of a transfer RNA. Nature. 1988 May 12;333(6169):140–145. doi: 10.1038/333140a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber P. W., Wool I. G. Nuclease protection analysis of ribonucleoprotein complexes: use of the cytotoxic ribonuclease alpha-sarcin to determine the binding sites for Escherichia coli ribosomal proteins L5, L18, and L25 on 5S rRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):322–326. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber P. W., Wool I. G. Use of the cytotoxic nuclease alpha-sarcin to identify the binding site on eukaryotic 5 S ribosomal ribonucleic acid for the ribosomal protein L5. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 5;261(7):3002–3005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keene J. D., Schubert M., Lazzarini R. A., Rosenberg M. Nucleotide sequence homology at the 3' termini of RNA from vesicular stomatitis virus and its defective interfering particles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3225–3229. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg P. A., Melton D. A. Functional messenger RNAs are produced by SP6 in vitro transcription of cloned cDNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7057–7070. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krämer A., Keller W., Appel B., Lührmann R. The 5' terminus of the RNA moiety of U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles is required for the splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):299–307. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90551-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurilla M. G., Keene J. D. The leader RNA of vesicular stomatitis virus is bound by a cellular protein reactive with anti-La lupus antibodies. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):837–845. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90541-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Steitz J. A. Antibodies to small nuclear RNAs complexed with proteins are produced by patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5495–5499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutz-Freyermuth C., Keene J. D., Lutz-Reyermuth C. The U1 RNA-binding site of the U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein (snRNP)-associated A protein suggests a similarity with U2 snRNPs. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):2975–2982. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.2975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Reed R. The role of small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles in pre-mRNA splicing. Nature. 1987 Feb 19;325(6106):673–678. doi: 10.1038/325673a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan J. F., Groebe D. R., Witherell G. W., Uhlenbeck O. C. Oligoribonucleotide synthesis using T7 RNA polymerase and synthetic DNA templates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 11;15(21):8783–8798. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.21.8783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M., Pettersson I., Hinterberger M., Karmas A., Steitz J. A. The U1 small nuclear RNA-protein complex selectively binds a 5' splice site in vitro. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):509–518. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90432-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M., Steitz J. A. Sequence of U1 RNA from Drosophila melanogaster: implications for U1 secondary structure and possible involvement in splicing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6351–6368. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normanly J., Ogden R. C., Horvath S. J., Abelson J. Changing the identity of a transfer RNA. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):213–219. doi: 10.1038/321213a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T. Protein-DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:293–321. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patton J. R., Pederson T. The Mr 70,000 protein of the U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle binds to the 5' stem-loop of U1 RNA and interacts with Sm domain proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):747–751. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Query C. C., Bentley R. C., Keene J. D. A common RNA recognition motif identified within a defined U1 RNA binding domain of the 70K U1 snRNP protein. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):89–101. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90175-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Query C. C., Keene J. D. A human autoimmune protein associated with U1 RNA contains a region of homology that is cross-reactive with retroviral p30gag antigen. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):211–220. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90148-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romaniuk P. J., Lowary P., Wu H. N., Stormo G., Uhlenbeck O. C. RNA binding site of R17 coat protein. Biochemistry. 1987 Mar 24;26(6):1563–1568. doi: 10.1021/bi00380a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampson J. R., DiRenzo A. B., Behlen L. S., Uhlenbeck O. C. Nucleotides in yeast tRNAPhe required for the specific recognition by its cognate synthetase. Science. 1989 Mar 10;243(4896):1363–1366. doi: 10.1126/science.2646717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A. Splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Science. 1987 Feb 13;235(4790):766–771. doi: 10.1126/science.3544217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siliciano P. G., Jones M. H., Guthrie C. Saccharomyces cerevisiae has a U1-like small nuclear RNA with unexpected properties. Science. 1987 Sep 18;237(4821):1484–1487. doi: 10.1126/science.3306922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spritz R. A., Strunk K., Surowy C. S., Hoch S. O., Barton D. E., Francke U. The human U1-70K snRNP protein: cDNA cloning, chromosomal localization, expression, alternative splicing and RNA-binding. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 23;15(24):10373–10391. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.24.10373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theissen H., Etzerodt M., Reuter R., Schneider C., Lottspeich F., Argos P., Lührmann R., Philipson L. Cloning of the human cDNA for the U1 RNA-associated 70K protein. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3209–3217. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04631.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woppmann A., Rinke J., Lührmann R. Direct cross-linking of snRNP proteins F and 70K to snRNAs by ultra-violet radiation in situ. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Dec 9;16(23):10985–11004. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.23.10985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. N., Uhlenbeck O. C. Role of a bulged A residue in a specific RNA-protein interaction. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 15;26(25):8221–8227. doi: 10.1021/bi00399a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuo C. Y., Weiner A. M. Genetic analysis of the role of human U1 snRNA in mRNA splicing: I. Effect of mutations in the highly conserved stem-loop I of U1. Genes Dev. 1989 May;3(5):697–707. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.5.697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang Y., Weiner A. M. A compensatory base change in U1 snRNA suppresses a 5' splice site mutation. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):827–835. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker M., Stiegler P. Optimal computer folding of large RNA sequences using thermodynamics and auxiliary information. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):133–148. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]