Abstract
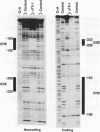
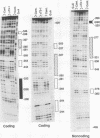
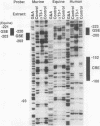
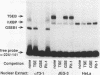
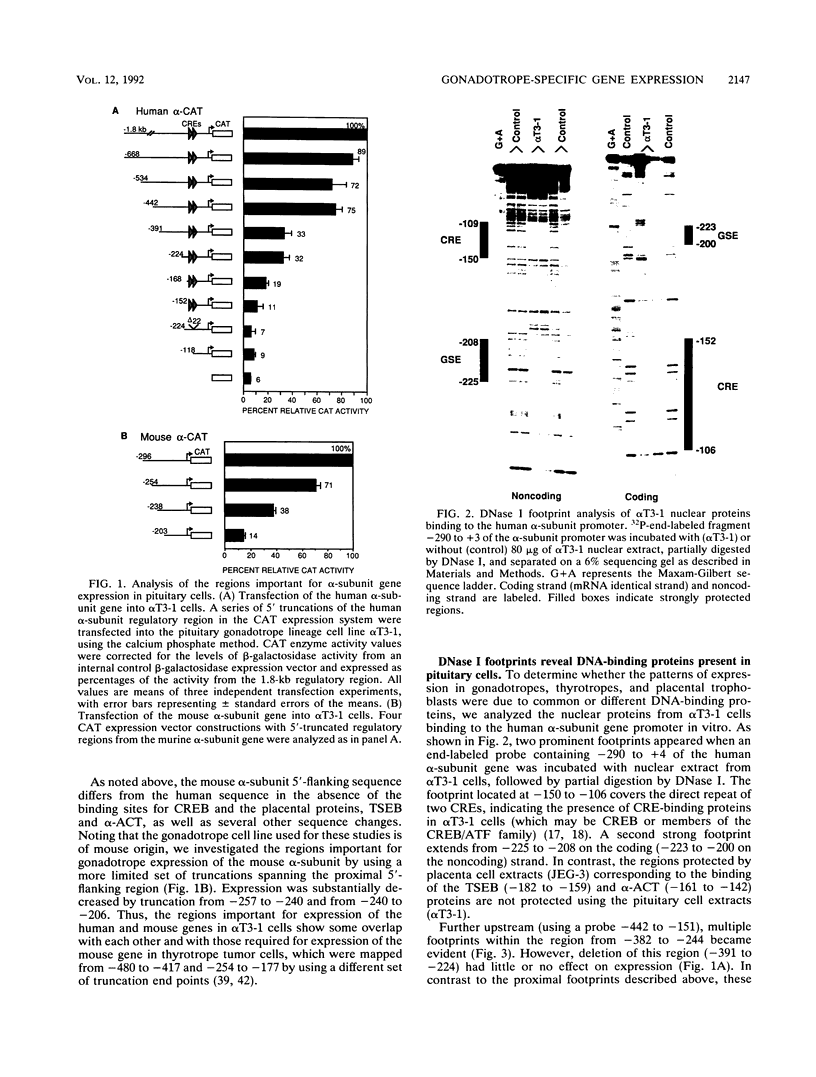
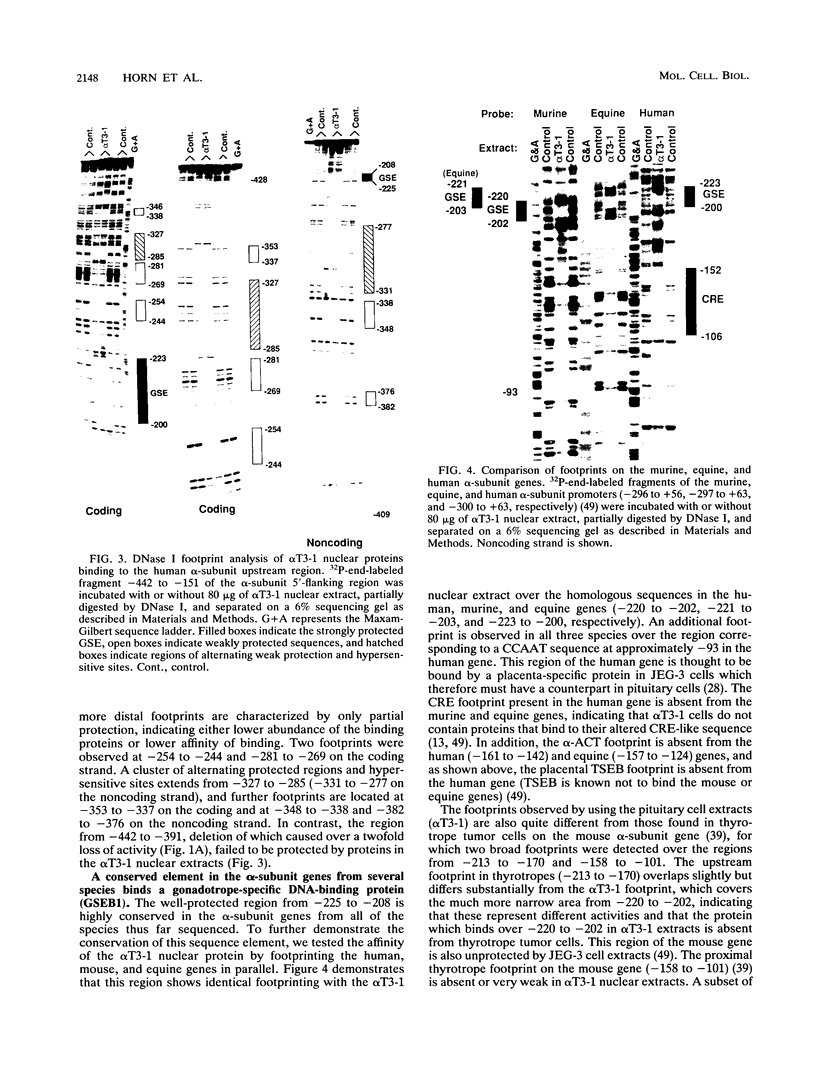
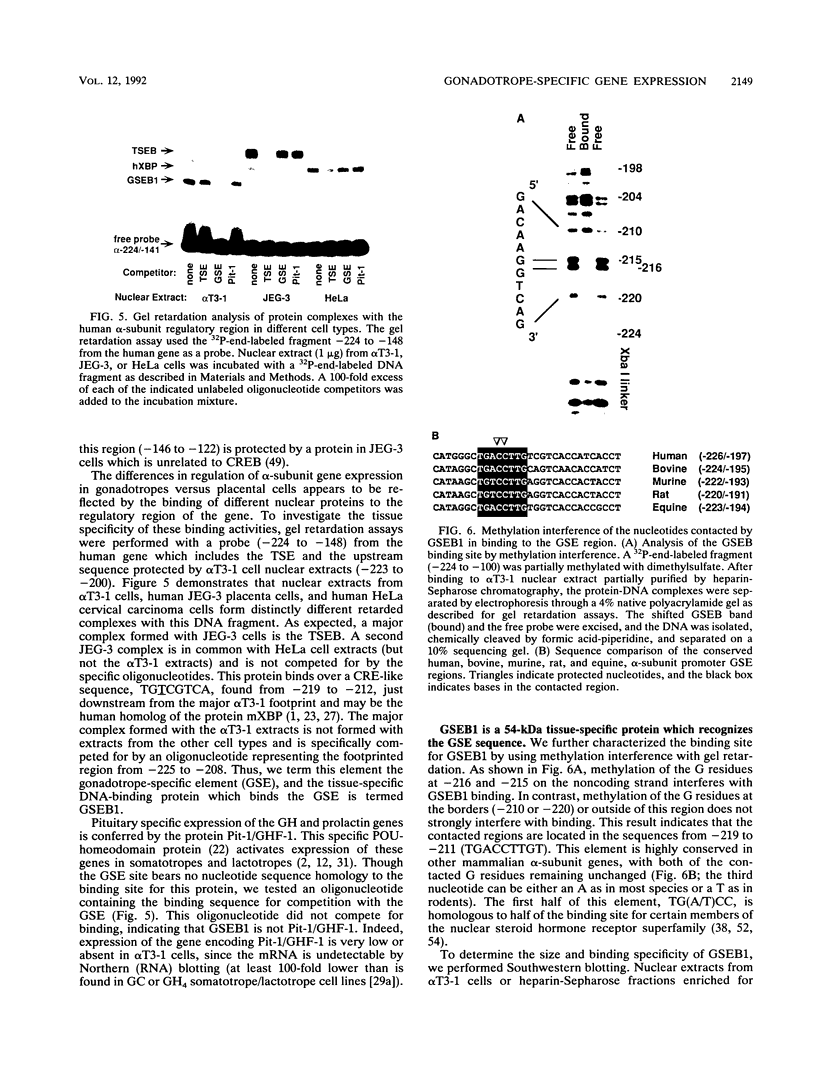
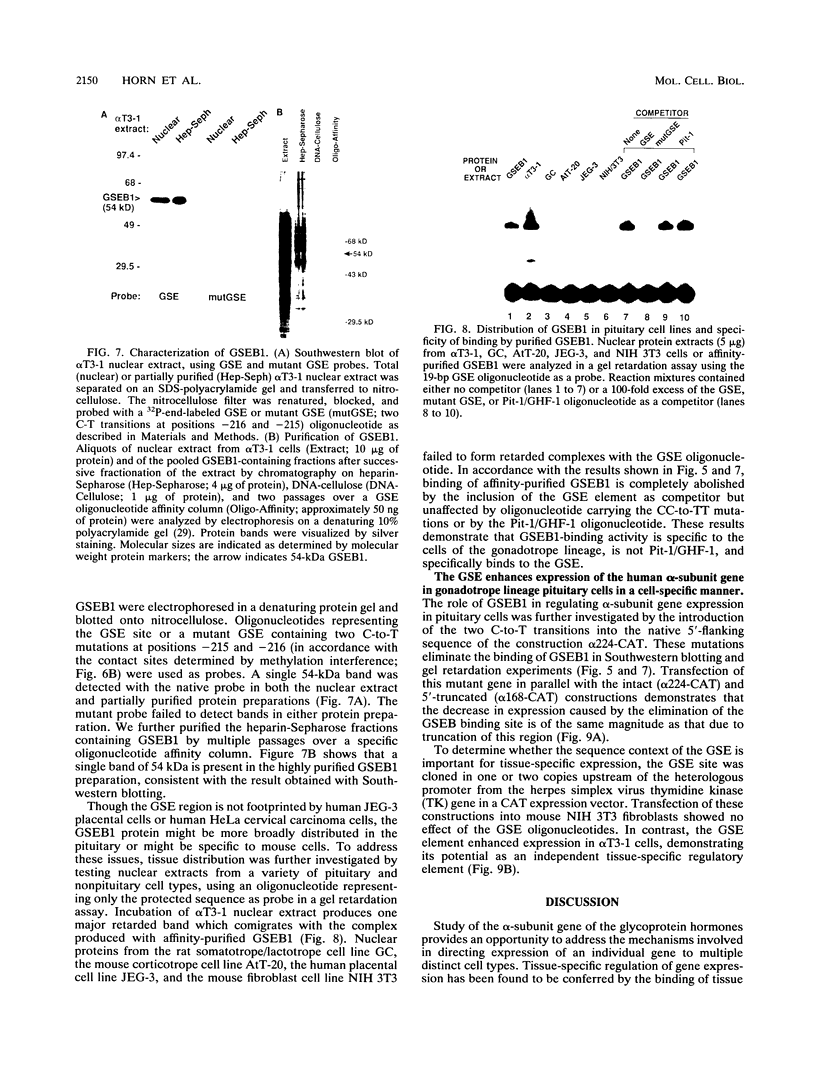
The molecular mechanisms for the development of multiple distinct endocrine cell types in the anterior pituitary have been an area of intensive investigation. Though the homeodomain protein Pit-1/GHF-1 is known to be involved in differentiation of the somatotrope and lactotrope lineages, which produce growth hormone and prolactin, respectively, little is known of the transcriptional regulators important for the gonadotrope cell lineage, which produces the glycoprotein hormones luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone. Using transgenic mice and transfection into a novel gonadotrope lineage cell line, we have identified a regulatory element that confers gonadotrope-specific expression to the glycoprotein hormone alpha-subunit gene. A tissue-specific factor that binds to this element is purified and characterized as a 54-kDa protein which is present uniquely in cells of the gonadotrope lineage and is not Pit-1/GHF-1. The human and equine alpha-subunit genes are also expressed in placental cells. However, the previously characterized placental transcription factors designated TSEB and alpha-ACT are not found in the pituitary gonadotrope cells, indicating that independent mechanisms confer expression of these genes in the two different tissues.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen B., Kennedy G. C., Nilson J. H. A cis-acting element located between the cAMP response elements and CCAAT box augments cell-specific expression of the glycoprotein hormone alpha subunit gene. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 15;265(35):21874–21880. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodner M., Castrillo J. L., Theill L. E., Deerinck T., Ellisman M., Karin M. The pituitary-specific transcription factor GHF-1 is a homeobox-containing protein. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):505–518. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90037-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokar J. A., Keri R. A., Farmerie T. A., Fenstermaker R. A., Andersen B., Hamernik D. L., Yun J., Wagner T., Nilson J. H. Expression of the glycoprotein hormone alpha-subunit gene in the placenta requires a functional cyclic AMP response element, whereas a different cis-acting element mediates pituitary-specific expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5113–5122. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinster R. L., Chen H. Y., Messing A., van Dyke T., Levine A. J., Palmiter R. D. Transgenic mice harboring SV40 T-antigen genes develop characteristic brain tumors. