Abstract
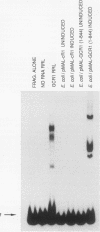
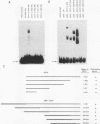
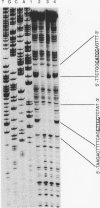
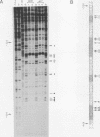
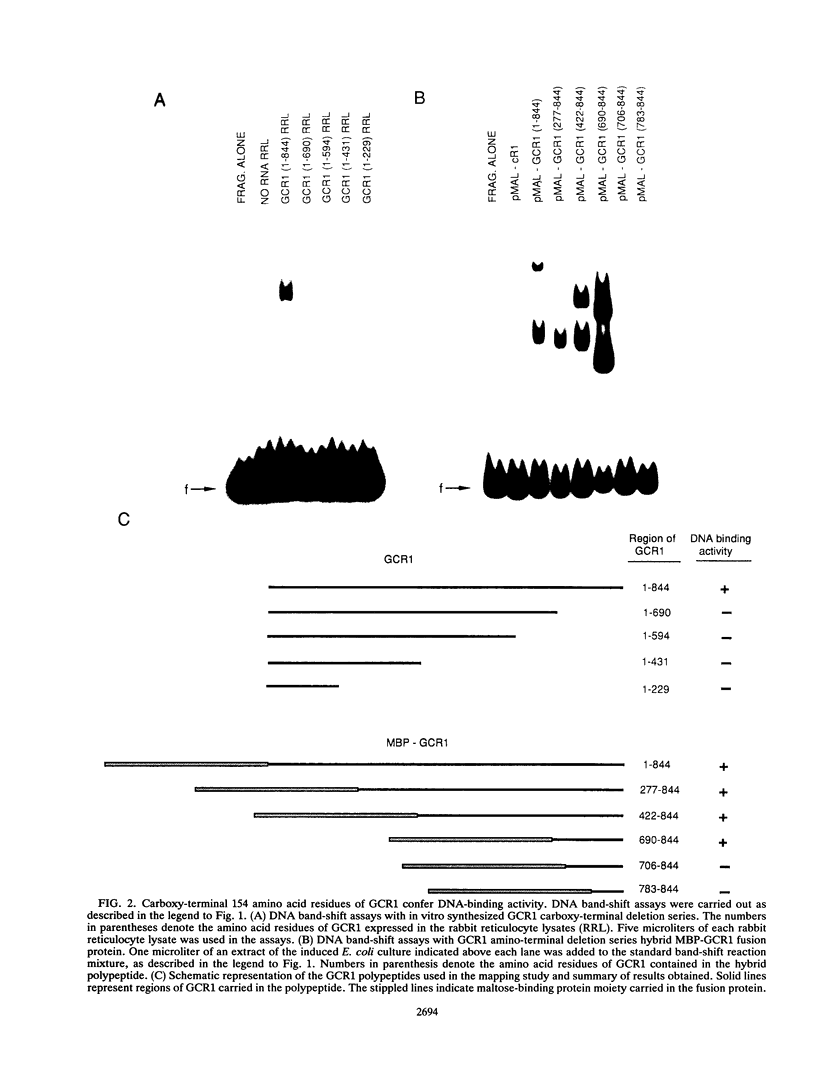
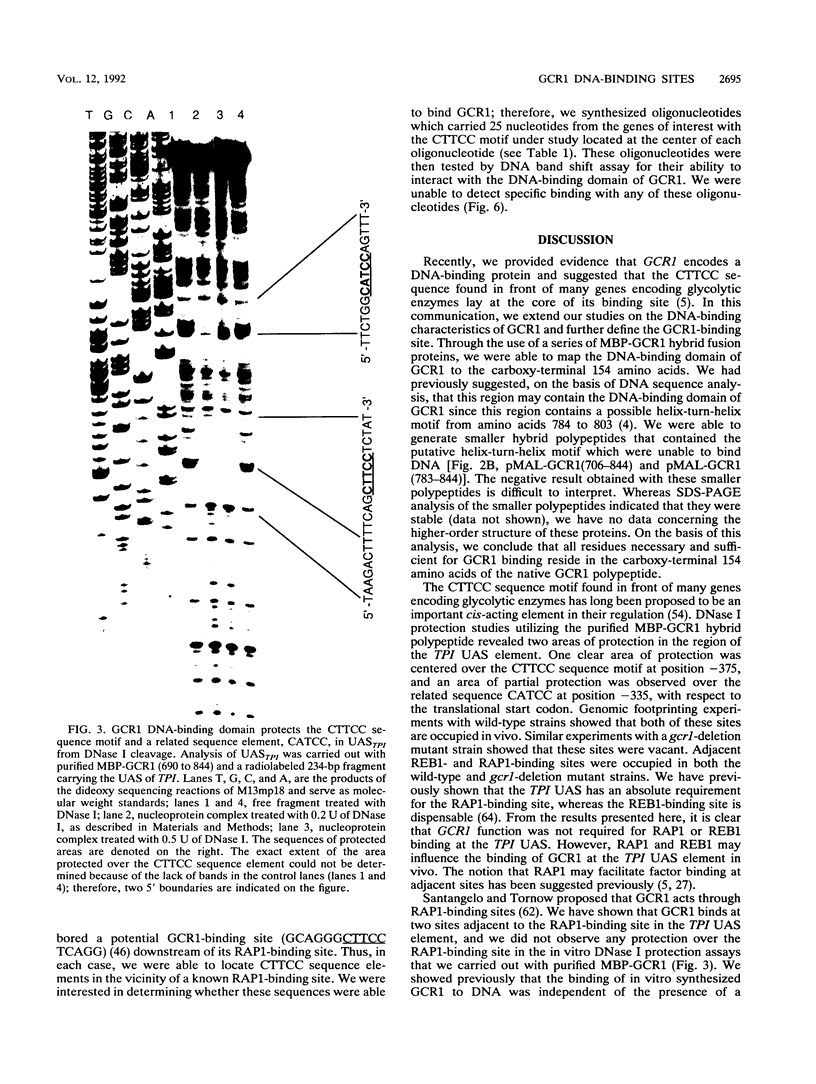
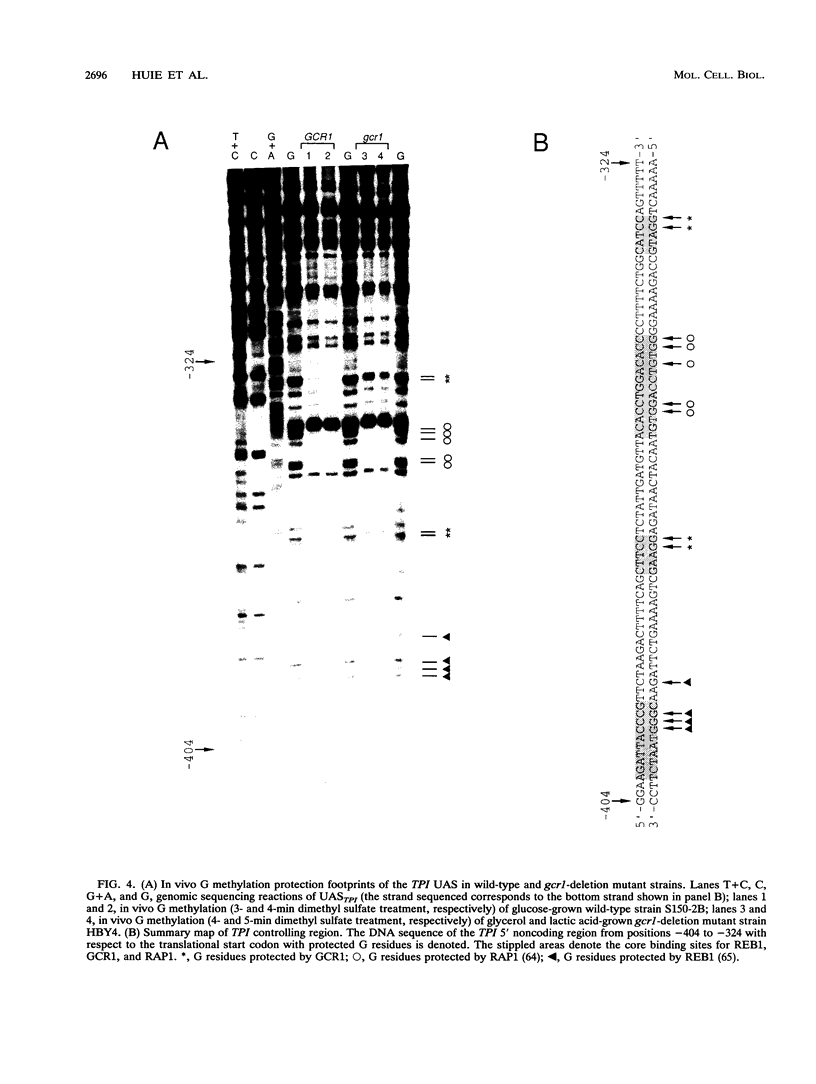
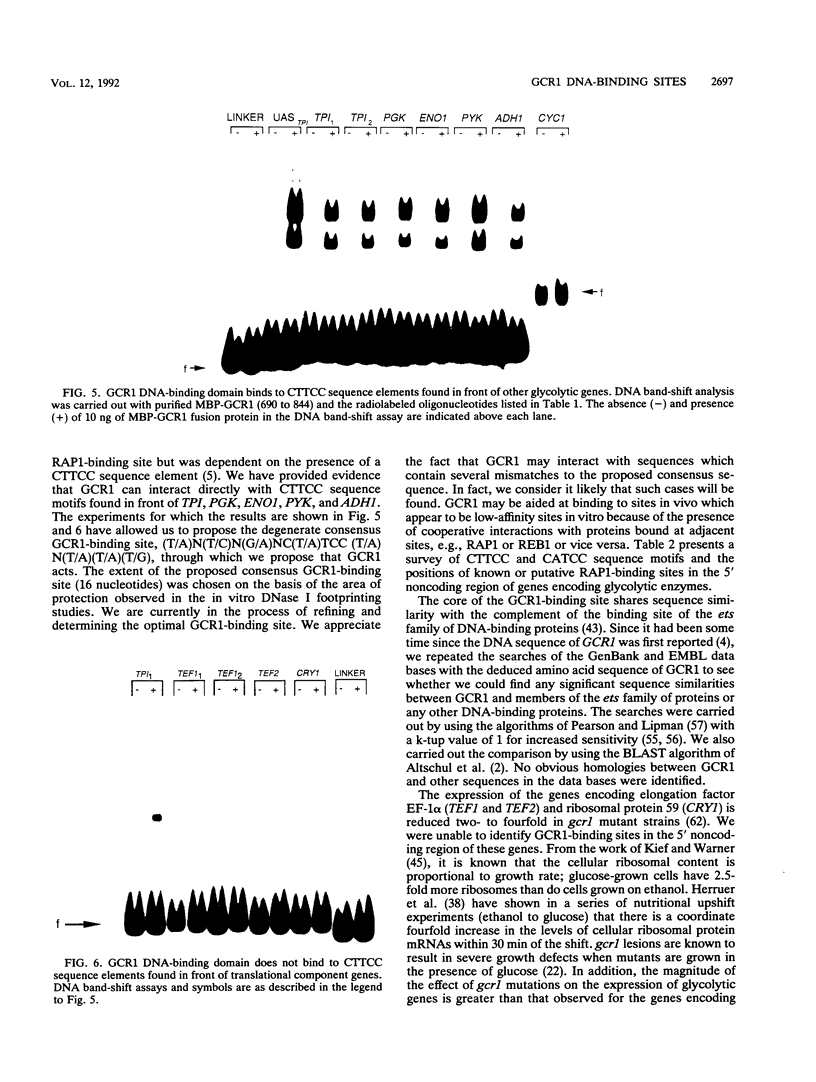
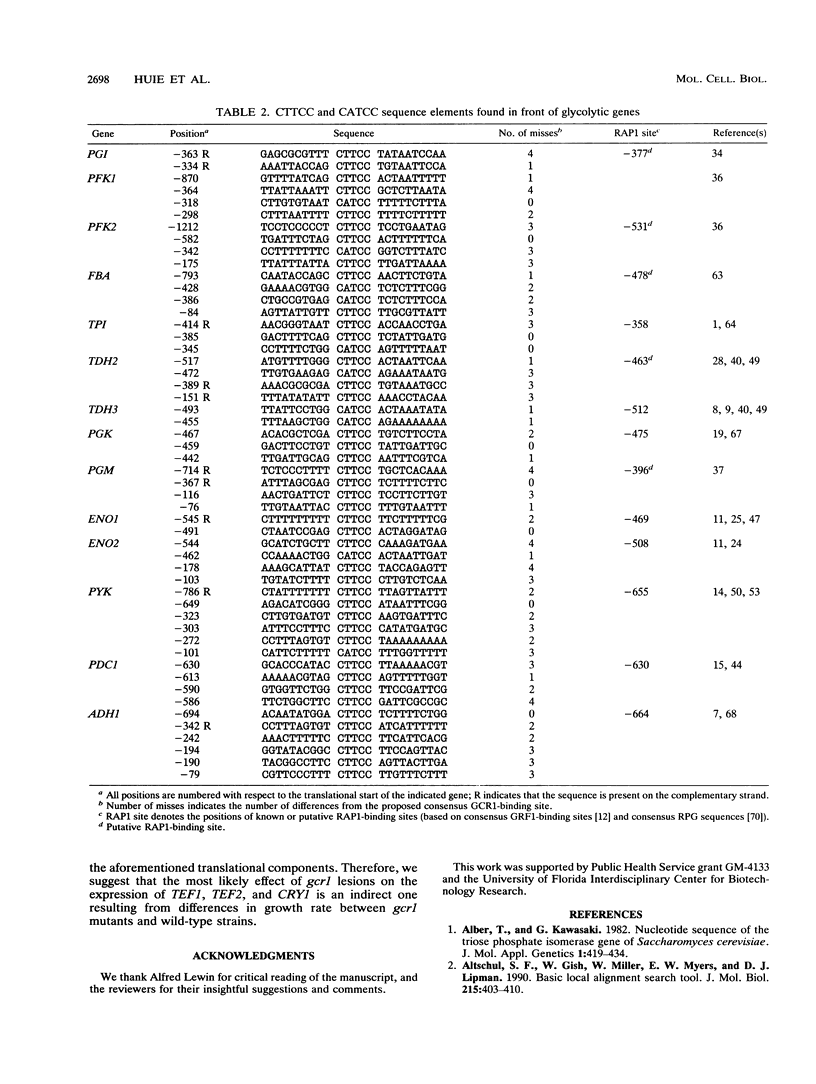
GCR1 gene function is required for high-level glycolytic gene expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Recently, we suggested that the CTTCC sequence motif found in front of many genes encoding glycolytic enzymes lay at the core of the GCR1-binding site. Here we mapped the DNA-binding domain of GCR1 to the carboxy-terminal 154 amino acids of the polypeptide. DNase I protection studies showed that a hybrid MBP-GCR1 fusion protein protected a region of the upstream activating sequence of TPI (UASTPI), which harbored the CTTCC sequence motif, and suggested that the fusion protein might also interact with a region of the UAS that contained the related sequence CATCC. A series of in vivo G methylation protection experiments of the native TPI promoter were carried out with wild-type and gcr1 deletion mutant strains. The G doublets that correspond to the C doublets in each site were protected in the wild-type strain but not in the gcr1 mutant strain. These data demonstrate that the UAS of TPI contains two GCR1-binding sites which are occupied in vivo. Furthermore, adjacent RAP1/GRF1/TUF- and REB1/GRF2/QBP/Y-binding sites in UASTPI were occupied in the backgrounds of both strains. In addition, DNA band-shift assays were used to show that the MBP-GCR1 fusion protein was able to form nucleoprotein complexes with oligonucleotides that contained CTTCC sequence elements found in front of other glycolytic genes, namely, PGK, ENO1, PYK, and ADH1, all of which are dependent on GCR1 gene function for full expression. However, we were unable to detect specific interactions with CTTCC sequence elements found in front of the translational component genes TEF1, TEF2, and CRY1. Taken together, these experiments have allowed us to propose a consensus GCR1-binding site which is 5'-(T/A)N(T/C)N(G/A)NC(T/A)TCC(T/A)N(T/A)(T/A)(T/G)-3'.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alber T., Kawasaki G. Nucleotide sequence of the triose phosphate isomerase gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(5):419–434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker H. V. GCR1 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae encodes a DNA binding protein whose binding is abolished by mutations in the CTTCC sequence motif. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9443–9447. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker H. V. Glycolytic gene expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: nucleotide sequence of GCR1, null mutants, and evidence for expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3774–3784. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennetzen J. L., Hall B. D. The primary structure of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene for alcohol dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3018–3025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bitter G. A., Chang K. K., Egan K. M. A multi-component upstream activation sequence of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene promoter. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Dec;231(1):22–32. doi: 10.1007/BF00293817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bitter G. A., Egan K. M. Expression of heterologous genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae from vectors utilizing the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene promoter. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(3):263–274. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90002-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandl C. J., Struhl K. A nucleosome-positioning sequence is required for GCN4 to activate transcription in the absence of a TATA element. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4256–4265. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brindle P. K., Holland J. P., Willett C. E., Innis M. A., Holland M. J. Multiple factors bind the upstream activation sites of the yeast enolase genes ENO1 and ENO2: ABFI protein, like repressor activator protein RAP1, binds cis-acting sequences which modulate repression or activation of transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4872–4885. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchman A. R., Kimmerly W. J., Rine J., Kornberg R. D. Two DNA-binding factors recognize specific sequences at silencers, upstream activating sequences, autonomously replicating sequences, and telomeres in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):210–225. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchman A. R., Lue N. F., Kornberg R. D. Connections between transcriptional activators, silencers, and telomeres as revealed by functional analysis of a yeast DNA-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;8(12):5086–5099. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.12.5086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. L., Tekamp-Olson P., Najarian R. The isolation, characterization, and sequence of the pyruvate kinase gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2193–2201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler G., Dawes I. W., McConnell D. J. TUF factor binds to the upstream region of the pyruvate decarboxylase structural gene (PDC1) of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Sep;223(3):449–456. doi: 10.1007/BF00264453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capieaux E., Vignais M. L., Sentenac A., Goffeau A. The yeast H+-ATPase gene is controlled by the promoter binding factor TUF. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7437–7446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers A., Stanway C., Kingsman A. J., Kingsman S. M. The UAS of the yeast PGK gene is composed of multiple functional elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Sep 12;16(17):8245–8260. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.17.8245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers A., Stanway C., Tsang J. S., Henry Y., Kingsman A. J., Kingsman S. M. ARS binding factor 1 binds adjacent to RAP1 at the UASs of the yeast glycolytic genes PGK and PYK1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 25;18(18):5393–5399. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.18.5393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers A., Tsang J. S., Stanway C., Kingsman A. J., Kingsman S. M. Transcriptional control of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae PGK gene by RAP1. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5516–5524. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chasman D. I., Lue N. F., Buchman A. R., LaPointe J. W., Lorch Y., Kornberg R. D. A yeast protein that influences the chromatin structure of UASG and functions as a powerful auxiliary gene activator. Genes Dev. 1990 Apr;4(4):503–514. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.4.503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clifton D., Fraenkel D. G. The gcr (glycolysis regulation) mutation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):13074–13078. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clifton D., Weinstock S. B., Fraenkel D. G. Glycolysis mutants in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1978 Jan;88(1):1–11. doi: 10.1093/genetics/88.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen R., Holland J. P., Yokoi T., Holland M. J. Identification of a regulatory region that mediates glucose-dependent induction of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae enolase gene ENO2. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2287–2297. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen R., Yokoi T., Holland J. P., Pepper A. E., Holland M. J. Transcription of the constitutively expressed yeast enolase gene ENO1 is mediated by positive and negative cis-acting regulatory sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2753–2761. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cottrelle P., Thiele D., Price V. L., Memet S., Micouin J. Y., Marck C., Buhler J. M., Sentenac A., Fromageot P. Cloning, nucleotide sequence, and expression of one of two genes coding for yeast elongation factor 1 alpha. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):3090–3096. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devlin C., Tice-Baldwin K., Shore D., Arndt K. T. RAP1 is required for BAS1/BAS2- and GCN4-dependent transcription of the yeast HIS4 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;11(7):3642–3651. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.7.3642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edens L., Bom I., Ledeboer A. M., Maat J., Toonen M. Y., Visser C., Verrips C. T. Synthesis and processing of the plant protein thaumatin in yeast. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):629–633. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90394-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ephrussi A., Church G. M., Tonegawa S., Gilbert W. B lineage--specific interactions of an immunoglobulin enhancer with cellular factors in vivo. Science. 1985 Jan 11;227(4683):134–140. doi: 10.1126/science.3917574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedor M. J., Lue N. F., Kornberg R. D. Statistical positioning of nucleosomes by specific protein-binding to an upstream activating sequence in yeast. J Mol Biol. 1988 Nov 5;204(1):109–127. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90603-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green J. B., Wright A. P., Cheung W. Y., Lancashire W. E., Hartley B. S. The structure and regulation of phosphoglucose isomerase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Dec;215(1):100–106. doi: 10.1007/BF00331310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Lalonde B., Gifford P., Alani E. Distinctly regulated tandem upstream activation sites mediate catabolite repression of the CYC1 gene of S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):503–511. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90243-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinisch J., Vogelsang K., Hollenberg C. P. Transcriptional control of yeast phosphofructokinase gene expression. FEBS Lett. 1991 Sep 2;289(1):77–82. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80912-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinisch J., von Borstel R. C., Rodicio R. Sequence and localization of the gene encoding yeast phosphoglycerate mutase. Curr Genet. 