Abstract
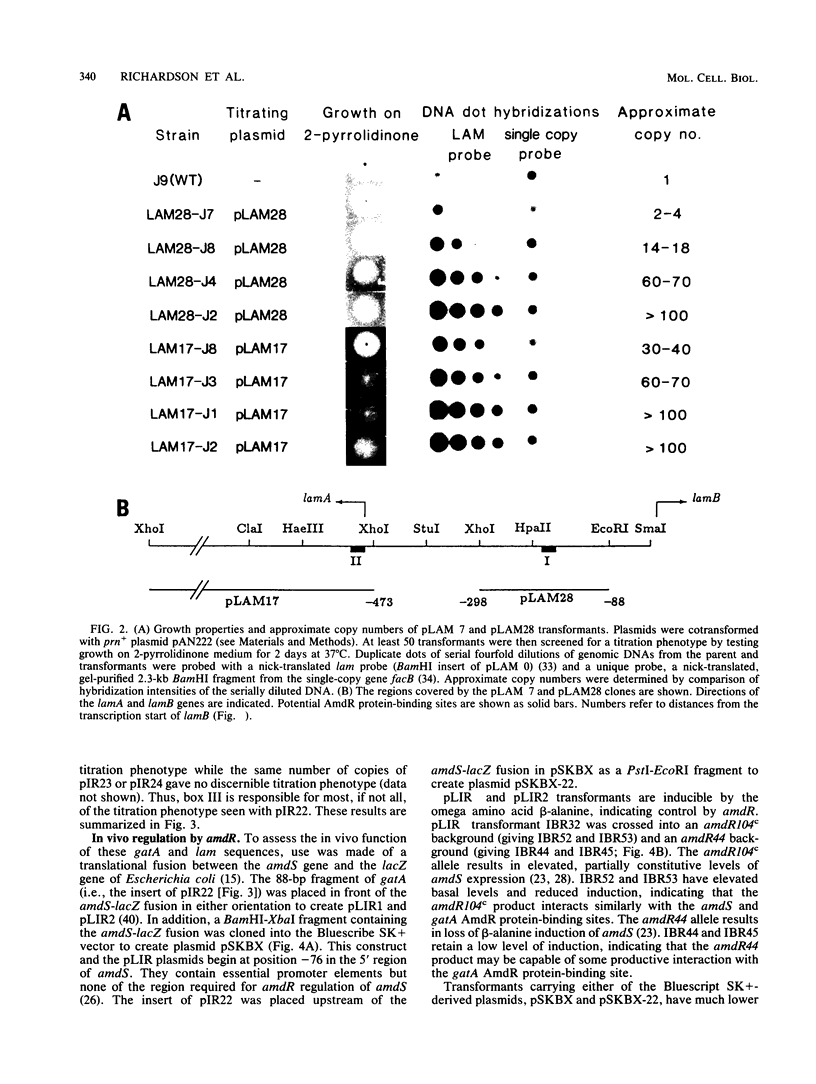
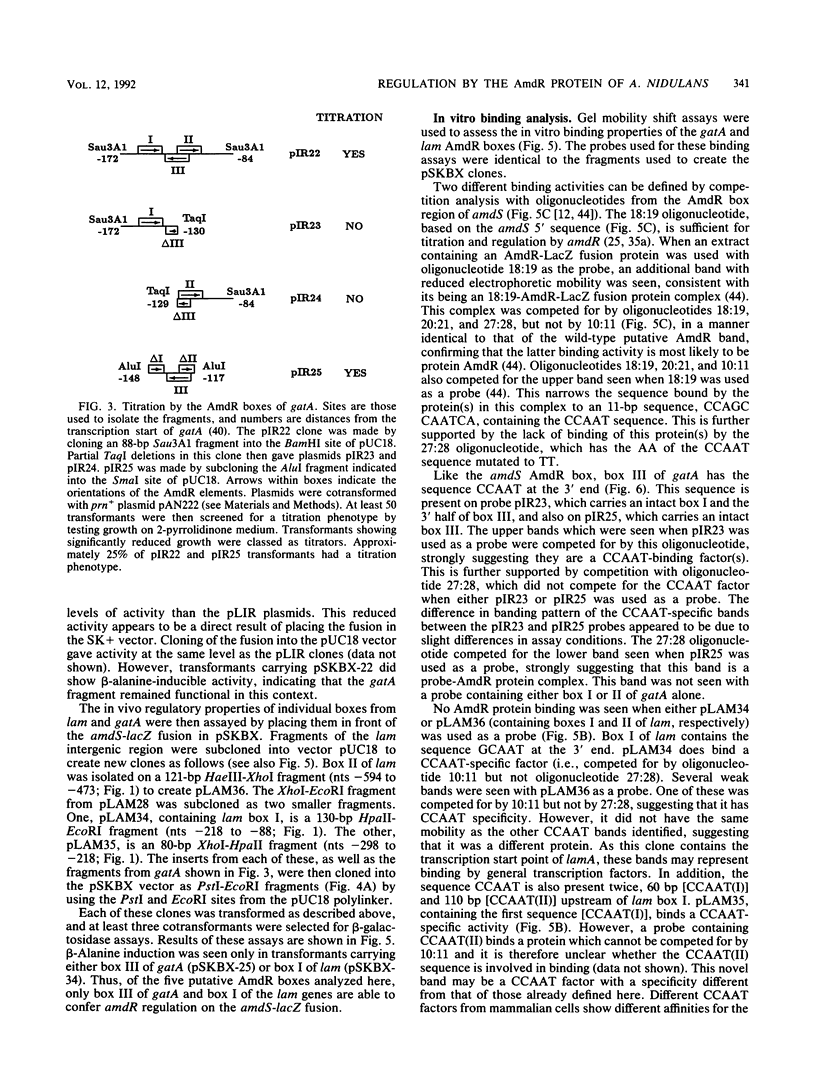
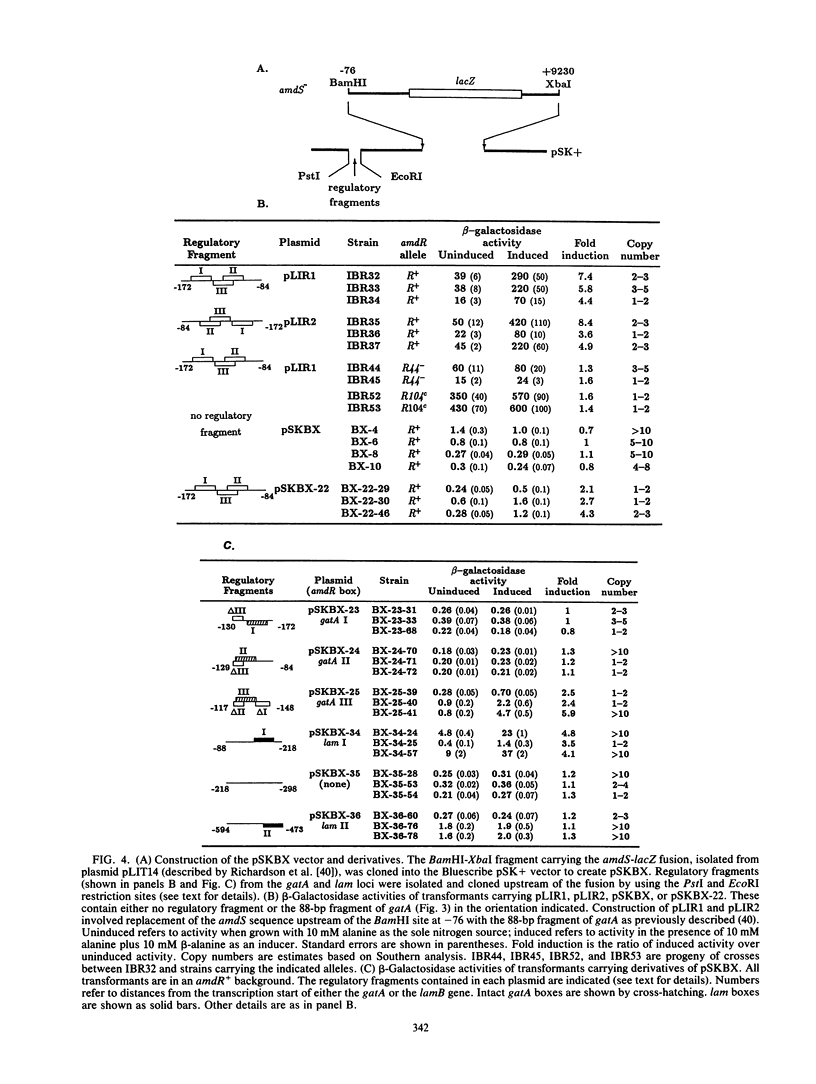
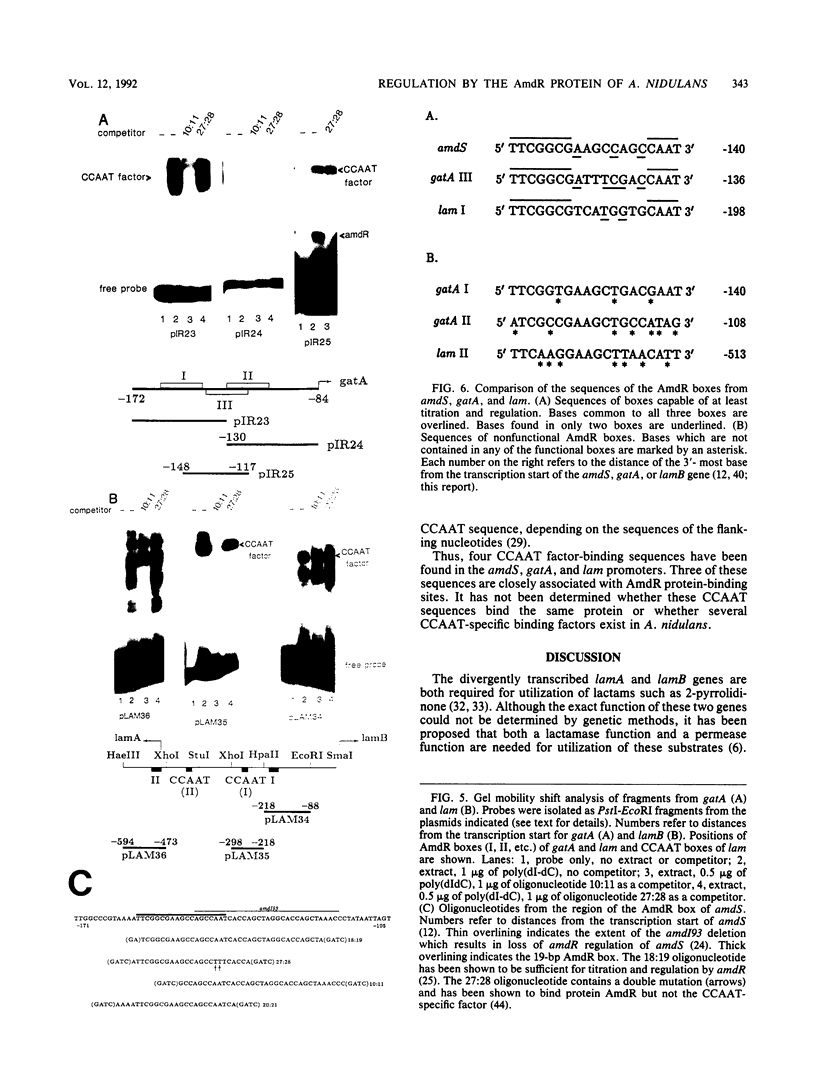
The lam locus of Aspergillus nidulans consists of two divergently transcribed genes, lamA and lamB, involved in the utilization of lactams such as 2-pyrrolidinone. Both genes are under the control of the positive regulatory gene amdR and are subject to carbon and nitrogen metabolite repression. The lamB gene and the region between the two genes have been sequenced, and the start points of transcription have been determined. Within the lam locus are two sequences with homology to elements, required for AmdR regulation, found in the 5' regions of the coregulated genes amdS and gatA. In vitro and in vivo assays were used to investigate the lam and gatA regulatory elements. One of the three gatA elements and one of the two lam elements were shown to bind AmdR protein in vivo and activate transcription. With a gel shift mobility assay, in vitro binding of AmdR protein to the functional gatA element was detected. Both the functional gatA and lam boxes contain within them a CAAT sequence. In vitro binding analysis indicates that a CCAAT-specific factor(s) binds at these sequences, adjacent to or overlapping the AmdR protein-binding site.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams T. H., Timberlake W. E. Upstream elements repress premature expression of an Aspergillus developmental regulatory gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4912–4919. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrianopoulos A., Hynes M. J. Cloning and analysis of the positively acting regulatory gene amdR from Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3532–3541. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrianopoulos A., Hynes M. J. Sequence and functional analysis of the positively acting regulatory gene amdR from Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):3194–3203. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.3194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arst H. N., Jr, Cove D. J. Nitrogen metabolite repression in Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Gen Genet. 1973 Nov 2;126(2):111–141. doi: 10.1007/BF00330988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arst H. N., Jr Integrator gene in Aspergillus nidulans. Nature. 1976 Jul 15;262(5565):231–234. doi: 10.1038/262231a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arst H. N., Jr, Penfold H. A., Bailey C. R. Lactam utilisation in Aspergillus nidulans: evidence for a fourth gene under the control of the integrator gene intA. