Abstract
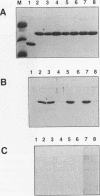
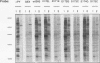
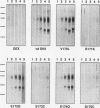
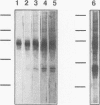
We have constructed a series of point mutations in the highly conserved FLVRES motif of the src homology 2 (SH2) domain of the abl tyrosine kinase. Mutant SH2 domains were expressed in bacteria, and their ability to bind to tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins was examined in vitro. Three mutants were greatly reduced in their ability to bind both phosphotyrosine itself and tyrosine-phosphorylated cellular proteins. All of the mutants that retained activity bound to the same set of tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins as did the wild type, suggesting that binding specificity was unaffected. These results implicate the FLVRES motif in direct binding to phosphotyrosine. When the mutant SH2 domains were inserted into an activated abl kinase and expressed in murine fibroblasts, decreased in vitro phosphotyrosine binding correlated with decreased transforming ability. This finding implies that SH2-phosphotyrosine interactions are involved in transmission of positive growth signals by the nonreceptor tyrosine kinases, most likely via the assembly of multiprotein complexes with other tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins.
Full text
PDF

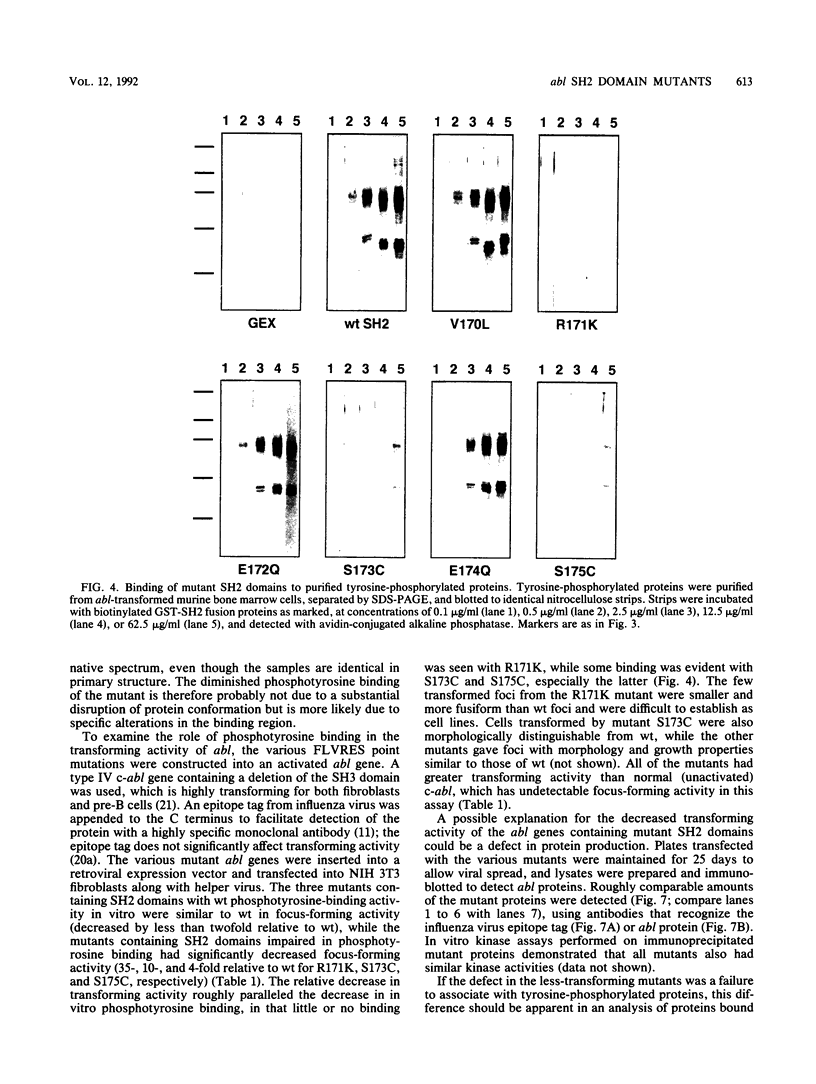
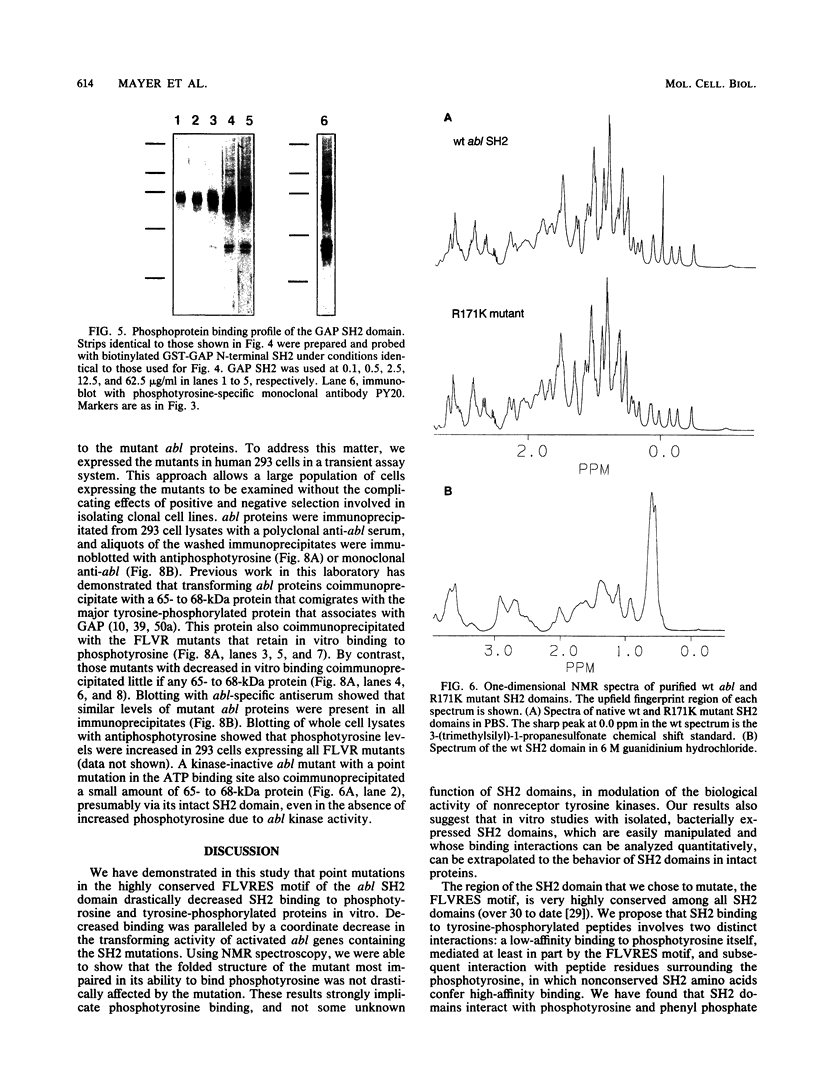




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D., Koch C. A., Grey L., Ellis C., Moran M. F., Pawson T. Binding of SH2 domains of phospholipase C gamma 1, GAP, and Src to activated growth factor receptors. Science. 1990 Nov 16;250(4983):979–982. doi: 10.1126/science.2173144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant D., Parsons J. T. Site-directed mutagenesis of the src gene of Rous sarcoma virus: construction and characterization of a deletion mutant temperature sensitive for transformation. J Virol. 1982 Nov;44(2):683–691. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.2.683-691.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Auger K. R., Carpenter C., Duckworth B., Graziani A., Kapeller R., Soltoff S. Oncogenes and signal transduction. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):281–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90639-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross F. R., Garber E. A., Pellman D., Hanafusa H. A short sequence in the p60src N terminus is required for p60src myristylation and membrane association and for cell transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1834–1842. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross F. R., Hanafusa H. Local mutagenesis of Rous sarcoma virus: the major sites of tyrosine and serine phosphorylation of pp60src are dispensable for transformation. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):597–607. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90392-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeClue J. E., Martin G. S. Linker insertion-deletion mutagenesis of the v-src gene: isolation of host- and temperature-dependent mutants. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):542–554. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.542-554.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeClue J. E., Sadowski I., Martin G. S., Pawson T. A conserved domain regulates interactions of the v-fps protein-tyrosine kinase with the host cell. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9064–9068. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis C., Moran M., McCormick F., Pawson T. Phosphorylation of GAP and GAP-associated proteins by transforming and mitogenic tyrosine kinases. Nature. 1990 Jan 25;343(6256):377–381. doi: 10.1038/343377a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field J., Nikawa J., Broek D., MacDonald B., Rodgers L., Wilson I. A., Lerner R. A., Wigler M. Purification of a RAS-responsive adenylyl cyclase complex from Saccharomyces cerevisiae by use of an epitope addition method. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2159–2165. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui Y., Hanafusa H. Requirement of phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase modification for its association with p60src. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):1972–1979. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui Y., O'Brien M. C., Hanafusa H. Deletions in the SH2 domain of p60v-src prevent association with the detergent-insoluble cellular matrix. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1207–1213. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Zokas L., Kamps M. P. Monoclonal antibodies to phosphotyrosine. J Immunol Methods. 1988 May 9;109(2):277–285. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(88)90253-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Zokas L. Novel tyrosine kinase substrates from Rous sarcoma virus-transformed cells are present in the membrane skeleton. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;108(6):2401–2408. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.6.2401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt-Clermont P. J., Kim J. W., Machesky L. M., Rhee S. G., Pollard T. D. Regulation of phospholipase C-gamma 1 by profilin and tyrosine phosphorylation. Science. 1991 Mar 8;251(4998):1231–1233. doi: 10.1126/science.1848725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):42–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai H., Varmus H. E. Mutations in src homology regions 2 and 3 of activated chicken c-src that result in preferential transformation of mouse or chicken cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8592–8596. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai H., Varmus H. E. SH2 mutants of c-src that are host dependent for transformation are trans-dominant inhibitors of mouse cell transformation by activated c-src. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12B):2342–2352. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12b.2342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai H., Varmus H. E. Site-directed mutagenesis of the SH2- and SH3-coding domains of c-src produces varied phenotypes, including oncogenic activation of p60c-src. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1307–1318. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson P., Baltimore D. N-terminal mutations activate the leukemogenic potential of the myristoylated form of c-abl. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):449–456. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03397.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. A., Stone J. C. Delineation of functional determinants in the transforming protein of Fujinami sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3337–3349. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3337-3349.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Buss J. E., Sefton B. M. Mutation of NH2-terminal glycine of p60src prevents both myristoylation and morphological transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4625–4628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H. K., Kim J. W., Zilberstein A., Margolis B., Kim J. G., Schlessinger J., Rhee S. G. PDGF stimulation of inositol phospholipid hydrolysis requires PLC-gamma 1 phosphorylation on tyrosine residues 783 and 1254. Cell. 1991 May 3;65(3):435–441. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90461-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura N., Yoshida M. Small deletion in src of Rous sarcoma virus modifying transformation phenotypes: identification of 207-nucleotide deletion and its smaller product with protein kinase activity. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):985–992. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.985-992.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kmiecik T. E., Shalloway D. Activation and suppression of pp60c-src transforming ability by mutation of its primary sites of tyrosine phosphorylation. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):65–73. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90756-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C. A., Anderson D., Moran M. F., Ellis C., Pawson T. SH2 and SH3 domains: elements that control interactions of cytoplasmic signaling proteins. Science. 