Abstract
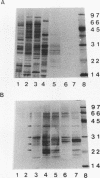
The Moloney murine leukemia virus causes thymic leukemias when injected into newborn mice. A major genetic determinant of the thymic disease specificity of the Moloney virus genetically maps to two protein binding sites in the Moloney virus enhancer, the leukemia virus factor b site and the adjacent core site. Point mutations introduced into either of these sites significantly shifts the disease specificity of the Moloney virus from thymic leukemia to erythroleukemia (N. A. Speck, B. Renjifo, E. Golemis, T. Frederickson, J. Hartley, and N. Hopkins, Genes Dev. 4:233-242, 1990). We have purified several polypeptides that bind to the core site in the Moloney virus enhancer. These proteins were purified from calf thymus nuclear extracts by selective pH denaturation, followed by chromatography on heparin-Sepharose, nonspecific double-stranded DNA-cellulose, and core oligonucleotide-coupled affinity columns. We have achieved greater than 13,000-fold purification of the core-binding factors (CBFs), with an overall yield of approximately 19%. Analysis of purified protein fractions by sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis reveals more than 10 polypeptides. Each of the polypeptides was recovered from an SDS-polyacrylamide gel, and those in the molecular size range of 19 to 35 kDa were demonstrated to have core-binding activity. The purified CBFs were shown by DNase I footprint analyses to bind the core site in the Moloney virus enhancer specifically, and also to core motifs in the enhancers from a simian immunodeficiency virus, the immunoglobulin mu chain, and T-cell receptor gamma-chain genes.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alt F. W., Rosenberg N., Enea V., Siden E., Baltimore D. Multiple immunoglobulin heavy-chain gene transcripts in Abelson murine leukemia virus-transformed lymphoid cell lines. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;2(4):386–400. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.4.386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkenmeier E. H., Gwynn B., Howard S., Jerry J., Gordon J. I., Landschulz W. H., McKnight S. L. Tissue-specific expression, developmental regulation, and genetic mapping of the gene encoding CCAAT/enhancer binding protein. Genes Dev. 1989 Aug;3(8):1146–1156. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.8.1146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boral A. L., Okenquist S. A., Lenz J. Identification of the SL3-3 virus enhancer core as a T-lymphoma cell-specific element. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):76–84. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.76-84.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celander D., Haseltine W. A. Tissue-specific transcription preference as a determinant of cell tropism and leukaemogenic potential of murine retroviruses. Nature. 1984 Nov 8;312(5990):159–162. doi: 10.1038/312159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti L., Guyader M., Alizon M., Daniel M. D., Desrosiers R. C., Tiollais P., Sonigo P. Sequence of simian immunodeficiency virus from macaque and its relationship to other human and simian retroviruses. Nature. 1987 Aug 6;328(6130):543–547. doi: 10.1038/328543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatis P. A., Holland C. A., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P., Hopkins N. Role for the 3' end of the genome in determining disease specificity of Friend and Moloney murine leukemia viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4408–4411. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatis P. A., Holland C. A., Silver J. E., Frederickson T. N., Hopkins N., Hartley J. W. A 3' end fragment encompassing the transcriptional enhancers of nondefective Friend virus confers erythroleukemogenicity on Moloney leukemia virus. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):248–254. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.248-254.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Franza B. R., Jr Fos and Jun: the AP-1 connection. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):395–397. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90024-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DesGroseillers L., Jolicoeur P. Mapping the viral sequences conferring leukemogenicity and disease specificity in Moloney and amphotropic murine leukemia viruses. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):448–456. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.448-456.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DesGroseillers L., Jolicoeur P. The tandem direct repeats within the long terminal repeat of murine leukemia viruses are the primary determinant of their leukemogenic potential. J Virol. 1984 Dec;52(3):945–952. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.3.945-952.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DesGroseillers L., Rassart E., Jolicoeur P. Thymotropism of murine leukemia virus is conferred by its long terminal repeat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4203–4207. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DesGroseillers L., Villemur R., Jolicoeur P. The high leukemogenic potential of Gross passage A murine leukemia virus maps in the region of the genome corresponding to the long terminal repeat and to the 3' end of env. J Virol. 1983 Jul;47(1):24–32. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.1.24-32.