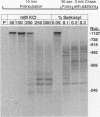
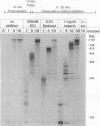
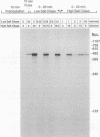
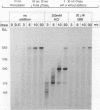
Abstract
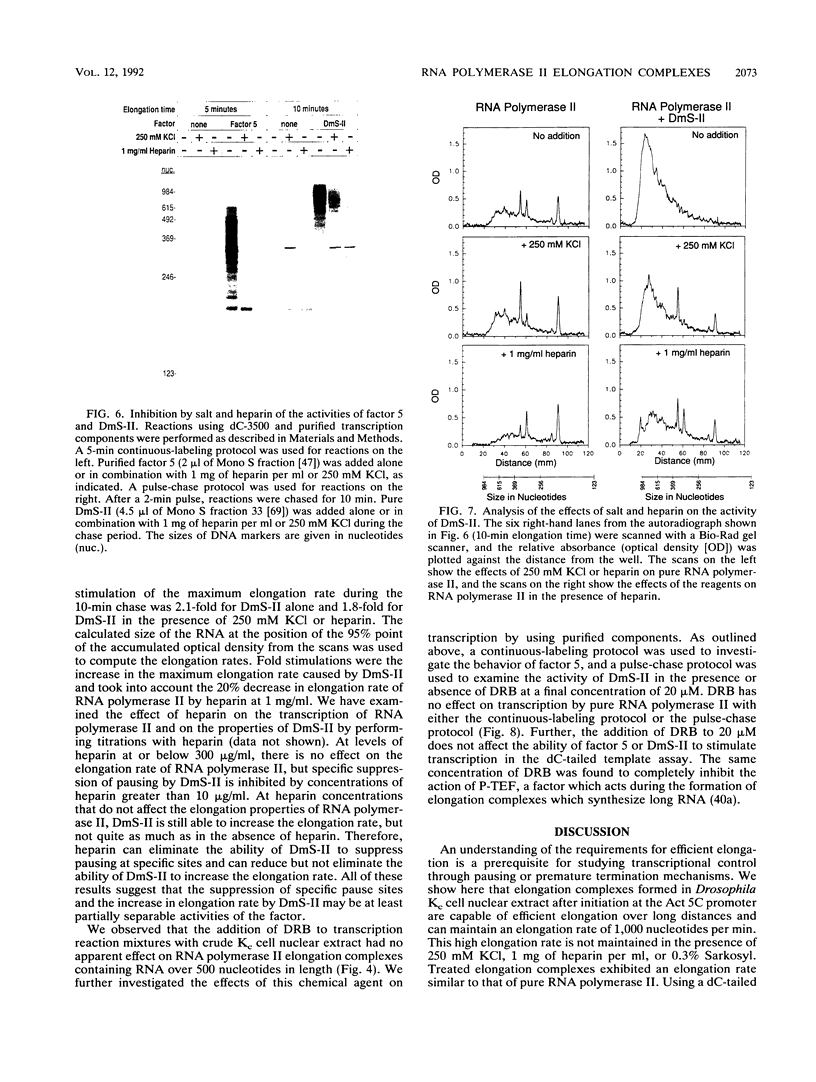
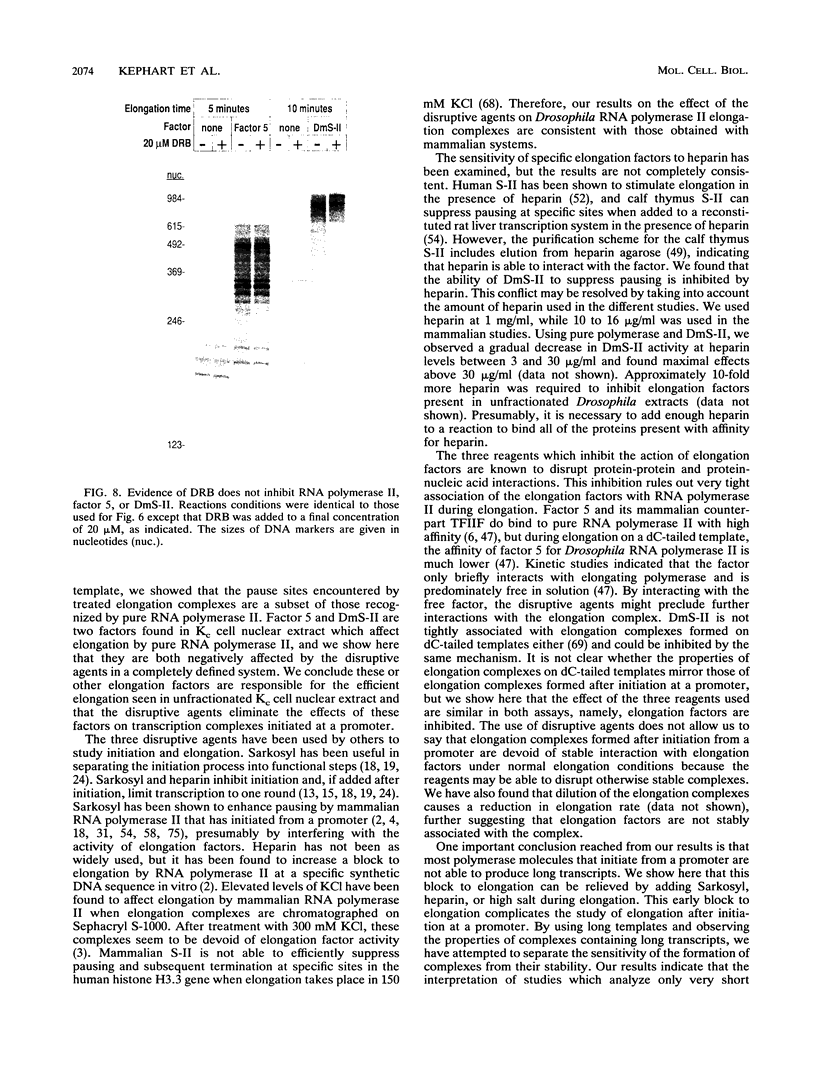
We show that nuclear extract from Drosophila Kc cells supports efficient elongation by RNA polymerase II initiated from the actin 5C promoter. The addition of 0.3% Sarkosyl, 1 mg of heparin per ml, or 250 mM KCl immediately after initiation has two effects. First, the elongation rate is reduced 80 to 90% as a result of the inhibition of elongation factors. Second, there is an increase in the amount of long runoff RNA, suggesting that there is an early block to elongation that is relieved by the disruptive reagents. Consistent with the first effect, we find that the ability of factor 5 (TFIIF) to stimulate the elongation rate is inhibited by the disruptive agents when assayed in a defined system containing pure RNA polymerase II and a dC-tailed template. The disruptive agents also inhibit the ability of DmS-II to suppress transcriptional pausing but only slightly reduce the ability of DmS-II to increase the elongation rate twofold. The pause sites encountered by RNA polymerase II after initiation at a promoter and subsequent treatment with the disruptive reagents are also recognized by pure polymerase transcribing a dC-tailed template. It has been suggested that 5,6-dichloro-1-beta-D-ribofuranosylbenzimidazole inhibits RNA polymerase II during elongation, but we find that the purine nucleoside analog has no effect on elongation complexes containing RNA over 500 nucleotides in length or on the action of factor 5 or DmS-II in the defined system.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bender T. P., Thompson C. B., Kuehl W. M. Differential expression of c-myb mRNA in murine B lymphomas by a block to transcription elongation. Science. 1987 Sep 18;237(4821):1473–1476. doi: 10.1126/science.3498214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengal E., Aloni Y. A block of transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II at synthetic sites in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 15;264(17):9791–9798. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengal E., Flores O., Krauskopf A., Reinberg D., Aloni Y. Role of the mammalian transcription factors IIF, IIS, and IIX during elongation by RNA polymerase II. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1195–1206. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengal E., Goldring A., Aloni Y. Transcription complexes synthesizing attenuated RNA can serve as a model system for analyzing elongation factors. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 15;264(32):18926–18932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton Z. F., Killeen M., Sopta M., Ortolan L. G., Greenblatt J. RAP30/74: a general initiation factor that binds to RNA polymerase II. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1602–1613. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton Z. F., Ortolan L. G., Greenblatt J. Proteins that bind to RNA polymerase II are required for accurate initiation of transcription at the adenovirus 2 major late promoter. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2923–2930. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04588.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cai H., Luse D. S. Transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in vitro. Properties of preinitiation, initiation, and elongation complexes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 5;262(1):298–304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chafin D. R., Claussen T. J., Price D. H. Identification and purification of a yeast protein that affects elongation by RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):9256–9262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Z., Harless M. L., Wright D. A., Kellems R. E. Identification and characterization of transcriptional arrest sites in exon 1 of the human adenosine deaminase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4555–4564. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinsky J. M., Maa M. C., Ramamurthy V., Kellems R. E. Adenosine deaminase gene expression. Tissue-dependent regulation of transcriptional elongation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):14561–14565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chodosh L. A., Fire A., Samuels M., Sharp P. A. 5,6-Dichloro-1-beta-D-ribofuranosylbenzimidazole inhibits transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 5;264(4):2250–2257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collart M. A., Tourkine N., Belin D., Vassalli P., Jeanteur P., Blanchard J. M. c-fos gene transcription in murine macrophages is modulated by a calcium-dependent block to elongation in intron 1. