Abstract
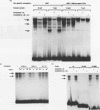
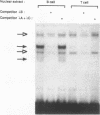
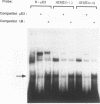
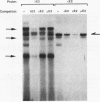
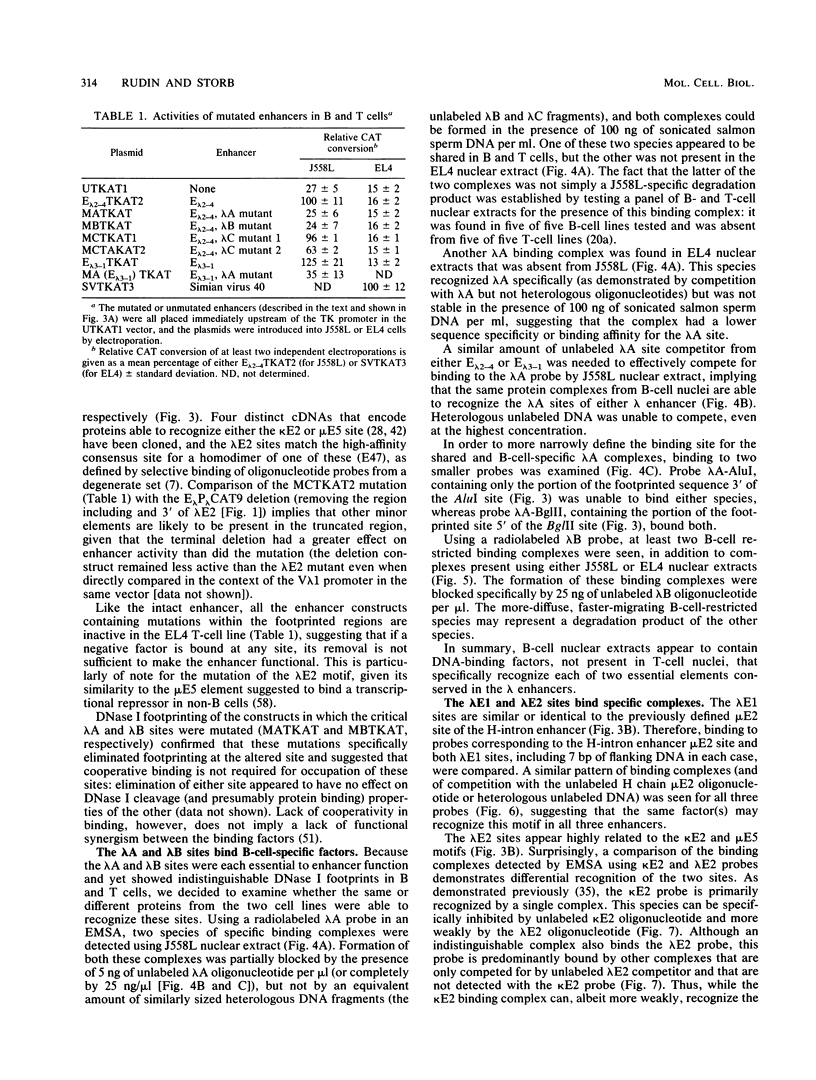
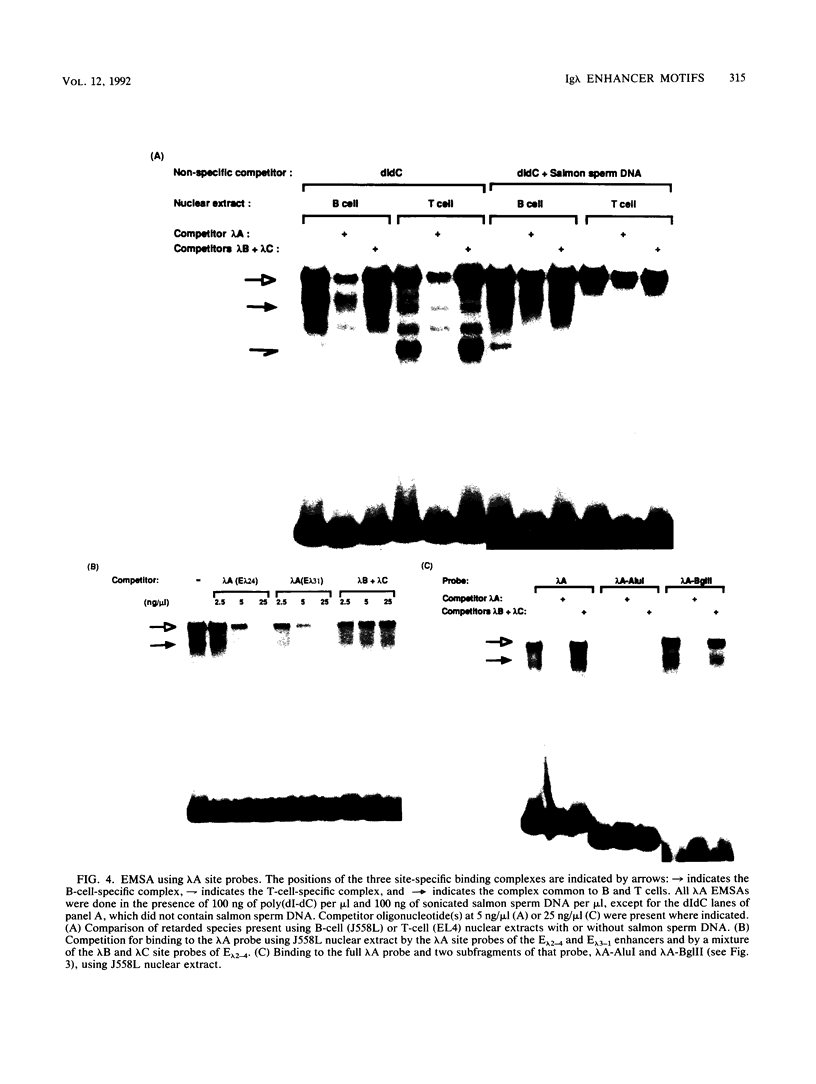
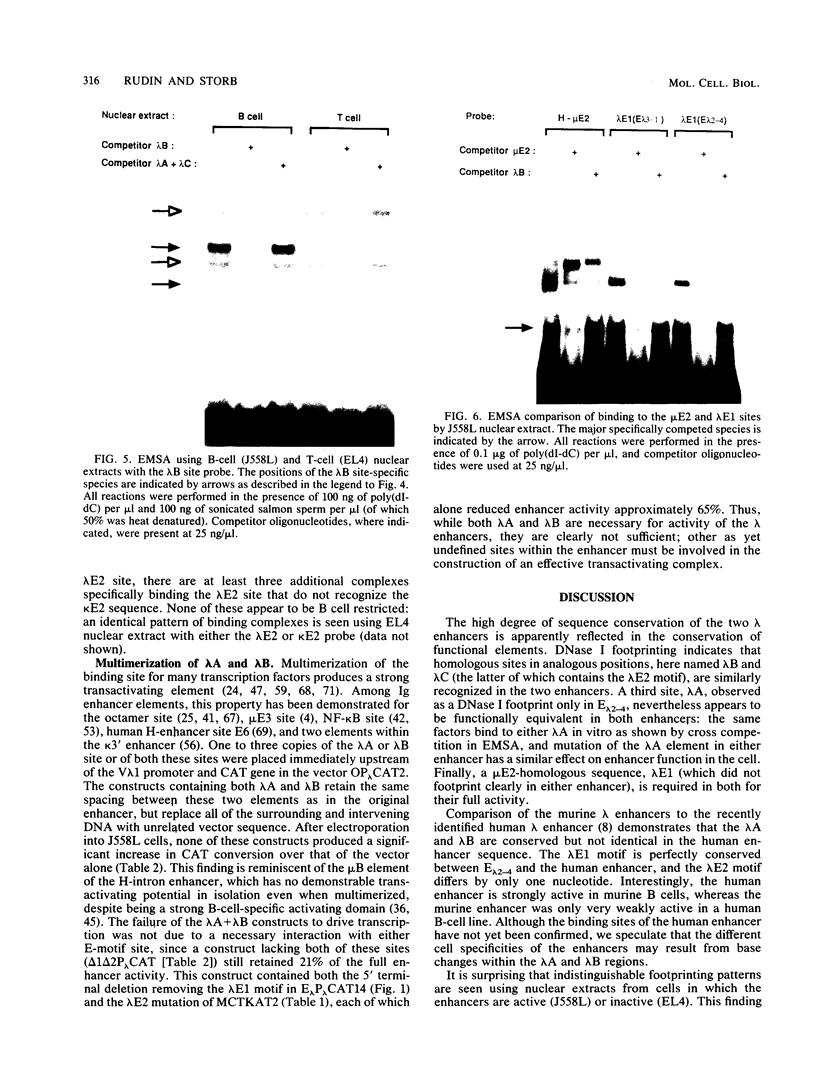
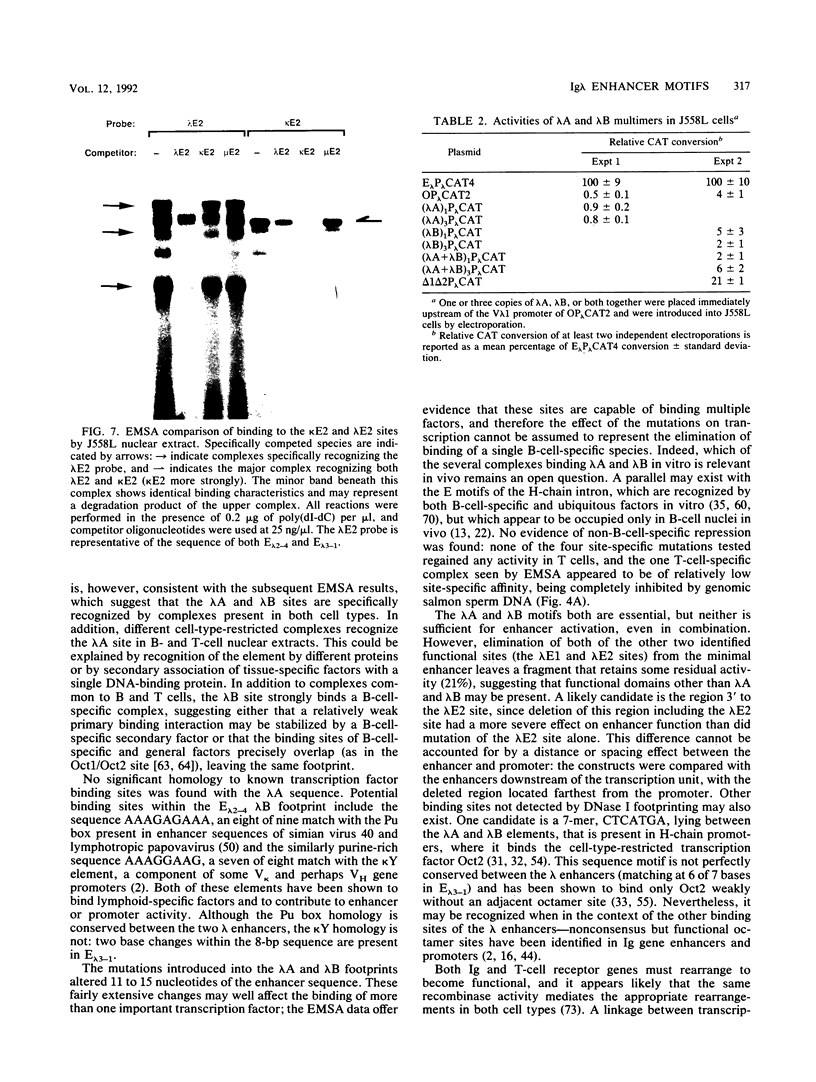
Two highly homologous enhancers associated with the two murine immunoglobulin lambda constant-region clusters were recently identified. In order to better understand the molecular basis for the developmental stage- and cell-type-restricted expression of lambda genes, we have undertaken an analysis of the putative regulatory domains of these enhancers. By using a combination of DNase I footprinting, electrophoretic mobility shift assay, and site-specific mutations, four candidate protein binding sites have been identified at analogous positions in both enhancers. A mutation of any of these sites decreases enhancer activity. Two of the sites, lambda A and lambda B, are essential for enhancer function, and both of these sites appear to bind both B-cell-specific and general factors. Nevertheless, isolated lambda A and lambda B sites show no evidence of inherent transactivating potential, alone or together, even when present in up to three copies. We suggest that the generation of transactivating signals from these enhancers may require the complex interaction of multiple B-cell-specific and nonspecific DNA-binding factors.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alt F. W., Blackwell T. K., DePinho R. A., Reth M. G., Yancopoulos G. D. Regulation of genome rearrangement events during lymphocyte differentiation. Immunol Rev. 1986 Feb;89:5–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1986.tb01470.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atchison M. L., Delmas V., Perry R. P. A novel upstream element compensates for an ineffectual octamer motif in an immunoglobulin V kappa promoter. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3109–3117. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07508.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atchison M. L., Perry R. P. The role of the kappa enhancer and its binding factor NF-kappa B in the developmental regulation of kappa gene transcription. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):121–128. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90362-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckmann H., Su L. K., Kadesch T. TFE3: a helix-loop-helix protein that activates transcription through the immunoglobulin enhancer muE3 motif. Genes Dev. 1990 Feb;4(2):167–179. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.2.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg J., McDowell M., Jäck H. M., Wabl M. Immunoglobulin lambda gene rearrangement can precede kappa gene rearrangement. Dev Immunol. 1990;1(1):53–57. doi: 10.1155/1990/56014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell T. K., Moore M. W., Yancopoulos G. D., Suh H., Lutzker S., Selsing E., Alt F. W. Recombination between immunoglobulin variable region gene segments is enhanced by transcription. Nature. 1986 Dec 11;324(6097):585–589. doi: 10.1038/324585a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell T. K., Weintraub H. Differences and similarities in DNA-binding preferences of MyoD and E2A protein complexes revealed by binding site selection. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1104–1110. doi: 10.1126/science.2174572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomberg B. B., Rudin C. M., Storb U. Identification and localization of an enhancer for the human lambda L chain Ig gene complex. J Immunol. 1991 Oct 1;147(7):2354–2358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calame K. L. Immunoglobulin gene transcription: molecular mechanisms. Trends Genet. 1989 Dec;5(12):395–399. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90197-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson S., Wu G. E. A linkage map of the mouse immunoglobulin lambda light chain locus. Immunogenetics. 1989;29(3):173–179. doi: 10.1007/BF00373642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cebra J. J., Colberg J. E., Dray S. Rabbit lymphoid cells differentiated with respect to alpha-, gamma-, and mu- heavy polypeptide chains and to allotypic markers Aa1 and Aa2. J Exp Med. 1966 Mar 1;123(3):547–558. doi: 10.1084/jem.123.3.547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Ephrussi A., Gilbert W., Tonegawa S. Cell-type-specific contacts to immunoglobulin enhancers in nuclei. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):798–801. doi: 10.1038/313798a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleclough C., Perry R. P., Karjalainen K., Weigert M. Aberrant rearrangements contribute significantly to the allelic exclusion of immunoglobulin gene expression. Nature. 1981 Apr 2;290(5805):372–378. doi: 10.1038/290372a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook G. P., Neuberger M. S. Lymphoid-specific transcriptional activation by components of the IgH enhancer: studies on the E2/E3 and octanucleotide elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 25;18(12):3565–3571. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.12.3565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Currie R. A., Roeder R. G. Identification of an octamer-binding site in the mouse kappa light-chain immunoglobulin enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4239–4247. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durdik J., Moore M. W., Selsing E. Novel kappa light-chain gene rearrangements in mouse lambda light chain-producing B lymphocytes. Nature. 1984 Feb 23;307(5953):749–752. doi: 10.1038/307749a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eccles S., Sarner N., Vidal M., Cox A., Grosveld F. Enhancer sequences located 3' of the mouse immunoglobulin lambda locus specify high-level expression of an immunoglobulin lambda gene in B cells of transgenic mice. New Biol. 1990 Sep;2(9):801–811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engler P., Roth P., Kim J. Y., Storb U. Factors affecting the rearrangement efficiency of an Ig test gene. J Immunol. 1991 Apr 15;146(8):2826–2835. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ephrussi A., Church G. M., Tonegawa S., Gilbert W. B lineage--specific interactions of an immunoglobulin enhancer with cellular factors in vivo. Science. 1985 Jan 11;227(4683):134–140. doi: 10.1126/science.3917574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrier P., Krippl B., Blackwell T. K., Furley A. J., Suh H., Winoto A., Cook W. D., Hood L., Costantini F., Alt F. W. Separate elements control DJ and VDJ rearrangement in a transgenic recombination substrate. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):117–125. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08087.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromental C., Kanno M., Nomiyama H., Chambon P. Cooperativity and hierarchical levels of functional organization in the SV40 enhancer. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):943–953. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90109-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerster T., Matthias P., Thali M., Jiricny J., Schaffner W. Cell type-specificity elements of the immunoglobulin heavy chain gene enhancer. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1323–1330. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02371.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gollahon K. A., Hagman J., Brinster R. L., Storb U. Ig lambda-producing B cells do not show feedback inhibition of gene rearrangement. J Immunol. 1988 Oct 15;141(8):2771–2780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagman J., Rudin C. M., Haasch D., Chaplin D., Storb U. A novel enhancer in the immunoglobulin lambda locus is duplicated and functionally independent of NF kappa B. Genes Dev. 1990 Jun;4(6):978–992. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.6.978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henthorn P., Kiledjian M., Kadesch T. Two distinct transcription factors that bind the immunoglobulin enhancer microE5/kappa 2 motif. Science. 1990 Jan 26;247(4941):467–470. doi: 10.1126/science.2105528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hieter P. A., Korsmeyer S. J., Waldmann T. A., Leder P. Human immunoglobulin kappa light-chain genes are deleted or rearranged in lambda-producing B cells. Nature. 1981 Apr 2;290(5805):368–372. doi: 10.1038/290368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho S. N., Hunt H. D., Horton R. M., Pullen J. K., Pease L. R. Site-directed mutagenesis by overlap extension using the polymerase chain reaction. Gene. 1989 Apr 15;77(1):51–59. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90358-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemler I., Schreiber E., Müller M. M., Matthias P., Schaffner W. Octamer transcription factors bind to two different sequence motifs of the immunoglobulin heavy chain promoter. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):2001–2008. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03607.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landolfi N. F., Yin X. M., Capra J. D., Tucker P. W. A conserved heptamer upstream of the IgH promoter region octamer can be the site of a coordinate protein-DNA interaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jun 24;16(12):5503–5514. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.12.5503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBowitz J. H., Clerc R. G., Brenowitz M., Sharp P. A. The Oct-2 protein binds cooperatively to adjacent octamer sites. Genes Dev. 1989 Oct;3(10):1625–1638. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.10.1625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefranc G., Lefranc M. P. Regulation of the immunoglobulin gene transcription. Biochimie. 1990 Jan;72(1):7–17. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(90)90167-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenardo M., Pierce J. W., Baltimore D. Protein-binding sites in Ig gene enhancers determine transcriptional activity and inducibility. Science. 