Abstract
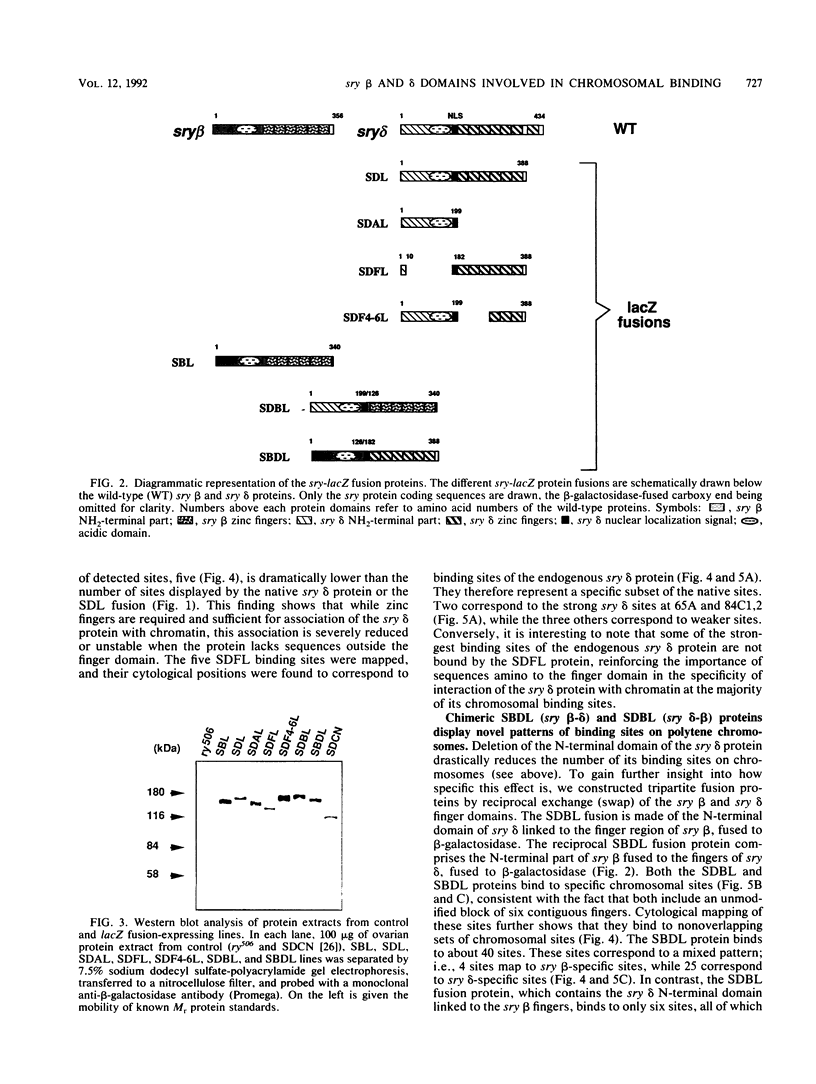
The closely related Drosophila serendipity (sry) beta and delta zinc finger proteins display consensus in vitro DNA recognition sequences differing by 4 of 13 nucleotide positions and bind in vivo to distinct sets of sites on polytene chromosomes. We compared the pattern of in vivo chromosomal binding of deleted forms of the sry delta protein fused to beta-galactosidase and expressed in Drosophila transgenic lines. Results show that the carboxy-terminal DNA-binding finger domain is required and sufficient for binding at specific chromosomal sites but that this binding does not nearly reproduce the wild-type pattern. An NH2-terminal domain of the sry delta protein is essential to its specificity of in vivo interaction with chromatin. In vitro and in vivo experiments using reciprocal finger swap between the sry beta and delta proteins suggest that the in vivo specificity is dependent on selective protein-protein contacts at defined chromosomal sites, in addition to DNA specific recognition.
