Abstract
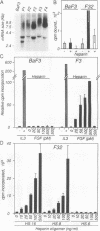
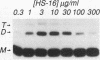
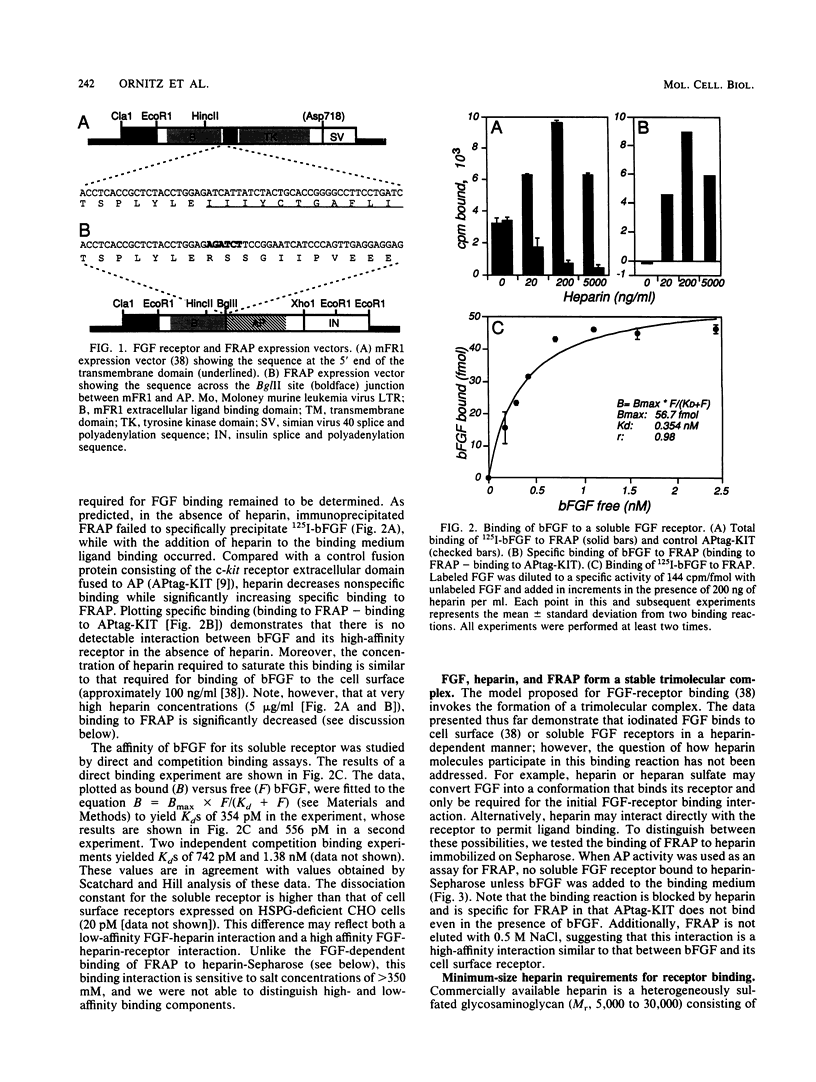
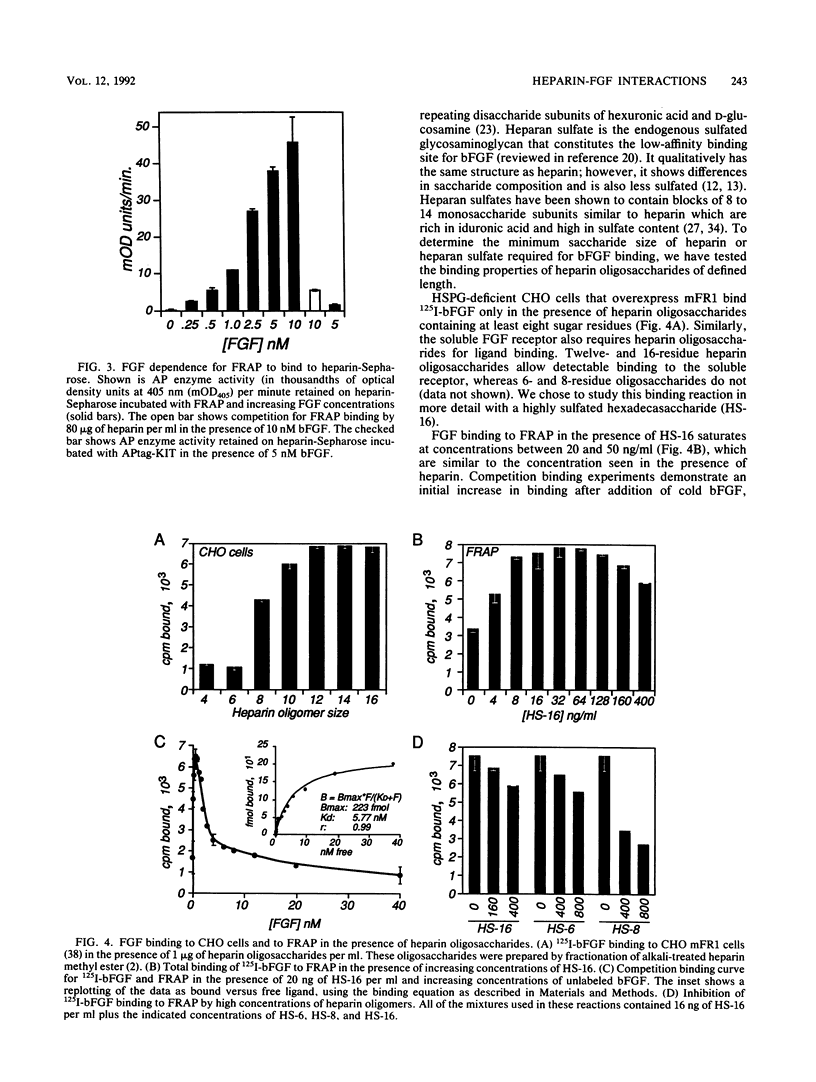
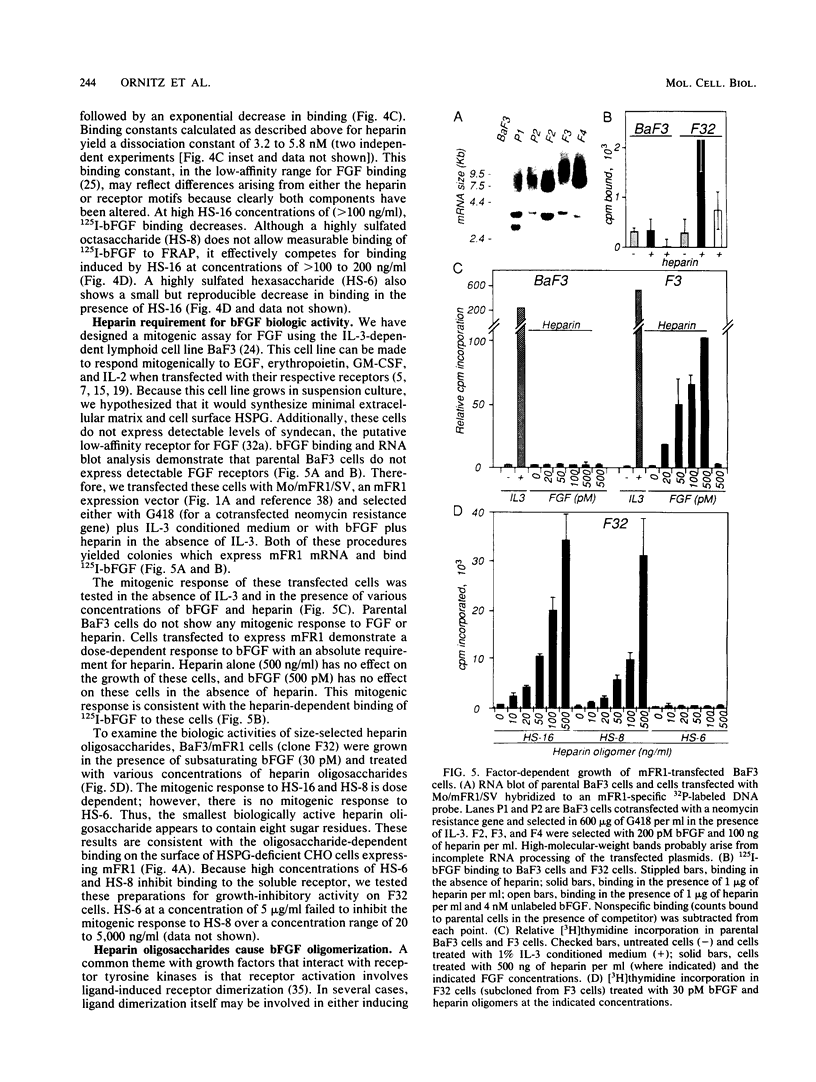
Heparin is required for the binding of basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) to high-affinity receptors on cells deficient in cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycan. So that this heparin requirement could be evaluated in the absence of other cell surface molecules, we designed a simple assay based on a genetically engineered soluble form of murine FGF receptor 1 (mFR1) tagged with placental alkaline phosphatase. Using this assay, we showed that FGF-receptor binding has an absolute requirement for heparin. By using a cytokine-dependent lymphoid cell line engineered to express mFR1, we also showed that FGF-induced mitogenic activity is heparin dependent. Furthermore, we tested a series of small heparin oligosaccharides of defined lengths for their abilities to support bFGF-receptor binding and biologic activity. We found that a heparin oligosaccharide with as few as eight sugar residues is sufficient to support these activities. We also demonstrated that heparin facilitates FGF dimerization, a property that may be important for receptor activation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baird A., Schubert D., Ling N., Guillemin R. Receptor- and heparin-binding domains of basic fibroblast growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2324–2328. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bashkin P., Doctrow S., Klagsbrun M., Svahn C. M., Folkman J., Vlodavsky I. Basic fibroblast growth factor binds to subendothelial extracellular matrix and is released by heparitinase and heparin-like molecules. Biochemistry. 1989 Feb 21;28(4):1737–1743. doi: 10.1021/bi00430a047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger J., Hauber J., Hauber R., Geiger R., Cullen B. R. Secreted placental alkaline phosphatase: a powerful new quantitative indicator of gene expression in eukaryotic cells. Gene. 1988 Jun 15;66(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90219-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrus L. W., Olwin B. B. Isolation of a receptor for acidic and basic fibroblast growth factor from embryonic chick. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18647–18653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M. K., Downward J., Miyajima A., Maruyama K., Arai K., Mulligan R. C. Transfer of functional EGF receptors to an IL3-dependent cell line. J Cell Physiol. 1988 Nov;137(2):293–298. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041370212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook P. W., Mattox P. A., Keeble W. W., Pittelkow M. R., Plowman G. D., Shoyab M., Adelman J. P., Shipley G. D. A heparin sulfate-regulated human keratinocyte autocrine factor is similar or identical to amphiregulin. