Abstract
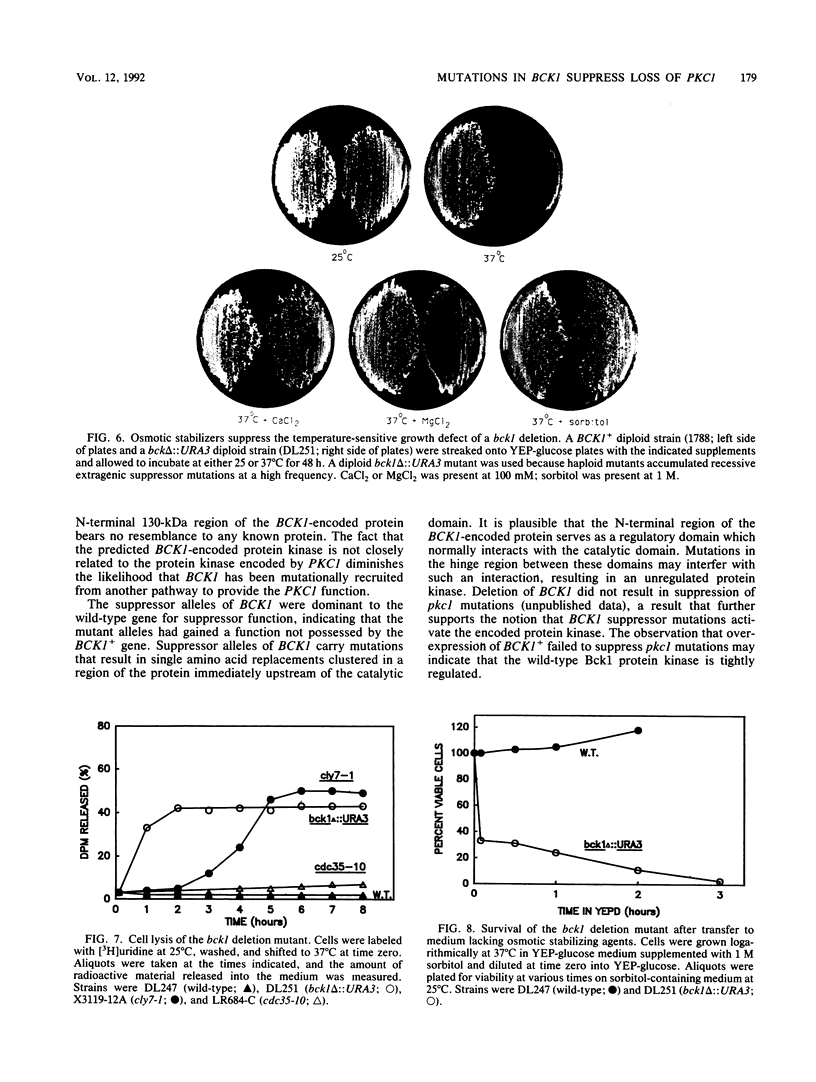
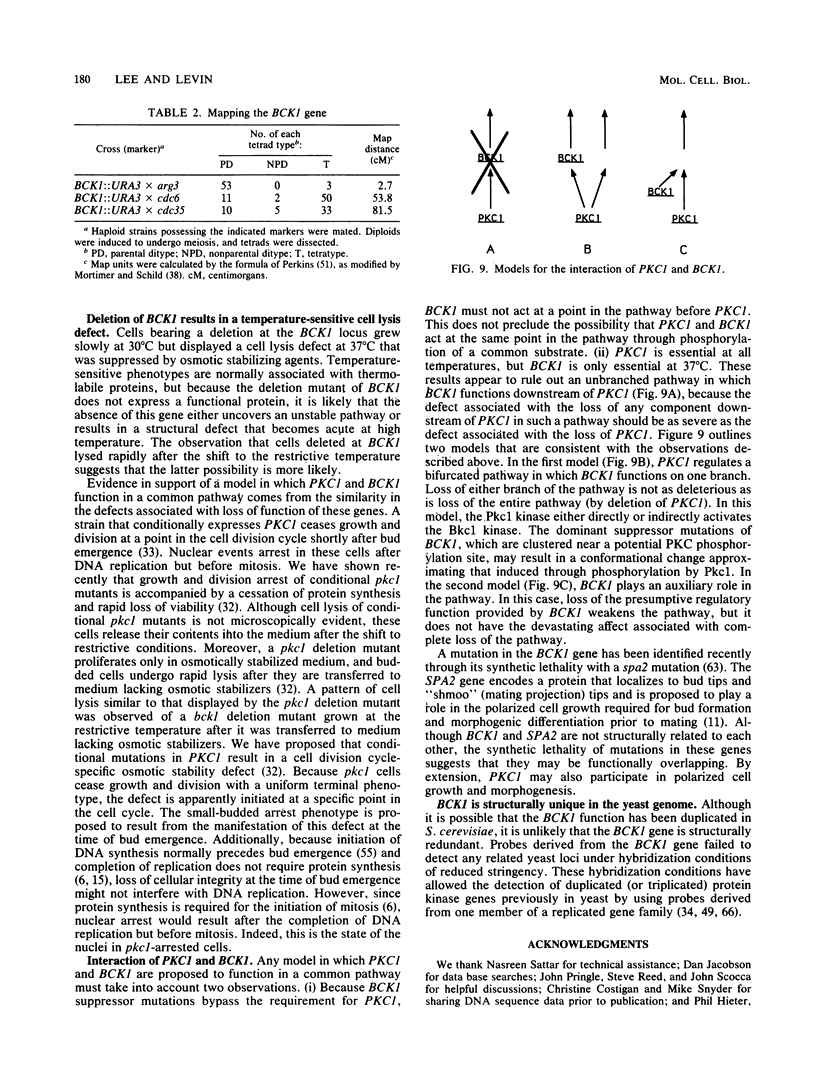
The PKC1 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae encodes a homolog of mammalian protein kinase C that is required for yeast cell growth and division. To identify additional components of the pathway in which PKC1 functions, we isolated extragenic suppressors of a pkc1 deletion mutant. All of the suppressor mutations were dominant for suppressor function and defined a single locus, which was designated BCK1 (for bypass of C kinase). A molecular clone of one suppressor allele, BCK1-20, was isolated on a centromere-containing plasmid through its ability to rescue a conditional pkc1 mutant. The BCK1 gene possesses a 4.4-kb uninterrupted open reading frame predicted to encode a 163-kDa protein kinase. The BCK1 gene product is not closely related to any known protein kinase, sharing only 45% amino acid identity with its closest known relative (the STE11-encoded protein kinase) through a region restricted to its putative C-terminal catalytic domain. Deletion of BCK1 resulted in a temperature-sensitive cell lysis defect, which was suppressed by osmotic stabilizing agents. Because pkc1 mutants also display a cell lysis defect, we suggest that PKC1 and BCK1 may normally function within the same pathway. Suppressor alleles of BCK1 differed from the wild-type gene in a region surrounding a potential PKC phosphorylation site immediately upstream of the predicted catalytic domain. This region may serve as a hinge between domains whose interaction is regulated by PKC1.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angel P., Imagawa M., Chiu R., Stein B., Imbra R. J., Rahmsdorf H. J., Jonat C., Herrlich P., Karin M. Phorbol ester-inducible genes contain a common cis element recognized by a TPA-modulated trans-acting factor. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90611-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A., Baltimore D. Activation of DNA-binding activity in an apparently cytoplasmic precursor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):211–217. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90382-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., LaCroute F., Fink G. R. A positive selection for mutants lacking orotidine-5'-phosphate decarboxylase activity in yeast: 5-fluoro-orotic acid resistance. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;197(2):345–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00330984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D. J., Church D. Protein synthesis requirements for nuclear division, cytokinesis, and cell separation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;11(7):3691–3698. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.7.3691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu R., Imagawa M., Imbra R. J., Bockoven J. R., Karin M. Multiple cis- and trans-acting elements mediate the transcriptional response to phorbol esters. Nature. 1987 Oct 15;329(6140):648–651. doi: 10.1038/329648a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colamonici O. R., Trepel J. B., Vidal C. A., Neckers L. M. Phorbol ester induces c-sis gene transcription in stem cell line K-562. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1847–1850. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coughlin S. R., Lee W. M., Williams P. W., Giels G. M., Williams L. T. c-myc gene expression is stimulated by agents that activate protein kinase C and does not account for the mitogenic effect of PDGF. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):243–251. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90029-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farley J., Auerbach S. Protein kinase C activation induces conductance changes in Hermissenda photoreceptors like those seen in associative learning. Nature. 