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2826–2831. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conaway R. C., Conaway J. W. ATP activates transcription initiation from promoters by RNA polymerase II in a reversible step prior to RNA synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):2962–2968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppola J. A., Field A. S., Luse D. S. Promoter-proximal pausing by RNA polymerase II in vitro: transcripts shorter than 20 nucleotides are not capped. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1251–1255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores O., Maldonado E., Reinberg D. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II. Factors IIE and IIF independently interact with RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8913–8921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser N. W., Sehgal P. B., Darnell J. E. DRB-induced premature termination of late adenovirus transcription. Nature. 1978 Apr 13;272(5654):590–593. doi: 10.1038/272590a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fyrberg E. A., Kindle K. L., Davidson N., Kindle K. L. The actin genes of Drosophila: a dispersed multigene family. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):365–378. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90511-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., Roeder R. G. Separation and partial characterization of three functional steps in transcription initiation by human RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 5;260(13):8163–8172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirashima S., Hirai H., Nakanishi Y., Natori S. Molecular cloning and characterization of cDNA for eukaryotic transcription factor S-II. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 15;263(8):3858–3863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horikoshi M., Sekimizu K., Natori S. Analysis of the stimulatory factor of RNA polymerase II in the initiation and elongation complex. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):608–611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izban M. G., Luse D. S. Transcription on nucleosomal templates by RNA polymerase II in vitro: inhibition of elongation with enhancement of sequence-specific pausing. Genes Dev. 1991 Apr;5(4):683–696. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.4.683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadesch T. R., Chamberlin M. J. Studies of in vitro transcription by calf thymus RNA polymerase II using a novel duplex DNA template. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):5286–5295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T. Assembly and disassembly of the Drosophila RNA polymerase II complex during transcription. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 15;265(5):2624–2631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanai A., Kuzuhara T., Sekimizu K., Natori S. Heterogeneity and tissue-specific expression of eukaryotic transcription factor S-II-related protein mRNA. J Biochem. 1991 May;109(5):674–677. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane C. M., Chamberlin M. J. Studies on transcription of 3'-extended DNA templates by mammalian RNA polymerase II. Partial purification and characterization of a factor from HeLa cells that facilitates renaturation of the DNA template. Biochemistry. 1985 Apr 23;24(9):2254–2262. doi: 10.1021/bi00330a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane C. M. Renaturase and ribonuclease H: a novel mechanism that influences transcript displacement by RNA polymerase II in vitro. Biochemistry. 1988 May 3;27(9):3187–3196. doi: 10.1021/bi00409a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerppola T. K., Kane C. M. Analysis of the signals for transcription termination by purified RNA polymerase II. Biochemistry. 1990 Jan 9;29(1):269–278. doi: 10.1021/bi00453a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerppola T. K., Kane C. M. Intrinsic sites of transcription termination and pausing in the c-myc gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4389–4394. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler M., Aloni Y. The block to transcription elongation at the SV40 attenuation site is decreased in vitro by oligomers complementary to segments of the attenuator RNA. Gene. 1989 Dec 7;84(1):65–72. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90140-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler M., Ben-Asher E., Aloni Y. Elements modulating the block of transcription elongation at the adenovirus 2 attenuation site. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 15;264(17):9785–9790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krauskopf A., Bengal E., Aloni Y. The block to transcription elongation at the minute virus of mice attenuator is regulated by cellular elongation factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;11(7):3515–3521. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.7.3515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krauskopf A., Resnekov O., Aloni Y. A cis downstream element participates in regulation of in vitro transcription initiation from the P38 promoter of minute virus of mice. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):354–360. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.354-360.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laspia M. F., Rice A. P., Mathews M. B. HIV-1 Tat protein increases transcriptional initiation and stabilizes elongation. Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90290-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laspia M. F., Rice A. P., Mathews M. B. Synergy between HIV-1 Tat and adenovirus E1A is principally due to stabilization of transcriptional elongation. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12B):2397–2408. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12b.2397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lattier D. L., States J. C., Hutton J. J., Wiginton D. A. Cell type-specific transcriptional regulation of the human adenosine deaminase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 11;17(3):1061–1076. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.3.1061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linn S. C., Luse D. S. RNA polymerase II elongation complexes paused after the synthesis of 15- or 35-base transcripts have different structures. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1508–1522. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luse D. S., Jacob G. A. Abortive initiation by RNA polymerase II in vitro at the adenovirus 2 major late promoter. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 5;262(31):14990–14997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luse D. S., Kochel T., Kuempel E. D., Coppola J. A., Cai H. Transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in vitro. At least two nucleotides must be added to form a stable ternary complex. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 5;262(1):289–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maa M. C., Chinsky J. M., Ramamurthy V., Martin B. D., Kellems R. E. Identification of transcription stop sites at the 5' and 3' ends of the murine adenosine deaminase gene. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 25;265(21):12513–12519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall N. F., Price D. H. Control of formation of two distinct classes of RNA polymerase II elongation complexes. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 May;12(5):2078–2090. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.5.2078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall T. K., Guo H., Price D. H. Drosophila RNA polymerase II elongation factor DmS-II has homology to mouse S-II and sequence similarity to yeast PPR2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 11;18(21):6293–6298. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.21.6293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller H., Asselin C., Dufort D., Yang J. Q., Gupta K., Marcu K. B., Nepveu A. A cis-acting element in the promoter region of the murine c-myc gene is necessary for transcriptional block. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5340–5349. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muntoni F., Strong P. N. Transcription of the dystrophin gene in Duchenne muscular dystrophy muscle. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jul 31;252(1-2):95–98. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80896-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. S., Topol J. A Drosophila RNA polymerase II transcription factor contains a promoter-region-specific DNA-binding activity. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):357–369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90229-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price D. H., Parker C. S. The 3' end of drosophila histone H3 mRNA is produced by a processing activity in vitro. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):423–429. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90497-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price D. H., Sluder A. E., Greenleaf A. L. Dynamic interaction between a Drosophila transcription factor and RNA polymerase II. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1465–1475. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price D. H., Sluder A. E., Greenleaf A. L. Fractionation of transcription factors for RNA polymerase II from Drosophila Kc cell nuclear extracts. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3244–3255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramamurthy V., Maa M. C., Harless M. L., Wright D. A., Kellems R. E. Sequence requirements for transcriptional arrest in exon 1 of the murine adenosine deaminase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1484–1491. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappaport J., Reinberg D., Zandomeni R., Weinmann R. Purification and functional characterization of transcription factor SII from calf thymus. Role in RNA polymerase II elongation. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):5227–5232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Re G. G., Antoun G. R., Zipf T. F. Modulation of a constitutive transcriptional block at exon-1 controls human c-myc oncogene expression. Oncogene. 1990 Aug;5(8):1247–1250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy C. D., Reddy E. P. Differential binding of nuclear factors to the intron 1 sequences containing the transcriptional pause site correlates with c-myb expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7326–7330. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinberg D., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II. Purification and functional analysis of initiation factors IIB and IIE. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3310–3321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinberg D., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II. Transcription factor IIS stimulates elongation of RNA chains. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3331–3337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reines D., Chamberlin M. J., Kane C. M. Transcription elongation factor SII (TFIIS) enables RNA polymerase II to elongate through a block to transcription in a human gene in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10799–10809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reines D., Wells D., Chamberlin M. J., Kane C. M. Identification of intrinsic termination sites in vitro for RNA polymerase II within eukaryotic gene sequences. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jul 20;196(2):299–312. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90691-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renan M. J. Does NF-kappa B relieve the transcription block in c-myc? Cancer Lett. 1989 Sep 15;47(1-2):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0304-3835(89)90170-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnekov O., Ben-Asher E., Bengal E., Choder M., Hay N., Kessler M., Ragimov N., Seiberg M., Skolnik-David H., Aloni Y. Transcription termination in animal viruses and cells. Gene. 1988 Dec 10;72(1-2):91–104. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90130-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnekov O., Kessler M., Aloni Y. RNA secondary structure is an integral part of the in vitro mechanism of attenuation in simian virus 40. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 15;264(17):9953–9959. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rougvie A. E., Lis J. T. Postinitiation transcriptional control in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):6041–6045. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.6041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rougvie A. E., Lis J. T. The RNA polymerase II molecule at the 5' end of the uninduced hsp70 gene of D. melanogaster is transcriptionally engaged. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):795–804. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91087-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safer B., Yang L., Tolunay H. E., Anderson W. F. Isolation of stable preinitiation, initiation, and elongation complexes from RNA polymerase II-directed transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2632–2636. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Sentenac A., Fromageot P. Interaction of a new polypeptide with yeast RNA polymerase B. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 10;255(1):12–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider-Schaulies J., Schimpl A., Wecker E. Kinetics of cellular oncogene expression in mouse lymphocytes. II. Regulation of c-fos and c-myc gene expression. Eur J Immunol. 1987 May;17(5):713–718. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehgal P. B., Derman E., Molloy G. R., Tamm I., Darnell J. E. 5,6-Dichloro-1-Beta-D-ribofuranosylbenzimidazole inhibits initiation of nuclear heterogeneous RNA chains in HeLa cells. Science. 1976 Oct 22;194(4263):431–433. doi: 10.1126/science.982026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiberg M., Kessler M., Levine A. J., Aloni Y. Human RNA polymerase II can prematurely terminate transcription of the adenovirus type 2 late transcription unit at a precise site that resembles a prokaryotic termination signal. Virus Genes. 1987 Nov;1(1):97–116. doi: 10.1007/BF00125689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekimizu K., Mizuno D., Natori S. Localization of a factor stimulating RNA polymerase II in the nucleoplasm, revealed by immunofluorescence. Exp Cell Res. 1979 Nov;124(1):63–72. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90257-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selby M. J., Bain E. S., Luciw P. A., Peterlin B. M. Structure, sequence, and position of the stem-loop in tar determine transcriptional elongation by tat through the HIV-1 long terminal repeat. Genes Dev. 1989 Apr;3(4):547–558. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.4.547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SivaRaman L., Reines D., Kane C. M. Purified elongation factor SII is sufficient to promote read-through by purified RNA polymerase II at specific termination sites in the human histone H3.3 gene. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 25;265(24):14554–14560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sluder A. E., Greenleaf A. L., Price D. H. Properties of a Drosophila RNA polymerase II elongation factor. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8963–8969. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sluder A. E., Price D. H., Greenleaf A. L. Elongation by Drosophila RNA polymerase II. Transcription of 3'-extended DNA templates. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 15;263(20):9917–9925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer C. A., Groudine M. Molecular analysis of the c-myc transcription elongation block. Implications for the generation of Burkitt's lymphoma. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;599:12–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb42360.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer C. A., Groudine M. Transcription elongation and eukaryotic gene regulation. Oncogene. 1990 Jun;5(6):777–785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toohey M. G., Jones K. A. In vitro formation of short RNA polymerase II transcripts that terminate within the HIV-1 and HIV-2 promoter-proximal downstream regions. Genes Dev. 1989 Mar;3(3):265–282. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.3.265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ucker D. S., Yamamoto K. R. Early events in the stimulation of mammary tumor virus RNA synthesis by glucocorticoids. Novel assays of transcription rates. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7416–7420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiest D. K., Hawley D. K. In vitro analysis of a transcription termination site for RNA polymerase II. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5782–5795. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S., Bishop J. M. DNA sequences that mediate attenuation of transcription from the mouse protooncogene myc. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):505–509. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zandomeni R., Mittleman B., Bunick D., Ackerman S., Weinmann R. Mechanism of action of dichloro-beta-D-ribofuranosylbenzimidazole: effect on in vitro transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3167–3170. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]