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2547–2557. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Andrea A. D., Yoshimura A., Youssoufian H., Zon L. I., Koo J. W., Lodish H. F. The cytoplasmic region of the erythropoietin receptor contains nonoverlapping positive and negative growth-regulatory domains. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):1980–1987. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson A. E., Cousens L. S., Weaver L. H., Matthews B. W. Three-dimensional structure of human basic fibroblast growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3441–3445. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan J. G., Leder P. The kit ligand: a cell surface molecule altered in steel mutant fibroblasts. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):185–194. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90299-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Langer R., Linhardt R. J., Haudenschild C., Taylor S. Angiogenesis inhibition and tumor regression caused by heparin or a heparin fragment in the presence of cortisone. Science. 1983 Aug 19;221(4612):719–725. doi: 10.1126/science.6192498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox G. M., Schiffer S. G., Rohde M. F., Tsai L. B., Banks A. R., Arakawa T. Production, biological activity, and structure of recombinant basic fibroblast growth factor and an analog with cysteine replaced by serine. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18452–18458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher J. T., Lyon M., Steward W. P. Structure and function of heparan sulphate proteoglycans. Biochem J. 1986 Jun 1;236(2):313–325. doi: 10.1042/bj2360313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher J. T., Walker A. Molecular distinctions between heparan sulphate and heparin. Analysis of sulphation patterns indicates that heparan sulphate and heparin are separate families of N-sulphated polysaccharides. Biochem J. 1985 Sep 15;230(3):665–674. doi: 10.1042/bj2300665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Ferrara N., Schweigerer L., Neufeld G. Structural characterization and biological functions of fibroblast growth factor. Endocr Rev. 1987 May;8(2):95–114. doi: 10.1210/edrv-8-2-95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatakeyama M., Mori H., Doi T., Taniguchi T. A restricted cytoplasmic region of IL-2 receptor beta chain is essential for growth signal transduction but not for ligand binding and internalization. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):837–845. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90607-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashiyama S., Abraham J. A., Miller J., Fiddes J. C., Klagsbrun M. A heparin-binding growth factor secreted by macrophage-like cells that is related to EGF. Science. 