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):367–379. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90367-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrin J. M., Jameson J. L. Regulation of transfected glycoprotein hormone alpha-gene expression in primary pituitary cell cultures. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Oct;3(10):1643–1651. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-10-1643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castrillo J. L., Theill L. E., Karin M. Function of the homeodomain protein GHF1 in pituitary cell proliferation. Science. 1991 Jul 12;253(5016):197–199. doi: 10.1126/science.1677216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S., Altschmied J., Herbsman O., Caron M. G., Mellon P. L., Lefkowitz R. J. A cAMP response element in the beta 2-adrenergic receptor gene confers transcriptional autoregulation by cAMP. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 5;265(31):19330–19335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell R. B., Boime I. Differential expression of the human gonadotropin alpha gene in ectopic and eutopic cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):3157–3167. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delegeane A. M., Ferland L. H., Mellon P. L. Tissue-specific enhancer of the human glycoprotein hormone alpha-subunit gene: dependence on cyclic AMP-inducible elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):3994–4002. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.3994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dollé P., Castrillo J. L., Theill L. E., Deerinck T., Ellisman M., Karin M. Expression of GHF-1 protein in mouse pituitaries correlates both temporally and spatially with the onset of growth hormone gene activity. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):809–820. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90095-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenstermaker R. A., Farmerie T. A., Clay C. M., Hamernik D. L., Nilson J. H. Different combinations of regulatory elements may account for expression of the glycoprotein hormone alpha-subunit gene in primate and horse placenta. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Oct;4(10):1480–1487. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-10-1480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox N., Solter D. Expression and regulation of the pituitary- and placenta-specific human glycoprotein hormone alpha-subunit gene is restricted to the pituitary in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;8(12):5470–5476. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.12.5470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez G. A., Yamamoto K. K., Fischer W. H., Karr D., Menzel P., Biggs W., 3rd, Vale W. W., Montminy M. R. A cluster of phosphorylation sites on the cyclic AMP-regulated nuclear factor CREB predicted by its sequence. Nature. 