Abstract
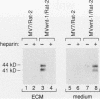
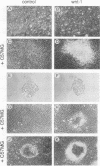
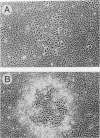
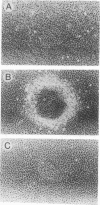
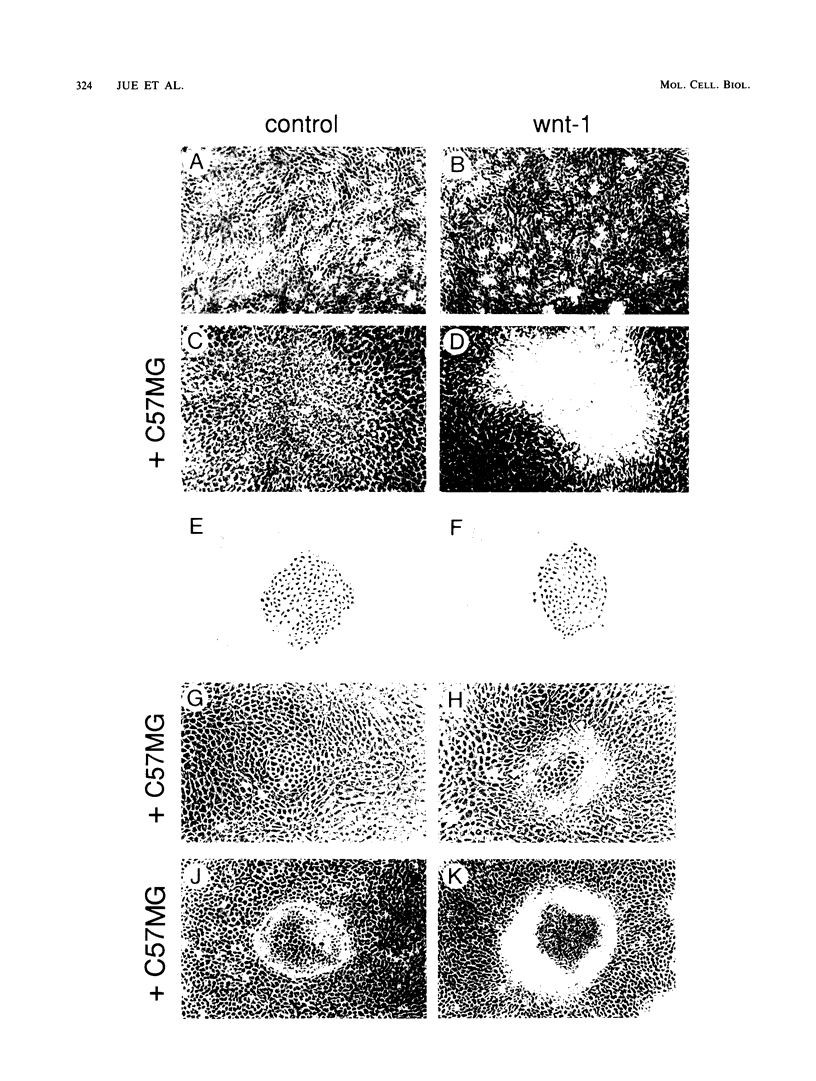
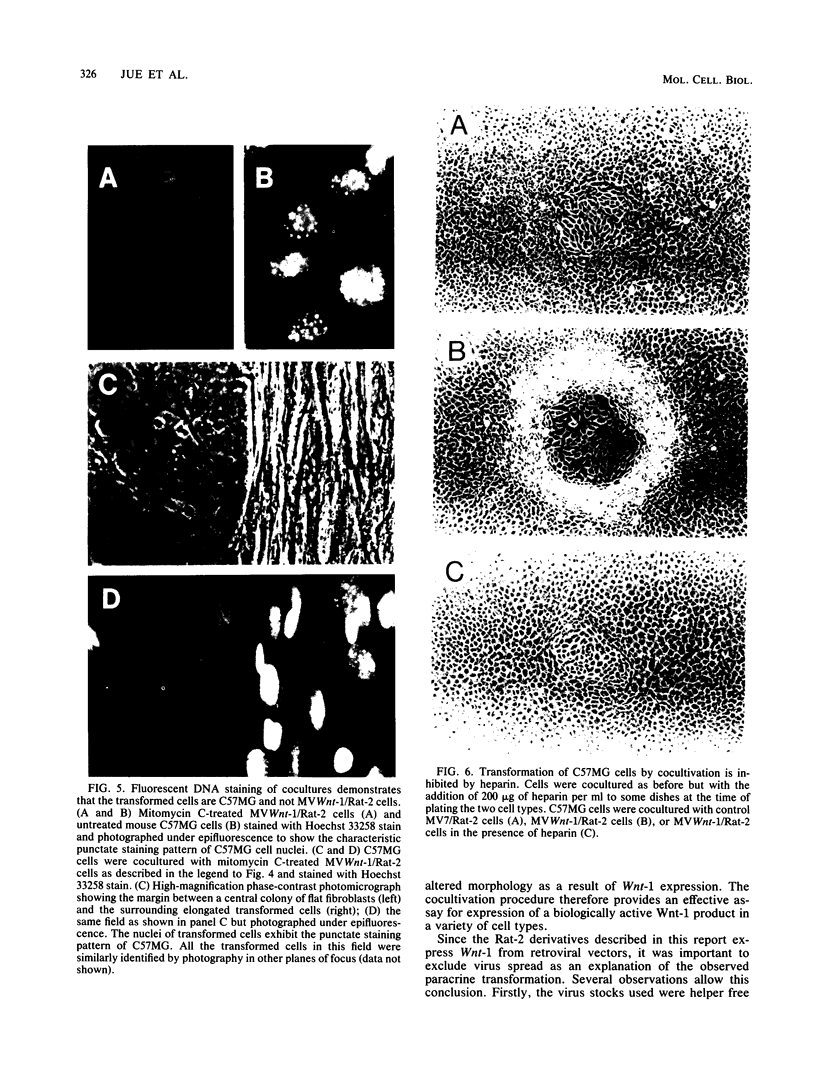
The mouse Wnt-1 gene plays an essential role in fetal brain development and can contribute to tumorigenesis when activated aberrantly in the mammary gland. The gene encodes secretory glycoproteins associated with the extracellular or pericellular matrix, and it has been proposed that Wnt-1, as well as its Drosophila homolog wingless, may function in intercellular signalling. We show here that fibroblasts expressing Wnt-1 protein, although not transformed themselves, are able to elicit morphological transformation of neighboring C57MG mammary epithelial cells in coculture experiments. Heparin inhibits this effect, possibly by displacing Wnt-1 protein from its normal site of action. Our results indicate that the Wnt-1 gene can act via a paracrine mechanism in cell culture and strongly support the notion that in vivo the gene may function in cell-to-cell communication.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker N. E. Molecular cloning of sequences from wingless, a segment polarity gene in Drosophila: the spatial distribution of a transcript in embryos. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1765–1773. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02429.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. M., Wildin R. S., Prendergast T. J., Varmus H. E. A retrovirus vector expressing the putative mammary oncogene int-1 causes partial transformation of a mammary epithelial cell line. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):1001–1009. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90699-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. C., Shank P. R., Morris V. L., Cardiff R., Varmus H. E. Integration of the DNA of mouse mammary tumor virus in virus-infected normal and neoplastic tissue of the mouse. Cell. 1979 Feb;16(2):333–345. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiNardo S., Heemskerk J. Molecular and cellular interactions responsible for intrasegmental patterning during Drosophila embryogenesis. Semin Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;1(3):173–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiNardo S., Sher E., Heemskerk-Jongens J., Kassis J. A., O'Farrell P. H. Two-tiered regulation of spatially patterned engrailed gene expression during Drosophila embryogenesis. Nature. 1988 Apr 14;332(6165):604–609. doi: 10.1038/332604a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavin B. J., McMahon J. A., McMahon A. P. Expression of multiple novel Wnt-1/int-1-related genes during fetal and adult mouse development. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12B):2319–2332. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12b.2319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heemskerk J., DiNardo S., Kostriken R., O'Farrell P. H. Multiple modes of engrailed regulation in the progression towards cell fate determination. Nature. 1991 Aug 1;352(6334):404–410. doi: 10.1038/352404a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschmeier P. T., Housey G. M., Johnson M. D., Perkins A. S., Weinstein I. B. Construction and characterization of a retroviral vector demonstrating efficient expression of cloned cDNA sequences. DNA. 1988 Apr;7(3):219–225. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martizez Arias A., Baker N. E., Ingham P. W. Role of segment polarity genes in the definition and maintenance of cell states in the Drosophila embryo. Development. 1988 May;103(1):157–170. doi: 10.1242/dev.103.1.157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J. A helping hand from proteoglycans. Curr Biol. 1991 Apr;1(2):117–119. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(91)90296-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon A. P., Bradley A. The Wnt-1 (int-1) proto-oncogene is required for development of a large region of the mouse brain. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1073–1085. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90385-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon J. A., McMahon A. P. Nucleotide sequence, chromosomal localization and developmental expression of the mouse int-1-related gene. Development. 1989 Nov;107(3):643–650. doi: 10.1242/dev.107.3.643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mester J., Wagenaar E., Sluyser M., Nusse R. Activation of int-1 and int-2 mammary oncogenes in hormone-dependent and -independent mammary tumors of GR mice. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1073–1078. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1073-1078.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nusse R., Brown A., Papkoff J., Scambler P., Shackleford G., McMahon A., Moon R., Varmus H. A new nomenclature for int-1 and related genes: the Wnt gene family. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):231–231. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90633-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nusse R. The int genes in mammary tumorigenesis and in normal development. Trends Genet. 1988 Oct;4(10):291–295. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90172-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nusse R., Varmus H. E. Many tumors induced by the mouse mammary tumor virus contain a provirus integrated in the same region of the host genome. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):99–109. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90409-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nusse R., van Ooyen A., Cox D., Fung Y. K., Varmus H. Mode of proviral activation of a putative mammary oncogene (int-1) on mouse chromosome 15. Nature. 1984 Jan 12;307(5947):131–136. doi: 10.1038/307131a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nüsslein-Volhard C., Wieschaus E. Mutations affecting segment number and polarity in Drosophila. Nature. 1980 Oct 30;287(5785):795–801. doi: 10.1038/287795a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papkoff J., Schryver B. Secreted int-1 protein is associated with the cell surface. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2723–2730. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peifer M., Wieschaus E. The segment polarity gene armadillo encodes a functionally modular protein that is the Drosophila homolog of human plakoglobin. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1167–1176. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90413-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggleman B., Schedl P., Wieschaus E. Spatial expression of the Drosophila segment polarity gene armadillo is posttranscriptionally regulated by wingless. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):549–560. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90451-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijsewijk F. A., van Lohuizen M., van Ooyen A., Nusse R. Construction of a retroviral cDNA version of the int-1 mammary oncogene and its expression in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 24;14(2):693–702. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.2.693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijsewijk F., Schuermann M., Wagenaar E., Parren P., Weigel D., Nusse R. The Drosophila homolog of the mouse mammary oncogene int-1 is identical to the segment polarity gene wingless. Cell. 1987 Aug 14;50(4):649–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90038-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijsewijk F., van Deemter L., Wagenaar E., Sonnenberg A., Nusse R. Transfection of the int-1 mammary oncogene in cuboidal RAC mammary cell line results in morphological transformation and tumorigenicity. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):127–131. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04729.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roelink H., Nusse R. Expression of two members of the Wnt family during mouse development--restricted temporal and spatial patterns in the developing neural tube. Genes Dev. 1991 Mar;5(3):381–388. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.3.381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roelink H., Wagenaar E., Lopes da Silva S., Nusse R. Wnt-3, a gene activated by proviral insertion in mouse mammary tumors, is homologous to int-1/Wnt-1 and is normally expressed in mouse embryos and adult brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4519–4523. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert D., LaCorbiere M., Klier F. G., Birdwell C. A role for adherons in neural retina cell adhesion. J Cell Biol. 1983 Apr;96(4):990–998. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.4.990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shackleford G. M., Varmus H. E. Expression of the proto-oncogene int-1 is restricted to postmeiotic male germ cells and the neural tube of mid-gestational embryos. Cell. 1987 Jul 3;50(1):89–95. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90665-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. R., Capecchi M. R. Targeted disruption of the murine int-1 proto-oncogene resulting in severe abnormalities in midbrain and cerebellar development. Nature. 1990 Aug 30;346(6287):847–850. doi: 10.1038/346847a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukamoto A. S., Grosschedl R., Guzman R. C., Parslow T., Varmus H. E. Expression of the int-1 gene in transgenic mice is associated with mammary gland hyperplasia and adenocarcinomas in male and female mice. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):619–625. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90220-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaidya A. B., Lasfargues E. Y., Sheffield J. B., Coutinho W. G. Murine mammary tumor virus (MuMTV) infection of an epithelial cell line established from C57BL/6 mouse mammary glands. Virology. 1978 Oct 1;90(1):12–22. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90328-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieschaus E., Riggleman R. Autonomous requirements for the segment polarity gene armadillo during Drosophila embryogenesis. Cell. 1987 Apr 24;49(2):177–184. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90558-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson D. G., Bailes J. A., McMahon A. P. Expression of the proto-oncogene int-1 is restricted to specific neural cells in the developing mouse embryo. Cell. 1987 Jul 3;50(1):79–88. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90664-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yayon A., Klagsbrun M., Esko J. D., Leder P., Ornitz D. M. Cell surface, heparin-like molecules are required for binding of basic fibroblast growth factor to its high affinity receptor. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):841–848. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90512-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Ooyen A., Nusse R. Structure and nucleotide sequence of the putative mammary oncogene int-1; proviral insertions leave the protein-encoding domain intact. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):233–240. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90209-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Heuvel M., Nusse R., Johnston P., Lawrence P. A. Distribution of the wingless gene product in Drosophila embryos: a protein involved in cell-cell communication. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):739–749. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90020-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]