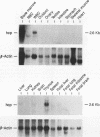
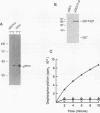
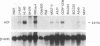
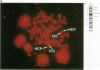
Abstract
Protein tyrosine phosphorylation has been implicated in the growth and functional responses of hematopoietic cells. Recently, approaches have been developed to characterize the protein tyrosine phosphatases that may contribute to regulation of protein tyrosine phosphorylation. One novel protein tyrosine phosphatase was expressed predominantly in hematopoietic cells. Hematopoietic cell phosphatase encodes a 68-kDa protein that contains a single phosphatase conserved domain. Unlike other known protein tyrosine phosphatases, hematopoietic cell phosphatase contains two src homology 2 domains. We also cloned the human homolog, which has 95% amino acid sequence identity. Both the murine and human gene products have tyrosine-specific phosphatase activity, and both are expressed predominantly in hematopoietic cells. Importantly, the human gene maps to chromosome 12 region p12-p13. This region is associated with rearrangements in approximately 10% of cases of acute lymphocytic leukemia in children.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avanzi G. C., Lista P., Giovinazzo B., Miniero R., Saglio G., Benetton G., Coda R., Cattoretti G., Pegoraro L. Selective growth response to IL-3 of a human leukaemic cell line with megakaryoblastic features. Br J Haematol. 1988 Jul;69(3):359–366. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1988.tb02374.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown-Shimer S., Johnson K. A., Lawrence J. B., Johnson C., Bruskin A., Green N. R., Hill D. E. Molecular cloning and chromosome mapping of the human gene encoding protein phosphotyrosyl phosphatase 1B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5148–5152. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll A. J., Raimondi S. C., Williams D. L., Behm F. G., Borowitz M., Castleberry R. P., Harris M. B., Patterson R. B., Pullen D. J., Crist W. M. tdic(9;12): a nonrandom chromosome abnormality in childhood B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a Pediatric Oncology Group Study. Blood. 1987 Dec;70(6):1962–1965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charbonneau H., Tonks N. K., Kumar S., Diltz C. D., Harrylock M., Cool D. E., Krebs E. G., Fischer E. H., Walsh K. A. Human placenta protein-tyrosine-phosphatase: amino acid sequence and relationship to a family of receptor-like proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5252–5256. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charbonneau H., Tonks N. K., Walsh K. A., Fischer E. H. The leukocyte common antigen (CD45): a putative receptor-linked protein tyrosine phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7182–7186. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chernoff J., Schievella A. R., Jost C. A., Erikson R. L., Neel B. G. Cloning of a cDNA for a major human protein-tyrosine-phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2735–2739. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland J. L., Dean M., Rosenberg N., Wang J. Y., Rapp U. R. Tyrosine kinase oncogenes abrogate interleukin-3 dependence of murine myeloid cells through signaling pathways involving c-myc: conditional regulation of c-myc transcription by temperature-sensitive v-abl. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5685–5695. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook W. D., Metcalf D., Nicola N. A., Burgess A. W., Walker F. Malignant transformation of a growth factor-dependent myeloid cell line by Abelson virus without evidence of an autocrine mechanism. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):677–683. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80048-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cool D. E., Tonks N. K., Charbonneau H., Fischer E. H., Krebs E. G. Expression of a human T-cell protein-tyrosine-phosphatase in baby hamster kidney cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):7280–7284. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.7280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cool D. E., Tonks N. K., Charbonneau H., Walsh K. A., Fischer E. H., Krebs E. G. cDNA isolated from a human T-cell library encodes a member of the protein-tyrosine-phosphatase family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5257–5261. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Esch F. S., Taylor S. S., Hunter T. Phosphorylation sites in enolase and lactate dehydrogenase utilized by tyrosine protein kinases in vivo and in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7835–7841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean M., Cleveland J. L., Rapp U. R., Ihle J. N. Role of myc in the abrogation of IL3 dependence of myeloid FDC-P1 cells. Oncogene Res. 1987 Aug;1(3):279–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiseman E., Bolen J. B. src-related tyrosine protein kinases as signaling components in hematopoietic cells. Cancer Cells. 