1987 Jun 19;236(4808):1573–1577. doi: 10.1126/science.3109035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libermann T. A., Lenardo M., Baltimore D. Involvement of a second lymphoid-specific enhancer element in the regulation of immunoglobulin heavy-chain gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):3155–3162. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.3155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer K. B., Neuberger M. S. The immunoglobulin kappa locus contains a second, stronger B-cell-specific enhancer which is located downstream of the constant region. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):1959–1964. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03601.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer K. B., Sharpe M. J., Surani M. A., Neuberger M. S. The importance of the 3'-enhancer region in immunoglobulin kappa gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 11;18(19):5609–5615. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.19.5609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Baltimore D. A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):777–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90682-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Immerglück M. M., Schaffner W., Matthias P. Transcription factor Oct-2A contains functionally redundant activating domains and works selectively from a promoter but not from a remote enhancer position in non-lymphoid (HeLa) cells. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1625–1634. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08282.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller B., Reth M. Ordered activation of the Ig lambda locus in Abelson B cell lines. J Exp Med. 1988 Dec 1;168(6):2131–2137. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.6.2131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelms K., Hromas R., Van Ness B. Identification of a second inducible DNA-protein interaction in the kappa immunoglobulin enhancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 25;18(4):1037–1043. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.4.1037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelms K., Van Ness B. Identification of an octamer-binding site in the human kappa light-chain enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3843–3846. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelsen B., Kadesch T., Sen R. Complex regulation of the immunoglobulin mu heavy-chain gene enhancer: microB, a new determinant of enhancer function. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):3145–3154. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.3145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen D. A., Chou J., MacKrell A. J., Casadaban M. J., Steiner D. F. Expression of a preproinsulin-beta-galactosidase gene fusion in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5198–5202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ondek B., Shepard A., Herr W. Discrete elements within the SV40 enhancer region display different cell-specific enhancer activities. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):1017–1025. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04854.