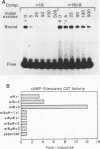
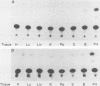
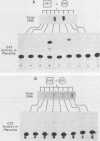
Abstract
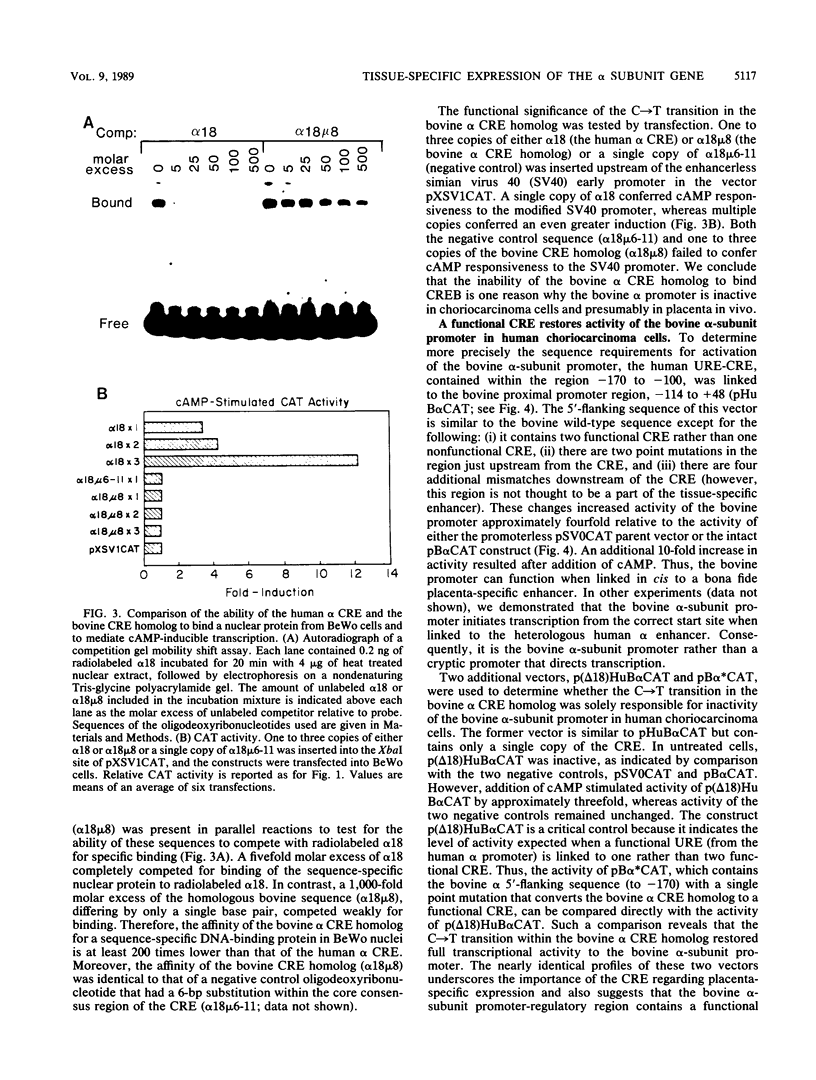
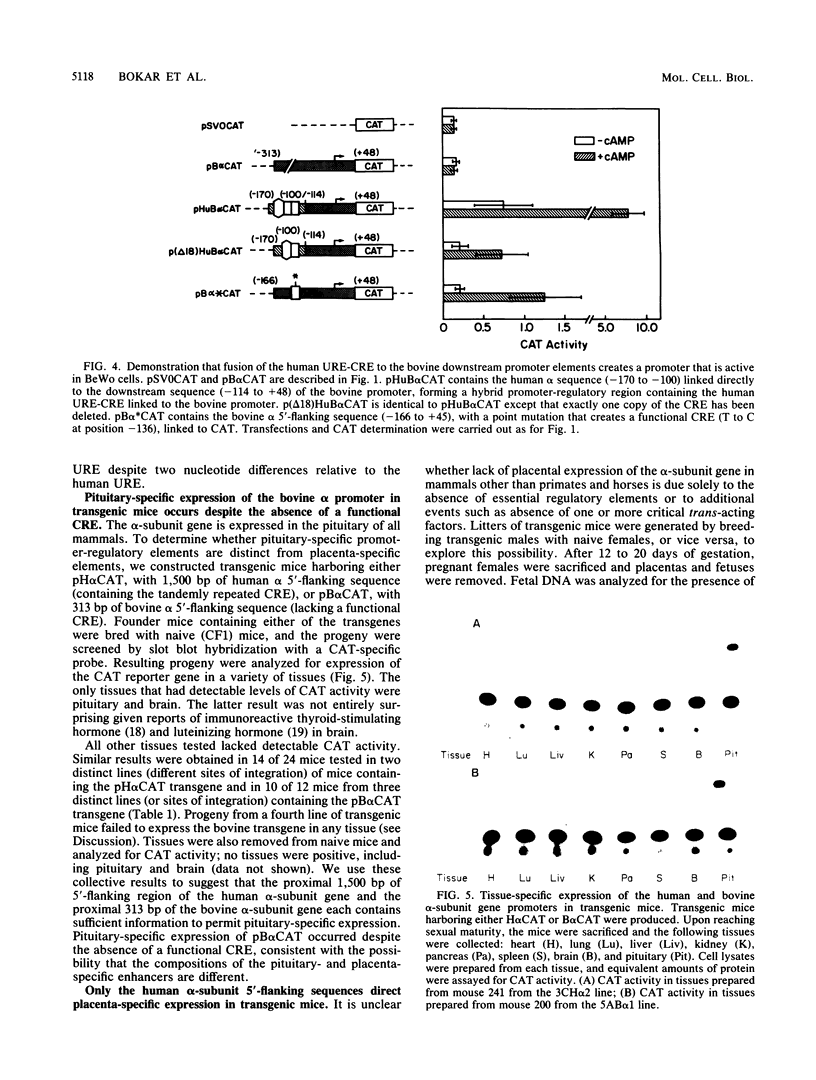
The single-copy gene encoding the alpha subunit of glycoprotein hormones is expressed in the pituitaries of all mammals and in the placentas of only primates and horses. We have systematically analyzed the promoter-regulatory elements of the human and bovine alpha-subunit genes to elucidate the molecular mechanisms underlying their divergent patterns of tissue-specific expression. This analysis entailed the use of transient expression assays in a chorionic gonadotropin-secreting human choriocarcinoma cell line, protein-DNA binding assays, and expression of chimeric forms of human or bovine alpha subunit genes in transgenic mice. From the results, we conclude that placental expression of the human alpha-subunit gene requires a functional cyclic AMP response element (CRE) that is present as a tandem repeat in the promoter-regulatory region. In contrast, the promoter-regulatory region of the bovine alpha-subunit gene, as well as of the rat and mouse genes, was found to contain a single CRE homolog that differed from its human counterpart by a single nucleotide. This difference substantially reduced the binding affinity of the bovine CRE homolog for the nuclear protein that bound to the human alpha CRE and thereby rendered the bovine alpha-subunit promoter inactive in human choriocarcinoma cells. However, conversion of the bovine alpha CRE homolog to an authentic alpha CRE restored activity to the bovine alpha-subunit promoter in choriocarcinoma cells. Similarly, a human but not a bovine alpha transgene was expressed in placenta in transgenic mice. Thus, placenta-specific expression of the human alpha-subunit gene may be the consequence of the recent evolution of a functional CRE. Expression of the human alpha transgene in mouse placenta further suggests that evolution of placenta-specific trans-acting factors preceded the appearance of this element. Finally, in contrast to their divergent patterns of placental expression, both the human and bovine alpha-subunit transgenes were expressed in mouse pituitary, indicating differences in the composition of the enhancers required for pituitary- and placenta-specific expression.