1991 Feb 22;251(4996):936–939. doi: 10.1126/science.1840698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karasuyama H., Melchers F. Establishment of mouse cell lines which constitutively secrete large quantities of interleukin 2, 3, 4 or 5, using modified cDNA expression vectors. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Jan;18(1):97–104. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiefer M. C., Stephans J. C., Crawford K., Okino K., Barr P. J. Ligand-affinity cloning and structure of a cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycan that binds basic fibroblast growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):6985–6989. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.6985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura T., Hayashida K., Sakamaki K., Yokota T., Arai K., Miyajima A. Reconstitution of functional receptors for human granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF): evidence that the protein encoded by the AIC2B cDNA is a subunit of the murine GM-CSF receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5082–5086. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klagsbrun M. The affinity of fibroblast growth factors (FGFs) for heparin; FGF-heparan sulfate interactions in cells and extracellular matrix. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;2(5):857–863. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(90)90084-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lax I., Mitra A. K., Ravera C., Hurwitz D. R., Rubinstein M., Ullrich A., Stroud R. M., Schlessinger J. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) induces oligomerization of soluble, extracellular, ligand-binding domain of EGF receptor. A low resolution projection structure of the ligand-binding domain. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 25;266(21):13828–13833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathey-Prevot B., Nabel G., Palacios R., Baltimore D. Abelson virus abrogation of interleukin-3 dependence in a lymphoid cell line. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):4133–4135. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.4133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscatelli D. High and low affinity binding sites for basic fibroblast growth factor on cultured cells: absence of a role for low affinity binding in the stimulation of plasminogen activator production by bovine capillary endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 1987 Apr;131(1):123–130. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041310118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscatelli D. Metabolism of receptor-bound and matrix-bound basic fibroblast growth factor by bovine capillary endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;107(2):753–759. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.2.753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nader H. B., Dietrich C. P., Buonassisi V., Colburn P. Heparin sequences in the heparan sulfate chains of an endothelial cell proteoglycan. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3565–3569. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palacios R., Steinmetz M. Il-3-dependent mouse clones that express B-220 surface antigen, contain Ig genes in germ-line configuration, and generate B lymphocytes in vivo. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):727–734. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80053-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapraeger A. C., Krufka A., Olwin B. B. Requirement of heparan sulfate for bFGF-mediated fibroblast growth and myoblast differentiation. Science. 1991 Jun 21;252(5013):1705–1708. doi: 10.1126/science.1646484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R., Gallagher J., Spooncer E., Allen T. D., Bloomfield F., Dexter T. M. Heparan sulphate bound growth factors: a mechanism for stromal cell mediated haemopoiesis. Nature. 1988 Mar 24;332(6162):376–378. doi: 10.1038/332376a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E. Proteoglycans in cell regulation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13369–13372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Yamaguchi Y. Proteoglycans as modulators of growth factor activities. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):867–869. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90308-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sudhalter J., Folkman J., Svahn C. M., Bergendal K., D'Amore P. A. Importance of size, sulfation, and anticoagulant activity in the potentiation of acidic fibroblast growth factor by heparin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 25;264(12):6892–6897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnbull J. E., Gallagher J. T. Distribution of iduronate 2-sulphate residues in heparan sulphate. Evidence for an ordered polymeric structure. Biochem J. 1991 Feb 1;273(Pt 3):553–559. doi: 10.1042/bj2730553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90801-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlodavsky I., Folkman J., Sullivan R., Fridman R., Ishai-Michaeli R., Sasse J., Klagsbrun M. Endothelial cell-derived basic fibroblast growth factor: synthesis and deposition into subendothelial extracellular matrix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2292–2296. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yayon A., Klagsbrun M., Esko J. D., Leder P., Ornitz D. M. Cell surface, heparin-like molecules are required for binding of basic fibroblast growth factor to its high affinity receptor. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):841–848. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90512-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]