Abstract
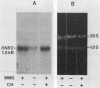
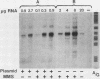
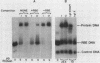
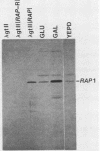
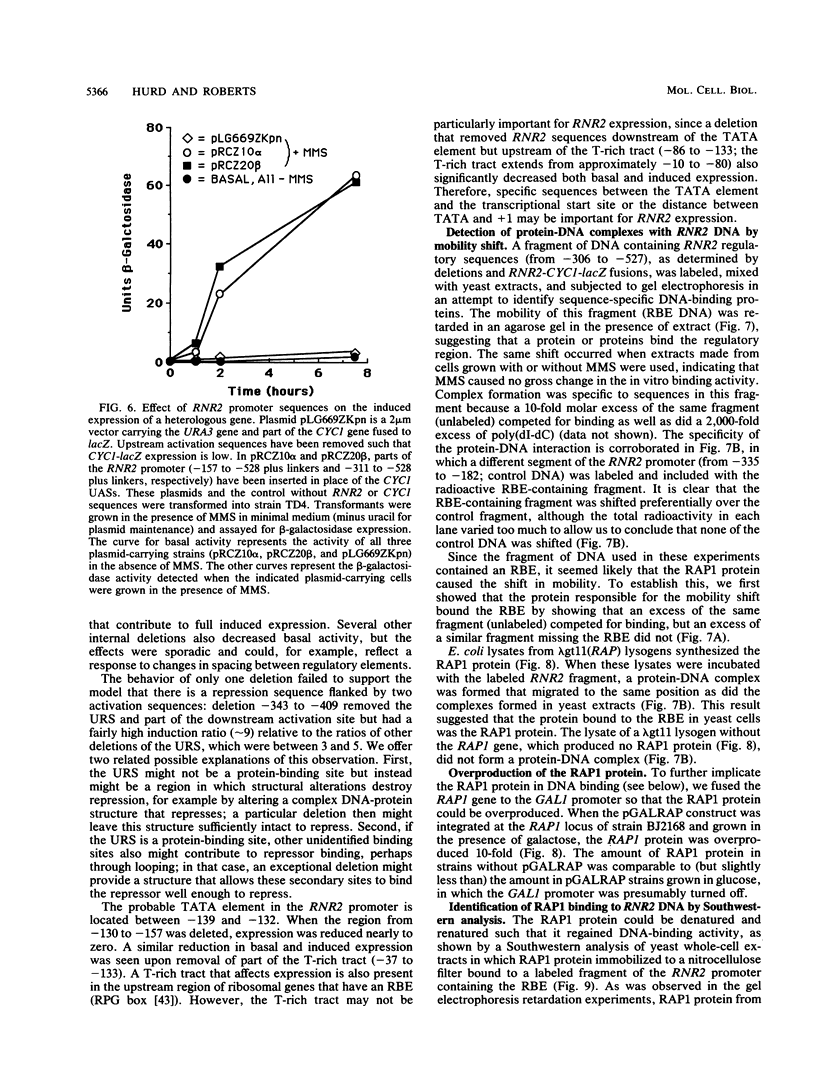
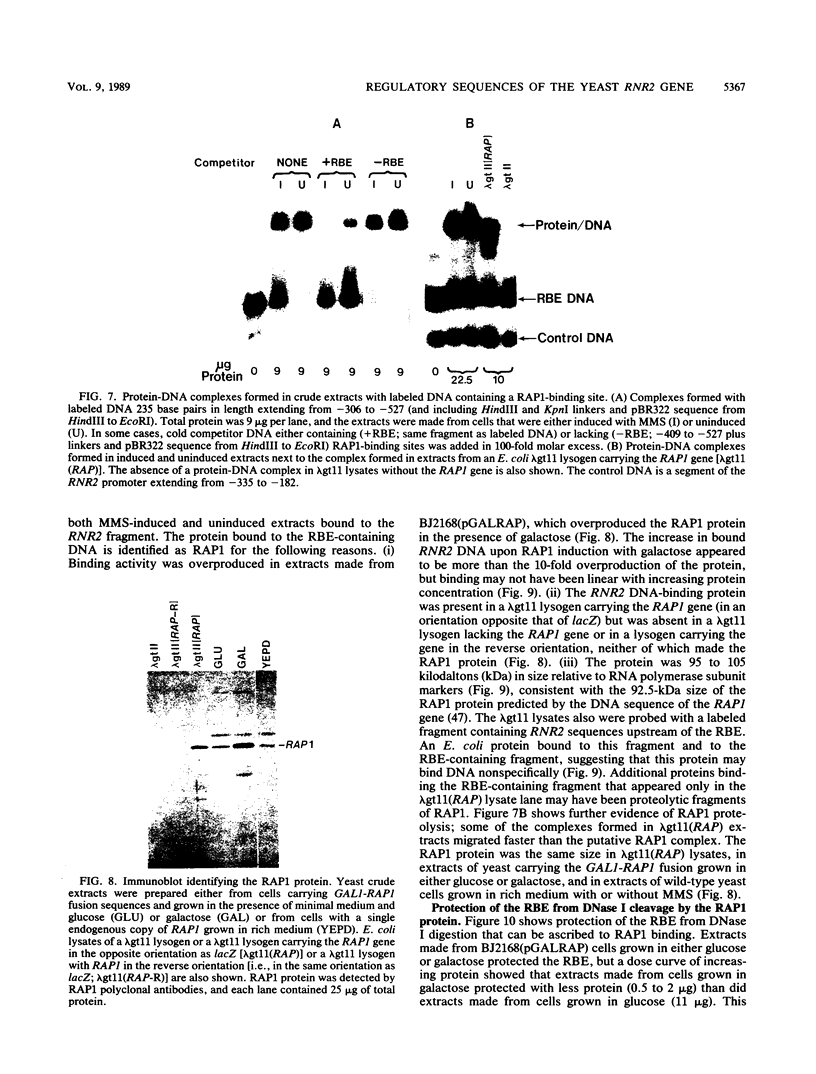
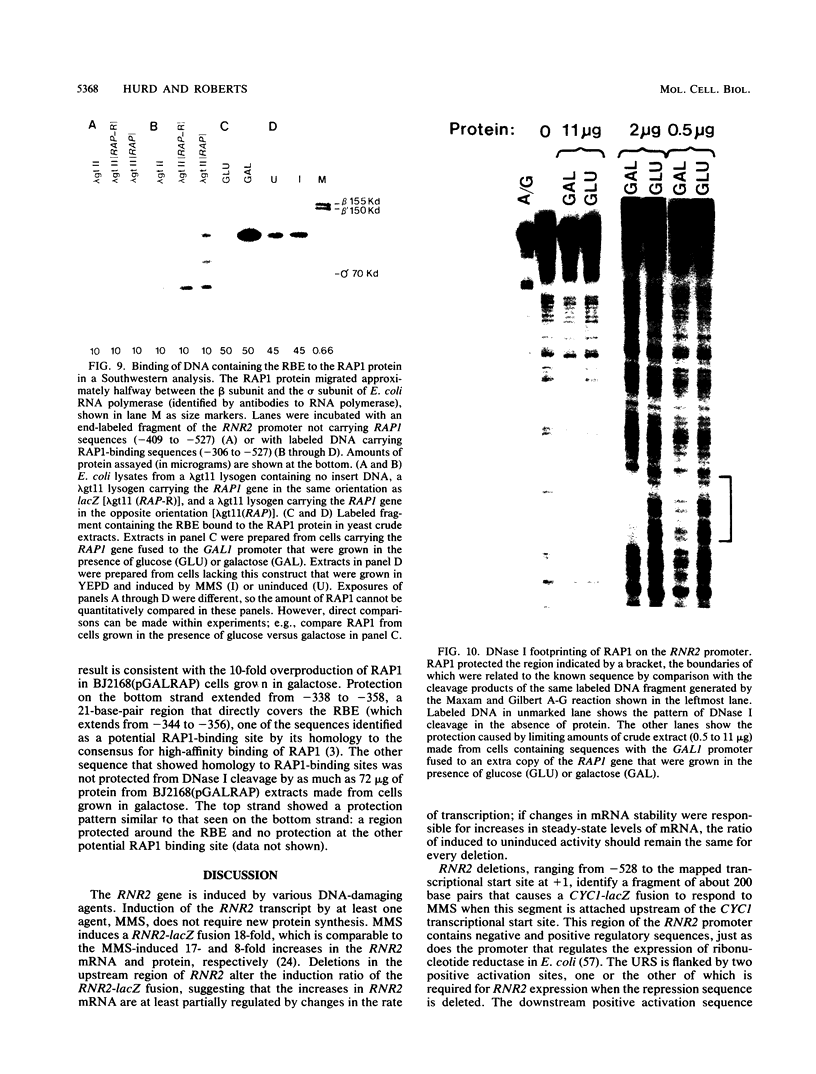
The small subunit of ribonucleotide reductase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae (RNR2) was induced 3- to 20-fold by a variety of DNA-damaging agents. Induction of the RNR2 transcript by at least one of these agents, methyl methanesulfonate, did not require protein synthesis. To identify sequences involved in the regulation of RNR2, we introduced deletions upstream of the transcription start site. Sequences required for induction were contained within a 200-base-pair region that could confer methyl methanesulfonate inducibility on the heterologous CYC1 promoter. This region contained a repression sequence and at least two positive activation sites. One of these activation sites bound RAP1, a protein known to associate with mating-type silencers and the upstream activation sequences of a number of genes. The behavior of deletions of the repression sequence suggests that induction of RNR2 may occur, at least in part, through relief of repression.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berman J., Tachibana C. Y., Tye B. K. Identification of a telomere-binding activity from yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3713–3717. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bram R. J., Kornberg R. D. Specific protein binding to far upstream activating sequences in polymerase II promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):43–47. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchman A. R., Kimmerly W. J., Rine J., Kornberg R. D. Two DNA-binding factors recognize specific sequences at silencers, upstream activating sequences, autonomously replicating sequences, and telomeres in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):210–225. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchman A. R., Lue N. F., Kornberg R. D. Connections between transcriptional activators, silencers, and telomeres as revealed by functional analysis of a yeast DNA-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;8(12):5086–5099. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.12.5086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J., Martinez-Arias A., Shapira S. K., Chou J. Beta-galactosidase gene fusions for analyzing gene expression in escherichia coli and yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:293–308. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00063-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celenza J. L., Carlson M. A yeast gene that is essential for release from glucose repression encodes a protein kinase. Science. 1986 Sep 12;233(4769):1175–1180. doi: 10.1126/science.3526554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen R., Yokoi T., Holland J. P., Pepper A. E., Holland M. J. Transcription of the constitutively expressed yeast enolase gene ENO1 is mediated by positive and negative cis-acting regulatory sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2753–2761. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elledge S. J., Davis R. W. Identification and isolation of the gene encoding the small subunit of ribonucleotide reductase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae: DNA damage-inducible gene required for mitotic viability. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2783–2793. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favaloro J., Treisman R., Kamen R. Transcription maps of polyoma virus-specific RNA: analysis by two-dimensional nuclease S1 gel mapping. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):718–749. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedor M. J., Lue N. F., Kornberg R. D. Statistical positioning of nucleosomes by specific protein-binding to an upstream activating sequence in yeast. J Mol Biol. 1988 Nov 5;204(1):109–127. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90603-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filpula D., Fuchs J. A. Regulation of ribonucleoside diphosphate reductase synthesis in Escherichia coli: increased enzyme synthesis as a result of inhibition of deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1977 Apr;130(1):107–113. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.1.107-113.