Full text
PDF

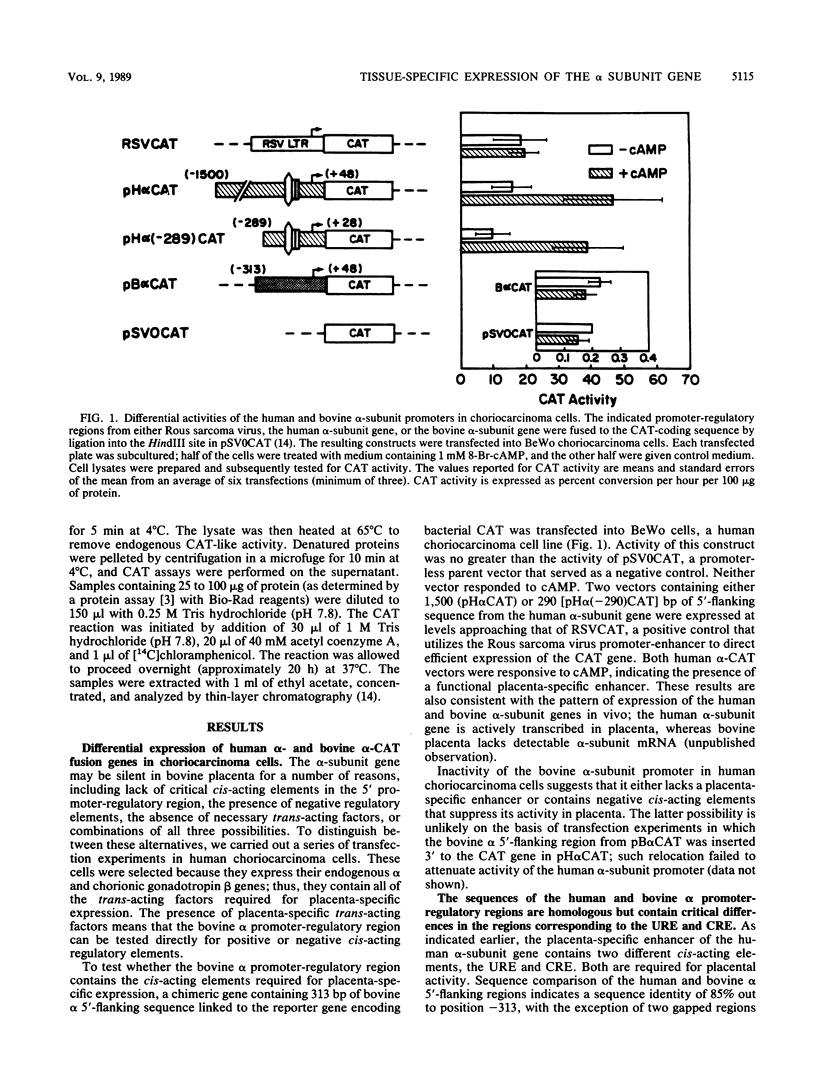





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen B., Milsted A., Kennedy G., Nilson J. H. Cyclic AMP and phorbol esters interact synergistically to regulate expression of the chorionic gonadotropin genes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 25;263(30):15578–15583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokar J. A., Roesler W. J., Vandenbark G. R., Kaetzel D. M., Hanson R. W., Nilson J. H. Characterization of the cAMP responsive elements from the genes for the alpha-subunit of glycoprotein hormones and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP). Conserved features of nuclear protein binding between tissues and species. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 25;263(36):19740–19747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnside J., Buckland P. R., Chin W. W. Isolation and characterization of the gene encoding the alpha-subunit of the rat pituitary glycoprotein hormones. Gene. 1988 Oct 15;70(1):67–74. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90105-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delegeane A. M., Ferland L. H., Mellon P. L. Tissue-specific enhancer of the human glycoprotein hormone alpha-subunit gene: dependence on cyclic AMP-inducible elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):3994–4002. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.3994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch P. J., Hoeffler J. P., Jameson J. L., Habener J. F. Cyclic AMP and phorbol ester-stimulated transcription mediated by similar DNA elements that bind distinct proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7922–7926. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch P. J., Jameson J. L., Habener J. F. Cyclic AMP responsiveness of human gonadotropin-alpha gene transcription is directed by a repeated 18-base pair enhancer. Alpha-promoter receptivity to the enhancer confers cell-preferential expression. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 5;262(25):12169–12174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiddes J. C., Talmadge K. Structure, expression, and evolution of the genes for the human glycoprotein hormones. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1984;40:43–78. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571140-1.50006-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox N., Solter D. Expression and regulation of the pituitary- and placenta-specific human glycoprotein hormone alpha-subunit gene is restricted to the pituitary in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;8(12):5470–5476. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.12.5470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin R. G., Moncman C. L., Rottman F. M., Nilson J. H. Characterization and nucleotide sequence of the gene for the common alpha subunit of the bovine pituitary glycoprotein hormones. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Oct 11;11(19):6873–6882. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.19.6873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon D. F., Wood W. M., Ridgway E. C. Organization and nucleotide sequence of the mouse alpha-subunit gene of the pituitary glycoprotein hormones. DNA. 1988 Dec;7(10):679–690. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haisenleder D. J., Khoury S., Zmeili S. M., Papavasiliou S., Ortolano G. A., Dee C., Duncan J. A., Marshall J. C. The frequency of gonadotropin-releasing hormone secretion regulates expression of alpha and luteinizing hormone beta-subunit messenger ribonucleic acids in male rats. Mol Endocrinol. 1987 Nov;1(11):834–838. doi: 10.1210/mend-1-11-834. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamernik D. L., Crowder M. E., Nilson J. H., Nett T. M. Measurement of messenger ribonucleic acid for luteinizing hormone beta-subunit, alpha-subunit, growth hormone, and prolactin after hypothalamic pituitary disconnection in ovariectomized ewes. Endocrinology. 1986 Dec;119(6):2704–2710. doi: 10.1210/endo-119-6-2704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeffler J. P., Meyer T. E., Yun Y., Jameson J. L., Habener J. F. Cyclic AMP-responsive DNA-binding protein: structure based on a cloned placental cDNA. Science. 