Abstract
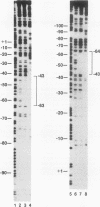
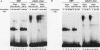
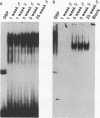
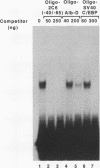
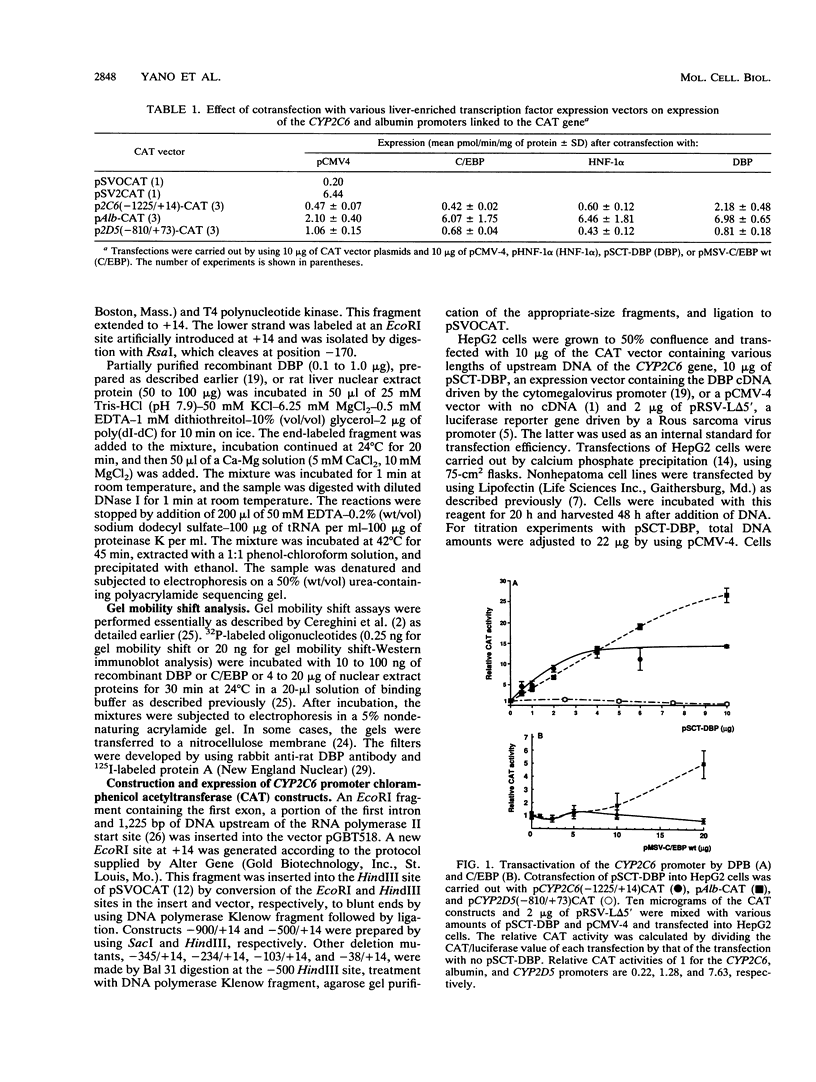
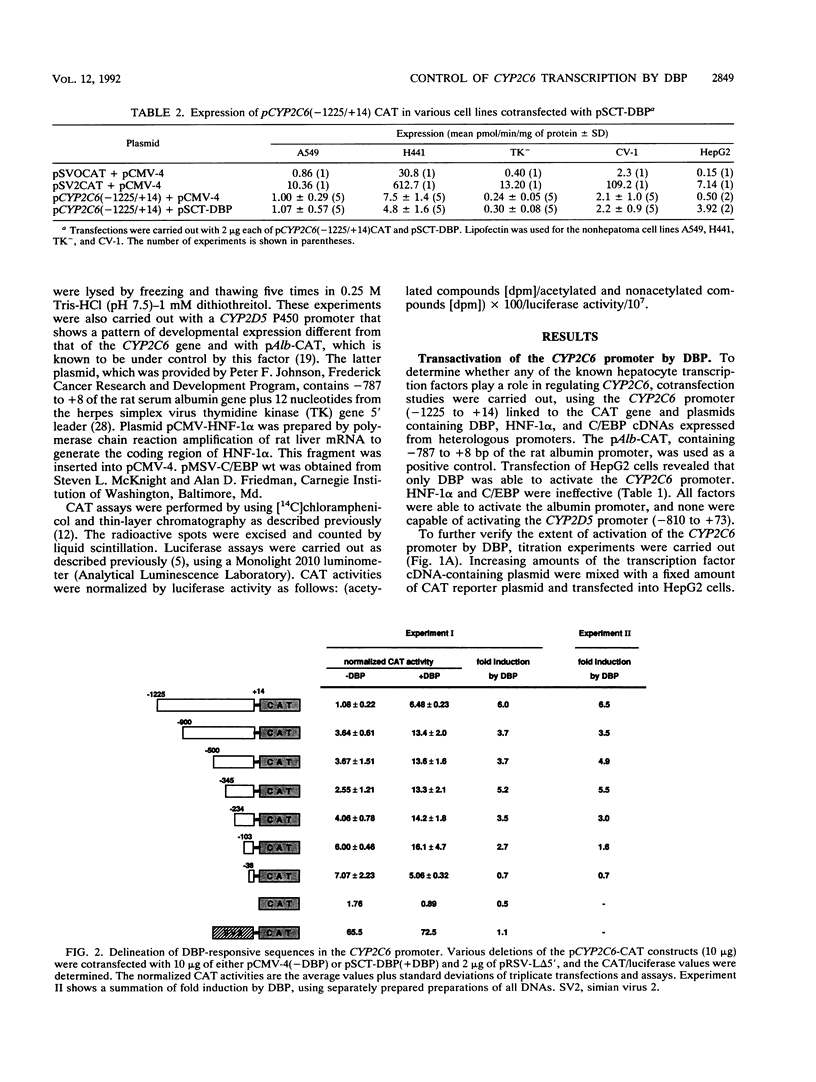
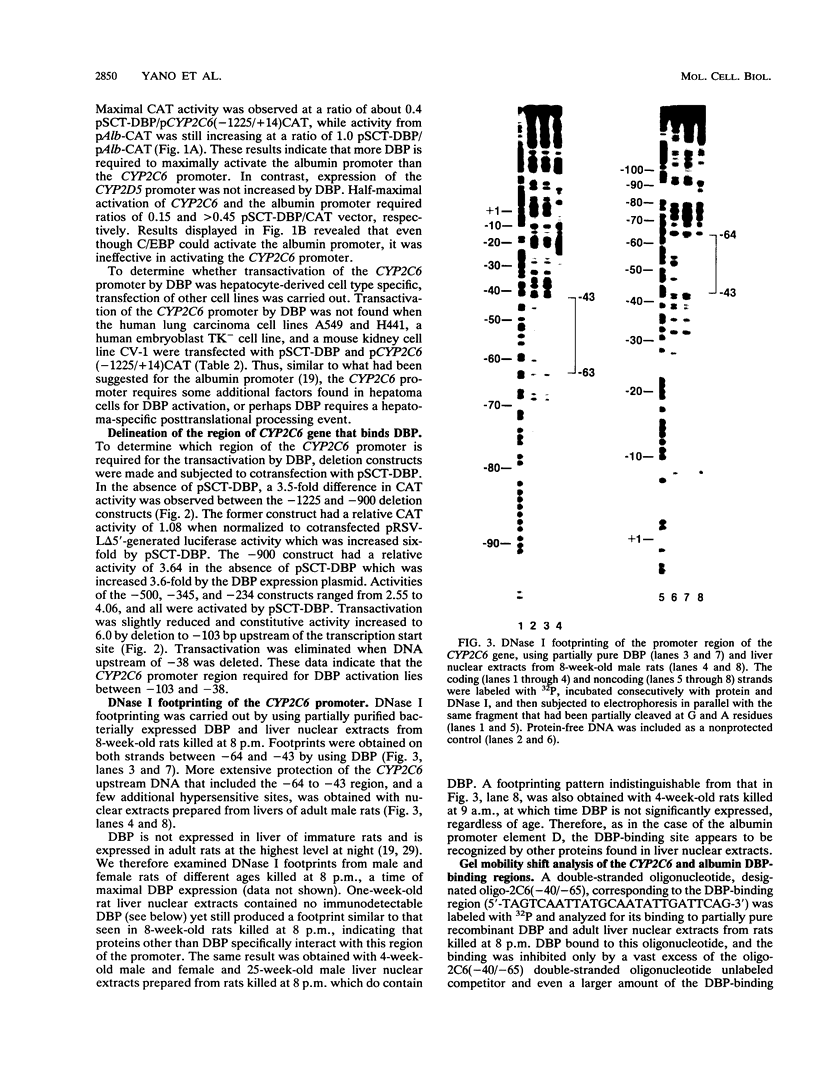
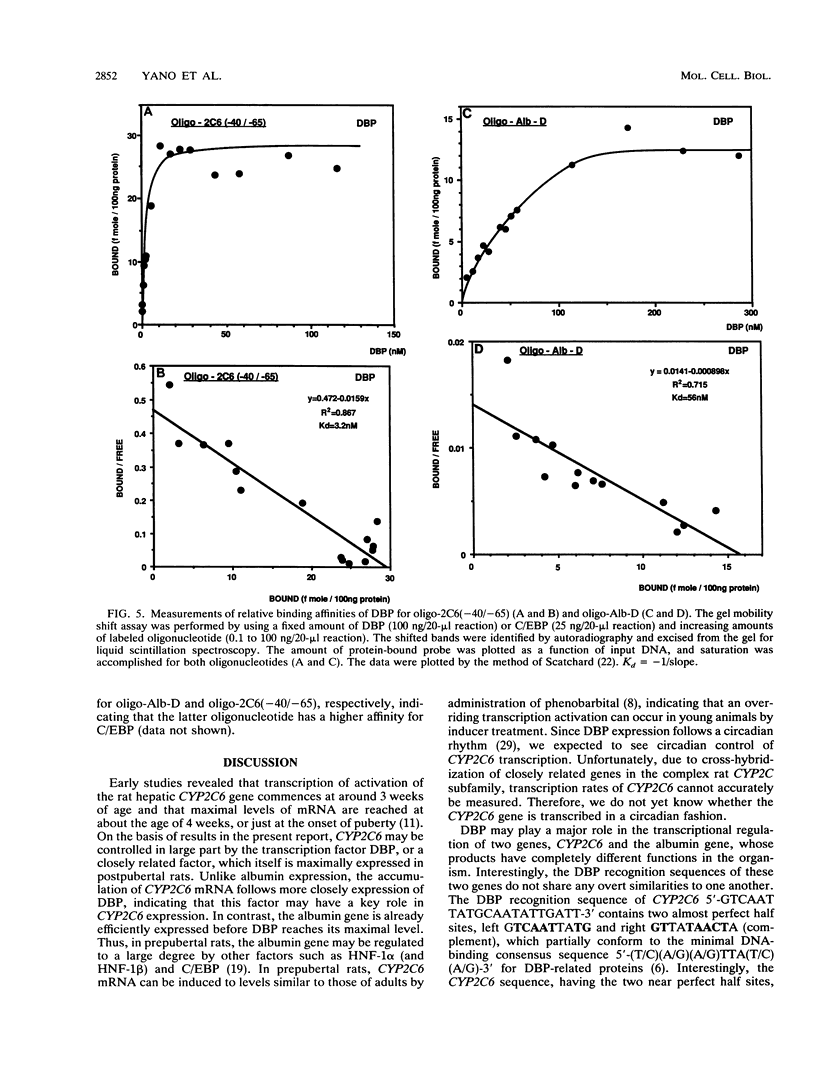
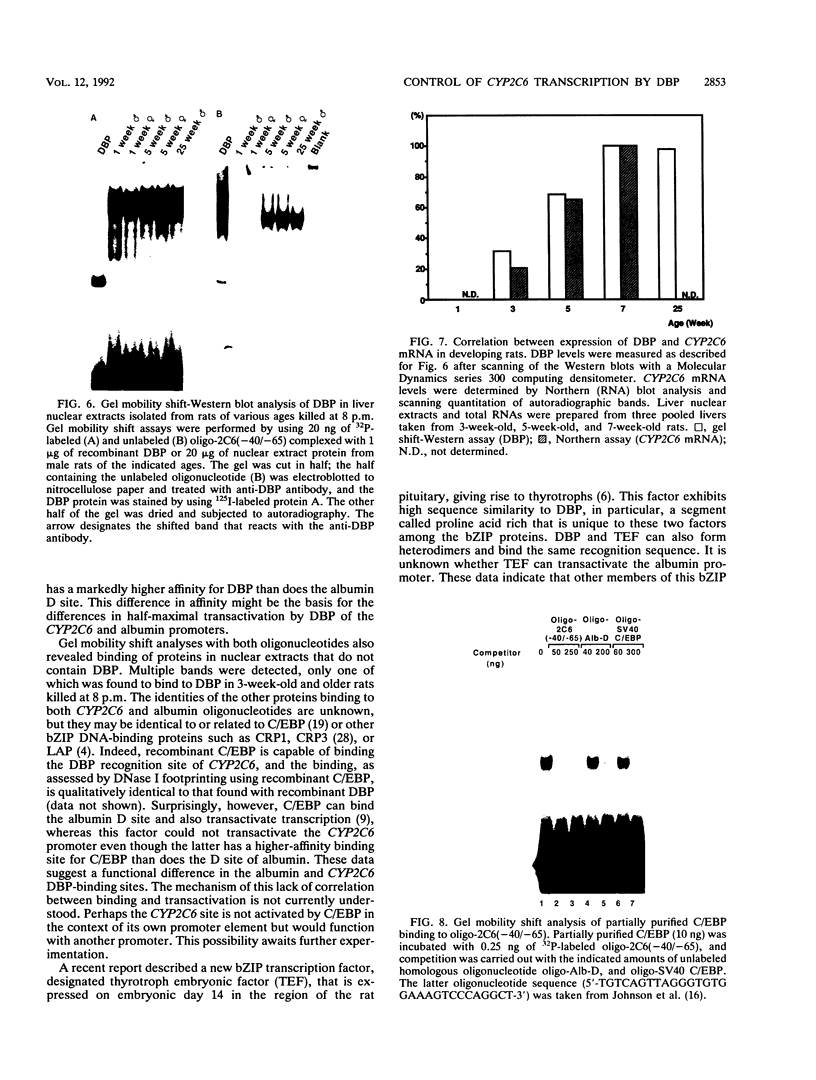
The CYP2C6 gene becomes maximally transcriptionally activated in livers of postpubertal rats. We examined the role of upstream DNA and liver-specific transcription factors in regulation of this promoter by use of transient transfection of heterologous chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene constructs and vectors containing cDNAs encoding the liver-enriched transcription factors HNF-1 alpha, C/EBP, and DBP. Only DBP was able to activate the CYP2C6 promoter in HepG2 cells. Transactivation was not observed in one mouse and two human nonhepatic origin cell lines tested. Analysis of various constructs in which CYP2C6 upstream DNA was deleted revealed that DNA between -38 to -103 was involved in DBP-mediated activation. A partially purified preparation of DBP produced a footprint between -43 and -64 bp upstream of the transcription start site. A 32P-labeled double-stranded oligonucleotide, containing sequence information corresponding to -40 to -65, bound to both partially pure DBP and extracts from livers of rats as young as 1 week and as old as 25 weeks of age, as assessed by gel mobility shift analysis. This binding was eliminated by coincubation with excess unlabeled -40/-65 double-stranded