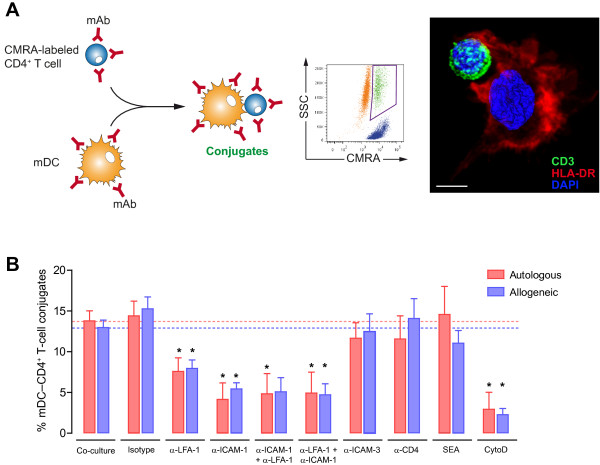
Figure 2.
Blocking of ICAM-1 and LFA-1 impairs conjugate formation between mDC and primary CD4+ T cells. A.Left. Experimental procedure for quantification of cell conjugates between mDC and CMRA-labeled CD4+ T cells in the presence or absence of several reagents. Cell conjugates were analyzed by flow cytometry as in Figure 1B. Right. Phenotype of mDC-CD4+ T cell contact by confocal microscopy. HLA-DR and CD3 molecules were stained to unequivocally identify the mDC and the CD4+ T cell, respectively. Confocal Z-stacks were acquired every 0.25 μm steps and processed with Volocity 6.1 software (improvision, PerkinElmer) using the maximum fluorescent intensity projection for HLA-DR and CD3 stainings and the isosurface modeling for DAPI-stained nucleus (scale bar: 5 μm). B. Comparative quantification of cellular conjugates after 2 hours of autologous (red bars) or allogeneic co-cultures (blue bars) between mDC and non-activated CD4+ T cells. Blocking of LFA-1 and ICAM-1 significantly inhibited the formation of autologous and allogeneic conjugates. Both autologous and allogeneic conjugates were equally affected by the blocking reagents. No differences were detected between autologous and allogeneic co-cultures. The α-ICAM-1 + α-LFA-1 condition represents separate pre-incubation of mDC with α-ICAM-1 mAb and CD4+ T cells with α-LFA-1 mAb, before launching co-culture, while the α-LFA-1 + α-ICAM-1 condition designates separate pre-incubation of mDC with α-LFA-1 mAb and CD4+ T cells with α-ICAM-1 mAb. Asterisks indicate significant differences compared with negative controls (p < 0.05); mAb conditions were compared with an isotype control, whereas SEA and cytochalasin D were compared with medium. Data are expressed as mean and SEM from at least three independent experiments including cells from at least six different donors.