Abstract
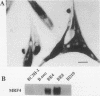
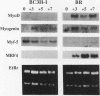
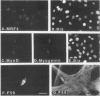
Expression of MRF4, a myogenic regulatory factor of the basic helix-loop-helix type, produced multiple changes in the myogenic program of the BC3H-1 cell line. BC3H-1 cells that stably expressed exogenous MRF4 were prepared and termed BR cell lines. Upon differentiation, the BR cells were found to have three muscle-specific properties (endogenous MyoD expression, myoblast fusion, and fast myosin light-chain 1 expression) that the parent BC3H-1 cells did not have. Of the four known myogenic regulatory factors (MyoD, myogenin, Myf-5, and MRF4), only MRF4 was capable of activating expression of the endogenous BC3H-1 myoD gene. In addition, the pattern of Myf-5 expression in BR cells was the opposite of that in BC3H-1 cells. Myf-5 expression was low in BR myoblasts and showed a small increase upon myotube formation, whereas Myf-5 expression was high in BC3H-1 myoblasts and decreased upon differentiation. Though the MRF4-transfected BR cells fused to form large myotubes and expressed fast myosin light-chain 1, the pattern of myosin heavy-chain isoform expression was the same in the BR and the nonfusing parent BC3H-1 cells, suggesting that factors in addition to the MyoD family members regulate myosin heavy-chain isoform expression patterns in BC3H-1 cells. In contrast to the changes produced by MRF4 expression, overexpression of Myf-5 did not alter BC3H-1 myogenesis. The results suggest that differential expression of the myogenic regulatory factors of the MyoD family may be one mechanism for generating cells with diverse myogenic phenotypes.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen R. E., Boxhorn L. K. Regulation of skeletal muscle satellite cell proliferation and differentiation by transforming growth factor-beta, insulin-like growth factor I, and fibroblast growth factor. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Feb;138(2):311–315. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041380213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barton P. J., Buckingham M. E. The myosin alkali light chain proteins and their genes. Biochem J. 1985 Oct 15;231(2):249–261. doi: 10.1042/bj2310249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benezra R., Davis R. L., Lockshon D., Turner D. L., Weintraub H. The protein Id: a negative regulator of helix-loop-helix DNA binding proteins. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):49–59. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90214-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blau H. M., Pavlath G. K., Hardeman E. C., Chiu C. P., Silberstein L., Webster S. G., Miller S. C., Webster C. Plasticity of the differentiated state. Science. 1985 Nov 15;230(4727):758–766. doi: 10.1126/science.2414846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block N. E., Menick D. R., Robinson K. A., Buse M. G. Effect of denervation on the expression of two glucose transporter isoforms in rat hindlimb muscle. J Clin Invest. 1991 Nov;88(5):1546–1552. doi: 10.1172/JCI115465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bober E., Lyons G. E., Braun T., Cossu G., Buckingham M., Arnold H. H. The muscle regulatory gene, Myf-6, has a biphasic pattern of expression during early mouse development. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;113(6):1255–1265. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.6.1255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun T., Bober E., Buschhausen-Denker G., Kohtz S., Grzeschik K. H., Arnold H. H., Kotz S. Differential expression of myogenic determination genes in muscle cells: possible autoactivation by the Myf gene products. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3617–3625. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08535.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun T., Bober E., Winter B., Rosenthal N., Arnold H. H. Myf-6, a new member of the human gene family of myogenic determination factors: evidence for a gene cluster on chromosome 12. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):821–831. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08179.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun T., Buschhausen-Denker G., Bober E., Tannich E., Arnold H. H. A novel human muscle factor related to but distinct from MyoD1 induces myogenic conversion in 10T1/2 fibroblasts. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):701–709. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03429.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan T. J., Edmondson D. G., Olson E. N. Aberrant regulation of MyoD1 contributes to the partially defective myogenic phenotype of BC3H1 cells. J Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;110(4):929–937. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.4.929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty T., Brennan T., Olson E. Differential trans-activation of a muscle-specific enhancer by myogenic helix-loop-helix proteins is separable from DNA binding. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 15;266(5):2878–2882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty T., Olson E. N. Domains outside of the DNA-binding domain impart target gene specificity to myogenin and MRF4. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;11(12):6103–6108. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.12.6103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheley S., Anderson R. A reproducible microanalytical method for the detection of specific RNA sequences by dot-blot hybridization. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):15–19. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90339-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cossu G., Molinaro M. Cell heterogeneity in the myogenic lineage. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1987;23:185–208. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60625-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Weintraub H., Lassar A. B. Expression of a single transfected cDNA converts fibroblasts to myoblasts. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):987–1000. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90585-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmondson D. G., Olson E. N. A gene with homology to the myc similarity region of MyoD1 is expressed during myogenesis and is sufficient to activate the muscle differentiation program. Genes Dev. 1989 May;3(5):628–640. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.5.628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel L., White J. M. Antibodies to 100- and 60-kDa surface proteins inhibit substratum attachment and differentiation of rodent skeletal myoblasts. Dev Biol. 1990 Jul;140(1):196–208. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(90)90067-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florini J. R., Magri K. A., Ewton D. Z., James P. L., Grindstaff K., Rotwein P. S. "Spontaneous" differentiation of skeletal myoblasts is dependent upon autocrine secretion of insulin-like growth factor-II. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15917–15923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster R. F., Thompson J. M., Kaufman S. J. A laminin substrate promotes myogenesis in rat skeletal muscle cultures: analysis of replication and development using antidesmin and anti-BrdUrd monoclonal antibodies. Dev Biol. 1987 Jul;122(1):11–20. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90327-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinterberger T. J., Sassoon D. A., Rhodes S. J., Konieczny S. F. Expression of the muscle regulatory factor MRF4 during somite and skeletal myofiber development. Dev Biol. 1991 Sep;147(1):144–156. doi: 10.1016/s0012-1606(05)80014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassar A. B., Davis R. L., Wright W. E., Kadesch T., Murre C., Voronova A., Baltimore D., Weintraub H. Functional activity of myogenic HLH proteins requires hetero-oligomerization with E12/E47-like proteins in vivo. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):305–315. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90620-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassar A. B., Thayer M. J., Overell R. W., Weintraub H. Transformation by activated ras or fos prevents myogenesis by inhibiting expression of MyoD1. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90101-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. B., Crow M. T., Stockdale F. E. Slow and fast myosin heavy chain content defines three types of myotubes in early muscle cell cultures. J Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;101(5 Pt 1):1643–1650. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.5.1643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. B. Myoblasts, myosins, MyoDs, and the diversification of muscle fibers. Neuromuscul Disord. 1991;1(1):7–17. doi: 10.1016/0960-8966(91)90038-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. B. Myogenic programs of mouse muscle cell lines: expression of myosin heavy chain isoforms, MyoD1, and myogenin. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):1149–1159. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.1149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. B. Regulation of acetylcholine receptors in the mouse muscle cell line, C2. Exp Cell Res. 1984 Sep;154(1):256–269. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(84)90685-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. B., Stockdale F. E. Developmental origins of skeletal muscle fibers: clonal analysis of myogenic cell lineages based on expression of fast and slow myosin heavy chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3860–3864. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. B., Stockdale F. E. Developmental regulation of the multiple myogenic cell lineages of the avian embryo. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2197–2208. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. B., Teal S. B., Stockdale F. E. Evolutionarily conserved sequences of striated muscle myosin heavy chain isoforms. Epitope mapping by cDNA expression. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 5;264(22):13122–13130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miner J. H., Wold B. Herculin, a fourth member of the MyoD family of myogenic regulatory genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1089–1093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molina M. I., Kropp K. E., Gulick J., Robbins J. The sequence of an embryonic myosin heavy chain gene and isolation of its corresponding cDNA. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6478–6488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgenstern J. P., Land H. A series of mammalian expression vectors and characterisation of their expression of a reporter gene in stably and transiently transfected cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 25;18(4):1068–1068. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.4.1068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson C. A., Gordon H., Hall Z. W., Paterson B. M., Blau H. M. Negative control of the helix-loop-helix family of myogenic regulators in the NFB mutant. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):493–502. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90014-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reznikoff C. A., Brankow D. W., Heidelberger C. Establishment and characterization of a cloned line of C3H mouse embryo cells sensitive to postconfluence inhibition of division. Cancer Res. 1973 Dec;33(12):3231–3238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes S. J., Konieczny S. F. Identification of MRF4: a new member of the muscle regulatory factor gene family. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2050–2061. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert D., Harris A. J., Devine C. E., Heinemann S. Characterization of a unique muscle cell line. J Cell Biol. 1974 May;61(2):398–413. doi: 10.1083/jcb.61.2.398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed J., Hauschka S. D. Clonal analysis of vertebrate myogenesis. VIII. Fibroblasts growth factor (FGF)-dependent and FGF-independent muscle colony types during chick wing development. Dev Biol. 1988 Jul;128(1):40–49. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90264-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. H., Miller J. B. Distinct myogenic programs of embryonic and fetal mouse muscle cells: expression of the perinatal myosin heavy chain isoform in vitro. Dev Biol. 1992 Jan;149(1):16–26. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(92)90260-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg E. A., Spizz G., Perry M. E., Olson E. N. A ras-dependent pathway abolishes activity of a muscle-specific enhancer upstream from the muscle creatine kinase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):594–601. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stockdale F. E. The myogenic lineage: evidence for multiple cellular precursors during avian limb development. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1990 Jun;194(2):71–75. doi: 10.3181/00379727-194-43058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X. H., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A., Baltimore D. Id proteins Id1 and Id2 selectively inhibit DNA binding by one class of helix-loop-helix proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;11(11):5603–5611. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.11.5603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapscott S. J., Davis R. L., Thayer M. J., Cheng P. F., Weintraub H., Lassar A. B. MyoD1: a nuclear phosphoprotein requiring a Myc homology region to convert fibroblasts to myoblasts. Science. 1988 Oct 21;242(4877):405–411. doi: 10.1126/science.3175662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taubman M. B., Smith C. W., Izumo S., Grant J. W., Endo T., Andreadis A., Nadal-Ginard B. The expression of sarcomeric muscle-specific contractile protein genes in BC3H1 cells: BC3H1 cells resemble skeletal myoblasts that are defective for commitment to terminal differentiation. J Cell Biol. 1989 May;108(5):1799–1806. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.5.1799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thayer M. J., Tapscott S. J., Davis R. L., Wright W. E., Lassar A. B., Weintraub H. Positive autoregulation of the myogenic determination gene MyoD1. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):241–248. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90838-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thayer M. J., Weintraub H. Activation and repression of myogenesis in somatic cell hybrids: evidence for trans-negative regulation of MyoD in primary fibroblasts. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):23–32. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90285-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vivarelli E., Brown W. E., Whalen R. G., Cossu G. The expression of slow myosin during mammalian somitogenesis and limb bud differentiation. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 1):2191–2197. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vivarelli E., Cossu G. Neural control of early myogenic differentiation in cultures of mouse somites. Dev Biol. 1986 Sep;117(1):319–325. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90374-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Davis R., Tapscott S., Thayer M., Krause M., Benezra R., Blackwell T. K., Turner D., Rupp R., Hollenberg S. The myoD gene family: nodal point during specification of the muscle cell lineage. Science. 1991 Feb 15;251(4995):761–766. doi: 10.1126/science.1846704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White N. K., Bonner P. H., Nelson D. R., Hauschka S. D. Clonal analysis of vertebrate myogenesis. IV. Medium-dependent classification of colony-forming cells. Dev Biol. 1975 Jun;44(2):346–361. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(75)90405-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright W. E., Sassoon D. A., Lin V. K. Myogenin, a factor regulating myogenesis, has a domain homologous to MyoD. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):607–617. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90583-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaffe D., Saxel O. Serial passaging and differentiation of myogenic cells isolated from dystrophic mouse muscle. Nature. 1977 Dec 22;270(5639):725–727. doi: 10.1038/270725a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yutzey K. E., Rhodes S. J., Konieczny S. F. Differential trans activation associated with the muscle regulatory factors MyoD1, myogenin, and MRF4. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):3934–3944. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.3934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]