1991 May 3;252(5006):668–674. doi: 10.1126/science.1708916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C. A., Moran M., Sadowski I., Pawson T. The common src homology region 2 domain of cytoplasmic signaling proteins is a positive effector of v-fps tyrosine kinase function. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4131–4140. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konopka J. B., Davis R. L., Watanabe S. M., Ponticelli A. S., Schiff-Maker L., Rosenberg N., Witte O. N. Only site-directed antibodies reactive with the highly conserved src-homologous region of the v-abl protein neutralize kinase activity. J Virol. 1984 Jul;51(1):223–232. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.1.223-232.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B., Li N., Koch A., Mohammadi M., Hurwitz D. R., Zilberstein A., Ullrich A., Pawson T., Schlessinger J. The tyrosine phosphorylated carboxyterminus of the EGF receptor is a binding site for GAP and PLC-gamma. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4375–4380. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07887.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda M., Mayer B. J., Fukui Y., Hanafusa H. Binding of transforming protein, P47gag-crk, to a broad range of phosphotyrosine-containing proteins. Science. 1990 Jun 22;248(4962):1537–1539. doi: 10.1126/science.1694307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda M., Mayer B. J., Hanafusa H. Identification of domains of the v-crk oncogene product sufficient for association with phosphotyrosine-containing proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1607–1613. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer B. J., Hamaguchi M., Hanafusa H. Characterization of p47gag-crk, a novel oncogene product with sequence similarity to a putative modulatory domain of protein-tyrosine kinases and phospholipase C. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1988;53(Pt 2):907–914. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1988.053.01.104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer B. J., Hanafusa H. Association of the v-crk oncogene product with phosphotyrosine-containing proteins and protein kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2638–2642. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer B. J., Hanafusa H. Mutagenic analysis of the v-crk oncogene: requirement for SH2 and SH3 domains and correlation between increased cellular phosphotyrosine and transformation. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3581–3589. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3581-3589.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer B. J., Jackson P. K., Baltimore D. The noncatalytic src homology region 2 segment of abl tyrosine kinase binds to tyrosine-phosphorylated cellular proteins with high affinity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):627–631. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran M. F., Koch C. A., Anderson D., Ellis C., England L., Martin G. S., Pawson T. Src homology region 2 domains direct protein-protein interactions in signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8622–8626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran M. F., Polakis P., McCormick F., Pawson T., Ellis C. Protein-tyrosine kinases regulate the phosphorylation, protein interactions, subcellular distribution, and activity of p21ras GTPase-activating protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):1804–1812. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.1804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishibe S., Wahl M. I., Hernández-Sotomayor S. M., Tonks N. K., Rhee S. G., Carpenter G. Increase of the catalytic activity of phospholipase C-gamma 1 by tyrosine phosphorylation. Science. 1990 Nov 30;250(4985):1253–1256. doi: 10.1126/science.1700866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien M. C., Fukui Y., Hanafusa H. Activation of the proto-oncogene p60c-src by point mutations in the SH2 domain. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2855–2862. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T. Non-catalytic domains of cytoplasmic protein-tyrosine kinases: regulatory elements in signal transduction. Oncogene. 1988 Nov;3(5):491–495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pendergast A. M., Muller A. J., Havlik M. H., Maru Y., Witte O. N. BCR sequences essential for transformation by the BCR-ABL oncogene bind to the ABL SH2 regulatory domain in a non-phosphotyrosine-dependent manner. Cell. 1991 Jul 12;66(1):161–171. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90148-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piwnica-Worms H., Saunders K. B., Roberts T. M., Smith A. E., Cheng S. H. Tyrosine phosphorylation regulates the biochemical and biological properties of pp60c-src. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):75–82. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90757-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds A. B., Kanner S. B., Wang H. C., Parsons J. T. Stable association of activated pp60src with two tyrosine-phosphorylated cellular proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):3951–3958. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.3951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg N., Witte O. N. The viral and cellular forms of the Abelson (abl) oncogene. Adv Virus Res. 1988;35:39–81. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60708-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski I., Stone J. C., Pawson T. A noncatalytic domain conserved among cytoplasmic protein-tyrosine kinases modifies the kinase function and transforming activity of Fujinami sarcoma virus P130gag-fps. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4396–4408. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiff-Maker L., Burns M. C., Konopka J. B., Clark S., Witte O. N., Rosenberg N. Monoclonal antibodies specific for v-abl- and c-abl-encoded molecules. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):1182–1186. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.1182-1186.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnik E. Y., Margolis B., Mohammadi M., Lowenstein E., Fischer R., Drepps A., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Cloning of PI3 kinase-associated p85 utilizing a novel method for expression/cloning of target proteins for receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):83–90. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90410-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder M. A., Bishop J. M., Colby W. W., Levinson A. D. Phosphorylation of tyrosine-416 is not required for the transforming properties and kinase activity of pp60v-src. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):891–901. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90074-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trahey M., Wong G., Halenbeck R., Rubinfeld B., Martin G. A., Ladner M., Long C. M., Crosier W. J., Watt K., Koths K. Molecular cloning of two types of GAP complementary DNA from human placenta. Science. 1988 Dec 23;242(4886):1697–1700. doi: 10.1126/science.3201259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90801-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verderame M. F., Kaplan J. M., Varmus H. E. A mutation in v-src that removes a single conserved residue in the SH-2 domain of pp60v-src restricts transformation in a host-dependent manner. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):338–348. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.338-348.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel U. S., Dixon R. A., Schaber M. D., Diehl R. E., Marshall M. S., Scolnick E. M., Sigal I. S., Gibbs J. B. Cloning of bovine GAP and its interaction with oncogenic ras p21. Nature. 1988 Sep 1;335(6185):90–93. doi: 10.1038/335090a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H. C., Parsons J. T. Deletions and insertions within an amino-terminal domain of pp60v-src inactivate transformation and modulate membrane stability. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):291–302. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.291-302.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]