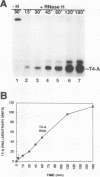
Abstract
Xenopus RNA polymerase III specifically initiates transcription on poly(dC)-tailed DNA templates in the absence of other class III transcription factors normally required for transcription initiation. In experimental analyses of transcription termination using DNA fragments with a 5S rRNA gene positioned downstream of the tailed end, only 40% of the transcribing polymerase molecules terminate at the normally efficient Xenopus borealis somatic-type 5S rRNA terminators; the remaining 60% read through these signals and give rise to runoff transcripts. We find that the nascent RNA strand is inefficiently displaced from the DNA template during transcription elongation. Interestingly, only polymerases synthesizing a displaced RNA terminate at the 5S rRNA gene terminators; when the nascent RNA is not displaced from the template, read-through transcripts are synthesized. RNAs with 3' ends at the 5S rRNA gene terminators are judged to result from authentic termination events on the basis of multiple criteria, including kinetic properties, the precise 3' ends generated, release of transcripts from the template, and recycling of the polymerase. Even though only 40% of the polymerase molecules ultimately terminate at either of the tandem 5S rRNA gene terminators, virtually all polymerases pause there, demonstrating that termination signal recognition can be experimentally uncoupled from polymerase release. Thus, termination is dependent on RNA strand displacement during transcription elongation, whereas termination signal recognition is not. We interpret our results in terms of a two-step model for transcription termination in which polymerase release is dependent on the fate of the nascent RNA strand during transcription elongation.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison D. S., Hall B. D. Effects of alterations in the 3' flanking sequence on in vivo and in vitro expression of the yeast SUP4-o tRNATyr gene. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2657–2664. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03984.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bieker J. J., Martin P. L., Roeder R. G. Formation of a rate-limiting intermediate in 5S RNA gene transcription. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):119–127. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90315-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkenmeier E. H., Brown D. D., Jordan E. A nuclear extract of Xenopus laevis oocytes that accurately transcribes 5S RNA genes. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):1077–1086. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90291-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Brown D. D. Nucleotide sequences in Xenopus 5S DNA required for transcription termination. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):261–270. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90522-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Wormington W. M., Brown D. D. Stable transcription complexes of Xenopus 5S RNA genes: a means to maintain the differentiated state. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):413–421. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90359-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell F. E., Jr, Setzer D. R. Displacement of Xenopus transcription factor IIIA from a 5S rRNA gene by a transcribing RNA polymerase. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;11(8):3978–3986. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.8.3978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulter D. E., Greenleaf A. L. A mutation in the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II alters RNA chain elongation in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 25;260(24):13190–13198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cozzarelli N. R., Gerrard S. P., Schlissel M., Brown D. D., Bogenhagen D. F. Purified RNA polymerase III accurately and efficiently terminates transcription of 5S RNA genes. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):829–835. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90540-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darby M. K., Andrews M. T., Brown D. D. Transcription complexes that program Xenopus 5S RNA genes are stable in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5516–5520. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dedrick R. L., Chamberlin M. J. Studies on transcription of 3'-extended templates by mammalian RNA polymerase II. Parameters that affect the initiation and elongation reactions. Biochemistry. 1985 Apr 23;24(9):2245–2253. doi: 10.1021/bi00330a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dedrick R. L., Kane C. M., Chamberlin M. J. Purified RNA polymerase II recognizes specific termination sites during transcription in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 5;262(19):9098–9108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis H., Wegnez M. Recherches biochimiques sur l'oogenése. 7. Synthése et maturation du RNA 5S dans les petitis oocytes de Xenopus laevis. Biochimie. 1973;55(9):1137–1151. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(73)80453-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson B. M., Roeder R. G. DNA sequences and transcription factor interactions of active and inactive forms of mammalian 5 S RNA genes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7926–7935. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelke D. R., Ng S. Y., Shastry B. S., Roeder R. G. Specific interaction of a purified transcription factor with an internal control region of 5S RNA genes. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80048-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fradkin L. G., Yoshinaga S. K., Berk A. J., Dasgupta A. Human transcription factor TFIIIC2 specifically interacts with a unique sequence in the Xenopus laevis 5S rRNA gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4941–4950. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiduschek E. P., Tocchini-Valentini G. P. Transcription by RNA polymerase III. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:873–914. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.004301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb E., Steitz J. A. Function of the mammalian La protein: evidence for its action in transcription termination by RNA polymerase III. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):851–861. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03446.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb E., Steitz J. A. The RNA binding protein La influences both the accuracy and the efficiency of RNA polymerase III transcription in vitro. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):841–850. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03445.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess J., Perez-Stable C., Wu G. J., Weir B., Tinoco I., Jr, Shen C. K. End-to-end transcription of an Alu family repeat. A new type of polymerase-III-dependent terminator and its evolutionary implication. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jul 5;184(1):7–21. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90039-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James P., Hall B. D. ret1-1, a yeast mutant affecting transcription termination by RNA polymerase III. Genetics. 1990 Jun;125(2):293–303. doi: 10.1093/genetics/125.2.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James P., Whelen S., Hall B. D. The RET1 gene of yeast encodes the second-largest subunit of RNA polymerase III. Structural analysis of the wild-type and ret1-1 mutant alleles. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 25;266(9):5616–5624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadesch T. R., Chamberlin M. J. Studies of in vitro transcription by calf thymus RNA polymerase II using a novel duplex DNA template. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):5286–5295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane C. M., Chamberlin M. J. Studies on transcription of 3'-extended DNA templates by mammalian RNA polymerase II. Partial purification and characterization of a factor from HeLa cells that facilitates renaturation of the DNA template. Biochemistry. 1985 Apr 23;24(9):2254–2262. doi: 10.1021/bi00330a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane C. M. Renaturase and ribonuclease H: a novel mechanism that influences transcript displacement by RNA polymerase II in vitro. Biochemistry. 1988 May 3;27(9):3187–3196. doi: 10.1021/bi00409a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Braun B. R., Nguyen L. H., Geiduschek E. P. S. cerevisiae TFIIIB is the transcription initiation factor proper of RNA polymerase III, while TFIIIA and TFIIIC are assembly factors. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):235–245. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90739-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Chamberlin M. J. Pausing and termination of transcription within the early region of bacteriophage T7 DNA in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 25;256(6):2777–2786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerppola T. K., Kane C. M. Analysis of the signals for transcription termination by purified RNA polymerase II. Biochemistry. 1990 Jan 9;29(1):269–278. doi: 10.1021/bi00453a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerppola T. K., Kane C. M. Intrinsic sites of transcription termination and pausing in the c-myc gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4389–4394. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassar A. B., Martin P. L., Roeder R. G. Transcription of class III genes: formation of preinitiation complexes. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):740–748. doi: 10.1126/science.6356356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau L. F., Roberts J. W., Wu R. RNA polymerase pausing and transcript release at the lambda tR1 terminator in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 10;258(15):9391–9397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto K., Takii T., Okada N. Characterization of a new termination signal for RNA polymerase III responsible for generation of a discrete-sized RNA transcribed from salmon total genomic DNA in a HeLa cell extract. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):1124–1131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazabraud A., Scherly D., Müller F., Rungger D., Clarkson S. G. Structure and transcription termination of a lysine tRNA gene from Xenopus laevis. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jun 20;195(4):835–845. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90488-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., McLachlan A. D., Klug A. Repetitive zinc-binding domains in the protein transcription factor IIIA from Xenopus oocytes. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1609–1614. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03825.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan W. D., Bear D. G., von Hippel P. H. Rho-dependent termination of transcription. II. Kinetics of mRNA elongation during transcription from the bacteriophage lambda PR promoter. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 10;258(15):9565–9574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan W. D., Bear D. G., von Hippel P. H. Specificity of release by Escherichia coli transcription termination factor rho of nascent mRNA transcripts initiated at the lambda PR. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8664–8671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt T. Transcription termination and the regulation of gene expression. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:339–372. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.002011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price D. H., Sluder A. E., Greenleaf A. L. Dynamic interaction between a Drosophila transcription factor and RNA polymerase II. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1465–1475. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price D. H., Sluder A. E., Greenleaf A. L. Fractionation of transcription factors for RNA polymerase II from Drosophila Kc cell nuclear extracts. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3244–3255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinberg D., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II. Transcription factor IIS stimulates elongation of RNA chains. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3331–3337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reines D., Chamberlin M. J., Kane C. M. Transcription elongation factor SII (TFIIS) enables RNA polymerase II to elongate through a block to transcription in a human gene in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10799–10809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reines D., Wells D., Chamberlin M. J., Kane C. M. Identification of intrinsic termination sites in vitro for RNA polymerase II within eukaryotic gene sequences. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jul 20;196(2):299–312. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90691-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segall J., Matsui T., Roeder R. G. Multiple factors are required for the accurate transcription of purified genes by RNA polymerase III. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11986–11991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setzer D. R., Brown D. D. Formation and stability of the 5 S RNA transcription complex. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2483–2492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shastry B. S., Ng S. Y., Roeder R. G. Multiple factors involved in the transcription of class III genes in Xenopus laevis. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):12979–12986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sluder A. E., Greenleaf A. L., Price D. H. Properties of a Drosophila RNA polymerase II elongation factor. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8963–8969. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sluder A. E., Price D. H., Greenleaf A. L. Elongation by Drosophila RNA polymerase II. Transcription of 3'-extended DNA templates. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 15;263(20):9917–9925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Clair E. W., Pisetsky D. S., Reich C. F., Chambers J. C., Keene J. D. Quantitative immunoassay of anti-La antibodies using purified recombinant La antigen. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Apr;31(4):506–514. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomizawa J., Masukata H. Factor-independent termination of transcription in a stretch of deoxyadenosine residues in the template DNA. Cell. 1987 Nov 20;51(4):623–630. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90131-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson J. B., Chandler D. W., Gralla J. D. Specific termination of in vitro transcription by calf thymus RNA polymerase III. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 11;12(13):5369–5384. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.13.5369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P., Brown D. D. Developmental regulation of two 5S ribosomal RNA genes. Science. 1988 Sep 23;241(4873):1626–1632. doi: 10.1126/science.241.4873.1626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P., Jordan E., Brown D. D. A bacteriophage RNA polymerase transcribes through a Xenopus 5S RNA gene transcription complex without disrupting it. Cell. 1986 Feb 14;44(3):381–389. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90459-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Dunstan H. M., Witte P. R., Smith T. P., Ottonello S., Sprague K. U. A class III transcription factor composed of RNA. Science. 1991 Apr 26;252(5005):542–546. doi: 10.1126/science.1708526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]