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filpula D., Fuchs J. A. Regulation of the synthesis of ribonucleoside diphosphate reductase in Escherichia coli: specific activity of the enzyme in relationship to perturbations of DNA replication. J Bacteriol. 1978 Aug;135(2):429–435. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.2.429-435.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto T., Wang J. C. Yeast DNA topoisomerase II. An ATP-dependent type II topoisomerase that catalyzes the catenation, decatenation, unknotting, and relaxation of double-stranded DNA rings. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 25;257(10):5866–5872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Lalonde B., Gifford P., Alani E. Distinctly regulated tandem upstream activation sites mediate catabolite repression of the CYC1 gene of S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):503–511. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90243-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Ptashne M. Fusion of Escherichia coli lacZ to the cytochrome c gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2199–2203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn S., Hoar E. T., Guarente L. Each of three "TATA elements" specifies a subset of the transcription initiation sites at the CYC-1 promoter of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8562–8566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanke P. D., Fuchs J. A. Regulation of ribonucleoside diphosphate reductase mRNA synthesis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jun;154(3):1040–1045. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.3.1040-1045.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanke P. D., Fuchs J. A. Requirement of protein synthesis for the induction of ribonucleoside diphosphate reductase mRNA in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;193(2):327–331. doi: 10.1007/BF00330689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harshman K. D., Moye-Rowley W. S., Parker C. S. Transcriptional activation by the SV40 AP-1 recognition element in yeast is mediated by a factor similar to AP-1 that is distinct from GCN4. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):321–330. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90393-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H. Three additional genes required for deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1973 Sep;115(3):966–974. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.3.966-974.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill J. E., Myers A. M., Koerner T. J., Tzagoloff A. Yeast/E. coli shuttle vectors with multiple unique restriction sites. Yeast. 1986 Sep;2(3):163–167. doi: 10.1002/yea.320020304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huet J., Cottrelle P., Cool M., Vignais M. L., Thiele D., Marck C., Buhler J. M., Sentenac A., Fromageot P. A general upstream binding factor for genes of the yeast translational apparatus. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3539–3547. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04114.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurd H. K., Roberts C. W., Roberts J. W. Identification of the gene for the yeast ribonucleotide reductase small subunit and its inducibility by methyl methanesulfonate. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3673–3677. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobsen B. K., Pelham H. R. Constitutive binding of yeast heat shock factor to DNA in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):5040–5042. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.5040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
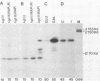
- Johnston L. H., White J. H., Johnson A. L., Lucchini G., Plevani P. The yeast DNA polymerase I transcript is regulated in both the mitotic cell cycle and in meiosis and is also induced after DNA damage. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5017–5030. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupiec M., Simchen G. Regulation of the RAD6 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae in the mitotic cell cycle and in meiosis. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Jun;203(3):538–543. doi: 10.1007/BF00422083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lammers M., Follmann H. Deoxyribonucleotide biosynthesis in yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae). A ribonucleotide reductase system of sufficient activity for DNA synthesis. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Apr 16;140(2):281–287. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08099.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lis J. T. Fractionation of DNA fragments by polyethylene glycol induced precipitation. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):347–353. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65044-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. W., Mount D. W. The SOS regulatory system of Escherichia coli. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):11–22. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
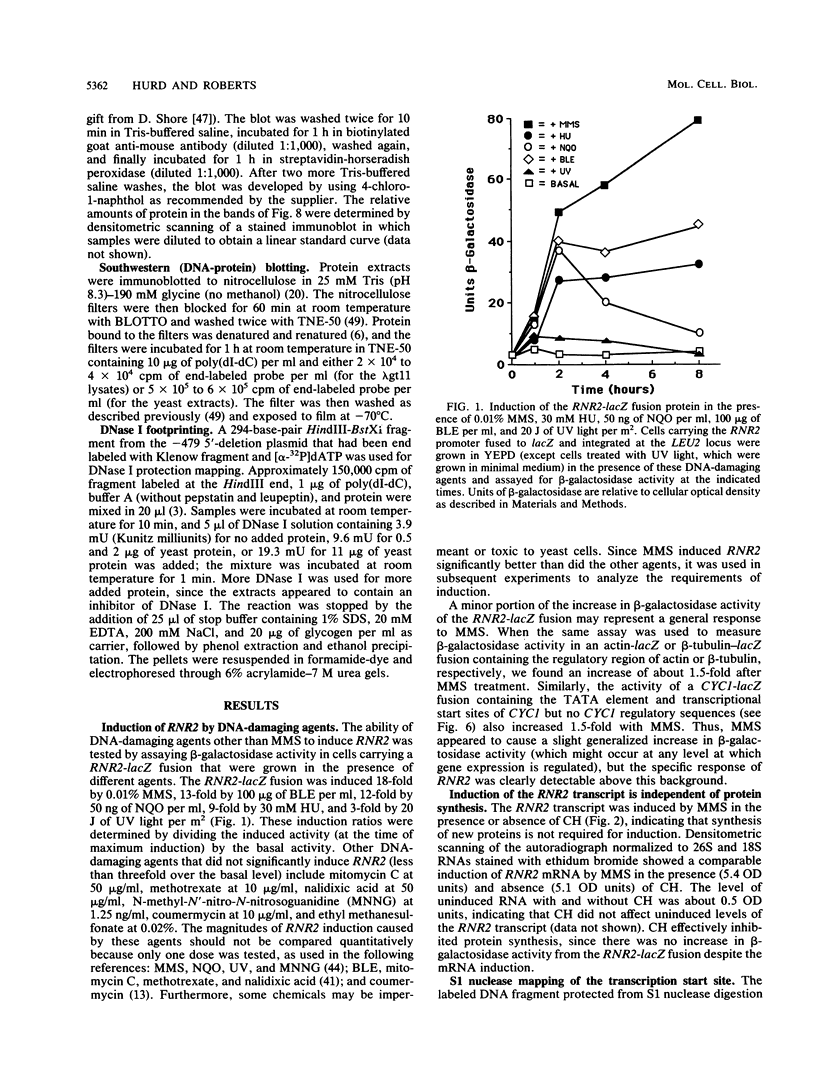
- Lowdon M., Vitols E. Ribonucleotide reductase activity during the cell cycle of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Sep;158(1):177–184. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90611-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto Y., Shigesada K., Hirano M., Imai M. Autogenous regulation of the gene for transcription termination factor rho in Escherichia coli: localization and function of its attenuators. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):945–958. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.945-958.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagawa F., Fink G. R. The relationship between the "TATA" sequence and transcription initiation sites at the HIS4 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8557–8561. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
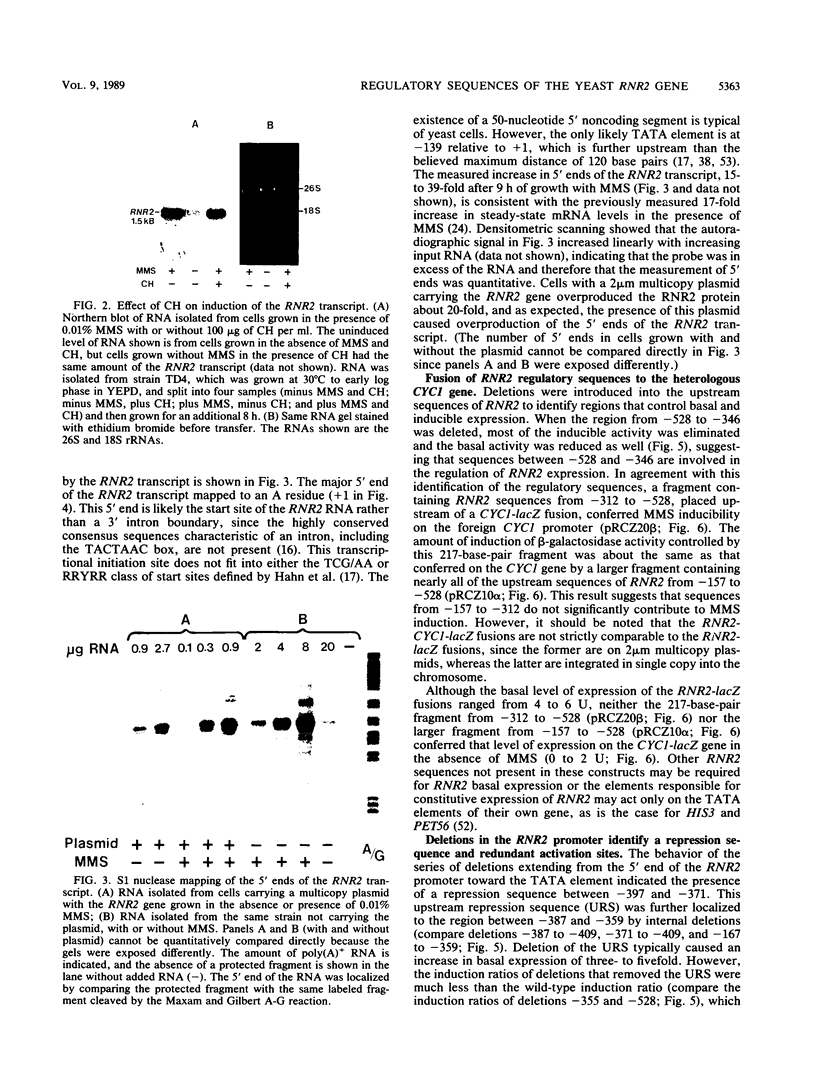
- Nishizawa M., Araki R., Teranishi Y. Identification of an upstream activating sequence and an upstream repressible sequence of the pyruvate kinase gene of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):442–451. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr-Weaver T. L., Szostak J. W., Rothstein R. J. Yeast transformation: a model system for the study of recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6354–6358. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson G. W., Nicolet C. M., Kalainov D., Friedberg E. C. A yeast excision-repair gene is inducible by DNA damaging agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1842–1846. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M., Casadaban M. J., Botstein D. Yeast genes fused to beta-galactosidase in Escherichia coli can be expressed normally in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2460–2464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
