Abstract
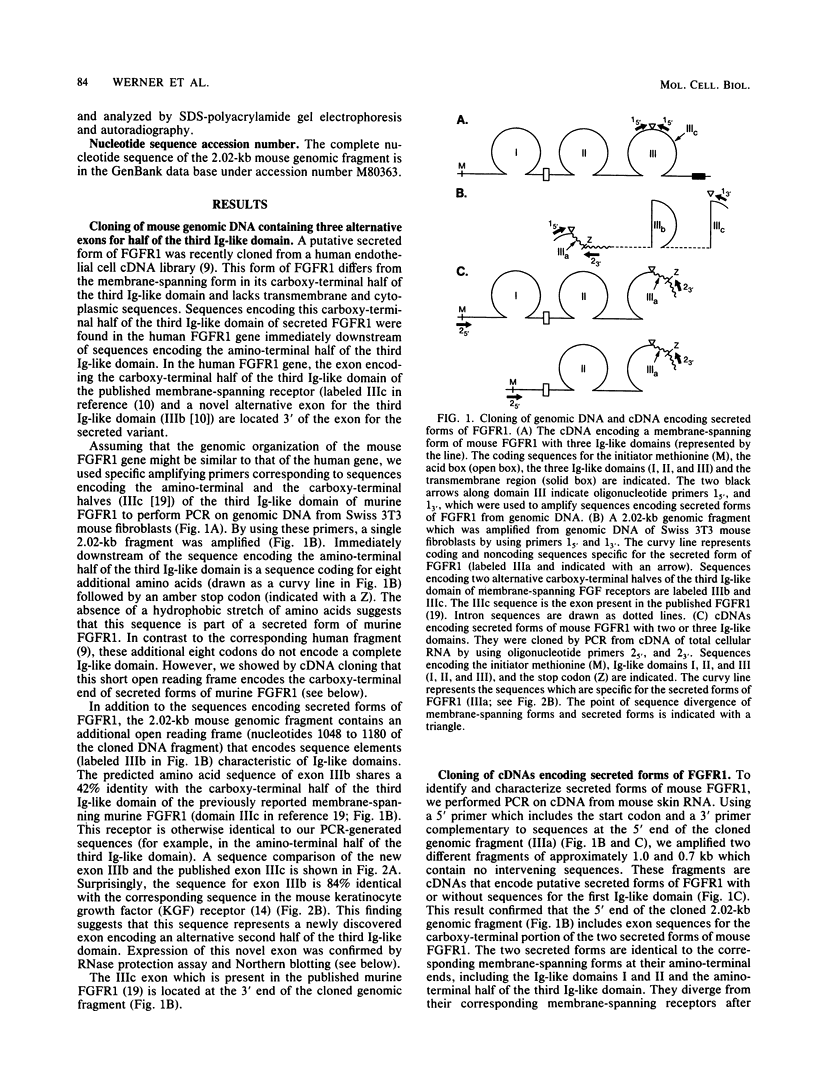
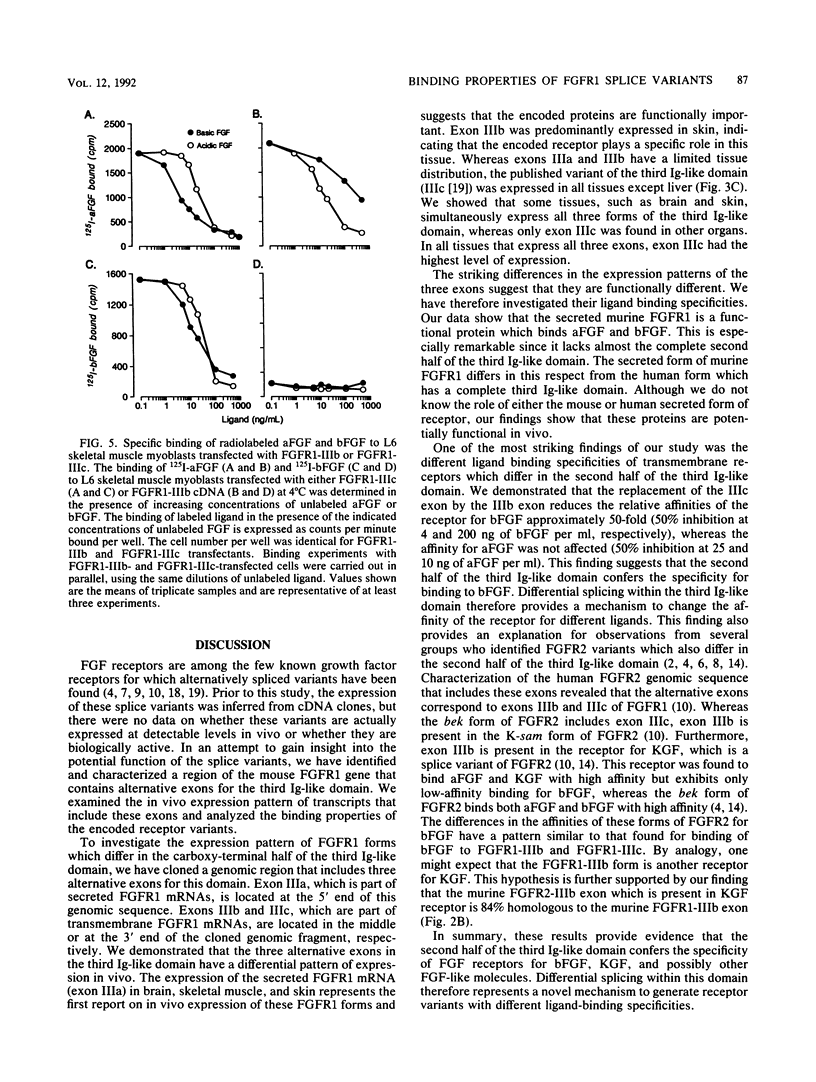
We have cloned a genomic region of the murine fibroblast growth factor (FGF) receptor 1 (FGFR1) gene that includes three alternative exons for the third immunoglobulinlike domain in the extracellular region of the receptor. The mRNA of one of these splice variants encodes a secreted receptor that lacks transmembrane and cytoplasmic sequences as well as a portion of the third immunoglobulinlike domain. Highest levels of mRNA encoding this variant were found in brain, skeletal muscle, and skin. We expressed this form of FGFR1 in CHO cells and showed that the recombinant secreted protein binds acidic FGF. We also discovered a novel alternative exon in the third immunoglobulinlike domain that encodes part of a transmembrane FGFR1 mRNA. This exon is highly homologous to the corresponding region of the keratinocyte growth factor receptor. Transcripts including this exon were present at highest levels in the skin. We cloned an FGFR1 cDNA which includes this exon and expressed this receptor variant in L6 rat skeletal muscle myoblasts. The new receptor variant had a 50-fold-lower affinity for basic FGF than does the published FGFR1 variant, whereas both forms of receptor bound acidic FGF with high affinity. These results show that the third immunoglobulinlike domain plays an important role in determining the binding specificities for different FGFs. Our data provide the first evidence that differential splicing in the extracellular region of a receptor gene generates receptor variants with different ligand-binding specificities.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Champion-Arnaud P., Ronsin C., Gilbert E., Gesnel M. C., Houssaint E., Breathnach R. Multiple mRNAs code for proteins related to the BEK fibroblast growth factor receptor. Oncogene. 1991 Jun;6(6):979–987. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dionne C. A., Crumley G., Bellot F., Kaplow J. M., Searfoss G., Ruta M., Burgess W. H., Jaye M., Schlessinger J. Cloning and expression of two distinct high-affinity receptors cross-reacting with acidic and basic fibroblast growth factors. EMBO J. 1990 Sep;9(9):2685–2692. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07454.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duan D. S., Pazin M. J., Fretto L. J., Williams L. T. A functional soluble extracellular region of the platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) beta-receptor antagonizes PDGF-stimulated responses. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 5;266(1):413–418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori Y., Odagiri H., Nakatani H., Miyagawa K., Naito K., Sakamoto H., Katoh O., Yoshida T., Sugimura T., Terada M. K-sam, an amplified gene in stomach cancer, is a member of the heparin-binding growth factor receptor genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5983–5987. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hou J. Z., Kan M. K., McKeehan K., McBride G., Adams P., McKeehan W. L. Fibroblast growth factor receptors from liver vary in three structural domains. Science. 1991 Feb 8;251(4994):665–668. doi: 10.1126/science.1846977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houssaint E., Blanquet P. R., Champion-Arnaud P., Gesnel M. C., Torriglia A., Courtois Y., Breathnach R. Related fibroblast growth factor receptor genes exist in the human genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):8180–8184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.8180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. E., Lee P. L., Lu J., Williams L. T. Diverse forms of a receptor for acidic and basic fibroblast growth factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4728–4736. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. E., Lu J., Chen H., Werner S., Williams L. T. The human fibroblast growth factor receptor genes: a common structural arrangement underlies the mechanisms for generating receptor forms that differ in their third immunoglobulin domain. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;11(9):4627–4634. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.9.4627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keegan K., Johnson D. E., Williams L. T., Hayman M. J. Isolation of an additional member of the fibroblast growth factor receptor family, FGFR-3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1095–1099. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P. L., Johnson D. E., Cousens L. S., Fried V. A., Williams L. T. Purification and complementary DNA cloning of a receptor for basic fibroblast growth factor. Science. 1989 Jul 7;245(4913):57–60. doi: 10.1126/science.2544996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki T., Fleming T. P., Bottaro D. P., Rubin J. S., Ron D., Aaronson S. A. Expression cDNA cloning of the KGF receptor by creation of a transforming autocrine loop. Science. 1991 Jan 4;251(4989):72–75. doi: 10.1126/science.1846048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partanen J., Mäkelä T. P., Eerola E., Korhonen J., Hirvonen H., Claesson-Welsh L., Alitalo K. FGFR-4, a novel acidic fibroblast growth factor receptor with a distinct expression pattern. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1347–1354. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07654.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasquale E. B. A distinctive family of embryonic protein-tyrosine kinase receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5812–5816. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petch L. A., Harris J., Raymond V. W., Blasband A., Lee D. C., Earp H. S. A truncated, secreted form of the epidermal growth factor receptor is encoded by an alternatively spliced transcript in normal rat tissue. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2973–2982. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid H. H., Wilks A. F., Bernard O. Two forms of the basic fibroblast growth factor receptor-like mRNA are expressed in the developing mouse brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1596–1600. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato M., Kitazawa T., Iwai T., Seki J., Sakato N., Kato J., Takeya T. Isolation of chicken-bek and a related gene; identification of structural variation in the ligand-binding domains of the FGF-receptor family. Oncogene. 1991 Jul;6(7):1279–1283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takebe Y., Seiki M., Fujisawa J., Hoy P., Yokota K., Arai K., Yoshida M., Arai N. SR alpha promoter: an efficient and versatile mammalian cDNA expression system composed of the simian virus 40 early promoter and the R-U5 segment of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 long terminal repeat. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):466–472. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner S., Hofschneider P. H., Roth W. K. Cells derived from sporadic and AIDS-related Kaposi's sarcoma reveal identical cytochemical and molecular properties in vitro. Int J Cancer. 1989 Jun 15;43(6):1137–1144. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910430629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]