Abstract
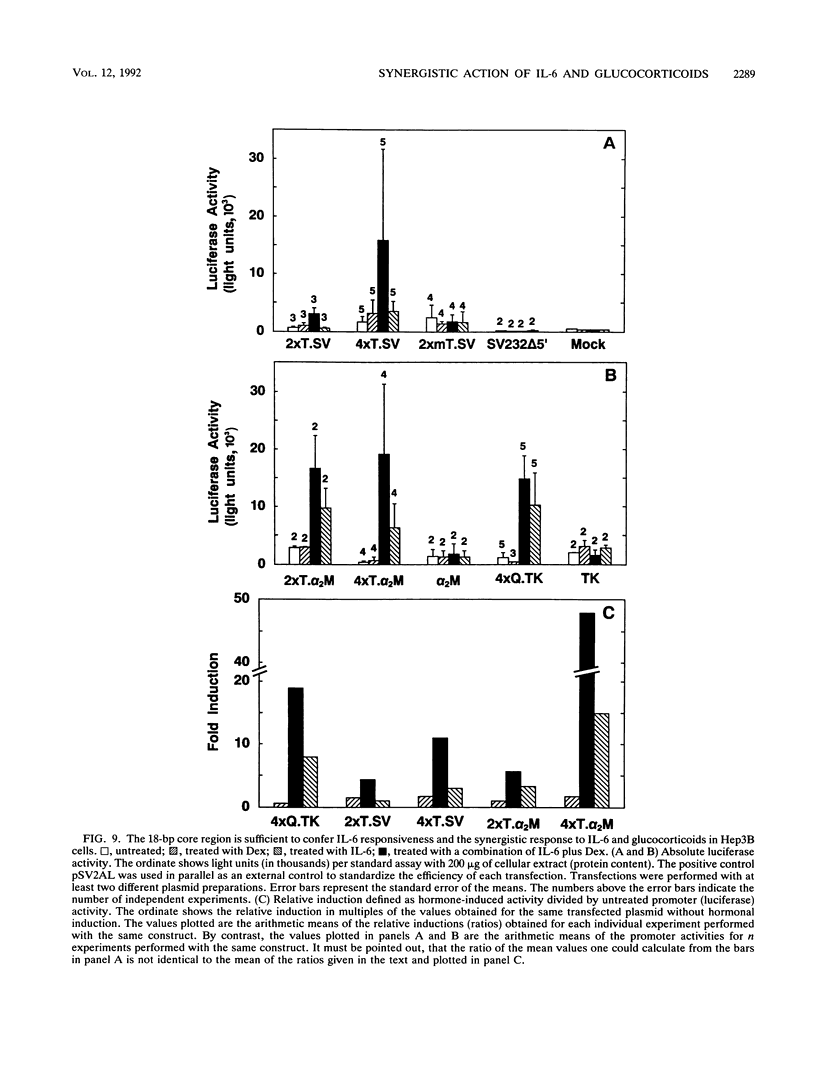
One class of genes coding for the acute-phase proteins (acute-phase genes) is induced by interleukin 6 (IL-6) through the human transcription factor NF-IL-6 and its rat homolog IL-6-DBP/LAP. A second class, represented by the rat alpha 2 macroglobulin gene, utilizes a different IL-6 response element (IL-6-RE) and different DNA-binding proteins interacting with this element, the so-called IL-6-RE binding proteins (IL-6 RE-BPs). Human Hep3B and HepG2 hepatoma, U266 myeloma, and CESS lymphoblastoid cells contain IL-6 RE-BPs that form complexes, with the IL-6-RE, with gel mobilities indistinguishable from those of the corresponding complexes of rat liver cells. The ability to form these complexes was induced by IL-6 in human hepatoma cells with a maximum reached after 4 h and required ongoing protein synthesis. Multiple copies of an 18-bp element containing the IL-6-RE core were sufficient to confer both induction by IL-6 and a synergistic induction by IL-6 plus glucocorticoids to minimal promoters. The synergism was blocked by the receptor antagonist RU486 and thus was dependent on the glucocorticoid receptor (GR). However, the 18-bp element contained no consensus GR-binding site, and recombinant GR did not bind at this sequence. Therefore, the synergism was probably achieved by an indirect effect of a glucocorticoid-activated intermediate gene on the IL-6 RE-BPs. The rat IL-6 RE-BP had a molecular weight of 102 +/- 10 kDa and was thus distinct from NF-IL-6 and IL-6-DBP/LAP. Therefore, IL-6 must activate two different classes of liver acute-phase genes through at least two different nuclear DNA-binding proteins: NF-IL-6/IL-6-DBP/LAP and the IL-6 RE-BP.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akira S., Isshiki H., Sugita T., Tanabe O., Kinoshita S., Nishio Y., Nakajima T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. A nuclear factor for IL-6 expression (NF-IL6) is a member of a C/EBP family. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1897–1906. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08316.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baulieu E. E. Contragestion and other clinical applications of RU 486, an antiprogesterone at the receptor. Science. 1989 Sep 22;245(4924):1351–1357. doi: 10.1126/science.2781282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann H., Gauldie J. Regulation of hepatic acute phase plasma protein genes by hepatocyte stimulating factors and other mediators of inflammation. Mol Biol Med. 1990 Apr;7(2):147–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann H. Hepatic acute phase reaction in vivo and in vitro. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1989 Feb;25(2):115–126. doi: 10.1007/BF02626167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann H., Jahreis G. P., Morella K. K. Interaction of cytokine- and glucocorticoid-response elements of acute-phase plasma protein genes. Importance of glucocorticoid receptor level and cell type for regulation of the elements from rat alpha 1-acid glycoprotein and beta-fibrinogen genes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 25;265(36):22275–22281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann H., Maquat L. E. Localization of DNA sequences involved in dexamethasone-dependent expression of the rat alpha 1-acid glycoprotein gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2551–2561. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann H., Prowse K. R., Marinković S., Won K. A., Jahreis G. P. Stimulation of hepatic acute phase response by cytokines and glucocorticoids. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;557:280-95, discussion 295-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb24021.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beato M. Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brechner T., Hocke G., Goel A., Fey G. H. Interleukin 6 response factor binds co-operatively at two adjacent sites in the promoter upstream region of the rat alpha 2-macroglobulin gene. Mol Biol Med. 1991 Apr;8(2):267–285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brüggemeier U., Kalff M., Franke S., Scheidereit C., Beato M. Ubiquitous transcription factor OTF-1 mediates induction of the MMTV promoter through synergistic interaction with hormone receptors. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):565–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90240-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Descombes P., Chojkier M., Lichtsteiner S., Falvey E., Schibler U. LAP, a novel member of the C/EBP gene family, encodes a liver-enriched transcriptional activator protein. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1541–1551. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond M. I., Miner J. N., Yoshinaga S. K., Yamamoto K. R. Transcription factor interactions: selectors of positive or negative regulation from a single DNA element. Science. 