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pernis B., Chiappino G., Kelus A. S., Gell P. G. Cellular localization of immunoglobulins with different allotypic specificities in rabbit lymphoid tissues. J Exp Med. 1965 Nov 1;122(5):853–876. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.5.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persiani D. M., Durdik J., Selsing E. Active lambda and kappa antibody gene rearrangement in Abelson murine leukemia virus-transformed pre-B cell lines. J Exp Med. 1987 Jun 1;165(6):1655–1674. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.6.1655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petterson M., Schaffner W. A purine-rich DNA sequence motif present in SV40 and lymphotropic papovavirus binds a lymphoid-specific factor and contributes to enhancer activity in lymphoid cells. Genes Dev. 1987 Nov;1(9):962–972. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.9.962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson M., Schaffner W. Synergistic activation of transcription by multiple binding sites for NF-kappa B even in absence of co-operative factor binding to DNA. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jul 20;214(2):373–380. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90187-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson S., Cook G. P., Brüggemann M., Williams G. T., Neuberger M. S. A second B cell-specific enhancer 3' of the immunoglobulin heavy-chain locus. Nature. 1990 Mar 8;344(6262):165–168. doi: 10.1038/344165a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce J. W., Lenardo M., Baltimore D. Oligonucleotide that binds nuclear factor NF-kappa B acts as a lymphoid-specific and inducible enhancer element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1482–1486. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poellinger L., Roeder R. G. Octamer transcription factors 1 and 2 each bind to two different functional elements in the immunoglobulin heavy-chain promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):747–756. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poellinger L., Yoza B. K., Roeder R. G. Functional cooperativity between protein molecules bound at two distinct sequence elements of the immunoglobulin heavy-chain promoter. Nature. 1989 Feb 9;337(6207):573–576. doi: 10.1038/337573a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pongubala J. M., Atchison M. L. Functional characterization of the developmentally controlled immunoglobulin kappa 3' enhancer: regulation by Id, a repressor of helix-loop-helix transcription factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):1040–1047. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.1040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prost E., Moore D. D. CAT vectors for analysis of eukaryotic promoters and enhancers. Gene. 1986;45(1):107–111. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90138-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruezinsky D., Beckmann H., Kadesch T. Modulation of the IgH enhancer's cell type specificity through a genetic switch. Genes Dev. 1991 Jan;5(1):29–37. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.1.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatt M. D., Rusconi S., Schaffner W. A single DNA-binding transcription factor is sufficient for activation from a distant enhancer and/or from a promoter position. EMBO J. 1990 Feb;9(2):481–487. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08134.