Abstract
In the last several years, significant work has been done studying hemoglobin (Hb) oxidative reactions and clearance mechanisms using both in vitro and in vivo model systems. One active research area involves the study of molecular chaperones and other proteins that are thought to mitigate the toxicity of acellular Hb. For example, the plasma protein haptoglobin (Hp) and the pre-erythroid protein alpha-hemoglobin-stabilizing protein (AHSP) bind to acellular Hb and alpha-subunits of Hb, respectively, to reduce these adverse effects. Moreover, there has been significant work studying hemopexin and alpha-1 microglobulin, both of which are thought to be involved with hemin degradation. These studies have coincided with the timely publication of the first crystal structure of the Hb-Hp complex. In constructing this Forum, we have invited a number of researchers in the area of Hb and myoglobin (Mb) redox biochemistry, as well as those who have contributed fundamentally to our knowledge of Hp function. Our goal has been to update this critically important research area, because we believe that it will ultimately impact the practice of transfusion medicine in a number of important ways. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 18, 2251–2253.
Free hemoglobin (Hb) in the circulatory system may arise from the transfusion of old blood or acellular Hb-based blood substitutes, or may result from various hematological conditions. For example, in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria, sickle-cell disease, and thalassemia syndromes, free Hb exists in concentrations of up to 10 μM during hemolytic events (12). Higher concentrations of acellular Hb (e.g.,>4000 μM) occur after infusion of the Hb-based oxygen carriers. The latter scenario has provided both the scientific and industrial communities with a unique opportunity to examine the toxicity associated with free Hb in animals and humans. The redox processes initiated by free Hb are diverse (11), and a growing body of experimental evidence suggests that they may cause and/or exacerbate a number of serious and potentially life-threatening conditions. For example, Hb is capable of driving a cascade of lipid oxidation reactions that result in F2-isoprostane production and vasoconstriction (11). Because of this and other recent work, Hb-centered oxidative reactions are now being examined with new vigor.
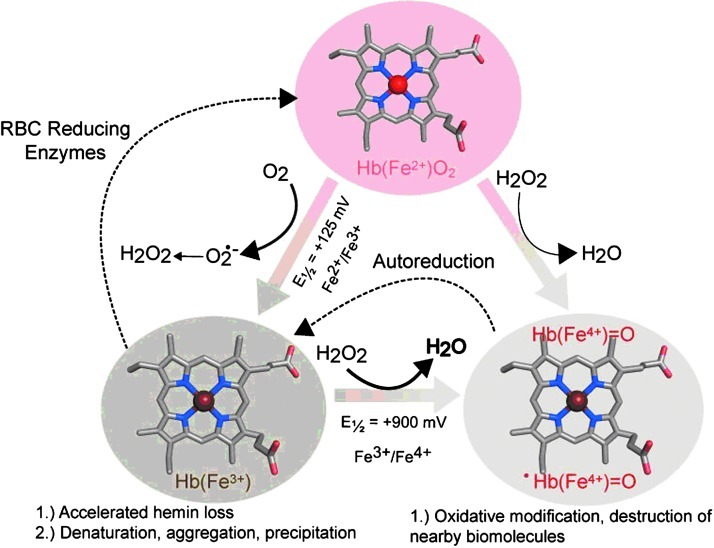
Several well-studied Hb- and myoglobin (Mb)-based redox reactions are presented in Figure 1. During the spontaneous oxidation of these proteins under physiological conditions, the heme iron atoms in each globin subunit convert from the ferrous (Fe2+) to ferric (Fe3+) form (5, 13). This process, also termed auto-oxidation, produces superoxide anion (O2•–), which dismutates both nonenzymatically and with the aid of superoxide dismutases to produce hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) (13). H2O2 can then be degraded by catalases, or it can react with Fe2+ or Fe3+ Hb to produce a highly reactive ferryl species (Fe4+) (11). In the case of H2O2-induced ferric-to-ferryl transitions, protein-based radicals have also been identified that are thought to readily migrate to the amino acid sites on the protein (11). Because Fe4+ proteins spontaneously reduce to the ferric state, this H2O2 consumption and reduction have led some investigators to regard Hb as a pseudoperoxidase (11). The thermodynamic driving force for oxidation of the heme iron, which is reflected by the Hb's redox potential (Eo½), is also shown in Figure 1.
FIG. 1.
Iron-centered oxidative transitions within hemoglobin (Hb). Hemin iron atoms within Hb undergo spontaneous oxidation from ferrous to ferric oxidation states. This process indirectly produces hydrogen peroxide, which can further react with ferric and ferrous Hb to produce ferryl species. Reductases within red blood cells keep the heme iron in the ferrous state. Redox potentials were obtained from Banerjee et al. (3). Figure constructed using the Illustrator (Adobe Systems Incorporated, Mountain View, CA) and PyMOL Molecular Graphics System (Schroödinger, LLC, New York, NY).
