Abstract
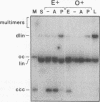
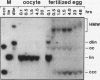
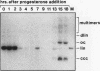
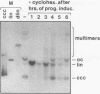
Mature Xenopus laevis eggs provide an elementary reaction system of illegitimate recombination which efficiently joins nonhomologous DNA ends (P. Pfeiffer and W. Vielmetter, Nucleic Acids Res. 16:907-924, 1988). Here we show that stage VI oocytes, known to express a system for homologous recombination (D. Carroll, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 80:6902-6906, 1983), are completely devoid of this joining system. Nonhomologous DNA end-to-end joining, however, attains full activity only at an extremely late stage of egg maturation. Cycloheximide inhibition patterns indicate that nonhomologous joining activity is regulated at the G2 restriction point of the cell cycle. Implications of homologous and nonhomologous recombination activities during egg maturation are discussed.
Full text
PDF
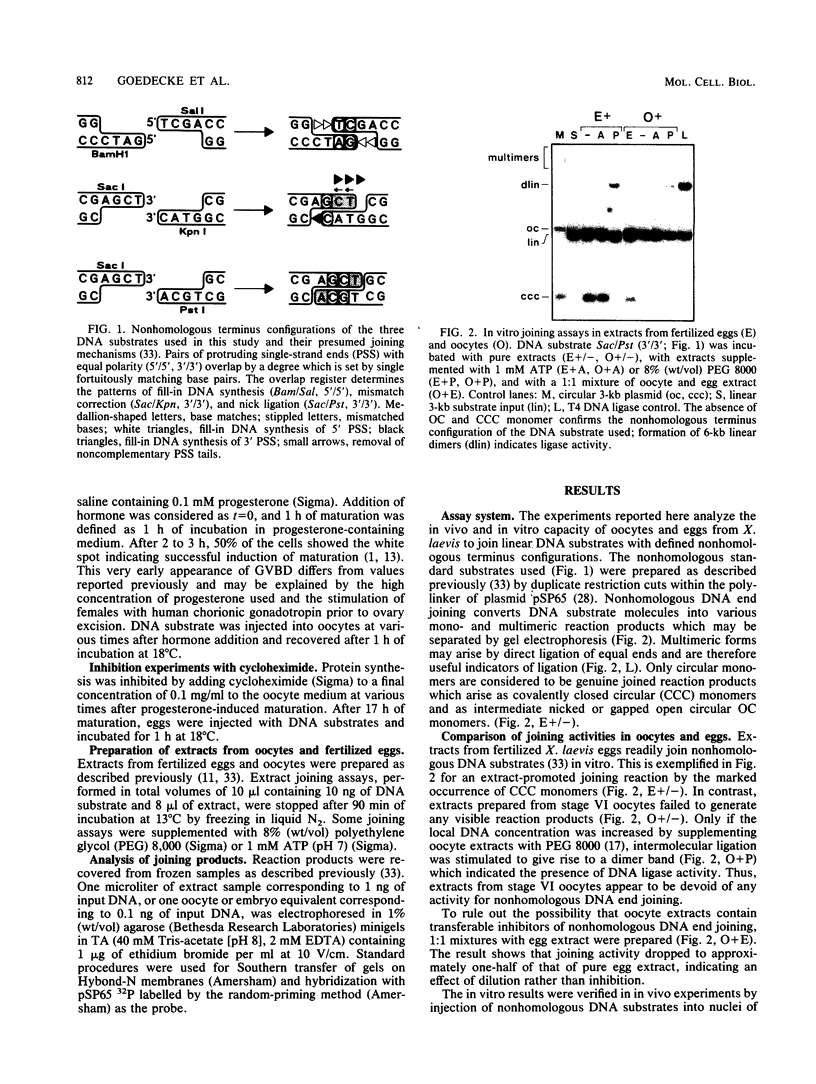
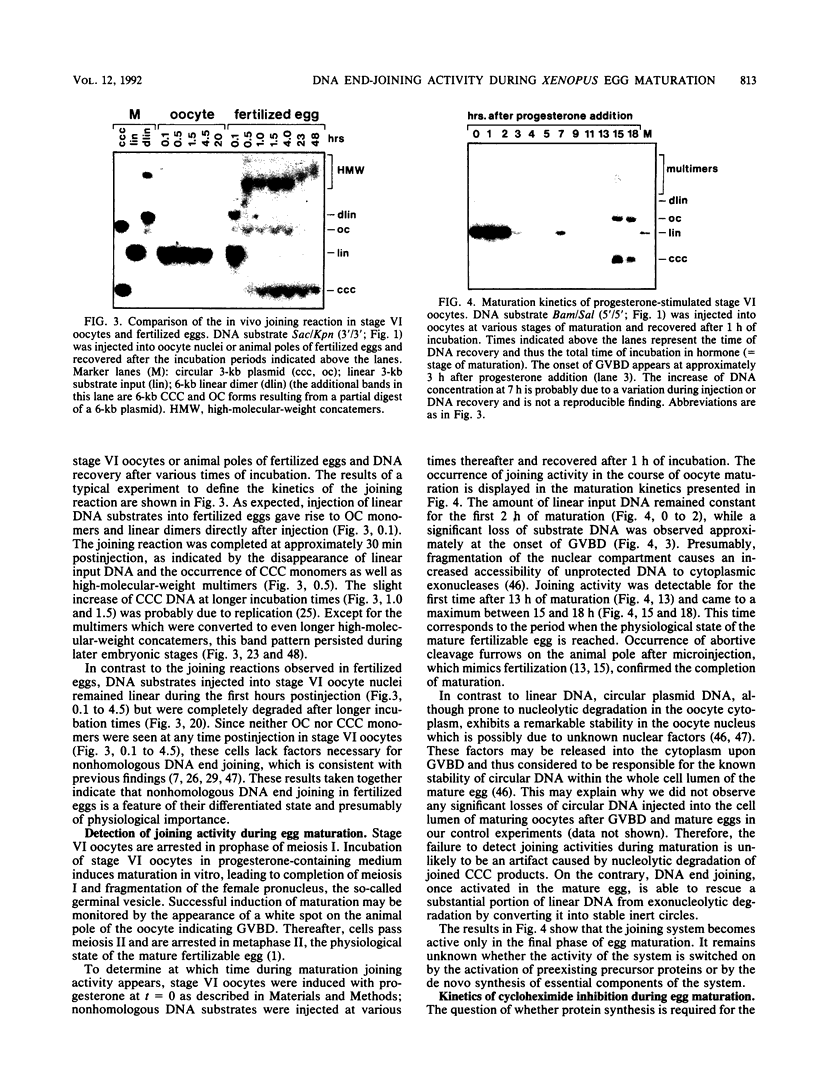



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baulieu E. E., Godeau F., Schorderet M., Schorderet-Slatkine S. Steroid-induced meiotic division in Xenopus laevis oocytes: surface and calcium. Nature. 1978 Oct 19;275(5681):593–598. doi: 10.1038/275593a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayne M. L., Alexander R. F., Benbow R. M. DNA binding protein from ovaries of the frog, Xenopus laevis which promotes concatenation of linear DNA. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jan 5;172(1):87–108. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90416-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendig M. M. Persistence and expression of histone genes injected into Xenopus eggs in early development. Nature. 1981 Jul 2;292(5818):65–67. doi: 10.1038/292065a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll D. Genetic recombination of bacteriophage lambda DNAs in Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6902–6906. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll D., Wright S. H., Wolff R. K., Grzesiuk E., Maryon E. B. Efficient homologous recombination of linear DNA substrates after injection into Xenopus laevis oocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2053–2061. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortese R., Harland R., Melton D. Transcription of tRNA genes in vivo: single-stranded compared to double-stranded templates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4147–4151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drury K. C., Schorderet-Slatkine S. Effects of cycloheximide on the "autocatalytic" nature of the maturation promoting factor (MPF) in oocytes of Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1975 Mar;4(3):269–274. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90175-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumont J. N. Oogenesis in Xenopus laevis (Daudin). I. Stages of oocyte development in laboratory maintained animals. J Morphol. 1972 Feb;136(2):153–179. doi: 10.1002/jmor.1051360203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glikin G. C., Ruberti I., Worcel A. Chromatin assembly in Xenopus oocytes: in vitro studies. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):33–41. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90298-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu H., Förster I., Rajewsky K. Sequence homologies, N sequence insertion and JH gene utilization in VHDJH joining: implications for the joining mechanism and the ontogenetic timing of Ly1 B cell and B-CLL progenitor generation. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2133–2140. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07382.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurdon J. B. Changes in somatic cell nuclei inserted into growing and maturing amphibian oocytes. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1968 Nov;20(3):401–414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurdon J. B., Melton D. A. Gene transfer in amphibian eggs and oocytes. Annu Rev Genet. 1981;15:189–218. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.15.120181.001201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy S., Aoufouchi S., Thiebaud P., Prigent C. DNA ligase I from Xenopus laevis eggs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Feb 25;19(4):701–705. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.4.701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harland R. M., Laskey R. A. Regulated replication of DNA microinjected into eggs of Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):761–771. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90439-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi K., Nakazawa M., Ishizaki Y., Hiraoka N., Obayashi A. Regulation of inter- and intramolecular ligation with T4 DNA ligase in the presence of polyethylene glycol. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Oct 10;14(19):7617–7631. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.19.7617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnen A., Hicks J. B., Fink G. R. Transformation of yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1929–1933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeggo P. A. Studies on mammalian mutants defective in rejoining double-strand breaks in DNA. Mutat Res. 1990 Jul;239(1):1–16. doi: 10.1016/0165-1110(90)90028-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanki J. P., Donoghue D. J. Progression from meiosis I to meiosis II in Xenopus oocytes requires de novo translation of the mosxe protooncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5794–5798. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato S., Anderson R. A., Camerini-Otero R. D. Foreign DNA introduced by calcium phosphate is integrated into repetitive DNA elements of the mouse L cell genome. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1787–1795. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maller J. L. Xenopus oocytes and the biochemistry of cell division. Biochemistry. 1990 Apr 3;29(13):3157–3166. doi: 10.1021/bi00465a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marini N. J., Benbow R. M. Differential compartmentalization of plasmid DNA microinjected into Xenopus laevis embryos relates to replication efficiency. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):299–308. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marini N. J., Etkin L. D., Benbow R. M. Persistence and replication of plasmid DNA microinjected into early embryos of Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1988 Jun;127(2):421–434. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90328-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maryon E., Carroll D. Characterization of recombination intermediates from DNA injected into Xenopus laevis oocytes: evidence for a nonconservative mechanism of homologous recombination. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):3278–3287. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.3278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maryon E., Carroll D. Degradation of linear DNA by a strand-specific exonuclease activity in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4862–4871. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertz J. E. Linear DNA does not form chromatin containing regularly spaced nucleosomes. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Dec;2(12):1608–1618. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.12.1608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Kirschner M. W. Dominoes and clocks: the union of two views of the cell cycle. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):614–621. doi: 10.1126/science.2683077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North P., Ganesh A., Thacker J. The rejoining of double-strand breaks in DNA by human cell extracts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 11;18(21):6205–6210. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.21.6205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer P., Vielmetter W. Joining of nonhomologous DNA double strand breaks in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):907–924. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins D. M., Ripley S., Henderson A. S., Axel R. Transforming DNA integrates into the host chromosome. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):29–39. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90267-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth D. B., Porter T. N., Wilson J. H. Mechanisms of nonhomologous recombination in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2599–2607. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth D. B., Wilson J. H. Nonhomologous recombination in mammalian cells: role for short sequence homologies in the joining reaction. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4295–4304. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth D. B., Wilson J. H. Relative rates of homologous and nonhomologous recombination in transfected DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3355–3359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. J. One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:202–211. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer S., Davis R. W. Replacement of chromosome segments with altered DNA sequences constructed in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4951–4955. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thode S., Schäfer A., Pfeiffer P., Vielmetter W. A novel pathway of DNA end-to-end joining. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):921–928. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90340-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman W. J., Masui Y. Effects of cyclohexamide on a cytoplasmic factor initiating meiotic naturation in Xenopus oocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1975 Mar 15;91(2):381–388. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(75)90118-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. H., Berget P. B., Pipas J. M. Somatic cells efficiently join unrelated DNA segments end-to-end. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;2(10):1258–1269. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.10.1258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. H., Gurdon J. B., Price J. Nuclear localisation of an oocyte component required for the stability of injected DNA. Nature. 1977 Jul 14;268(5616):150–152. doi: 10.1038/268150a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. H., Laskey R. A., Finch J., Gurdon J. B. Selective DNA conservation and chromatin assembly after injection of SV40 DNA into Xenopus oocytes. Dev Biol. 1978 May;64(1):178–188. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90069-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zierler M. K., Marini N. J., Stowers D. J., Benbow R. M. Stockpiling of DNA polymerases during oogenesis and embryogenesis in the frog, Xenopus laevis. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):974–981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]