1990 Oct;2(10):303–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escobedo J. A., Navankasattusas S., Kavanaugh W. M., Milfay D., Fried V. A., Williams L. T. cDNA cloning of a novel 85 kd protein that has SH2 domains and regulates binding of PI3-kinase to the PDGF beta-receptor. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):75–82. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90409-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer E. H., Charbonneau H., Tonks N. K. Protein tyrosine phosphatases: a diverse family of intracellular and transmembrane enzymes. Science. 1991 Jul 26;253(5018):401–406. doi: 10.1126/science.1650499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald M., Shenk T. The sequence 5'-AAUAAA-3'forms parts of the recognition site for polyadenylation of late SV40 mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90521-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu M. X., York J. D., Warshawsky I., Majerus P. W. Identification, cloning, and expression of a cytosolic megakaryocyte protein-tyrosine-phosphatase with sequence homology to cytoskeletal protein 4.1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5867–5871. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan K. L., Broyles S. S., Dixon J. E. A Tyr/Ser protein phosphatase encoded by vaccinia virus. Nature. 1991 Mar 28;350(6316):359–362. doi: 10.1038/350359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan K. L., Haun R. S., Watson S. J., Geahlen R. L., Dixon J. E. Cloning and expression of a protein-tyrosine-phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1501–1505. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatakeyama M., Kono T., Kobayashi N., Kawahara A., Levin S. D., Perlmutter R. M., Taniguchi T. Interaction of the IL-2 receptor with the src-family kinase p56lck: identification of novel intermolecular association. Science. 1991 Jun 14;252(5012):1523–1528. doi: 10.1126/science.2047859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horak I. D., Gress R. E., Lucas P. J., Horak E. M., Waldmann T. A., Bolen J. B. T-lymphocyte interleukin 2-dependent tyrosine protein kinase signal transduction involves the activation of p56lck. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1996–2000. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isfort R. J., Ihle J. N. Multiple hematopoietic growth factors signal through tyrosine phosphorylation. Growth Factors. 1990;2(2-3):213–220. doi: 10.3109/08977199009071507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isfort R., Huhn R. D., Frackelton A. R., Jr, Ihle J. N. Stimulation of factor-dependent myeloid cell lines with interleukin 3 induces tyrosine phosphorylation of several cellular substrates. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):19203–19209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanakura Y., Druker B., Cannistra S. A., Furukawa Y., Torimoto Y., Griffin J. D. Signal transduction of the human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and interleukin-3 receptors involves tyrosine phosphorylation of a common set of cytoplasmic proteins. Blood. 1990 Aug 15;76(4):706–715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan R., Morse B., Huebner K., Croce C., Howk R., Ravera M., Ricca G., Jaye M., Schlessinger J. Cloning of three human tyrosine phosphatases reveals a multigene family of receptor-linked protein-tyrosine-phosphatases expressed in brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):7000–7004. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.7000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keene P., Mendelow B., Pinto M. R., Bezwoda W., MacDougall L., Falkson G., Ruff P., Bernstein R. Abnormalities of chromosome 12p13 and malignant proliferation of eosinophils: a nonrandom association. Br J Haematol. 1987 Sep;67(1):25–31. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1987.tb02291.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kipreos E. T., Wang J. Y. Reversible dependence on growth factor interleukin-3 in myeloid cells expressing temperature sensitive v-abl oncogene. Oncogene Res. 1988 Feb;2(3):277–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausner R. D., Samelson L. E. T cell antigen receptor activation pathways: the tyrosine kinase connection. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):875–878. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90310-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C. A., Anderson D., Moran M. F., Ellis C., Pawson T. SH2 and SH3 domains: elements that control interactions of cytoplasmic signaling proteins. Science. 1991 May 3;252(5006):668–674. doi: 10.1126/science.1708916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koretzky G. A., Picus J., Schultz T., Weiss A. Tyrosine phosphatase CD45 is required for T-cell antigen receptor and CD2-mediated activation of a protein tyrosine kinase and interleukin 2 production. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2037–2041. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koyasu S., Tojo A., Miyajima A., Akiyama T., Kasuga M., Urabe A., Schreurs J., Arai K., Takaku F., Yahara I. Interleukin 3-specific tyrosine phosphorylation of a membrane glycoprotein of Mr 150,000 in multi-factor-dependent myeloid cell lines. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):3979–3984. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02740.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger N. X., Streuli M., Saito H. Structural diversity and evolution of human receptor-like protein tyrosine phosphatases. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3241–3252. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07523.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombroso P. J., Murdoch G., Lerner M. Molecular characterization of a protein-tyrosine-phosphatase enriched in striatum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7242–7246. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda M., Mayer B. J., Fukui Y., Hanafusa H. Binding of transforming protein, P47gag-crk, to a broad range of phosphotyrosine-containing proteins. Science. 1990 Jun 22;248(4962):1537–1539. doi: 10.1126/science.1694307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews R. J., Flores E., Thomas M. L. Protein tyrosine phosphatase domains from the protochordate Styela plicata. Immunogenetics. 1991;33(1):33–41. doi: 10.1007/BF00211693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer B. J., Hamaguchi M., Hanafusa H. A novel viral oncogene with structural similarity to phospholipase C. Nature. 1988 Mar 17;332(6161):272–275. doi: 10.1038/332272a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migliaccio G., Migliaccio A. R., Kreider B. L., Rovera G., Adamson J. W. Selection of lineage-restricted cell lines immortalized at different stages of hematopoietic differentiation from the murine cell line 32D. J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;109(2):833–841. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills G. B., May C., McGill M., Fung M., Baker M., Sutherland R., Greene W. C. Interleukin 2-induced tyrosine phosphorylation. Interleukin 2 receptor beta is tyrosine phosphorylated. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3561–3567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura O., D'Andrea A., Kabat D., Ihle J. N. Induction of tyrosine phosphorylation by the erythropoietin receptor correlates with mitogenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):4895–4902. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.4895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morla A. O., Schreurs J., Miyajima A., Wang J. Y. Hematopoietic growth factors activate the tyrosine phosphorylation of distinct sets of proteins in interleukin-3-dependent murine cell lines. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2214–2218. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishi M., Ohagi S., Steiner D. F. Novel putative protein tyrosine phosphatases identified by the polymerase chain reaction. FEBS Lett. 1990 Oct 1;271(1-2):178–180. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80400-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsu M., Hiles I., Gout I., Fry M. J., Ruiz-Larrea F., Panayotou G., Thompson A., Dhand R., Hsuan J., Totty N. Characterization of two 85 kd proteins that associate with receptor tyrosine kinases, middle-T/pp60c-src complexes, and PI3-kinase. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):91–104. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90411-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce J. H., Di Fiore P. P., Aaronson S. A., Potter M., Pumphrey J., Scott A., Ihle J. N. Neoplastic transformation of mast cells by Abelson-MuLV: abrogation of IL-3 dependence by a nonautocrine mechanism. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):685–693. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80049-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pingel J. T., Thomas M. L. Evidence that the leukocyte-common antigen is required for antigen-induced T lymphocyte proliferation. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1055–1065. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90504-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkel D., Landegent J., Collins C., Fuscoe J., Segraves R., Lucas J., Gray J. Fluorescence in situ hybridization with human chromosome-specific libraries: detection of trisomy 21 and translocations of chromosome 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9138–9142. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quelle F. W., Wojchowski D. M. Proliferative action of erythropoietin is associated with rapid protein tyrosine phosphorylation in responsive B6SUt.EP cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 5;266(1):609–614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raimondi S. C., Privitera E., Williams D. L., Look A. T., Behm F., Rivera G. K., Crist W. M., Pui C. H. New recurring chromosomal translocations in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 1991 May 1;77(9):2016–2022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raimondi S. C., Williams D. L., Callihan T., Peiper S., Rivera G. K., Murphy S. B. Nonrandom involvement of the 12p12 breakpoint in chromosome abnormalities of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 1986 Jul;68(1):69–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralph S. J., Thomas M. L., Morton C. C., Trowbridge I. S. Structural variants of human T200 glycoprotein (leukocyte-common antigen). EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1251–1257. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02361.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy E. P., Smith M. J., Srinivasan A. Nucleotide sequence of Abelson murine leukemia virus genome: structural similarity of its transforming gene product to other onc gene products with tyrosine-specific kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3623–3627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reedijk M., Liu X. Q., Pawson T. Interactions of phosphatidylinositol kinase, GTPase-activating protein (GAP), and GAP-associated proteins with the colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5601–5608. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J., Dilworth S. M., Laskey R. A., Dingwall C. Two interdependent basic domains in nucleoplasmin nuclear targeting sequence: identification of a class of bipartite nuclear targeting sequence. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):615–623. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90245-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski I., Stone J. C., Pawson T. A noncatalytic domain conserved among cytoplasmic protein-tyrosine kinases modifies the kinase function and transforming activity of Fujinami sarcoma virus P130gag-fps. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4396–4408. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samelson L. E., Phillips A. F., Luong E. T., Klausner R. D. Association of the fyn protein-tyrosine kinase with the T-cell antigen receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4358–4362. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sap J., D'Eustachio P., Givol D., Schlessinger J. Cloning and expression of a widely expressed receptor tyrosine phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6112–6116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw A. S., Amrein K. E., Hammond C., Stern D. F., Sefton B. M., Rose J. K. The lck tyrosine protein kinase interacts with the cytoplasmic tail of the CD4 glycoprotein through its unique amino-terminal domain. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):627–636. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw A. S., Chalupny J., Whitney J. A., Hammond C., Amrein K. E., Kavathas P., Sefton B. M., Rose J. K. Short related sequences in the cytoplasmic domains of CD4 and CD8 mediate binding to the amino-terminal domain of the p56lck tyrosine protein kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):1853–1862. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.1853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen S. H., Bastien L., Posner B. I., Chrétien P. A protein-tyrosine phosphatase with sequence similarity to the SH2 domain of the protein-tyrosine kinases. Nature. 1991 Aug 22;352(6337):736–739. doi: 10.1038/352736a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibuya M., Hanafusa H. Nucleotide sequence of Fujinami sarcoma virus: evolutionary relationship of its transforming gene with transforming genes of other sarcoma viruses. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):787–795. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90283-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnik E. Y., Margolis B., Mohammadi M., Lowenstein E., Fischer R., Drepps A., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Cloning of PI3 kinase-associated p85 utilizing a novel method for expression/cloning of target proteins for receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):83–90. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90410-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl M. L., Ferenz C. R., Kelleher K. L., Kriz R. W., Knopf J. L. Sequence similarity of phospholipase C with the non-catalytic region of src. Nature. 1988 Mar 17;332(6161):269–272. doi: 10.1038/332269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streuli M., Krueger N. X., Hall L. R., Schlossman S. F., Saito H. A new member of the immunoglobulin superfamily that has a cytoplasmic region homologous to the leukocyte common antigen. J Exp Med. 1988 Nov 1;168(5):1523–1530. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.5.1523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streuli M., Krueger N. X., Thai T., Tang M., Saito H. Distinct functional roles of the two intracellular phosphatase like domains of the receptor-linked protein tyrosine phosphatases LCA and LAR. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2399–2407. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07415.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streuli M., Krueger N. X., Tsai A. Y., Saito H. A family of receptor-linked protein tyrosine phosphatases in humans and Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8698–8702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suh P. G., Ryu S. H., Moon K. H., Suh H. W., Rhee S. G. Inositol phospholipid-specific phospholipase C: complete cDNA and protein sequences and sequence homology to tyrosine kinase-related oncogene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5419–5423. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeya T., Hanafusa H. Structure and sequence of the cellular gene homologous to the RSV src gene and the mechanism for generating the transforming virus. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):881–890. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas M. L. The leukocyte common antigen family. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:339–369. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.002011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tojo A., Kasuga M., Urabe A., Takaku F. Vanadate can replace interleukin 3 for transient growth of factor-dependent cells. Exp Cell Res. 1987 Jul;171(1):16–23. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(87)90247-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonks N. K., Charbonneau H., Diltz C. D., Fischer E. H., Walsh K. A. Demonstration that the leukocyte common antigen CD45 is a protein tyrosine phosphatase. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 29;27(24):8695–8701. doi: 10.1021/bi00424a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonks N. K., Diltz C. D., Fischer E. H. CD45, an integral membrane protein tyrosine phosphatase. Characterization of enzyme activity. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 25;265(18):10674–10680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonks N. K., Diltz C. D., Fischer E. H. Purification of the major protein-tyrosine-phosphatases of human placenta. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6722–6730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trahey M., Wong G., Halenbeck R., Rubinfeld B., Martin G. A., Ladner M., Long C. M., Crosier W. J., Watt K., Koths K. Molecular cloning of two types of GAP complementary DNA from human placenta. Science. 1988 Dec 23;242(4886):1697–1700. doi: 10.1126/science.3201259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner J. M., Brodsky M. H., Irving B. A., Levin S. D., Perlmutter R. M., Littman D. R. Interaction of the unique N-terminal region of tyrosine kinase p56lck with cytoplasmic domains of CD4 and CD8 is mediated by cysteine motifs. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):755–765. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90090-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varticovski L., Druker B., Morrison D., Cantley L., Roberts T. The colony stimulating factor-1 receptor associates with and activates phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):699–702. doi: 10.1038/342699a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veillette A., Bookman M. A., Horak E. M., Bolen J. B. The CD4 and CD8 T cell surface antigens are associated with the internal membrane tyrosine-protein kinase p56lck. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):301–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90053-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veillette A., Bookman M. A., Horak E. M., Samelson L. E., Bolen J. B. Signal transduction through the CD4 receptor involves the activation of the internal membrane tyrosine-protein kinase p56lck. Nature. 1989 Mar 16;338(6212):257–259. doi: 10.1038/338257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel U. S., Dixon R. A., Schaber M. D., Diehl R. E., Marshall M. S., Scolnick E. M., Sigal I. S., Gibbs J. B. Cloning of bovine GAP and its interaction with oncogenic ras p21. Nature. 1988 Sep 1;335(6185):90–93. doi: 10.1038/335090a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanashi Y., Kakiuchi T., Mizuguchi J., Yamamoto T., Toyoshima K. Association of B cell antigen receptor with protein tyrosine kinase Lyn. Science. 1991 Jan 11;251(4990):192–194. doi: 10.1126/science.1702903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Q., Tonks N. K. Isolation of a cDNA clone encoding a human protein-tyrosine phosphatase with homology to the cytoskeletal-associated proteins band 4.1, ezrin, and talin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):5949–5953. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.5949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yi T. L., Bolen J. B., Ihle J. N. Hematopoietic cells express two forms of lyn kinase differing by 21 amino acids in the amino terminus. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2391–2398. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yi T. L., Willman C. L. Cloning of the murine c-fgr proto-oncogene cDNA and induction of c-fgr expression by proliferation and activation factors in normal bone marrow-derived monocytic cells. Oncogene. 1989 Sep;4(9):1081–1087. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yi T., Cleveland J. L., Ihle J. N. Identification of novel protein tyrosine phosphatases of hematopoietic cells by polymerase chain reaction amplification. Blood. 1991 Nov 1;78(9):2222–2228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabel B. U., Naylor S. L., Sakaguchi A. Y., Bell G. I., Shows T. B. High-resolution chromosomal localization of human genes for amylase, proopiomelanocortin, somatostatin, and a DNA fragment (D3S1) by in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6932–6936. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]