Pivotal questions exist about the reactions outlined in Figure 1, particularly relating to how other proteins such as Hp, alpha-hemoglobin stabilizing protein (AHSP), albumin, hemopexin (Hpx), and alpha-1 microglobulin (A1M) might relate to them. For example, recent work has demonstrated that Hp infusion into animals is effective in ameliorating Hb-associated oxidative toxicity (2). Moreover, in vitro and in vivo studies show that AHSP modulates the oxidation state of the free alpha-subunits of Hb in a way that stabilizes them (9), and A1M plays a role in heme degradation (10). Collectively, this work highlights both the potential of these proteins for therapeutic use and the realization that they are a part of a conserved strategy that has evolved to mitigate the deleterious effects of iron-catalyzed oxidative reactions.
The crystal structure of the Hb-Hp complex has recently been resolved for the first time, thus providing a great deal of structural insight about Hp's functional properties (1). According to this report, serine protease domains within Hp form extensive interactions with both the alpha- and beta-subunits of Hb (1). Several amino acids of the beta-subunits of Hb that have previously been shown to be susceptible to oxidative damage are no longer solvent-exposed when Hp is bound (1). These and other studies of Hp have begun to make it clear how the oxidative damage and pro-oxidant activity of Hb are controlled in vivo.
In this issue of Antioxidants and Redox Signaling, we present a series of reviews and original research communications that outline the current state of research regarding the redox reactions of Hb and the relevant mechanisms of its toxicity and control. Bonaventura et al. (4) describe the relationship between Hb oxidation and oxygenation, both in cells and in the acellular environment. Their review also discusses the underlying redox reactions in the context of nitrosative stress, sickle-cell disease, and Hb-based oxygen carrier research. They also describe a spectroelectrochemical method designed to measure Hb redox potentials (E½), both in the presence and absence of proteins such as Hp and AHSP. This review is complimented by a review from Richards that describes our current understanding of the biochemical redox properties of Mb. This monomeric molecular model system presents a somewhat simpler and equally well-studied system as Hb, and comparisons between Hb and Mb have long been useful. In this review, Richards outlines known the Mb redox mechanisms and discusses how they relate to the structural biology of Hb and Mb.
More specific examples of the diverse cellular and physiological consequences associated with Hb redox reactivity are described in detail in subsequent reviews. Rifkind and Nagababu review the reactions of deleterious oxygen and nitrogen species and describe how these compounds can damage the red cell membranes, membrane proteins, lipids, and cytoskeletal elements during the aging process of red blood cells. They also describe the metabolic changes within red blood cells that can arise as a result of Hb-mediated redox reactivity. Cabrales reviews the effects of the presence of acellular Hb in plasma on tissue microcirculation and how mechanical and biochemical forces converge to produce a unique environment facing free Hb. The interplay between Hb redox reactions are discussed, including the reaction with nitric oxide (NO) in the context of the microcirculation. He also discusses how various redox reactions affect the overall toxicity and efficacy of Hb-based blood substitutes. In a separate review, Cabrales and Friedman together summarize NO scavenging by Hb and discuss the current theories as to why acellular Hb causes vasoconstriction and hypertension, as well as some newly discovered Hb enzymatic activities that can control these reactions.
Some of most intriguing insights as to how Hp function and the clearance mechanism of the Hp-Hb complex by the macrophage-specific receptor CD163 are outlined in two original research communications and two reviews in this issue. This includes work by Etzerodt et al. (7), who describe the in vivo mechanisms of Hb clearance through the CD163-Hp interactions. In a separate review, Etzerodt and Moestrup (8) discuss their work exploring the use of CD163 as a potential biomarker or therapeutic drug target for inflammatory responses. Ratanasopa et al. have modeled the Hb-Hp interactions with work that complements recent X-ray crystallographic findings regarding the Hp-Hb interactions. They also describe the Hp function in vivo and ongoing work investigating the potential clinical applications of Hp in modulating inflammatory responses. Cooper et al. (6) present new and intriguing findings in which they show by photometric and electron paramagnetic resonance methods that the interaction of Hp with Hb leads to the stabilization of Hb's own Fe4+ radicals, thus enabling the complex to safely dissipate these damaging radicals.