1989 Feb 23;337(6209):749–752. doi: 10.1038/337749a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habener J. F. Cyclic AMP response element binding proteins: a cornucopia of transcription factors. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Aug;4(8):1087–1094. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-8-1087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hai T. W., Liu F., Coukos W. J., Green M. R. Transcription factor ATF cDNA clones: an extensive family of leucine zipper proteins able to selectively form DNA-binding heterodimers. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2083–2090. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeffler J. P., Meyer T. E., Yun Y., Jameson J. L., Habener J. F. Cyclic AMP-responsive DNA-binding protein: structure based on a cloned placental cDNA. Science. 1988 Dec 9;242(4884):1430–1433. doi: 10.1126/science.2974179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn F., Bilezikjian L. M., Perrin M. H., Bosma M. M., Windle J. J., Huber K. S., Blount A. L., Hille B., Vale W., Mellon P. L. Intracellular responses to gonadotropin-releasing hormone in a clonal cell line of the gonadotrope lineage. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Mar;5(3):347–355. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-3-347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingraham H. A., Albert V. R., Chen R. P., Crenshaw 3d E. B., Elsholtz H. P., He X., Kapiloff M. S., Mangalam H. J., Swanson L. W., Treacy M. N. A family of POU-domain and Pit-1 tissue-specific transcription factors in pituitary and neuroendocrine development. Annu Rev Physiol. 1990;52:773–791. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.52.030190.004013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivashkiv L. B., Liou H. C., Kara C. J., Lamph W. W., Verma I. M., Glimcher L. H. mXBP/CRE-BP2 and c-Jun form a complex which binds to the cyclic AMP, but not to the 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate, response element. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1609–1621. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jameson J. L., Albanese C., Habener J. F. Distinct adjacent protein-binding domains in the glycoprotein hormone alpha gene interact independently with a cAMP-responsive enhancer. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 25;264(27):16190–16196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jameson J. L., Deutsch P. J., Gallagher G. D., Jaffe R. C., Habener J. F. trans-acting factors interact with a cyclic AMP response element to modulate expression of the human gonadotropin alpha gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3032–3040. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jameson J. L., Jaffe R. C., Deutsch P. J., Albanese C., Habener J. F. The gonadotropin alpha-gene contains multiple protein binding domains that interact to modulate basal and cAMP-responsive transcription. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 15;263(20):9879–9886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kara C. J., Liou H. C., Ivashkiv L. B., Glimcher L. H. A cDNA for a human cyclic AMP response element-binding protein which is distinct from CREB and expressed preferentially in brain. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1347–1357. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy G. C., Andersen B., Nilson J. H. The human alpha subunit glycoprotein hormone gene utilizes a unique CCAAT binding factor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 15;265(11):6279–6285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S., Crenshaw E. B., 3rd, Rawson E. J., Simmons D. M., Swanson L. W., Rosenfeld M. G. Dwarf locus mutants lacking three pituitary cell types result from mutations in the POU-domain gene pit-1. Nature. 1990 Oct 11;347(6293):528–533. doi: 10.1038/347528a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangalam H. J., Albert V. R., Ingraham H. A., Kapiloff M., Wilson L., Nelson C., Elsholtz H., Rosenfeld M. G. A pituitary POU domain protein, Pit-1, activates both growth hormone and prolactin promoters transcriptionally. Genes Dev. 1989 Jul;3(7):946–958. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.7.946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Goodbourn S., Fischer J. A. Regulation of inducible and tissue-specific gene expression. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1237–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.3296191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh J. L., Erfle M., Wykes E. J. The pIC plasmid and phage vectors with versatile cloning sites for recombinant selection by insertional inactivation. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(3):481–485. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinkoth J., Wahl G. Hybridization of nucleic acids immobilized on solid supports. Anal Biochem. 1984 May 1;138(2):267–284. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90808-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon P., Parker V., Gluzman Y., Maniatis T. Identification of DNA sequences required for transcription of the human alpha 1-globin gene in a new SV40 host-vector system. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):279–288. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90411-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miskimins W. K., Roberts M. P., McClelland A., Ruddle F. H. Use of a protein-blotting procedure and a specific DNA probe to identify nuclear proteins that recognize the promoter region of the transferrin receptor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):6741–6744. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.6741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- När A. M., Boutin J. M., Lipkin S. M., Yu V. C., Holloway J. M., Glass C. K., Rosenfeld M. G. The orientation and spacing of core DNA-binding motifs dictate selective transcriptional responses to three nuclear receptors. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1267–1279. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90021-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ocran K. W., Sarapura V. D., Wood W. M., Gordon D. F., Gutierrez-Hartmann A., Ridgway E. C. Identification of cis-acting promoter elements important for expression of the mouse glycoprotein hormone alpha-subunit gene in thyrotropes. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 May;4(5):766–772. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-5-766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson H., Edlund T. Sequence-specific interactions of nuclear factors with the insulin gene enhancer. Cell. 1986 Apr 11;45(1):35–44. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90535-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H. Globin gene regulation and switching: circa 1990. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):665–672. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90133-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarapura V. D., Wood W. M., Gordon D. F., Ocran K. W., Kao M. Y., Ridgway E. C. Thyrotrope expression and thyroid hormone inhibition map to different regions of the mouse glycoprotein hormone alpha-subunit gene promoter. Endocrinology. 1990 Sep;127(3):1352–1361. doi: 10.1210/endo-127-3-1352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Van Dyke M. W., Gregor P. D., Roeder R. G. Multiple forms of the human gene-specific transcription factor USF. I. Complete purification and identification of USF from HeLa cell nuclei. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 25;263(24):11985–11993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüle R., Muller M., Otsuka-Murakami H., Renkawitz R. Cooperativity of the glucocorticoid receptor and the CACCC-box binding factor. Nature. 1988 Mar 3;332(6159):87–90. doi: 10.1038/332087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed B., Sheen J. Y. A simple phase-extraction assay for chloramphenicol acyltransferase activity. Gene. 1988 Jul 30;67(2):271–277. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90403-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver B. J., Bokar J. A., Virgin J. B., Vallen E. A., Milsted A., Nilson J. H. Cyclic AMP regulation of the human glycoprotein hormone alpha-subunit gene is mediated by an 18-base-pair element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2198–2202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. M., Voss J. W., Ingraham H. A., Holloway J. M., Broide R. S., Rosenfeld M. G., Swanson L. W. Pituitary cell phenotypes involve cell-specific Pit-1 mRNA translation and synergistic interactions with other classes of transcription factors. Genes Dev. 1990 May;4(5):695–711. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.5.695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh R. P., Natarajan V. A rapid affinity method for isolation and characterization of sequence specific DNA binding factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Aug 31;147(1):65–70. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80087-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steger D. J., Altschmied J., Büscher M., Mellon P. L. Evolution of placenta-specific gene expression: comparison of the equine and human gonadotropin alpha-subunit genes. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Feb;5(2):243–255. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-2-243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tashjian A. H., Jr, Yasumura Y., Levine L., Sato G. H., Parker M. L. Establishment of clonal strains of rat pituitary tumor cells that secrete growth hormone. Endocrinology. 1968 Feb;82(2):342–352. doi: 10.1210/endo-82-2-342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tepper M. A., Roberts J. L. Evidence for only one beta-luteinizing hormone and no beta-chorionic gonadotropin gene in the rat. Endocrinology. 1984 Jul;115(1):385–391. doi: 10.1210/endo-115-1-385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truss M., Chalepakis G., Slater E. P., Mader S., Beato M. Functional interaction of hybrid response elements with wild-type and mutant steroid hormone receptors. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):3247–3258. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.3247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. Y., Sagami I., Wang H., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Interactions between a DNA-binding transcription factor (COUP) and a non-DNA binding factor (S300-II). Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):701–709. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90328-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umesono K., Murakami K. K., Thompson C. C., Evans R. M. Direct repeats as selective response elements for the thyroid hormone, retinoic acid, and vitamin D3 receptors. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1255–1266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90020-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windle J. J., Weiner R. I., Mellon P. L. Cell lines of the pituitary gonadotrope lineage derived by targeted oncogenesis in transgenic mice. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Apr;4(4):597–603. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-4-597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto M., Ko L. J., Leonard M. W., Beug H., Orkin S. H., Engel J. D. Activity and tissue-specific expression of the transcription factor NF-E1 multigene family. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1650–1662. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]