1988 Dec 9;242(4884):1430–1433. doi: 10.1126/science.2974179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hojvat S., Baker G., Kirsteins L., Lawrence A. M. TSH in the rat and monkey brain. Distribution, characterization and effect of hypophysectomy. Neuroendocrinology. 1982;34(5):327–332. doi: 10.1159/000123322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jameson J. L., Jaffe R. C., Deutsch P. J., Albanese C., Habener J. F. The gonadotropin alpha-gene contains multiple protein binding domains that interact to modulate basal and cAMP-responsive transcription. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 15;263(20):9879–9886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landefeld T. D., Kepa J., Karsch F. J. Regulation of alpha subunit synthesis by gonadal steroid feedback in the sheep anterior pituitary. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2390–2393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrane M. M., de Vente J., Yun J., Bloom J., Park E., Wynshaw-Boris A., Wagner T., Rottman F. M., Hanson R. W. Tissue-specific expression and dietary regulation of a chimeric phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase/bovine growth hormone gene in transgenic mice. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11443–11451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilson J. H., Nejedlik M. T., Virgin J. B., Crowder M. E., Nett T. M. Expression of alpha subunit and luteinizing hormone beta genes in the ovine anterior pituitary. Estradiol suppresses accumulation of mRNAS for both alpha subunit and luteinizing hormone beta. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12087–12090. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Chen H. Y., Brinster R. L. Differential regulation of metallothionein-thymidine kinase fusion genes in transgenic mice and their offspring. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):701–710. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90186-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papavasiliou S. S., Zmeili S., Khoury S., Landefeld T. D., Chin W. W., Marshall J. C. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone differentially regulates expression of the genes for luteinizing hormone alpha and beta subunits in male rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):4026–4029. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.4026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips C. L., Lin L. W., Wu J. C., Guzman K., Milsted A., Miller W. L. 17 Beta-estradiol and progesterone inhibit transcription of the genes encoding the subunits of ovine follicle-stimulating hormone. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Jul;2(7):641–649. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-7-641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce J. G., Parsons T. F. Glycoprotein hormones: structure and function. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:465–495. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roesler W. J., Vandenbark G. R., Hanson R. W. Cyclic AMP and the induction of eukaryotic gene transcription. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9063–9066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shupnik M. A., Chin W. W., Ross D. S., Downing M. F., Habener J. F., Ridgway E. C. Regulation by thyroxine of the mRNA encoding the alpha subunit of mouse thyrotropin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):15120–15124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver B. J., Bokar J. A., Virgin J. B., Vallen E. A., Milsted A., Nilson J. H. Cyclic AMP regulation of the human glycoprotein hormone alpha-subunit gene is mediated by an 18-base-pair element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2198–2202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner T. E., Hoppe P. C., Jollick J. D., Scholl D. R., Hodinka R. L., Gault J. B. Microinjection of a rabbit beta-globin gene into zygotes and its subsequent expression in adult mice and their offspring. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6376–6380. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. K., Gonzalez G. A., Biggs W. H., 3rd, Montminy M. R. Phosphorylation-induced binding and transcriptional efficacy of nuclear factor CREB. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):494–498. doi: 10.1038/334494a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]