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Nov 9;166(3):321–327. doi: 10.1007/BF00267625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum J. A., Geever R., Giles N. H. Expression of qa-1F activator protein: identification of upstream binding sites in the qa gene cluster and localization of the DNA-binding domain. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1256–1266. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carcamo J., Maldonado E., Cortes P., Ahn M. H., Ha I., Kasai Y., Flint J., Reinberg D. A TATA-like sequence located downstream of the transcription initiation site is required for expression of an RNA polymerase II transcribed gene. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1611–1622. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corrick C. M., Twomey A. P., Hynes M. J. The nucleotide sequence of the amdS gene of Aspergillus nidulans and the molecular characterization of 5' mutations. Gene. 1987;53(1):63–71. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cove D. J. The induction and repression of nitrate reductase in the fungus Aspergillus nidulans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jan 11;113(1):51–56. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6593(66)80120-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis M. A., Cobbett C. S., Hynes M. J. An amdS-lacZ fusion for studying gene regulation in Aspergillus. Gene. 1988 Mar 31;63(2):199–212. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90525-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis M. A., Hynes M. J. Complementation of areA- regulatory gene mutations of Aspergillus nidulans by the heterologous regulatory gene nit-2 of Neurospora crassa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3753–3757. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durrens P., Green P. M., Arst H. N., Jr, Scazzocchio C. Heterologous insertion of transforming DNA and generation of new deletions associated with transformation in Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Jun;203(3):544–549. doi: 10.1007/BF00422084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg D., Schwarz E., Komaromy M., Wall R. Analysis of membrane and surface protein sequences with the hydrophobic moment plot. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 15;179(1):125–142. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90309-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsburg S. L., Guarente L. Identification and characterization of HAP4: a third component of the CCAAT-bound HAP2/HAP3 heteromer. Genes Dev. 1989 Aug;3(8):1166–1178. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.8.1166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu Y. H., Marzluf G. A. nit-2, the major positive-acting nitrogen regulatory gene of Neurospora crassa, encodes a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5331–5335. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geever R. F., Huiet L., Baum J. A., Tyler B. M., Patel V. B., Rutledge B. J., Case M. E., Giles N. H. DNA sequence, organization and regulation of the qa gene cluster of Neurospora crassa. J Mol Biol. 1989 May 5;207(1):15–34. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90438-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes M. J. A mutation, adjacent to gene amdS, defining the site of action of positive-control gene amdR in Aspergillus nidulans. J Bacteriol. 1980 May;142(2):400–406. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.2.400-406.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes M. J., Corrick C. M., Kelly J. M., Littlejohn T. G. Identification of the sites of action for regulatory genes controlling the amdS gene of Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2589–2596. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes M. J., Corrick C. M., King J. A. Isolation of genomic clones containing the amdS gene of Aspergillus nidulans and their use in the analysis of structural and regulatory mutations. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Aug;3(8):1430–1439. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.8.1430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes M. J. Multiple independent control mechanisms affecting the acetamidase of Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Apr 25;161(1):59–65. doi: 10.1007/BF00266615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes M. J., Pateman J. A. The genetic analysis of regulation of amidase synthesis in Aspergillus nidulans. II. Mutants resistant to fluoroacetamide. Mol Gen Genet. 1970;108(2):107–116. doi: 10.1007/BF02430517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Eukaryotic transcriptional regulatory proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:799–839. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.004055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston M. A model fungal gene regulatory mechanism: the GAL genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Dec;51(4):458–476. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.4.458-476.