oligonucleotide and by an oligonucleotide corresponding to the D site of the rat albumin gene. A gel mobility shift-Western immunoblot analysis revealed that the -40/-65 sequence bound to DBP only in liver nuclear extracts from rats older than 3 weeks; maximal binding was observed by 7 weeks of age, and no binding was detected from 1-week-old rat liver extracts. Interestingly, the DBP-binding regions of both CYP2C6 and albumin bind to C/EBP, but this factor is capable of transactivating only the latter gene. Although the DBP-binding regions in these two genes share no obvious sequence similarities, the CYP2C6 region contains consensus palindromic half sites for DBP-related binding proteins and affinity for recombinant DBP of 17-fold greater than that of the D site of albumin. This difference in affinity is probably responsible for the markedly lower amounts of DBP required for half-maximal activation of the CYP2C6 promoter, as compared with the albumin promoter, in transactivation transfection assays. These data indicate that the CYP2C6 gene may be regulated, at least in part, by DBP, a liver transcription factor produced when rats reach puberty that may also be involved in maintenance of albumin gene transcription.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson S., Davis D. L., Dahlbäck H., Jörnvall H., Russell D. W. Cloning, structure, and expression of the mitochondrial cytochrome P-450 sterol 26-hydroxylase, a bile acid biosynthetic enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):8222–8229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cereghini S., Blumenfeld M., Yaniv M. A liver-specific factor essential for albumin transcription differs between differentiated and dedifferentiated rat hepatoma cells. Genes Dev. 1988 Aug;2(8):957–974. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.8.957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cereghini S., Raymondjean M., Carranca A. G., Herbomel P., Yaniv M. Factors involved in control of tissue-specific expression of albumin gene. Cell. 1987 Aug 14;50(4):627–638. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90036-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Descombes P., Chojkier M., Lichtsteiner S., Falvey E., Schibler U. LAP, a novel member of the C/EBP gene family, encodes a liver-enriched transcriptional activator protein. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1541–1551. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drolet D. W., Scully K. M., Simmons D. M., Wegner M., Chu K. T., Swanson L. W., Rosenfeld M. G. TEF, a transcription factor expressed specifically in the anterior pituitary during embryogenesis, defines a new class of leucine zipper proteins. Genes Dev. 1991 Oct;5(10):1739–1753. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.10.1739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felgner P. L., Gadek T. R., Holm M., Roman R., Chan H. W., Wenz M., Northrop J. P., Ringold G. M., Danielsen M. Lipofection: a highly efficient, lipid-mediated DNA-transfection procedure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7413–7417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedberg T., Waxman D. J., Atchison M., Kumar A., Haaparanta T., Raphael C., Adesnik M. Isolation and characterization of cDNA clones for cytochromes P-450 immunochemically related to rat hepatic P-450 form PB-1. Biochemistry. 1986 Dec 2;25(24):7975–7983. doi: 10.1021/bi00372a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A. D., Landschulz W. H., McKnight S. L. CCAAT/enhancer binding protein activates the promoter of the serum albumin gene in cultured hepatoma cells. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1314–1322. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. J., Song B. J., Hardwick J. P. Pregnenolone 16 alpha-carbonitrile-inducible P-450 gene family: gene conversion and differential regulation. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2969–2976. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. J. The molecular biology of cytochrome P450s. Pharmacol Rev. 1988 Dec;40(4):243–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski K., Carneiro M., Schibler U. Tissue-specific in vitro transcription from the mouse albumin promoter. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):767–776. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90519-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., Landschulz W. H., Graves B. J., McKnight S. L. Identification of a rat liver nuclear protein that binds to the enhancer core element of three animal viruses. Genes Dev. 1987 Apr;1(2):133–146. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.2.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F. Transcriptional activators in hepatocytes. Cell Growth Differ. 