1986 Jan 16;319(6050):220–223. doi: 10.1038/319220a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehrung S., Snyder M. The SPA2 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is important for pheromone-induced morphogenesis and efficient mating. J Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;111(4):1451–1464. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.4.1451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Ziff E. B. Stimulation of 3T3 cells induces transcription of the c-fos proto-oncogene. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):433–438. doi: 10.1038/311433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hereford L. M., Hartwell L. H. Role of protein synthesis in the replication of yeast DNA. Nat New Biol. 1973 Aug 1;244(135):129–131. doi: 10.1038/newbio244129a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hokin L. E. Receptors and phosphoinositide-generated second messengers. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:205–235. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.001225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- House C., Kemp B. E. Protein kinase C contains a pseudosubstrate prototope in its regulatory domain. Science. 1987 Dec 18;238(4834):1726–1728. doi: 10.1126/science.3686012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- House C., Wettenhall R. E., Kemp B. E. The influence of basic residues on the substrate specificity of protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 15;262(2):772–777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imagawa M., Chiu R., Karin M. Transcription factor AP-2 mediates induction by two different signal-transduction pathways: protein kinase C and cAMP. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90152-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imbra R. J., Karin M. Phorbol ester induces the transcriptional stimulatory activity of the SV40 enhancer. Nature. 1986 Oct 9;323(6088):555–558. doi: 10.1038/323555a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irniger S., Egli C. M., Braus G. H. Different classes of polyadenylation sites in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):3060–3069. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.3060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston M., Davis R. W. Sequences that regulate the divergent GAL1-GAL10 promoter in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1440–1448. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaibuchi K., Takai Y., Nishizuka Y. Protein kinase C and calcium ion in mitogenic response of macrophage-depleted human peripheral lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1366–1369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K., Cochran B. H., Stiles C. D., Leder P. Cell-specific regulation of the c-myc gene by lymphocyte mitogens and platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikkawa U., Kishimoto A., Nishizuka Y. The protein kinase C family: heterogeneity and its implications. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:31–44. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.000335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto A., Takai Y., Mori T., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Activation of calcium and phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by diacylglycerol, its possible relation to phosphatidylinositol turnover. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 25;255(6):2273–2276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruijer W., Cooper J. A., Hunter T., Verma I. M. Platelet-derived growth factor induces rapid but transient expression of the c-fos gene and protein. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):711–716. doi: 10.1038/312711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langford C. J., Gallwitz D. Evidence for an intron-contained sequence required for the splicing of yeast RNA polymerase II transcripts. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):519–527. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90433-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W., Haslinger A., Karin M., Tjian R. Activation of transcription by two factors that bind promoter and enhancer sequences of the human metallothionein gene and SV40. Nature. 1987 Jan 22;325(6102):368–372. doi: 10.1038/325368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin D. E., Fields F. O., Kunisawa R., Bishop J. M., Thorner J. A candidate protein kinase C gene, PKC1, is required for the S. cerevisiae cell cycle. Cell. 1990 Jul 27;62(2):213–224. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90360-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin D. E., Hammond C. I., Ralston R. O., Bishop J. M. Two yeast genes that encode unusual protein kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6035–6039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüscher B., Mitchell P. J., Williams T., Tjian R. Regulation of transcription factor AP-2 by the morphogen retinoic acid and by second messengers. Genes Dev. 1989 Oct;3(10):1507–1517. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.10.1507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madison D. V., Malenka R. C., Nicoll R. A. Phorbol esters block a voltage-sensitive chloride current in hippocampal pyramidal cells. Nature. 1986 Jun 12;321(6071):695–697. doi: 10.1038/321695a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortimer R. K., Schild D. Genetic map of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, edition 9. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Sep;49(3):181–213. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.3.181-213.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negro-Vilar A., Lapetina E. G. 1,2-Didecanoylglycerol and phorbol 12,13-dibutyrate enhance anterior pituitary hormone secretion in vitro. Endocrinology. 1985 Oct;117(4):1559–1564. doi: 10.1210/endo-117-4-1559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Studies and perspectives of protein kinase C. Science. 1986 Jul 18;233(4761):305–312. doi: 10.1126/science.3014651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The molecular heterogeneity of protein kinase C and its implications for cellular regulation. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):661–665. doi: 10.1038/334661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohmura E., Friesen H. G. 12-O-tetradecanoyl phorbol-13-acetate stimulates rat growth hormone (GH) release through different pathways from that of human pancreatic GH-releasing factor. Endocrinology. 1985 Feb;116(2):728–733. doi: 10.1210/endo-116-2-728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno S., Akita Y., Konno Y., Imajoh S., Suzuki K. A novel phorbol ester receptor/protein kinase, nPKC, distantly related to the protein kinase C family. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):731–741. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90091-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono Y., Fujii T., Ogita K., Kikkawa U., Igarashi K., Nishizuka Y. Protein kinase C zeta subspecies from rat brain: its structure, expression, and properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3099–3103. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono Y., Fujii T., Ogita K., Kikkawa U., Igarashi K., Nishizuka Y. The structure, expression, and properties of additional members of the protein kinase C family. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6927–6932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr-Weaver T. L., Szostak J. W., Rothstein R. J. Genetic applications of yeast transformation with linear and gapped plasmids. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:228–245. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paerl H. W., Bebout B. M. Direct measurement of o2-depleted microzones in marine oscillatoria: relation to n2 fixation. Science. 