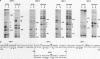Abstract
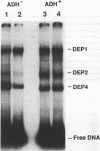
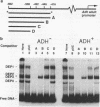
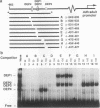
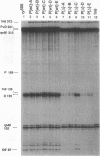
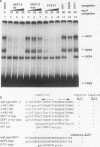
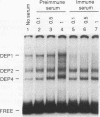
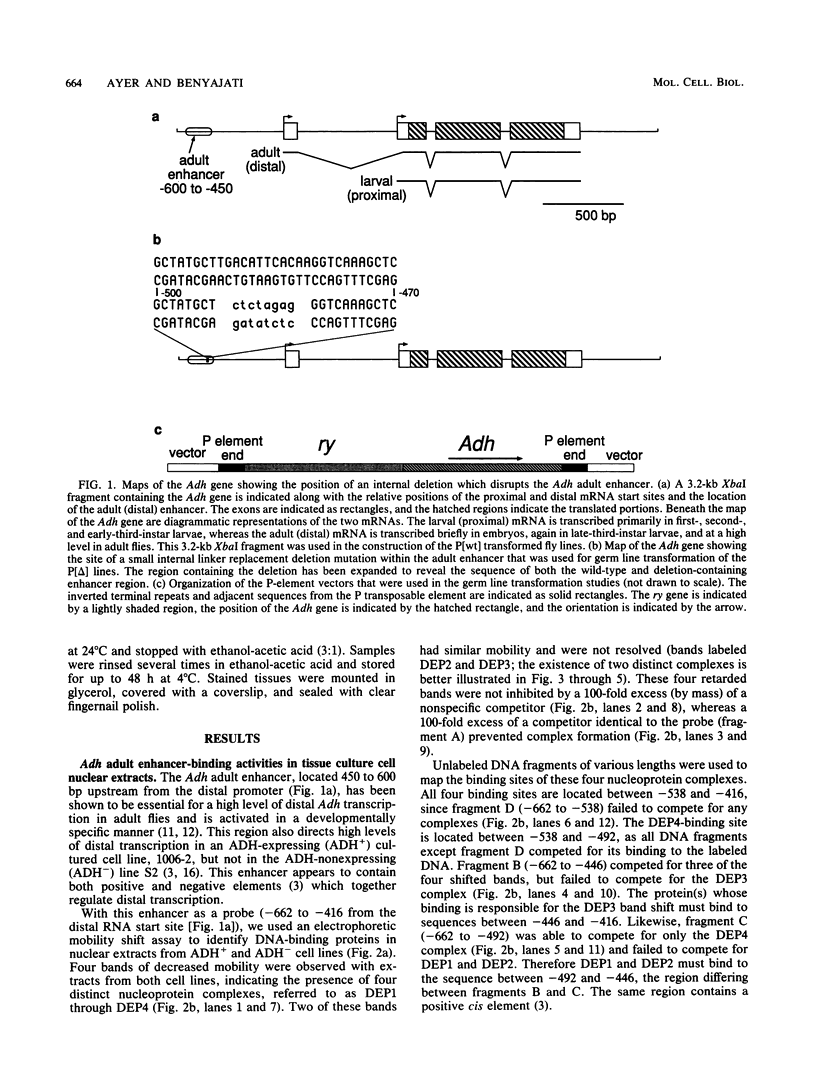
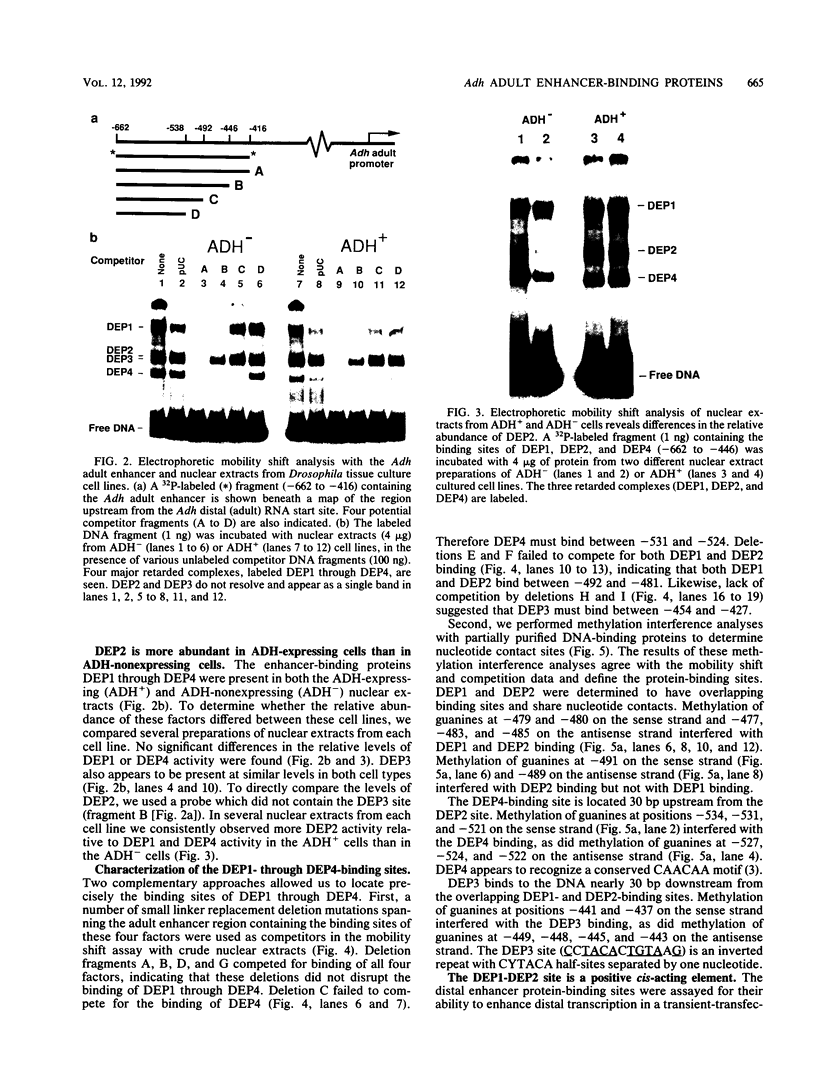
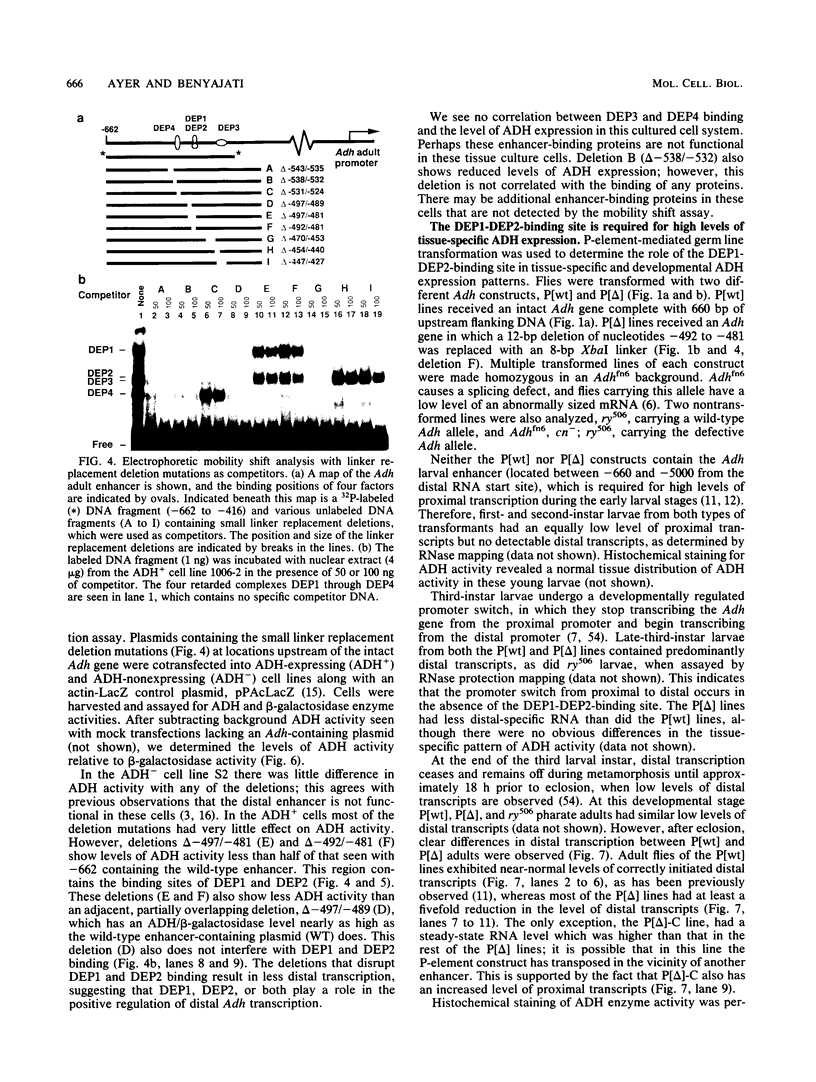
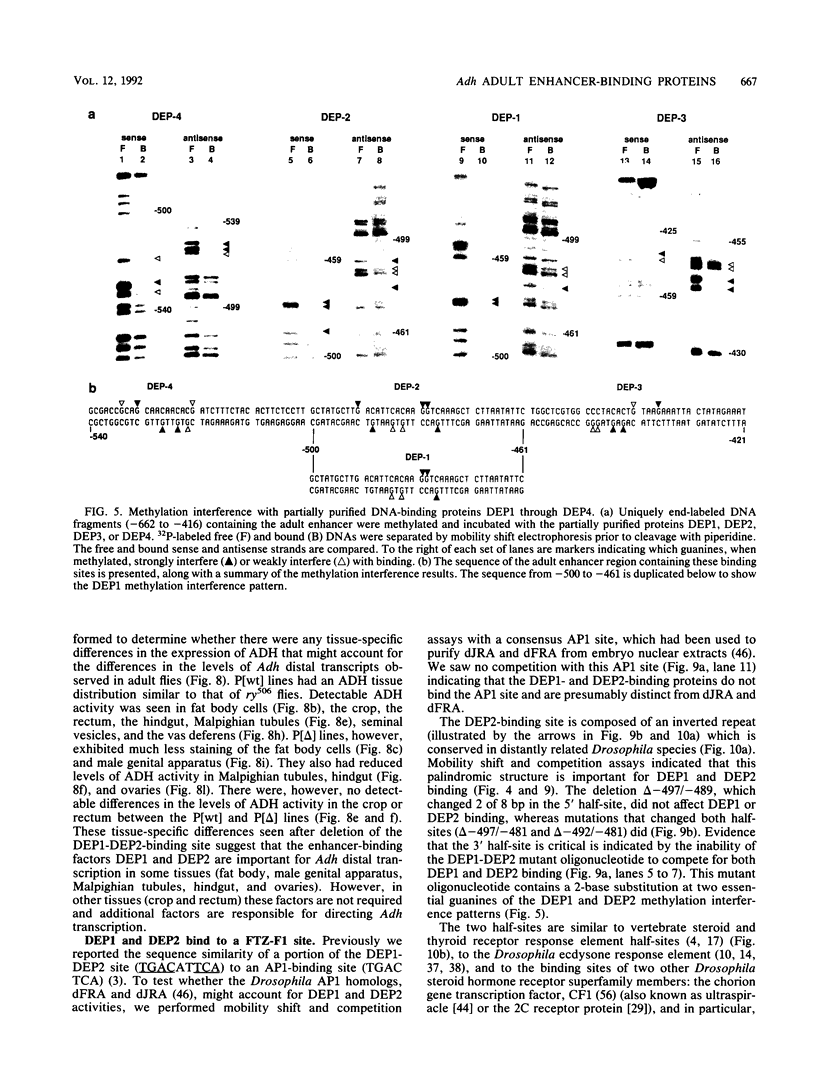
Developmental and tissue-specific transcription from the Adh distal promoter is regulated in part by the Adh adult enhancer, located 450 to 600 bp upstream from the distal RNA start site. We have characterized four proteins (DEP1 to DEP4), present in Drosophila tissue culture cell nuclear extracts, which bind to this enhancer. DEP1 and DEP2 bind to a positive cis-acting element (-492 to -481) and share nucleotide contacts. A small linker replacement deletion mutation, which disrupts the overlapping DEP1- and DEP2-binding sites, reduces Adh distal transcription in an alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH)-expressing cultured cell line, in the adult fat body (the major tissue of ADH expression), as well as in some but not all adult tissues where ADH is normally expressed. This enhancer element contains an imperfect palindromic sequence similar to steroid hormone receptor superfamily response elements. Binding-site screening of a lambda gt11 expression library has identified the steroid receptor superfamily member fushi tarazu factor 1 (FTZ-F1) as a protein that binds to this site. Anti-FTZ-F1 antibodies have identified DEP1 as FTZ-F1. DEP2 also binds to the FTZ-F1 site from the fushi tarazu zebra element, suggesting that DEP2 may also be a steroid receptor superfamily member. Our results raise the possibility that Adh regulation in certain adult tissues involves a hormone-mediated pathway. Because DEP1 (FTZ-F1) and DEP2 contact some of the same nucleotides within the positive cis element, it is unlikely that they can bind simultaneously. Such alternative binding may play a role in the tissue-specific and developmental transcription of Adh.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkinson P. W., Mills L. E., Starmer W. T., Sullivan D. T. Structure and evolution of the Adh genes of Drosophila mojavensis. Genetics. 1988 Nov;120(3):713–723. doi: 10.1093/genetics/120.3.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayer S., Benyajati C. Conserved enhancer and silencer elements responsible for differential Adh transcription in Drosophila cell lines. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3512–3523. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beato M. Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benyajati C., Ayer S., McKeon J., Ewel A., Huang J. Roles of cis-acting elements and chromatin structure in Drosophila alcohol dehydrogenase gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 12;15(19):7903–7920. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.19.7903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benyajati C., Place A. R., Wang N., Pentz E., Sofer W. Deletions at intervening sequence splice sites in the alcohol dehydrogenase gene of Drosophila. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 25;10(22):7261–7272. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.22.7261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benyajati C., Spoerel N., Haymerle H., Ashburner M. The messenger RNA for alcohol dehydrogenase in Drosophila melanogaster differs in its 5' end in different developmental stages. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):125–133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90341-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan M. D., Dickinson W. J. Complex developmental regulation of the Drosophila affinidisjuncta alcohol dehydrogenase gene in Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol. 1988 Jan;125(1):64–74. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90059-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright I. L. Developmental switch in chromatin structure associated with alternate promoter usage in the Drosophila melanogaster alcohol dehydrogenase gene. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):3097–3101. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02618.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherbas L., Lee K., Cherbas P. Identification of ecdysone response elements by analysis of the Drosophila Eip28/29 gene. Genes Dev. 1991 Jan;5(1):120–131. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.1.120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin V., Maniatis T. Identification of cis-regulatory elements required for larval expression of the Drosophila melanogaster alcohol dehydrogenase gene. Genetics. 1990 Mar;124(3):637–646. doi: 10.1093/genetics/124.3.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin V., Maniatis T. Role of transcriptional interference in the Drosophila melanogaster Adh promoter switch. Nature. 1989 Jan 19;337(6204):279–282. doi: 10.1038/337279a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin V., Maniatis T. The role of specific enhancer-promoter interactions in the Drosophila Adh promoter switch. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2191–2120. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobens L., Rudolph K., Berger E. M. Ecdysterone regulatory elements function as both transcriptional activators and repressors. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):1846–1853. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.1846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driever W., Nüsslein-Volhard C. The bicoid protein is a positive regulator of hunchback transcription in the early Drosophila embryo. Nature. 1989 Jan 12;337(6203):138–143. doi: 10.1038/337138a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England B. P., Heberlein U., Tjian R. Purified Drosophila transcription factor, Adh distal factor-1 (Adf-1), binds to sites in several Drosophila promoters and activates transcription. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 25;265(9):5086–5094. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):889–895. doi: 10.1126/science.3283939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewel A., Jackson J. R., Benyajati C. Alternative DNA-protein interactions in variable-length internucleosomal regions associated with Drosophila Adh distal promoter expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 11;18(7):1771–1781. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.7.1771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer J. A., Maniatis T. Drosophila Adh: a promoter element expands the tissue specificity of an enhancer. Cell. 1988 May 6;53(3):451–461. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90165-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer J. A., Maniatis T. Regulatory elements involved in Drosophila Adh gene expression are conserved in divergent species and separate elements mediate expression in different tissues. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1275–1289. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04357.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer J. A., Maniatis T. Structure and transcription of the Drosophila mulleri alcohol dehydrogenase genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 11;13(19):6899–6917. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.19.6899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraenkel G., Su J. Hormonal control of eclosion of flies from the puparium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1457–1459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garabedian M. J., Shepherd B. M., Wensink P. C. A tissue-specific transcription enhancer from the Drosophila yolk protein 1 gene. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):859–867. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90560-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass C. K., Devary O. V., Rosenfeld M. G. Multiple cell type-specific proteins differentially regulate target sequence recognition by the alpha retinoic acid receptor. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):729–738. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90139-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass C. K., Lipkin S. M., Devary O. V., Rosenfeld M. G. Positive and negative regulation of gene transcription by a retinoic acid-thyroid hormone receptor heterodimer. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):697–708. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90016-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heberlein U., England B., Tjian R. Characterization of Drosophila transcription factors that activate the tandem promoters of the alcohol dehydrogenase gene. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):965–977. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80077-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heberlein U., Tjian R. Temporal pattern of alcohol dehydrogenase gene transcription reproduced by Drosophila stage-specific embryonic extracts. Nature. 1988 Feb 4;331(6155):410–415. doi: 10.1038/331410a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Cloning exons of mapping of transcription: characterization of the Drosophila melanogaster alcohol dehydrogenase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jul 25;11(14):4735–4752. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.14.4735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henrich V. C., Sliter T. J., Lubahn D. B., MacIntyre A., Gilbert L. I. A steroid/thyroid hormone receptor superfamily member in Drosophila melanogaster that shares extensive sequence similarity with a mammalian homologue. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 25;18(14):4143–4148. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.14.4143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway J. M., Glass C. K., Adler S., Nelson C. A., Rosenfeld M. G. The C'-terminal interaction domain of the thyroid hormone receptor confers the ability of the DNA site to dictate positive or negative transcriptional activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):8160–8164. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.8160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Tjian R. Affinity purification of sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5889–5893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karess R. E., Rubin G. M. Analysis of P transposable element functions in Drosophila. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):135–146. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90534-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koelle M. R., Talbot W. S., Segraves W. A., Bender M. T., Cherbas P., Hogness D. S. The Drosophila EcR gene encodes an ecdysone receptor, a new member of the steroid receptor superfamily. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):59–77. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90572-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar V., Chambon P. The estrogen receptor binds tightly to its responsive element as a ligand-induced homodimer. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):145–156. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90017-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavorgna G., Ueda H., Clos J., Wu C. FTZ-F1, a steroid hormone receptor-like protein implicated in the activation of fushi tarazu. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):848–851. doi: 10.1126/science.1709303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockett T. J., Ashburner M. Temporal and spatial utilization of the alcohol dehydrogenase gene promoters during the development of Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol. 1989 Aug;134(2):430–437. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(89)90115-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo Y., Amin J., Voellmy R. Ecdysterone receptor is a sequence-specific transcription factor involved in the developmental regulation of heat shock genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;11(7):3660–3675. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.7.3660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maschat F., Dubertret M. L., Lepesant J. A. Transformation mapping of the regulatory elements of the ecdysone-inducible P1 gene of Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2913–2917. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mlodzik M., Hiromi Y., Weber U., Goodman C. S., Rubin G. M. The Drosophila seven-up gene, a member of the steroid receptor gene superfamily, controls photoreceptor cell fates. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):211–224. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90737-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses K., Heberlein U., Ashburner M. The Adh gene promoters of Drosophila melanogaster and Drosophila orena are functionally conserved and share features of sequence structure and nuclease-protected sites. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):539–548. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murtha M. T., Cavener D. R. Ecdysteroid regulation of glucose dehydrogenase and alcohol dehydrogenase gene expression in Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol. 1989 Sep;135(1):66–73. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(89)90158-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nauber U., Pankratz M. J., Kienlin A., Seifert E., Klemm U., Jäckle H. Abdominal segmentation of the Drosophila embryo requires a hormone receptor-like protein encoded by the gap gene knirps. Nature. 1988 Dec 1;336(6198):489–492. doi: 10.1038/336489a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connell P. O., Rosbash M. Sequence, structure, and codon preference of the Drosophila ribosomal protein 49 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 11;12(13):5495–5513. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.13.5495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oro A. E., McKeown M., Evans R. M. Relationship between the product of the Drosophila ultraspiracle locus and the vertebrate retinoid X receptor. Nature. 1990 Sep 20;347(6290):298–301. doi: 10.1038/347298a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oro A. E., Ong E. S., Margolis J. S., Posakony J. W., McKeown M., Evans R. M. The Drosophila gene knirps-related is a member of the steroid-receptor gene superfamily. Nature. 1988 Dec 1;336(6198):493–496. doi: 10.1038/336493a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins K. K., Dailey G. M., Tjian R. In vitro analysis of the Antennapedia P2 promoter: identification of a new Drosophila transcription factor. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1615–1626. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins K. K., Dailey G. M., Tjian R. Novel Jun- and Fos-related proteins in Drosophila are functionally homologous to enhancer factor AP-1. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4265–4273. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03324.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pignoni F., Baldarelli R. M., Steingrímsson E., Diaz R. J., Patapoutian A., Merriam J. R., Lengyel J. A. The Drosophila gene tailless is expressed at the embryonic termini and is a member of the steroid receptor superfamily. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):151–163. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90249-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posakony J. W., Fischer J. A., Maniatis T. Identification of DNA sequences required for the regulation of Drosophila alcohol dehydrogenase gene expression. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1985;50:515–520. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1985.050.01.063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson H. M., Preston C. R., Phillis R. W., Johnson-Schlitz D. M., Benz W. K., Engels W. R. A stable genomic source of P element transposase in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1988 Mar;118(3):461–470. doi: 10.1093/genetics/118.3.461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothe M., Nauber U., Jäckle H. Three hormone receptor-like Drosophila genes encode an identical DNA-binding finger. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):3087–3094. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08460.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowan R. G., Dickinson W. J. Nucleotide sequence of the genomic region encoding alcohol dehydrogenase in Drosophila affinidisjuncta. J Mol Evol. 1988 Dec;28(1-2):43–54. doi: 10.1007/BF02143496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M., Spradling A. C. Vectors for P element-mediated gene transfer in Drosophila. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 24;11(18):6341–6351. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.18.6341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segraves W. A., Hogness D. S. The E75 ecdysone-inducible gene responsible for the 75B early puff in Drosophila encodes two new members of the steroid receptor superfamily. Genes Dev. 1990 Feb;4(2):204–219. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.2.204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shea M. J., King D. L., Conboy M. J., Mariani B. D., Kafatos F. C. Proteins that bind to Drosophila chorion cis-regulatory elements: a new C2H2 zinc finger protein and a C2C2 steroid receptor-like component. Genes Dev. 1990 Jul;4(7):1128–1140. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.7.1128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simcox A. A., Sobeih M. M., Shearn A. Establishment and characterization of continuous cell lines derived from temperature-sensitive mutants of Drosophila melanogaster. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1985 Jan;11(1):63–70. doi: 10.1007/BF01534735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinhauer W. R., Walsh R. C., Kalfayan L. J. Sequence and structure of the Drosophila melanogaster ovarian tumor gene and generation of an antibody specific for the ovarian tumor protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5726–5732. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. Y., Carlstedt-Duke J., Weigel N. L., Dahlman K., Gustafsson J. A., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Molecular interactions of steroid hormone receptor with its enhancer element: evidence for receptor dimer formation. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):361–369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90059-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda H., Sonoda S., Brown J. L., Scott M. P., Wu C. A sequence-specific DNA-binding protein that activates fushi tarazu segmentation gene expression. Genes Dev. 1990 Apr;4(4):624–635. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.4.624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinson C. R., LaMarco K. L., Johnson P. F., Landschulz W. H., McKnight S. L. In situ detection of sequence-specific DNA binding activity specified by a recombinant bacteriophage. Genes Dev. 1988 Jul;2(7):801–806. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.7.801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahli W., Martinez E. Superfamily of steroid nuclear receptors: positive and negative regulators of gene expression. FASEB J. 1991 Jun;5(9):2243–2249. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.9.1860615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. H., Tsai S. Y., Cook R. G., Beattie W. G., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. COUP transcription factor is a member of the steroid receptor superfamily. Nature. 1989 Jul 13;340(6229):163–166. doi: 10.1038/340163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson T. E., Fahrner T. J., Johnston M., Milbrandt J. Identification of the DNA binding site for NGFI-B by genetic selection in yeast. Science. 1991 May 31;252(5010):1296–1300. doi: 10.1126/science.1925541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]