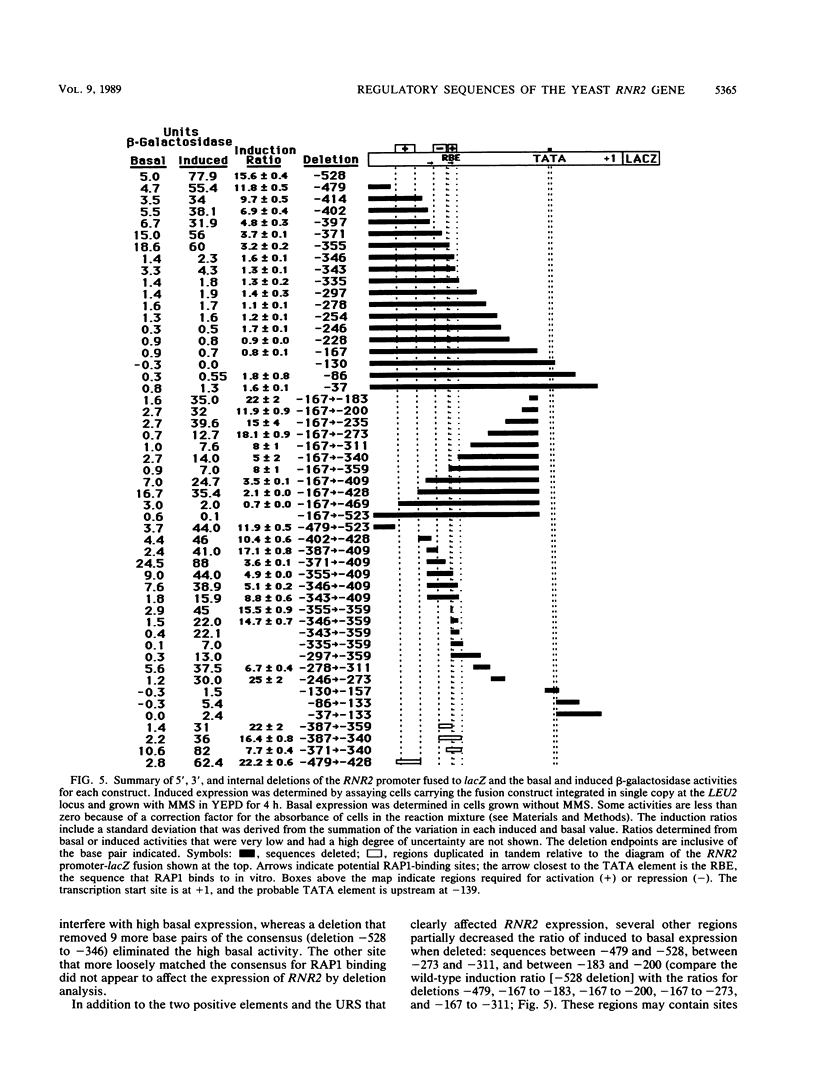
- Rotenberg M. O., Woolford J. L., Jr Tripartite upstream promoter element essential for expression of Saccharomyces cerevisiae ribosomal protein genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):674–687. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruby S. W., Szostak J. W. Specific Saccharomyces cerevisiae genes are expressed in response to DNA-damaging agents. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):75–84. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sclafani R. A., Fangman W. L. Yeast gene CDC8 encodes thymidylate kinase and is complemented by herpes thymidine kinase gene TK. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5821–5825. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore D., Nasmyth K. Purification and cloning of a DNA binding protein from yeast that binds to both silencer and activator elements. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90095-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore D., Stillman D. J., Brand A. H., Nasmyth K. A. Identification of silencer binding proteins from yeast: possible roles in SIR control and DNA replication. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):461–467. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04776.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., LeBowitz J. H., Baldwin A. S., Jr, Sharp P. A. Molecular cloning of an enhancer binding protein: isolation by screening of an expression library with a recognition site DNA. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):415–423. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80034-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger P. K., Pelham H. R. Purification and characterization of a heat-shock element binding protein from yeast. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):3035–3041. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02609.