Abstract
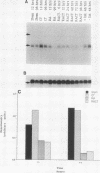
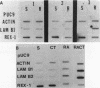
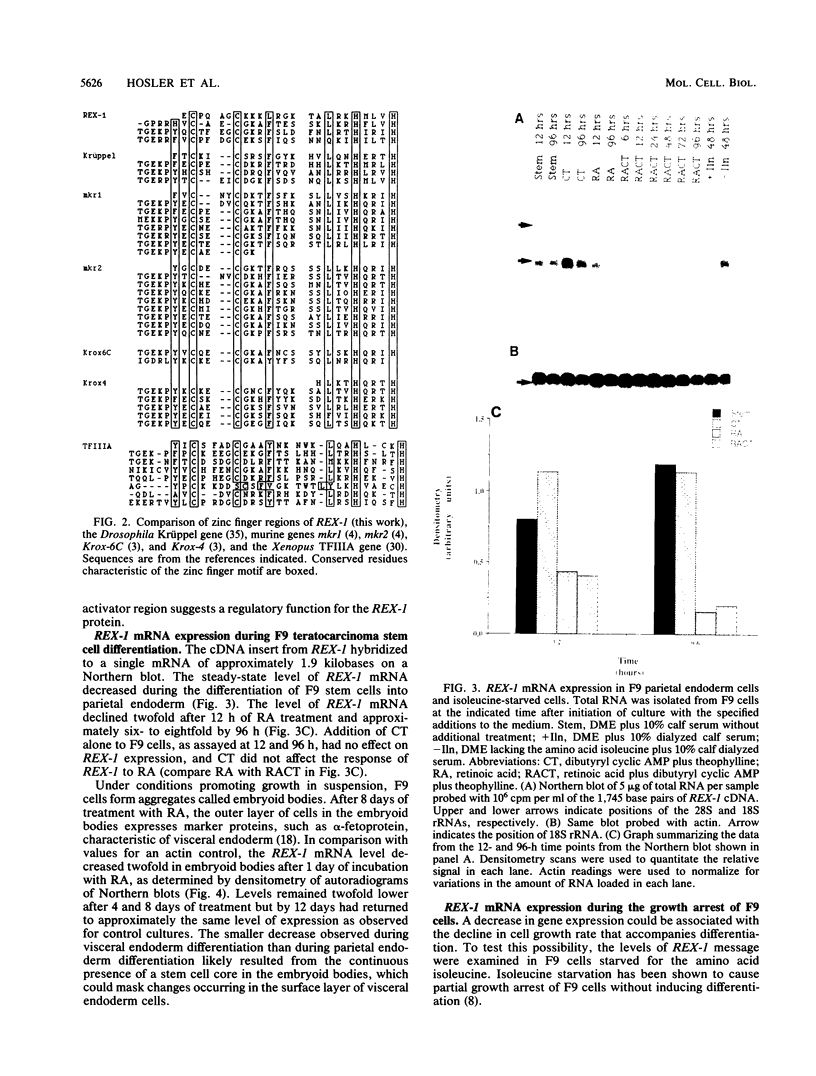
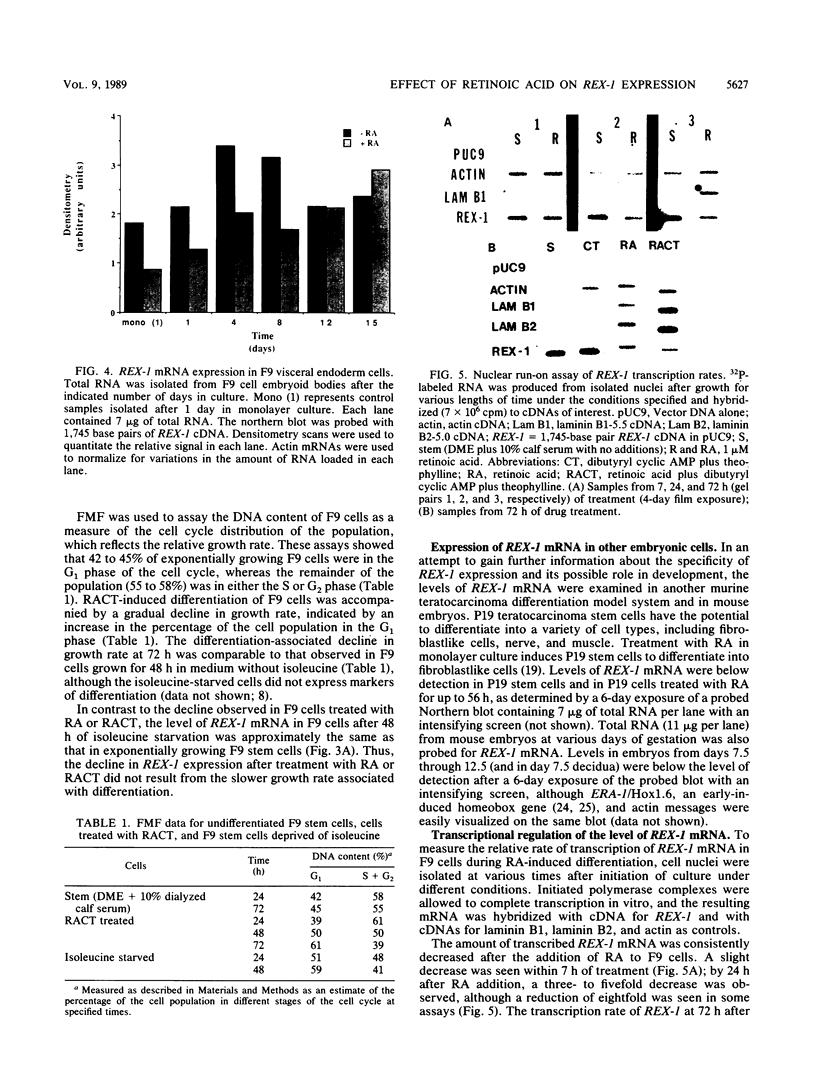
In the presence of retinoic acid (RA), cultured F9 murine teratocarcinoma stem cells differentiate into nontumorigenic cells resembling the extraembryonic endoderm of the early mouse embryo. By differential hybridization screening of an F9 cell cDNA library, we isolated a 1,745-nucleotide cDNA for a gene, REX-1 (for reduced expression), whose steady-state mRNA level began to decline in F9 cells in monolayer culture within 12 h after the addition of RA. By 48 to 96 h after RA treatment of F9 cells in monolayer culture, the REX-1 steady-state mRNA level was more than sevenfold lower than the level in undifferentiated F9 stem cells. The REX-1 mRNA decrease did not result from the reduction in cell growth rate associated with the differentiation process, since the REX-1 mRNA level did not decline in F9 cells that were partially growth arrested after 48 h of isoleucine deprivation. The RA-associated REX-1 mRNA decrease resulted primarily from a reduction in the transcription rate of the REX-1 gene in the presence of RA. In contrast to results in F9 cells, we have been unable thus far to detect REX-1 mRNA in day 7.5 to 12.5 mouse embryo RNA samples or in the P19 teratocarcinoma stem cell line. The putative REX-1 protein identified by DNA sequence analysis contains four repeats of the zinc finger nucleic acid-binding motif and a potential acidic activator domain, suggesting that REX-1 encodes a regulatory protein. The REX-1 gene is not identical to the previously reported murine genes that encode zinc finger-containing proteins.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Breier G., Bućan M., Francke U., Colberg-Poley A. M., Gruss P. Sequential expression of murine homeo box genes during F9 EC cell differentiation. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2209–2215. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04486.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavrier P., Lemaire P., Revelant O., Bravo R., Charnay P. Characterization of a mouse multigene family that encodes zinc finger structures. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1319–1326. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury K., Deutsch U., Gruss P. A multigene family encoding several "finger" structures is present and differentially active in mammalian genomes. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):771–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90074-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury K., Rohdewohld H., Gruss P. Specific and ubiquitous expression of different Zn finger protein genes in the mouse. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 11;16(21):9995–10011. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.21.9995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colberg-Poley A. M., Voss S. D., Chowdhury K., Gruss P. Structural analysis of murine genes containing homoeo box sequences and their expression in embryonal carcinoma cells. 1985 Apr 25-May 1Nature. 314(6013):713–718. doi: 10.1038/314713a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croce C. M., Linnenbach A., Huebner K., Parnes J. R., Margulies D. H., Appella E., Seidman J. G. Control of expression of histocompatibility antigens (H-2) and beta 2-microglobulin in F9 teratocarcinoma stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5754–5758. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean M., Levine R. A., Campisi J. c-myc regulation during retinoic acid-induced differentiation of F9 cells is posttranscriptional and associated with growth arrest. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):518–524. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dony C., Kessel M., Gruss P. Post-transcriptional control of myc and p53 expression during differentiation of the embryonal carcinoma cell line F9. Nature. 1985 Oct 17;317(6038):636–639. doi: 10.1038/317636a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duprey P., Morello D., Vasseur M., Babinet C., Condamine H., Brûlet P., Jacob F. Expression of the cytokeratin endo A gene during early mouse embryogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8535–8539. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. J., Kaufman M. H. Establishment in culture of pluripotential cells from mouse embryos. Nature. 1981 Jul 9;292(5819):154–156. doi: 10.1038/292154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M., Hollenberg S. M. Zinc fingers: gilt by association. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90522-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner R. L., Rossant J. Investigation of the fate of 4-5 day post-coitum mouse inner cell mass cells by blastocyst injection. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1979 Aug;52:141–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giguere V., Ong E. S., Segui P., Evans R. M. Identification of a receptor for the morphogen retinoic acid. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):624–629. doi: 10.1038/330624a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Ziff E. B. Stimulation of 3T3 cells induces transcription of the c-fos proto-oncogene. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):433–438. doi: 10.1038/311433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griep A. E., DeLuca H. F. Decreased c-myc expression is an early event in retinoic acid-induced differentiation of F9 teratocarcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5539–5543. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogan B. L., Taylor A., Adamson E. Cell interactions modulate embryonal carcinoma cell differentiation into parietal or visceral endoderm. Nature. 1981 May 21;291(5812):235–237. doi: 10.1038/291235a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones-Villeneuve E. M., McBurney M. W., Rogers K. A., Kalnins V. I. Retinoic acid induces embryonal carcinoma cells to differentiate into neurons and glial cells. J Cell Biol. 1982 Aug;94(2):253–262. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.2.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joyner A. L., Kornberg T., Coleman K. G., Cox D. R., Martin G. R. Expression during embryogenesis of a mouse gene with sequence homology to the Drosophila engrailed gene. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):29–37. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90009-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Courey A. J., Ladika J., Tjian R. Distinct regions of Sp1 modulate DNA binding and transcriptional activation. Science. 1988 Dec 16;242(4885):1566–1570. doi: 10.1126/science.3059495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaRosa G. J., Gudas L. J. An early effect of retinoic acid: cloning of an mRNA (Era-1) exhibiting rapid and protein synthesis-independent induction during teratocarcinoma stem cell differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):329–333. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaRosa G. J., Gudas L. J. Early retinoic acid-induced F9 teratocarcinoma stem cell gene ERA-1: alternate splicing creates transcripts for a homeobox-containing protein and one lacking the homeobox. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3906–3917. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaire P., Revelant O., Bravo R., Charnay P. Two mouse genes encoding potential transcription factors with identical DNA-binding domains are activated by growth factors in cultured cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4691–4695. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine R. A., LaRosa G. J., Gudas L. J. Isolation of cDNA clones for genes exhibiting reduced expression after differentiation of murine teratocarcinoma stem cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):2142–2150. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.2142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. R. Isolation of a pluripotent cell line from early mouse embryos cultured in medium conditioned by teratocarcinoma stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7634–7638. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., McLachlan A. D., Klug A. Repetitive zinc-binding domains in the protein transcription factor IIIA from Xenopus oocytes. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1609–1614. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03825.