Full text
PDF



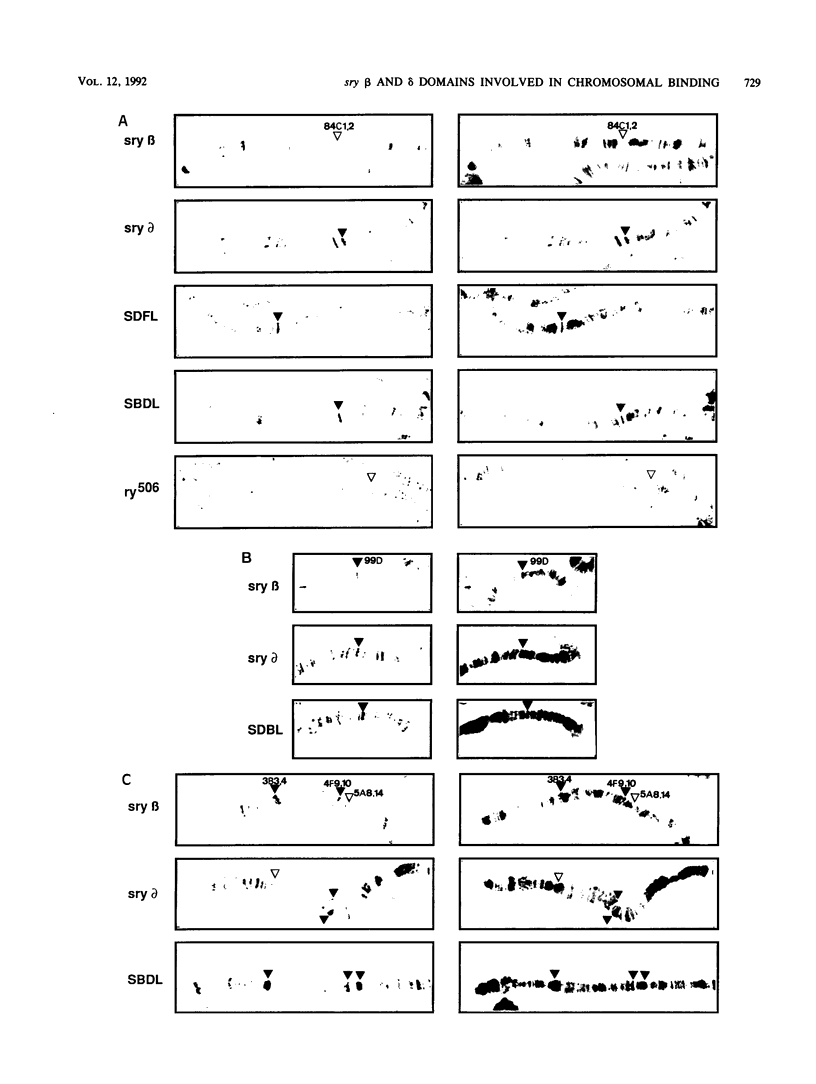
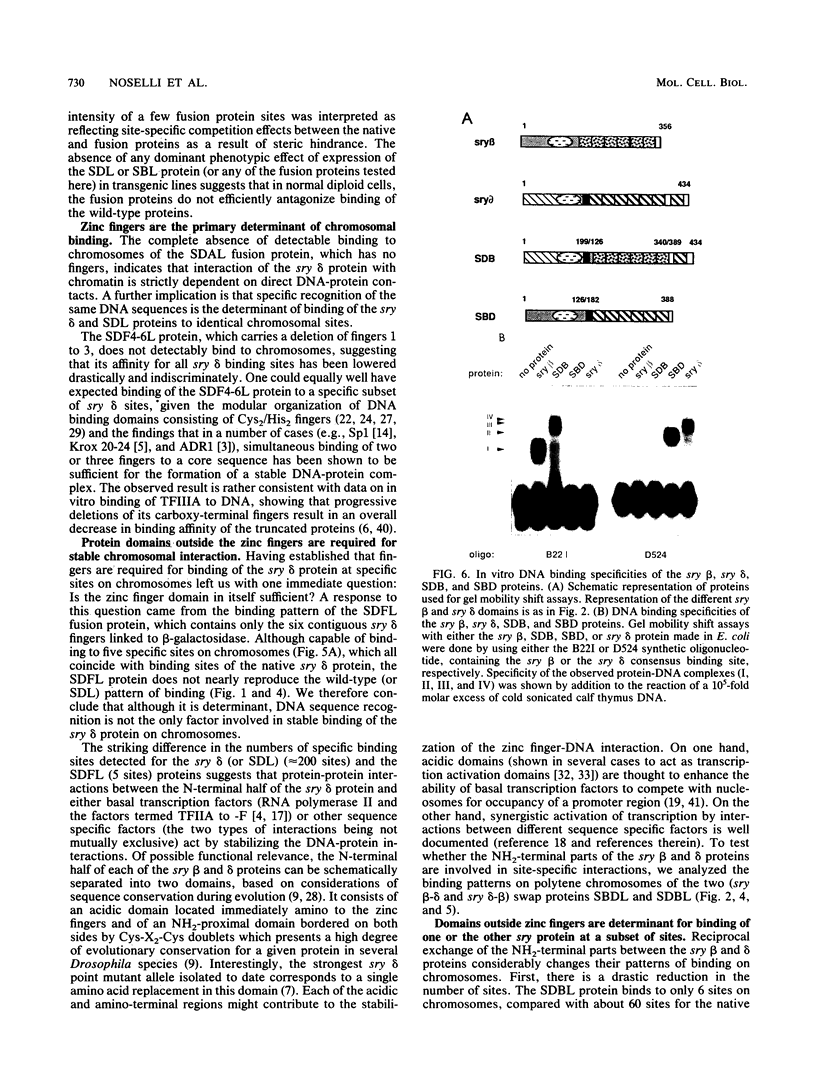



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bellefroid E. J., Poncelet D. A., Lecocq P. J., Revelant O., Martial J. A. The evolutionarily conserved Krüppel-associated box domain defines a subfamily of eukaryotic multifingered proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3608–3612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg J. M. Zinc finger domains: hypotheses and current knowledge. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1990;19:405–421. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.19.060190.002201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg H., Eisen A., Sledziewski A., Bader D., Young E. T. Two zinc fingers of a yeast regulatory protein shown by genetic evidence to be essential for its function. 1987 Jul 30-Aug 5Nature. 328(6129):443–445. doi: 10.1038/328443a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buratowski S., Hahn S., Guarente L., Sharp P. A. Five intermediate complexes in transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):549–561. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90578-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavrier P., Lemaire P., Revelant O., Bravo R., Charnay P. Characterization of a mouse multigene family that encodes zinc finger structures. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1319–1326. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen J. H., Hansen P. K., Lillelund O., Thøgersen H. C. Sequence-specific binding of the N-terminal three-finger fragment of Xenopus transcription factor IIIA to the internal control region of a 5S RNA gene. FEBS Lett. 1991 Apr 9;281(1-2):181–184. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80388-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M., Hollenberg S. M. Zinc fingers: gilt by association. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90522-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel A. D., Kim P. S. Modular structure of transcription factors: implications for gene regulation. Cell. 1991 May 31;65(5):717–719. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90378-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser R. L., Wolfner M. F., Lis J. T. Spatial and temporal pattern of hsp26 expression during normal development. EMBO J. 1986 Apr;5(4):747–754. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04277.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi S., Scott M. P. What determines the specificity of action of Drosophila homeodomain proteins? Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):883–894. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90492-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabisch R., Bautz E. K. Differential distribution of RNA polymerase B and nonhistone chromosomal proteins in polytene chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J. 1983;2(3):395–402. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01436.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Carner K. R., Masiarz F. R., Tjian R. Isolation of cDNA encoding transcription factor Sp1 and functional analysis of the DNA binding domain. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1079–1090. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90594-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knöchel W., Pöting A., Köster M., el Baradi T., Nietfeld W., Bouwmeester T., Pieler T. Evolutionary conserved modules associated with zinc fingers in Xenopus laevis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6097–6100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewin B. Commitment and activation at pol II promoters: a tail of protein-protein interactions. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1161–1164. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90675-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li R., Knight J. D., Jackson S. P., Tjian R., Botchan M. R. Direct interaction between Sp1 and the BPV enhancer E2 protein mediates synergistic activation of transcription. Cell. 1991 May 3;65(3):493–505. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90467-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. S., Green M. R. Mechanism of action of an acidic transcriptional activator in vitro. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):971–981. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90321-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., McLachlan A. D., Klug A. Repetitive zinc-binding domains in the protein transcription factor IIIA from Xenopus oocytes. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1609–1614. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03825.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nardelli J., Gibson T. J., Vesque C., Charnay P. Base sequence discrimination by zinc-finger DNA-binding domains. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):175–178. doi: 10.1038/349175a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nietfeld W., el-Baradi T., Mentzel H., Pieler T., Köster M., Pöting A., Knöchel W. Second-order repeats in Xenopus laevis finger proteins. J Mol Biol. 1989 Aug 20;208(4):639–659. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90155-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noselli S., Vincent A. A Drosophila nuclear localisation signal included in an 18 amino acid fragment from the serendipity delta zinc finger protein. FEBS Lett. 1991 Mar 11;280(1):167–170. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80229-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavletich N. P., Pabo C. O. Zinc finger-DNA recognition: crystal structure of a Zif268-DNA complex at 2.1 A. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):809–817. doi: 10.1126/science.2028256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payre F., Noselli S., Lefrère V., Vincent A. The closely related Drosophila sry beta and sry delta zinc finger proteins show differential embryonic expression and distinct patterns of binding sites on polytene chromosomes. Development. 1990 Sep;110(1):141–149. doi: 10.1242/dev.110.1.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payre F., Vincent A. Finger proteins and DNA-specific recognition: distinct patterns of conserved amino acids suggest different evolutionary modes. FEBS Lett. 1988 Jul 18;234(2):245–250. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80091-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payre F., Vincent A. Genomic targets of the serendipity beta and delta zinc finger proteins and their respective DNA recognition sites. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2533–2541. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07793.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payre F., Yanicostas C., Vincent A. Serendipity delta, a Drosophila zinc finger protein present in embryonic nuclei at the onset of zygotic gene transcription. Dev Biol. 1989 Dec;136(2):469–480. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(89)90272-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M., Gann A. A. Activators and targets. Nature. 1990 Jul 26;346(6282):329–331. doi: 10.1038/346329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. How eukaryotic transcriptional activators work. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):683–689. doi: 10.1038/335683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson H. M., Preston C. R., Phillis R. W., Johnson-Schlitz D. M., Benz W. K., Engels W. R. A stable genomic source of P element transposase in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1988 Mar;118(3):461–470. doi: 10.1093/genetics/118.3.461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M., Spradling A. C. Vectors for P element-mediated gene transfer in Drosophila. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 24;11(18):6341–6351. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.18.6341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent A., Colot H. V., Rosbash M. Blastoderm-specific and read-through transcription of the sry alpha gene transformed into the Drosophila genome. Dev Biol. 1986 Dec;118(2):480–487. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90019-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent A., Colot H. V., Rosbash M. Sequence and structure of the serendipity locus of Drosophila melanogaster. A densely transcribed region including a blastoderm-specific gene. J Mol Biol. 1985 Nov 5;186(1):149–166. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90265-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vrana K. E., Churchill M. E., Tullius T. D., Brown D. D. Mapping functional regions of transcription factor TFIIIA. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1684–1696. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Workman J. L., Taylor I. C., Kingston R. E. Activation domains of stably bound GAL4 derivatives alleviate repression of promoters by nucleosomes. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):533–544. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90237-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zink B., Engström Y., Gehring W. J., Paro R. Direct interaction of the Polycomb protein with Antennapedia regulatory sequences in polytene chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):153–162. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07931.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zink B., Paro R. In vivo binding pattern of a trans-regulator of homoeotic genes in Drosophila melanogaster. Nature. 1989 Feb 2;337(6206):468–471. doi: 10.1038/337468a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]