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillies S. D., Morrison S. L., Oi V. T., Tonegawa S. A tissue-specific transcription enhancer element is located in the major intron of a rearranged immunoglobulin heavy chain gene. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golemis E. A., Speck N. A., Hopkins N. Alignment of U3 region sequences of mammalian type C viruses: identification of highly conserved motifs and implications for enhancer design. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):534–542. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.534-542.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golemis E., Li Y., Fredrickson T. N., Hartley J. W., Hopkins N. Distinct segments within the enhancer region collaborate to specify the type of leukemia induced by nondefective Friend and Moloney viruses. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):328–337. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.328-337.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Weaver D., Baltimore D., Costantini F. Introduction of a mu immunoglobulin gene into the mouse germ line: specific expression in lymphoid cells and synthesis of functional antibody. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):647–658. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90259-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hager D. A., Burgess R. R. Elution of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels, removal of sodium dodecyl sulfate, and renaturation of enzymatic activity: results with sigma subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase, wheat germ DNA topoisomerase, and other enzymes. Anal Biochem. 1980 Nov 15;109(1):76–86. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halligan B. D., Desiderio S. V. Identification of a DNA binding protein that recognizes the nonamer recombinational signal sequence of immunoglobulin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7019–7023. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrickson W., Schleif R. A dimer of AraC protein contacts three adjacent major groove regions of the araI DNA site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3129–3133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henthorn P., Kiledjian M., Kadesch T. Two distinct transcription factors that bind the immunoglobulin enhancer microE5/kappa 2 motif. Science. 1990 Jan 26;247(4941):467–470. doi: 10.1126/science.2105528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W., Sturm R. A., Clerc R. G., Corcoran L. M., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A., Ingraham H. A., Rosenfeld M. G., Finney M., Ruvkun G. The POU domain: a large conserved region in the mammalian pit-1, oct-1, oct-2, and Caenorhabditis elegans unc-86 gene products. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1513–1516. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishimoto A., Adachi A., Sakai K., Matsuyama M. Long terminal repeat of Friend-MCF virus contains the sequence responsible for erythroid leukemia. Virology. 1985 Feb;141(1):30–42. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90180-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., Landschulz W. H., Graves B. J., McKnight S. L. Identification of a rat liver nuclear protein that binds to the enhancer core element of three animal viruses. Genes Dev. 1987 Apr;1(2):133–146. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.2.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadesch T., Zervos P., Ruezinsky D. Functional analysis of the murine IgH enhancer: evidence for negative control of cell-type specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Oct 24;14(20):8209–8221. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.20.8209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Tjian R. Affinity purification of sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5889–5893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp D. J., Harris A. W., Cory S., Adams J. M. Expression of the immunoglobulin C mu gene in mouse T and B lymphoid and myeloid cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2876–2880. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenz J., Celander D., Crowther R. L., Patarca R., Perkins D. W., Haseltine W. A. Determination of the leukaemogenicity of a murine retrovirus by sequences within the long terminal repeat. 1984 Mar 29-Apr 4Nature. 308(5958):467–470. doi: 10.1038/308467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Golemis E., Hartley J. W., Hopkins N. Disease specificity of nondefective Friend and Moloney murine leukemia viruses is controlled by a small number of nucleotides. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):693–700. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.693-700.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LoSardo J. E., Boral A. L., Lenz J. Relative importance of elements within the SL3-3 virus enhancer for T-cell specificity. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1756–1763. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1756-1763.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LoSardo J. E., Cupelli L. A., Short M. K., Berman J. W., Lenz J. Differences in activities of murine retroviral long terminal repeats in cytotoxic T lymphocytes and T-lymphoma cells. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1087–1094. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1087-1094.