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ollo R., Maniatis T. Drosophila Krüppel gene product produced in a baculovirus expression system is a nuclear phosphoprotein that binds to DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5700–5704. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petkovich M., Brand N. J., Krust A., Chambon P. A human retinoic acid receptor which belongs to the family of nuclear receptors. Nature. 1987 Dec 3;330(6147):444–450. doi: 10.1038/330444a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. How eukaryotic transcriptional activators work. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):683–689. doi: 10.1038/335683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roguska M. A., Gudas L. J. An increase in prolyl-4-hydroxylase activity occurs during the retinoic acid-induced differentiation of mouse teratocarcinoma stem cell lines F9 and P19. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):13893–13896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruppert J. M., Kinzler K. W., Wong A. J., Bigner S. H., Kao F. T., Law M. L., Seuanez H. N., O'Brien S. J., Vogelstein B. The GLI-Kruppel family of human genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3104–3113. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer P. A., Trevor K., Oshima R. G. Molecular cloning and characterization of the Endo B cytokeratin expressed in preimplantation mouse embryos. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):538–547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. F., Waterman M. S. Identification of common molecular subsequences. J Mol Biol. 1981 Mar 25;147(1):195–197. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90087-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solter D., Shevinsky L., Knowles B. B., Strickland S. The induction of antigenic changes in a teratocarcinoma stem cell line (F9) by retinoic acid. Dev Biol. 1979 Jun;70(2):515–521. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90043-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland S., Mahdavi V. The induction of differentiation in teratocarcinoma stem cells by retinoic acid. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):393–403. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90008-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland S., Smith K. K., Marotti K. R. Hormonal induction of differentiation in teratocarcinoma stem cells: generation of parietal endoderm by retinoic acid and dibutyryl cAMP. Cell. 1980 Sep;21(2):347–355. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90471-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsonis P. A., Adamson E. D. Specific expression of homoeobox-containing genes during induced differentiation of embryonal carcinoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 May 29;137(1):520–527. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)91241-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. Y., Gudas L. J. Isolation of cDNA clones specific for collagen IV and laminin from mouse teratocarcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5880–5884. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. Y., LaRosa G. J., Gudas L. J. Molecular cloning of gene sequences transcriptionally regulated by retinoic acid and dibutyryl cyclic AMP in cultured mouse teratocarcinoma cells. Dev Biol. 1985 Jan;107(1):75–86. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90377-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickens M., Stephenson P. Role of the conserved AAUAAA sequence: four AAUAAA point mutants prevent messenger RNA 3' end formation. Science. 1984 Nov 30;226(4678):1045–1051. doi: 10.1126/science.6208611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zelent A., Krust A., Petkovich M., Kastner P., Chambon P. Cloning of murine alpha and beta retinoic acid receptors and a novel receptor gamma predominantly expressed in skin. Nature. 1989 Jun 29;339(6227):714–717. doi: 10.1038/339714a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Thé H., Marchio A., Tiollais P., Dejean A. A novel steroid thyroid hormone receptor-related gene inappropriately expressed in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):667–670. doi: 10.1038/330667a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]