1991 Jul;20(1-2):167–171. doi: 10.1007/BF00312781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herruer M. H., Mager W. H., Woudt L. P., Nieuwint R. T., Wassenaar G. M., Groeneveld P., Planta R. J. Transcriptional control of yeast ribosomal protein synthesis during carbon-source upshift. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 23;15(24):10133–10144. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.24.10133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess B., Boiteux A., Krüger J. Cooperation of glycolytic enzymes. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1969;7:149–167. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(69)90016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J. P., Holland M. J. Structural comparison of two nontandemly repeated yeast glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase genes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 25;255(6):2596–2605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland M. J., Yokoi T., Holland J. P., Myambo K., Innis M. A. The GCR1 gene encodes a positive transcriptional regulator of the enolase and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene families in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):813–820. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huet J., Cottrelle P., Cool M., Vignais M. L., Thiele D., Marck C., Buhler J. M., Sentenac A., Fromageot P. A general upstream binding factor for genes of the yeast translational apparatus. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3539–3547. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04114.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karim F. D., Urness L. D., Thummel C. S., Klemsz M. J., McKercher S. R., Celada A., Van Beveren C., Maki R. A., Gunther C. V., Nye J. A. The ETS-domain: a new DNA-binding motif that recognizes a purine-rich core DNA sequence. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1451–1453. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellermann E., Hollenberg C. P. The glucose-and ethanol-dependent regulation of PDC1 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae are controlled by two distinct promoter regions. Curr Genet. 1988 Oct;14(4):337–344. doi: 10.1007/BF00419991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kief D. R., Warner J. R. Coordinate control of syntheses of ribosomal ribonucleic acid and ribosomal proteins during nutritional shift-up in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Nov;1(11):1007–1015. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.11.1007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larkin J. C., Thompson J. R., Woolford J. L., Jr Structure and expression of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae CRY1 gene: a highly conserved ribosomal protein gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1764–1775. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machida M., Jigami Y., Tanaka H. Purification and characterization of a nuclear factor which binds specifically to the upstream activation sequence of Saccharomyces cerevisiae enolase 1 gene. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Sep 15;184(2):305–311. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15020.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAlister L., Holland M. J. Isolation and characterization of yeast strains carrying mutations in the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase genes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15013–15018. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil J. B., Dykshoorn P., Huy J. N., Small S. The DNA-binding protein RAP1 is required for efficient transcriptional activation of the yeast PYK glycolytic gene. Curr Genet. 1990 Dec;18(5):405–412. doi: 10.1007/BF00309909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow B. E., Johnson S. P., Warner J. R. Proteins that bind to the yeast rDNA enhancer. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):9061–9068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagashima K., Kasai M., Nagata S., Kaziro Y. Structure of the two genes coding for polypeptide chain elongation factor 1 alpha (EF-1 alpha) from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1986;45(3):265–273. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90024-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizawa M., Araki R., Teranishi Y. Identification of an upstream activating sequence and an upstream repressible sequence of the pyruvate kinase gene of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):442–451. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogden J. E., Stanway C., Kim S., Mellor J., Kingsman A. J., Kingsman S. M. Efficient expression of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae PGK gene depends on an upstream activation sequence but does not require TATA sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4335–4343. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive sequence comparison with FASTP and FASTA. Methods Enzymol. 1990;183:63–98. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)83007-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R. Searching protein sequence libraries: comparison of the sensitivity and selectivity of the Smith-Waterman and FASTA algorithms. Genomics. 1991 Nov;11(3):635–650. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90071-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer K., Arcangioli B., Guarente L. Yeast HAP1 activator competes with the factor RC2 for binding to the upstream activation site UAS1 of the CYC1 gene. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):9–18. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90750-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santangelo G. M., Tornow J. Efficient transcription of the glycolytic gene ADH1 and three translational component genes requires the GCR1 product, which can act through TUF/GRF/RAP binding sites. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):859–862. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwelberger H. G., Kohlwein S. D., Paltauf F. Molecular cloning, primary structure and disruption of the structural gene of aldolase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Mar 15;180(2):301–308. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14648.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott E. W., Allison H. E., Baker H. V. Characterization of TPI gene expression in isogeneic wild-type and gcr1-deletion mutant strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 11;18(23):7099–7107. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.23.7099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore D., Nasmyth K. Purification and cloning of a DNA binding protein from yeast that binds to both silencer and activator elements. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90095-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanway C., Mellor J., Ogden J. E., Kingsman A. J., Kingsman S. M. The UAS of the yeast PGK gene contains functionally distinct domains. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 11;15(17):6855–6873. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.17.6855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tornow J., Santangelo G. M. Efficient expression of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae glycolytic gene ADH1 is dependent upon a cis-acting regulatory element (UASRPG) found initially in genes encoding ribosomal proteins. Gene. 1990 May 31;90(1):79–85. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90441-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uemura H., Fraenkel D. G. gcr2, a new mutation affecting glycolytic gene expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6389–6396. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vignais M. L., Huet J., Buhler J. M., Sentenac A. Contacts between the factor TUF and RPG sequences. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 25;265(24):14669–14674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]