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley N. R., O'Connell M. A., Sharp P. A., Hopkins N. Nuclear factors that bind to the enhancer region of nondefective Friend murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4210–4223. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4210-4223.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercurio F., Karin M. Transcription factors AP-3 and AP-2 interact with the SV40 enhancer in a mutually exclusive manner. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1455–1460. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03528.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muesing M. A., Smith D. H., Cabradilla C. D., Benton C. V., Lasky L. A., Capon D. J. Nucleic acid structure and expression of the human AIDS/lymphadenopathy retrovirus. Nature. 1985 Feb 7;313(6002):450–458. doi: 10.1038/313450a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Baltimore D. A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):777–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90682-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redondo J. M., Hata S., Brocklehurst C., Krangel M. S. A T cell-specific transcriptional enhancer within the human T cell receptor delta locus. Science. 1990 Mar 9;247(4947):1225–1229. doi: 10.1126/science.2156339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renjifo B., Speck N. A., Winandy S., Hopkins N., Li Y. cis-acting elements in the U3 region of a simian immunodeficiency virus. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):3130–3134. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.3130-3134.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld P. J., Kelly T. J. Purification of nuclear factor I by DNA recognition site affinity chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):1398–1408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoro C., Mermod N., Andrews P. C., Tjian R. A family of human CCAAT-box-binding proteins active in transcription and DNA replication: cloning and expression of multiple cDNAs. Nature. 1988 Jul 21;334(6179):218–224. doi: 10.1038/334218a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., Sen R., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. A nuclear factor that binds to a conserved sequence motif in transcriptional control elements of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):154–158. doi: 10.1038/319154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speck N. A., Baltimore D. Six distinct nuclear factors interact with the 75-base-pair repeat of the Moloney murine leukemia virus enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1101–1110. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speck N. A., Renjifo B., Golemis E., Fredrickson T. N., Hartley J. W., Hopkins N. Mutation of the core or adjacent LVb elements of the Moloney murine leukemia virus enhancer alters disease specificity. Genes Dev. 1990 Feb;4(2):233–242. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.2.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speck N. A., Renjifo B., Hopkins N. Point mutations in the Moloney murine leukemia virus enhancer identify a lymphoid-specific viral core motif and 1,3-phorbol myristate acetate-inducible element. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):543–550. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.543-550.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer D. M., Hsiang Y. H., Goldman J. P., Raulet D. H. Identification of a T-cell-specific transcriptional enhancer located 3' of C gamma 1 in the murine T-cell receptor gamma locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):800–804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storb U., Pinkert C., Arp B., Engler P., Gollahon K., Manz J., Brady W., Brinster R. L. Transgenic mice with mu and kappa genes encoding antiphosphorylcholine antibodies. J Exp Med. 1986 Aug 1;164(2):627–641. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.2.627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornell A., Hallberg B., Grundström T. Binding of SL3-3 enhancer factor 1 transcriptional activators to viral and chromosomal enhancer sequences. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):42–50. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.42-50.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornell A., Hallberg B., Grundström T. Differential protein binding in lymphocytes to a sequence in the enhancer of the mouse retrovirus SL3-3. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1625–1637. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiher H., König M., Gruss P. Multiple point mutations affecting the simian virus 40 enhancer. Science. 1983 Feb 11;219(4585):626–631. doi: 10.1126/science.6297005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winoto A., Baltimore D. A novel, inducible and T cell-specific enhancer located at the 3' end of the T cell receptor alpha locus. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):729–733. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03432.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W., Boulikas T., Wray V. P., Hancock R. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao J. H., Davidson I., Matthes H., Garnier J. M., Chambon P. Cloning, expression, and transcriptional properties of the human enhancer factor TEF-1. Cell. 1991 May 17;65(4):551–568. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90088-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]