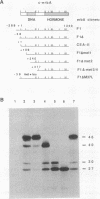
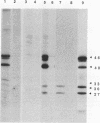
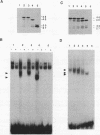
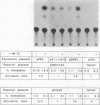
Abstract
ErbA/thyroid hormone receptor is a nuclear receptor that can affect transcription from promoters containing a thyroid hormone response element (TRE) in a thyroid hormone (T3)-dependent manner. We reported earlier that the thyroid hormone receptor is expressed in embryonic avian erythroid cells as a nested set of four proteins with a common C terminus. The full-length receptor is capable of both high-affinity binding to thyroid hormone and specific binding to DNA. We now report that the two smallest ErbA forms, which contain the hormone-binding domain but lack the N-terminal DNA-binding domain, have the same affinity for T3 as does full-length ErbA but are incapable of specific DNA binding. In transactivation assays, these N-terminally truncated proteins are able to specifically suppress both transcriptional repression and hormone-dependent transcriptional activation by the full-length ErbA. We also find that retinoic acid-dependent transactivation by retinoic acid receptors is inhibited by the truncated ErbA proteins. Furthermore, the smaller ErbA forms inhibit binding to TREs by full-length ErbA in vitro. Results from experiments involving site-specific mutagenesis of a conserved region within the hormone-binding domain of the smaller ErbA proteins indicate that the suppressive effect of the smaller receptor forms is independent of hormone binding and that this region is important in mediating protein-hormone as well as protein-protein interactions. We have also found that full-length ErbA homodimers can be detected only in the presence of a specific DNA-binding site. However, no association between full-length and the N-terminally truncated non-DNA-binding ErbA proteins could be detected, indicating that the complex either is unstable or does not form. Our results suggest that inhibition of receptor function occurs through transient formation of heterodimers which lack DNA-binding activity or by competition for factors which positively affect DNA binding by the full-length protein. This finding raises the possibility that thyroid hormone receptor transcriptional activity is autoregulated by means of alternative receptor translation products acting in a dominant negative manner.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acland P., Dixon M., Peters G., Dickson C. Subcellular fate of the int-2 oncoprotein is determined by choice of initiation codon. Nature. 1990 Feb 15;343(6259):662–665. doi: 10.1038/343662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baniahmad A., Steiner C., Köhne A. C., Renkawitz R. Modular structure of a chicken lysozyme silencer: involvement of an unusual thyroid hormone receptor binding site. Cell. 1990 May 4;61(3):505–514. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90532-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banker D. E., Bigler J., Eisenman R. N. The thyroid hormone receptor gene (c-erbA alpha) is expressed in advance of thyroid gland maturation during the early embryonic development of Xenopus laevis. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):5079–5089. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.5079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beato M. Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beebe J. S., Darling D. S., Chin W. W. 3,5,3'-triiodothyronine receptor auxiliary protein (TRAP) enhances receptor binding by interactions within the thyroid hormone response element. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Jan;5(1):85–93. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-1-85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benbrook D., Pfahl M. A novel thyroid hormone receptor encoded by a cDNA clone from a human testis library. Science. 1987 Nov 6;238(4828):788–791. doi: 10.1126/science.3672126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benezra R., Davis R. L., Lockshon D., Turner D. L., Weintraub H. The protein Id: a negative regulator of helix-loop-helix DNA binding proteins. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):49–59. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90214-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigler J., Eisenman R. N. c-erbA encodes multiple proteins in chicken erythroid cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4155–4161. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. J., Young W. S., 3rd, Weinberger C. Differential expression of alpha and beta thyroid hormone receptor genes in rat brain and pituitary. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):7250–7254. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.7250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brent G. A., Dunn M. K., Harney J. W., Gulick T., Larsen P. R., Moore D. D. Thyroid hormone aporeceptor represses T3-inducible promoters and blocks activity of the retinoic acid receptor. New Biol. 1989 Dec;1(3):329–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks A. R., Sweeney G., Old R. W. Structure and functional expression of a cloned Xenopus thyroid hormone receptor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 25;17(22):9395–9405. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.22.9395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnside J., Darling D. S., Chin W. W. A nuclear factor that enhances binding of thyroid hormone receptors to thyroid hormone response elements. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 15;265(5):2500–2504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conneely O. M., Kettelberger D. M., Tsai M. J., Schrader W. T., O'Malley B. W. The chicken progesterone receptor A and B isoforms are products of an alternate translation initiation event. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):14062–14064. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damm K., Thompson C. C., Evans R. M. Protein encoded by v-erbA functions as a thyroid-hormone receptor antagonist. Nature. 1989 Jun 22;339(6226):593–597. doi: 10.1038/339593a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desbois C., Aubert D., Legrand C., Pain B., Samarut J. A novel mechanism of action for v-ErbA: abrogation of the inactivation of transcription factor AP-1 by retinoic acid and thyroid hormone receptors. Cell. 1991 Nov 15;67(4):731–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90068-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Descombes P., Schibler U. A liver-enriched transcriptional activator protein, LAP, and a transcriptional inhibitory protein, LIP, are translated from the same mRNA. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):569–579. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90531-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evan G. I., Lewis G. K., Ramsay G., Bishop J. M. Isolation of monoclonal antibodies specific for human c-myc proto-oncogene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3610–3616. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M., Hollenberg S. M. Zinc fingers: gilt by association. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90522-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fawell S. E., Lees J. A., White R., Parker M. G. Characterization and colocalization of steroid binding and dimerization activities in the mouse estrogen receptor. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):953–962. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90343-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florkiewicz R. Z., Sommer A. Human basic fibroblast growth factor gene encodes four polypeptides: three initiate translation from non-AUG codons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):3978–3981. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.3978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forman B. M., Samuels H. H. Dimerization among nuclear hormone receptors. New Biol. 1990 Jul;2(7):587–594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forman B. M., Yang C. R., Au M., Casanova J., Ghysdael J., Samuels H. H. A domain containing leucine-zipper-like motifs mediate novel in vivo interactions between the thyroid hormone and retinoic acid receptors. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Oct;3(10):1610–1626. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-10-1610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrest D., Sjöberg M., Vennström B. Contrasting developmental and tissue-specific expression of alpha and beta thyroid hormone receptor genes. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1519–1528. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08270.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass C. K., Holloway J. M., Devary O. V., Rosenfeld M. G. The thyroid hormone receptor binds with opposite transcriptional effects to a common sequence motif in thyroid hormone and estrogen response elements. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):313–323. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90194-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass C. K., Lipkin S. M., Devary O. V., Rosenfeld M. G. Positive and negative regulation of gene transcription by a retinoic acid-thyroid hormone receptor heterodimer. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):697–708. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90016-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graupner G., Wills K. N., Tzukerman M., Zhang X. K., Pfahl M. Dual regulatory role for thyroid-hormone receptors allows control of retinoic-acid receptor activity. Nature. 1989 Aug 24;340(6235):653–656. doi: 10.1038/340653a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hann S. R., King M. W., Bentley D. L., Anderson C. W., Eisenman R. N. A non-AUG translational initiation in c-myc exon 1 generates an N-terminally distinct protein whose synthesis is disrupted in Burkitt's lymphomas. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):185–195. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90507-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harland R., Weintraub H. Translation of mRNA injected into Xenopus oocytes is specifically inhibited by antisense RNA. J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;101(3):1094–1099. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.3.1094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodin R. A., Lazar M. A., Wintman B. I., Darling D. S., Koenig R. J., Larsen P. R., Moore D. D., Chin W. W. Identification of a thyroid hormone receptor that is pituitary-specific. Science. 1989 Apr 7;244(4900):76–79. doi: 10.1126/science.2539642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izumo S., Mahdavi V. Thyroid hormone receptor alpha isoforms generated by alternative splicing differentially activate myosin HC gene transcription. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):539–542. doi: 10.1038/334539a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jang S. K., Wimmer E. Cap-independent translation of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA: structural elements of the internal ribosomal entry site and involvement of a cellular 57-kD RNA-binding protein. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1560–1572. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston R. F., Pickett S. C., Barker D. L. Autoradiography using storage phosphor technology. Electrophoresis. 1990 May;11(5):355–360. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150110503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig R. J., Lazar M. A., Hodin R. A., Brent G. A., Larsen P. R., Chin W. W., Moore D. D. Inhibition of thyroid hormone action by a non-hormone binding c-erbA protein generated by alternative mRNA splicing. Nature. 1989 Feb 16;337(6208):659–661. doi: 10.1038/337659a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Bifunctional messenger RNAs in eukaryotes. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):481–483. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90609-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. The scanning model for translation: an update. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):229–241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazar M. A., Berrodin T. J., Harding H. P. Differential DNA binding by monomeric, homodimeric, and potentially heteromeric forms of the thyroid hormone receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):5005–5015. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.5005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazar M. A., Hodin R. A., Darling D. S., Chin W. W. A novel member of the thyroid/steroid hormone receptor family is encoded by the opposite strand of the rat c-erbA alpha transcriptional unit. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):1128–1136. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.1128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazar M. A., Hodin R. A., Darling D. S., Chin W. W. Identification of a rat c-erbA alpha-related protein which binds deoxyribonucleic acid but does not bind thyroid hormone. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Oct;2(10):893–901. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-10-893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazar M. A., Jones K. E., Chin W. W. Isolation of a cDNA encoding human Rev-ErbA alpha: transcription from the noncoding DNA strand of a thyroid hormone receptor gene results in a related protein that does not bind thyroid hormone. DNA Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;9(2):77–83. doi: 10.1089/dna.1990.9.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macejak D. G., Sarnow P. Internal initiation of translation mediated by the 5' leader of a cellular mRNA. Nature. 1991 Sep 5;353(6339):90–94. doi: 10.1038/353090a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miksicek R., Heber A., Schmid W., Danesch U., Posseckert G., Beato M., Schütz G. Glucocorticoid responsiveness of the transcriptional enhancer of Moloney murine sarcoma virus. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):283–290. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90745-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuhashi T., Nikodem V. M. Regulation of expression of the alternative mRNAs of the rat alpha-thyroid hormone receptor gene. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8900–8904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuhashi T., Tennyson G. E., Nikodem V. M. Alternative splicing generates messages encoding rat c-erbA proteins that do not bind thyroid hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5804–5808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyajima N., Horiuchi R., Shibuya Y., Fukushige S., Matsubara K., Toyoshima K., Yamamoto T. Two erbA homologs encoding proteins with different T3 binding capacities are transcribed from opposite DNA strands of the same genetic locus. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):31–39. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90169-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray M. B., Towle H. C. Identification of nuclear factors that enhance binding of the thyroid hormone receptor to a thyroid hormone response element. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Sep;3(9):1434–1442. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-9-1434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray M. B., Zilz N. D., McCreary N. L., MacDonald M. J., Towle H. C. Isolation and characterization of rat cDNA clones for two distinct thyroid hormone receptors. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12770–12777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäkelä T. P., Saksela K., Alitalo K. Two N-myc polypeptides with distinct amino termini encoded by the second and third exons of the gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1545–1552. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai A., Sakurai A., Bell G. I., DeGroot L. J. Characterization of a third human thyroid hormone receptor coexpressed with other thyroid hormone receptors in several tissues. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Nov;2(11):1087–1092. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-11-1087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai A., Seino S., Sakurai A., Szilak I., Bell G. I., DeGroot L. J. Characterization of a thyroid hormone receptor expressed in human kidney and other tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2781–2785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer J. H., Schwartz H. L., Mariash C. N., Kinlaw W. B., Wong N. C., Freake H. C. Advances in our understanding of thyroid hormone action at the cellular level. Endocr Rev. 1987 Aug;8(3):288–308. doi: 10.1210/edrv-8-3-288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petty K. J., Desvergne B., Mitsuhashi T., Nikodem V. M. Identification of a thyroid hormone response element in the malic enzyme gene. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 5;265(13):7395–7400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prats H., Kaghad M., Prats A. C., Klagsbrun M., Lélias J. M., Liauzun P., Chalon P., Tauber J. P., Amalric F., Smith J. A. High molecular mass forms of basic fibroblast growth factor are initiated by alternative CUG codons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):1836–1840. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.1836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth M. B., Zahler A. M., Stolk J. A. A conserved family of nuclear phosphoproteins localized to sites of polymerase II transcription. J Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;115(3):587–596. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.3.587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuels H. H., Forman B. M., Horowitz Z. D., Ye Z. S. Regulation of gene expression by thyroid hormone. J Clin Invest. 1988 Apr;81(4):957–967. doi: 10.1172/JCI113449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sap J., Muñoz A., Damm K., Goldberg Y., Ghysdael J., Leutz A., Beug H., Vennström B. The c-erb-A protein is a high-affinity receptor for thyroid hormone. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):635–640. doi: 10.1038/324635a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sap J., Muñoz A., Schmitt J., Stunnenberg H., Vennström B. Repression of transcription mediated at a thyroid hormone response element by the v-erb-A oncogene product. Nature. 1989 Jul 20;340(6230):242–244. doi: 10.1038/340242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sap J., de Magistris L., Stunnenberg H., Vennström B. A major thyroid hormone response element in the third intron of the rat growth hormone gene. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):887–896. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08186.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuman J. D., Vinson C. R., McKnight S. L. Evidence of changes in protease sensitivity and subunit exchange rate on DNA binding by C/EBP. Science. 1990 Aug 17;249(4970):771–774. doi: 10.1126/science.2202050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. C., Weinberger C., Lebo R., Evans R. M. Identification of a novel thyroid hormone receptor expressed in the mammalian central nervous system. Science. 1987 Sep 25;237(4822):1610–1614. doi: 10.1126/science.3629259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger C., Thompson C. C., Ong E. S., Lebo R., Gruol D. J., Evans R. M. The c-erb-A gene encodes a thyroid hormone receptor. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):641–646. doi: 10.1038/324641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaoita Y., Brown D. D. A correlation of thyroid hormone receptor gene expression with amphibian metamorphosis. Genes Dev. 1990 Nov;4(11):1917–1924. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.11.1917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaoita Y., Shi Y. B., Brown D. D. Xenopus laevis alpha and beta thyroid hormone receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):7090–7094. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.7090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenke M., Muñoz A., Sap J., Vennström B., Beug H. v-erbA oncogene activation entails the loss of hormone-dependent regulator activity of c-erbA. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):1035–1049. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90068-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilz N. D., Murray M. B., Towle H. C. Identification of multiple thyroid hormone response elements located far upstream from the rat S14 promoter. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):8136–8143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Thé H., Vivanco-Ruiz M. M., Tiollais P., Stunnenberg H., Dejean A. Identification of a retinoic acid responsive element in the retinoic acid receptor beta gene. Nature. 1990 Jan 11;343(6254):177–180. doi: 10.1038/343177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]