1990 Sep 14;249(4974):1266–1272. doi: 10.1126/science.2119054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fey G. H., Gauldie J. The acute phase response of the liver in inflammation. Prog Liver Dis. 1990;9:89–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghazal P., Nelson J. A. Enhancement of RNA polymerase II initiation complexes by a novel DNA control domain downstream from the cap site of the cytomegalovirus major immediate-early promoter. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2299–2307. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2299-2307.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski K., Carneiro M., Schibler U. Tissue-specific in vitro transcription from the mouse albumin promoter. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):767–776. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90519-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Abraham L. J., Northemann W., Fey G. H. Acute-phase reaction induces a specific complex between hepatic nuclear proteins and the interleukin 6 response element of the rat alpha 2-macroglobulin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2364–2368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Sakaki Y. Dideoxy sequencing method using denatured plasmid templates. Anal Biochem. 1986 Feb 1;152(2):232–238. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90403-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinrich P. C., Castell J. V., Andus T. Interleukin-6 and the acute phase response. Biochem J. 1990 Feb 1;265(3):621–636. doi: 10.1042/bj2650621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helle M., Brakenhoff J. P., De Groot E. R., Aarden L. A. Interleukin 6 is involved in interleukin 1-induced activities. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Jun;18(6):957–959. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeck W., Rusconi S., Groner B. Down-regulation and phosphorylation of glucocorticoid receptors in cultured cells. Investigations with a monospecific antiserum against a bacterially expressed receptor fragment. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):14396–14402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito T., Tanahashi H., Misumi Y., Sakaki Y. Nuclear factors interacting with an interleukin-6 responsive element of rat alpha 2-macroglobulin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 25;17(22):9425–9435. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.22.9425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawano M., Hirano T., Matsuda T., Taga T., Horii Y., Iwato K., Asaoku H., Tang B., Tanabe O., Tanaka H. Autocrine generation and requirement of BSF-2/IL-6 for human multiple myelomas. Nature. 1988 Mar 3;332(6159):83–85. doi: 10.1038/332083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T. The biology of interleukin-6. Blood. 1989 Jul;74(1):1–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein E. S., DiLorenzo D., Posseckert G., Beato M., Ringold G. M. Sequences downstream of the glucocorticoid regulatory element mediate cycloheximide inhibition of steroid induced expression from the rat alpha 1-acid glycoprotein promoter: evidence for a labile transcription factor. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Dec;2(12):1343–1351. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-12-1343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles B. B., Howe C. C., Aden D. P. Human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines secrete the major plasma proteins and hepatitis B surface antigen. Science. 1980 Jul 25;209(4455):497–499. doi: 10.1126/science.6248960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunz D., Zimmermann R., Heisig M., Heinrich P. C. Identification of the promoter sequences involved in the interleukin-6 dependent expression of the rat alpha 2-macroglobulin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 11;17(3):1121–1138. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.3.1121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marinković S., Baumann H. Structure, hormonal regulation, and identification of the interleukin-6- and dexamethasone-responsive element of the rat haptoglobin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1573–1583. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Kingsbury R. Transcriptional control signals of a eukaryotic protein-coding gene. Science. 1982 Jul 23;217(4557):316–324. doi: 10.1126/science.6283634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neville D. M., Jr Molecular weight determination of protein-dodecyl sulfate complexes by gel electrophoresis in a discontinuous buffer system. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 25;246(20):6328–6334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordeen S. K., Suh B. J., Kühnel B., Hutchison C. A., 3rd Structural determinants of a glucocorticoid receptor recognition element. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Dec;4(12):1866–1873. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-12-1866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northemann W., Hattori M., Baffet G., Braciak T. A., Fletcher R. G., Abraham L. J., Gauldie J., Baumann M., Fey G. H. Production of interleukin 6 by hepatoma cells. Mol Biol Med. 1990 Jun;7(3):273–285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northemann W., Shiels B. R., Braciak T. A., Hanson R. W., Heinrich P. C., Fey G. H. Structure and acute-phase regulation of the rat alpha 2-macroglobulin gene. Biochemistry. 1988 Dec 27;27(26):9194–9203. doi: 10.1021/bi00426a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott M. O., Sperling L., Herbomel P., Yaniv M., Weiss M. C. Tissue-specific expression is conferred by a sequence from the 5' end of the rat albumin gene. EMBO J. 1984 Nov;3(11):2505–2510. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02164.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poli V., Cortese R. Interleukin 6 induces a liver-specific nuclear protein that binds to the promoter of acute-phase genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8202–8206. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poli V., Mancini F. P., Cortese R. IL-6DBP, a nuclear protein involved in interleukin-6 signal transduction, defines a new family of leucine zipper proteins related to C/EBP. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):643–653. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90459-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poli V., Silengo L., Altruda F., Cortese R. The analysis of the human hemopexin promoter defines a new class of liver-specific genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 25;17(22):9351–9365. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prowse K. R., Baumann H. Hepatocyte-stimulating factor, beta 2 interferon, and interleukin-1 enhance expression of the rat alpha 1-acid glycoprotein gene via a distal upstream regulatory region. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):42–51. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raynal M. C., Liu Z. Y., Hirano T., Mayer L., Kishimoto T., Chen-Kiang S. Interleukin 6 induces secretion of IgG1 by coordinated transcriptional activation and differential mRNA accumulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):8024–8028. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.8024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruef C., Budde K., Lacy J., Northemann W., Baumann M., Sterzel R. B., Coleman D. L. Interleukin 6 is an autocrine growth factor for mesangial cells. Kidney Int. 1990 Aug;38(2):249–257. doi: 10.1038/ki.1990.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro D. J., Sharp P. A., Wahli W. W., Keller M. J. A high-efficiency HeLa cell nuclear transcription extract. DNA. 1988 Jan-Feb;7(1):47–55. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taga T., Kawanishi Y., Hardy R. R., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. Receptors for B cell stimulatory factor 2. Quantitation, specificity, distribution, and regulation of their expression. J Exp Med. 1987 Oct 1;166(4):967–981. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.4.967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toniatti C., Arcone R., Majello B., Ganter U., Arpaia G., Ciliberto G. Regulation of the human C-reactive protein gene, a major marker of inflammation and cancer. Mol Biol Med. 1990 Jun;7(3):199–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truss M., Chalepakis G., Beato M. Contacts between steroid hormone receptors and thymines in DNA: an interference method. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):7180–7184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.7180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. R., Juan T. S., Wilde M. D., Fey G. H., Darlington G. J. A 58-base-pair region of the human C3 gene confers synergistic inducibility by interleukin-1 and interleukin-6. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6181–6191. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Won K. A., Baumann H. The cytokine response element of the rat alpha 1-acid glycoprotein gene is a complex of several interacting regulatory sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):3965–3978. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.3965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamasaki K., Taga T., Hirata Y., Yawata H., Kawanishi Y., Seed B., Taniguchi T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. Cloning and expression of the human interleukin-6 (BSF-2/IFN beta 2) receptor. Science. 1988 Aug 12;241(4867):825–828. doi: 10.1126/science.3136546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang-Yen H. F., Chambard J. C., Sun Y. L., Smeal T., Schmidt T. J., Drouin J., Karin M. Transcriptional interference between c-Jun and the glucocorticoid receptor: mutual inhibition of DNA binding due to direct protein-protein interaction. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1205–1215. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90396-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet J. R., Wood K. V., DeLuca M., Helinski D. R., Subramani S. Firefly luciferase gene: structure and expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):725–737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]