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90346-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siminovitch K. A., Bakhshi A., Goldman P., Korsmeyer S. J. A uniform deleting element mediates the loss of kappa genes in human B cells. Nature. 1985 Jul 18;316(6025):260–262. doi: 10.1038/316260a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., Sen R., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. A nuclear factor that binds to a conserved sequence motif in transcriptional control elements of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):154–158. doi: 10.1038/319154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staudt L. M., Singh H., Sen R., Wirth T., Sharp P. A., Baltimore D. A lymphoid-specific protein binding to the octamer motif of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Oct 16;323(6089):640–643. doi: 10.1038/323640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storb U., Haasch D., Arp B., Sanchez P., Cazenave P. A., Miller J. Physical linkage of mouse lambda genes by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis suggests that the rearrangement process favors proximate target sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):711–718. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabak H. F., Flavell R. A. A method for the recovery of DNA from agarose gels. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Jul;5(7):2321–2332. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.7.2321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Grossniklaus U., Herr W., Hernandez N. Activation of the U2 snRNA promoter by the octamer motif defines a new class of RNA polymerase II enhancer elements. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12B):1764–1778. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12b.1764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veldman G. M., Lupton S., Kamen R. Polyomavirus enhancer contains multiple redundant sequence elements that activate both DNA replication and gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):649–658. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger J., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. Distinct factors bind to apparently homologous sequences in the immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer. 1986 Aug 28-Sep 3Nature. 322(6082):846–848. doi: 10.1038/322846a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westin G., Schaffner W. A zinc-responsive factor interacts with a metal-regulated enhancer element (MRE) of the mouse metallothionein-I gene. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3763–3770. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03260.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yancopoulos G. D., Alt F. W. Developmentally controlled and tissue-specific expression of unrearranged VH gene segments. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):271–281. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90141-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yancopoulos G. D., Blackwell T. K., Suh H., Hood L., Alt F. W. Introduced T cell receptor variable region gene segments recombine in pre-B cells: evidence that B and T cells use a common recombinase. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):251–259. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90759-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]