Abstract
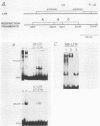
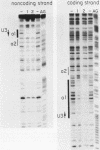
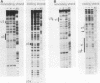
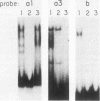
Avian leukosis virus (ALV) induces bursal lymphomas in chickens, after proviral integration next to the cellular myc proto-oncogene, and subsequent c-myc hyperexpression. Our previous work suggested that labile or short-lived cellular proteins interact with the viral long terminal repeat (LTR) enhancer, and binding of these proteins appeared to be essential for high rates of LTR-enhanced transcription (A. Ruddell, M. Linial, W. Schubach, and M. Groudine, J. Virol. 62:2728-2735, 1988). This lability is specific for B-lymphoid cell types, since T cells and fibroblasts show stable high rates of LTR-enhanced transcription and stable LTR-binding activity. Moreover, the lability of these proteins may be important in determining susceptibility to bursal lymphoma. In this study, we separated and characterized the labile and stable LTR-binding proteins and examined their lability and expression in different cell types. Gel shift and DNase I footprinting analyses indicated that at least five proteins interact with the 140-base-pair LTR enhancer region. These proteins were distinct by several criteria, including lability or stability after inhibition of protein synthesis, resistance to heat denaturation, chromatographic behavior, and expression in different cell types. Two binding proteins were present in many cell types and were specifically labile in B cells. A third binding protein showed hematopoietic-cell-type-specific expression and was also labile in B cells. These findings indicate that there is tissue-specific modulation of the lability and expression of ALV LTR-binding proteins, which may be important for regulation of LTR transcription enhancement and ALV bursal lymphomagenesis.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akiyama Y., Kato S. Two cell lines from lymphomas of Marek's disease. Biken J. 1974 Sep;17(3):105–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURMESTER B. R., FONTES A. K., WALTER W. G. Pathogenicity of a viral strain (RPL 12) causing avian visceral lymphomatosis and related neoplasms. III. Influence of host age and route of inoculation. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1960 Jun;24:1423–1442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baba T. W., Humphries E. H. Differential response to avian leukosis virus infection exhibited by two chicken lines. Virology. 1984 May;135(1):181–188. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90128-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baba T. W., Humphries E. H. Formation of a transformed follicle is necessary but not sufficient for development of an avian leukosis virus-induced lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):213–216. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bizub D., Katz R. A., Skalka A. M. Nucleotide sequence of noncoding regions in Rous-associated virus-2: comparisons delineate conserved regions important in replication and oncogenesis. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):557–565. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.557-565.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. W., Blais B. P., Robinson H. L. Long terminal repeat (LTR) sequences, env, and a region near the 5' LTR influence the pathogenic potential of recombinants between Rous-associated virus types 0 and 1. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3431–3437. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3431-3437.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. W., Robinson H. L. Influence of env and long terminal repeat sequences on the tissue tropism of avian leukosis viruses. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4828–4831. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4828-4831.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewert D. L., de Boer G. F. Avian lymphoid leukosis: mechanisms of lymphomagenesis. Adv Vet Sci Comp Med. 1988;32:37–55. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-039232-2.50006-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung Y. K., Fadly A. M., Crittenden L. B., Kung H. J. Avian lymphoid leukosis virus infection and DNA integration in the preleukotic bursal tissues: a comparative study of susceptible and resistant lines. Virology. 1982 Jun;119(2):411–421. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90100-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung Y. K., Lewis W. G., Crittenden L. B., Kung H. J. Activation of the cellular oncogene c-erbB by LTR insertion: molecular basis for induction of erythroblastosis by avian leukosis virus. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):357–368. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90417-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia J. A., Wu F. K., Mitsuyasu R., Gaynor R. B. Interactions of cellular proteins involved in the transcriptional regulation of the human immunodeficiency virus. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3761–3770. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02711.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hann S. R., Eisenman R. N. Proteins encoded by the human c-myc oncogene: differential expression in neoplastic cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2486–2497. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward W. S., Neel B. G., Astrin S. M. Activation of a cellular onc gene by promoter insertion in ALV-induced lymphoid leukosis. Nature. 1981 Apr 9;290(5806):475–480. doi: 10.1038/290475a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson S. P., Tjian R. O-glycosylation of eukaryotic transcription factors: implications for mechanisms of transcriptional regulation. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):125–133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90015-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., Landschulz W. H., Graves B. J., McKnight S. L. Identification of a rat liver nuclear protein that binds to the enhancer core element of three animal viruses. Genes Dev. 1987 Apr;1(2):133–146. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.2.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N. C., Rigby P. W., Ziff E. B. Trans-acting protein factors and the regulation of eukaryotic transcription: lessons from studies on DNA tumor viruses. Genes Dev. 1988 Mar;2(3):267–281. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.3.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanter M. R., Smith R. E., Hayward W. S. Rapid induction of B-cell lymphomas: insertional activation of c-myb by avian leukosis virus. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1423–1432. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1423-1432.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L. A., Tsichlis P., Khoury G. Multiple enhancer domains in the 3' terminus of the Prague strain of Rous sarcoma virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Aug 24;12(16):6427–6442. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.16.6427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linial M., Gunderson N., Groudine M. Enhanced transcription of c-myc in bursal lymphoma cells requires continuous protein synthesis. Science. 1985 Dec 6;230(4730):1126–1132. doi: 10.1126/science.2999973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Goodbourn S., Fischer J. A. Regulation of inducible and tissue-specific gene expression. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1237–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.3296191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabel G., Baltimore D. An inducible transcription factor activates expression of human immunodeficiency virus in T cells. Nature. 1987 Apr 16;326(6114):711–713. doi: 10.1038/326711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton P. A., Coffin J. M. Characterization of Rous sarcoma virus sequences essential for viral gene expression. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1171–1179. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1171-1179.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne G. S., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. Multiple arrangements of viral DNA and an activated host oncogene in bursal lymphomas. Nature. 1982 Jan 21;295(5846):209–214. doi: 10.1038/295209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piette J., Kryszke M. H., Yaniv M. Specific interaction of cellular factors with the B enhancer of polyoma virus. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2675–2685. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03987.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizer E., Humphries E. H. RAV-1 insertional mutagenesis: disruption of the c-myb locus and development of avian B-cell lymphomas. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1630–1640. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1630-1640.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purchase H. G., Gilmour D. G., Romero C. H., Okazaki W. Post-infection genetic resistance to avian lymphoid leukosis resides in B target cell. Nature. 1977 Nov 3;270(5632):61–62. doi: 10.1038/270061a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson H. L., Blais B. M., Tsichlis P. N., Coffin J. M. At least two regions of the viral genome determine the oncogenic potential of avian leukosis viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1225–1229. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddell A., Linial M., Schubach W., Groudine M. Lability of leukosis virus enhancer-binding proteins in avian hematopoeitic cells. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2728–2735. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2728-2735.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan W. A., Jr, Franza B. R., Jr, Gilman M. Z. Two distinct cellular phosphoproteins bind to the c-fos serum response element. EMBO J. 1989 Jun;8(6):1785–1792. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03572.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryden T. A., Beemon K. Avian retroviral long terminal repeats bind CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):1155–1164. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.1155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salter D. W., Smith E. J., Hughes S. H., Wright S. E., Fadly A. M., Witter R. L., Crittenden L. B. Gene insertion into the chicken germ line by retroviruses. Poult Sci. 1986 Aug;65(8):1445–1458. doi: 10.3382/ps.0651445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider R., Gander I., Müller U., Mertz R., Winnacker E. L. A sensitive and rapid gel retention assay for nuclear factor I and other DNA-binding proteins in crude nuclear extracts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 11;14(3):1303–1317. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.3.1303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sealey L., Chalkley R. At least two nuclear proteins bind specifically to the Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):787–798. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger P. K., Lewis M. J., Pelham H. R. Heat shock factor is regulated differently in yeast and HeLa cells. Nature. 1987 Sep 3;329(6134):81–84. doi: 10.1038/329081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speck N. A., Baltimore D. Six distinct nuclear factors interact with the 75-base-pair repeat of the Moloney murine leukemia virus enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1101–1110. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanstrom R., DeLorbe W. J., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. Nucleotide sequence of cloned unintegrated avian sarcoma virus DNA: viral DNA contains direct and inverted repeats similar to those in transposable elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):124–128. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. K., Gonzalez G. A., Biggs W. H., 3rd, Montminy M. R. Phosphorylation-induced binding and transcriptional efficacy of nuclear factor CREB. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):494–498. doi: 10.1038/334494a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]