Another review in this issue is by Varnado et al. (14), who discuss the recent developments in the area of blood-substitute research and recombinant Hb-based oxygen carriers. Their review addresses current protein-engineering strategies aimed at solving known problems relating to protein stability and redox reactivity. They also describe previous developments that have successfully been used to overcome known issues associated with acellular Hb toxicity (e.g., renal toxicity and short half-life).
Together, these submissions suggest that Hb redox chemistry and the mechanisms of its control will play an increasingly prominent role in our efforts to understand the physiological and pathophysiologal effects of acellular Hb in a variety of clinical settings. Although much work remains to be done, a full understanding of these events will, no doubt, greatly inform Hb-based oxygen carrier research and infusion-related complications. We thank the authors for their work in this area and hope that the readers find it to be as interesting and promising as we do.
Abbreviations Used
- A1M
alpha-1 microglobulin
- AHSP
alpha-hemoglobin-stabilizing protein
- Hb
hemoglobin
- H2O2
hydrogen peroxide
- Hp
haptoglobin
- Hpx
hemopexin
- Mb
myoglobin
- NO
nitric oxide
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by the CBER MODSCI program and National Institutes of Health Grant HL110900.
References
- 1.Andersen CB. Torvund-Jensen M. Nielsen MJ. Pinto de Oliveira CL. Hersleth H-P. Andersen NH. Pedersen JS. Andersen GR. Moestrup SK. Structure of the haptoglobin-hemoglobin complex. Nature. 2012;489:456–459. doi: 10.1038/nature11369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Baek JH. D'Agnillo F. Vallelian F. Pereira CP. Williams MC. Jia Y, et al. Hemoglobin driven pathophysiology is an in vivo consequence of the red blood cell storage lesion that can be attenuated in guinea pigs by haptoglobin therapy. J Clin Invest. 2012;122:1444–1458. doi: 10.1172/JCI59770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Banerjee S. Jia Y. Siburt CJP. Abraham B. Wood F. Bonaventura C. Henkens R. Crumbliss AL. Alayash AI. Haptoglobin alters oxygenation and oxidation of hemoglobin and decreases propagation of peroxide-induced oxidative reactions. Free Radical Biol Med. 2012;53:1317–1326. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2012.07.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bonaventura C. Henkens R. Alayash AI. Banerjee S. Crumbliss AL. Molecular controls of the oxygenation and redox reactions of hemoglobin. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013;18:2298–2313. doi: 10.1089/ars.2012.4947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Brantley RE., Jr. Smerdon SJ. Wilkinson AJ. Singleton EW. Olson JS. The mechanism of autooxidation of myoglobin. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:6995–7010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Cooper CE. Schaer DJ. Buehler PW. Wilson MT. Reeder BJ. Silkstone G. Svistunenko DA. Bulow L. Alayash AI. Haptoglobin binding stabilizes hemoglobin ferryl iron and the globin radical on tyrosine β145. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013;18:2264–2273. doi: 10.1089/ars.2012.4547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Etzerodt A. Kjolby M. Nielsen MJ. Maniecki M. Svendsen P. Moestrup SK. Plasma clearance of hemoglobin and haptoglobin in mice and effect of CD163 gene targeting disruption. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013;18:2254–2263. doi: 10.1089/ars.2012.4605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Etzerodt A. Moestrup SK. CD163 and inflammation: biological, diagnostic, and therapeutic aspects. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013;18:2352–2363. doi: 10.1089/ars.2012.4834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Feng L. Zhou S. Gu L. Gell DA. Mackay JP. Weiss MJ. Gow AJ. Shi Y. Structure of oxidized [alpha]-haemoglobin bound to AHSP reveals a protective mechanism for haem. Nature. 2005;435:697–701. doi: 10.1038/nature03609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Larsson J. Allhorn M. Åkerström B. The lipocalin α1-microglobulin binds heme in different species. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2004;432:196–204. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2004.09.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Reeder BJ. The redox activity of hemoglobins: from physiologic functions to pathologic mechanisms. Antioxid Redox Signaling. 2010;13:1087–1123. doi: 10.1089/ars.2009.2974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Rother RP. Bell L. Hillmen P. Gladwin MT. The clinical sequalae of intravascular hemolysis and extracellular plasma hemoglobin. JAMA. 2005;293:1653–1662. doi: 10.1001/jama.293.13.1653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Shikama K. The molecular mechanism of autoxidation for myoglobin and hemoglobin: a venerable puzzle. Chem Rev. 1998;98:1357–1373. doi: 10.1021/cr970042e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Varnado CL. Mollan TL. Birukou I. Smith BJZ. Henderson DP. Olson JS. Development of recombinant hemoglobin-based oxygen carriers. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013;18:2314–2328. doi: 10.1089/ars.2012.4917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]