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Constitutive and inducible Saccharomyces cerevisiae promoters: evidence for two distinct molecular mechanisms. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3847–3853. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Promoters, activator proteins, and the mechanism of transcriptional initiation in yeast. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):295–297. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90277-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelander L., Reichard P. Reduction of ribonucleotides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:133–158. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomizawa J. I., Ohmori H., Bird R. E. Origin of replication of colicin E1 plasmid DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):1865–1869. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.1865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuggle C. K., Fuchs J. A. Regulation of the operon encoding ribonucleotide reductase in Escherichia coli: evidence for both positive and negative control. EMBO J. 1986 May;5(5):1077–1085. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04325.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinert T. A., Hartwell L. H. The RAD9 gene controls the cell cycle response to DNA damage in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Science. 1988 Jul 15;241(4863):317–322. doi: 10.1126/science.3291120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woudt L. P., Smit A. B., Mager W. H., Planta R. J. Conserved sequence elements upstream of the gene encoding yeast ribosomal protein L25 are involved in transcription activation. EMBO J. 1986 May;5(5):1037–1040. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04319.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yocum R. R., Hanley S., West R., Jr, Ptashne M. Use of lacZ fusions to delimit regulatory elements of the inducible divergent GAL1-GAL10 promoter in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):1985–1998. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Yeast RNA polymerase II genes: isolation with antibody probes. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):778–782. doi: 10.1126/science.6356359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]