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnstone I. L., McCabe P. C., Greaves P., Gurr S. J., Cole G. E., Brow M. A., Unkles S. E., Clutterbuck A. J., Kinghorn J. R., Innis M. A. Isolation and characterisation of the crnA-niiA-niaD gene cluster for nitrate assimilation in Aspergillus nidulans. Gene. 1990 Jun 15;90(2):181–192. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90178-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz M. E., Hynes M. J. Characterization of the amdR-controlled lamA and lamB genes of Aspergillus nidulans. Genetics. 1989 Jun;122(2):331–339. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.2.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz M. E., Hynes M. J. Gene function identified by interspecific transformation. Gene. 1989 May 15;78(1):167–171. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90324-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz M. E., Hynes M. J. Isolation and analysis of the acetate regulatory gene, facB, from Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5696–5701. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly J. M., Hynes M. J. Multiple copies of the amdS gene of Aspergillus nidulans cause titration of trans-acting regulatory proteins. Curr Genet. 1987;12(1):21–31. doi: 10.1007/BF00420723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrander J., Kempe T., Messing J. Construction of improved M13 vectors using oligodeoxynucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K. C., Mann D. A. Rapid transfer of DNA from agarose gels to nylon membranes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7207–7221. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson I. B., Hurley S. K., Hynes M. J. Cloning and molecular characterisation of the amdR controlled gatA gene of Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 May;217(1):118–125. doi: 10.1007/BF00330950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Baltimore D. The "initiator" as a transcription control element. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90176-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Schmidt M. C., Berk A. J., Baltimore D. Transcriptional activation by Sp1 as directed through TATA or initiator: specific requirement for mammalian transcription factor IID. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4509–4513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Heeswijck R., Hynes M. J. The amdR product and a CCAAT-binding factor bind to adjacent, possibly overlapping DNA sequences in the promoter region of the Aspergillus nidulans amdS gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 May 25;19(10):2655–2660. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.10.2655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]