1988 Jul 22;241(4864):442–445. doi: 10.1126/science.241.4864.442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pausch M. H., Kaim D., Kunisawa R., Admon A., Thorner J. Multiple Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase genes in a unicellular eukaryote. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1511–1522. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07671.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins D. D. Biochemical Mutants in the Smut Fungus Ustilago Maydis. Genetics. 1949 Sep;34(5):607–626. doi: 10.1093/genetics/34.5.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persons D. A., Wilkison W. O., Bell R. M., Finn O. J. Altered growth regulation and enhanced tumorigenicity of NIH 3T3 fibroblasts transfected with protein kinase C-I cDNA. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):447–458. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80037-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes N., Connell L., Errede B. STE11 is a protein kinase required for cell-type-specific transcription and signal transduction in yeast. Genes Dev. 1990 Nov;4(11):1862–1874. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.11.1862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivin C. J., Fangman W. L. Cell cycle phase expansion in nitrogen-limited cultures of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Biol. 1980 Apr;85(1):96–107. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.1.96. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. J. One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:202–211. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E., Rodriguez-Pena A., Coombs M., Sinnett-Smith J. Diacylglycerol stimulates DNA synthesis and cell division in mouse 3T3 cells: role of Ca2+-sensitive phospholipid-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5748–5752. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Hieter P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siliciano P. G., Tatchell K. Transcription and regulatory signals at the mating type locus in yeast. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):969–978. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90431-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai Y., Kishimoto A., Kikkawa U., Mori T., Nishizuka Y. Unsaturated diacylglycerol as a possible messenger for the activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Dec 28;91(4):1218–1224. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91197-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda T., Cameron S., Sass P., Zoller M., Wigler M. Three different genes in S. cerevisiae encode the catalytic subunits of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Cell. 1987 Jul 17;50(2):277–287. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90223-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Arsdell S. W., Stetler G. L., Thorner J. The yeast repeated element sigma contains a hormone-inducible promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):749–759. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vollrath D., Davis R. W., Connelly C., Hieter P. Physical mapping of large DNA by chromosome fragmentation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):6027–6031. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.6027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winston F., Chumley F., Fink G. R. Eviction and transplacement of mutant genes in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:211–228. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01016-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaret K. S., Sherman F. DNA sequence required for efficient transcription termination in yeast. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):563–573. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90211-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]