1990 Jan;1(1):47–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maire P., Wuarin J., Schibler U. The role of cis-acting promoter elements in tissue-specific albumin gene expression. Science. 1989 Apr 21;244(4902):343–346. doi: 10.1126/science.2711183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsunaga T., Nagata K., Holsztynska E. J., Lapenson D. P., Smith A., Kato R., Gelboin H. V., Waxman D. J., Gonzalez F. J. Gene conversion and differential regulation in the rat P-450 IIA gene subfamily. Purification, catalytic activity, cDNA and deduced amino acid sequence, and regulation of an adult male-specific hepatic testosterone 15 alpha-hydroxylase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):17995–18002. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller C. R., Maire P., Schibler U. DBP, a liver-enriched transcriptional activator, is expressed late in ontogeny and its tissue specificity is determined posttranscriptionally. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):279–291. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90808-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebert D. W., Jones J. E. Regulation of the mammalian cytochrome P1-450 (CYP1A1) gene. Int J Biochem. 1989;21(3):243–252. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(89)90182-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebert D. W., Nelson D. R., Coon M. J., Estabrook R. W., Feyereisen R., Fujii-Kuriyama Y., Gonzalez F. J., Guengerich F. P., Gunsalus I. C., Johnson E. F. The P450 superfamily: update on new sequences, gene mapping, and recommended nomenclature. DNA Cell Biol. 1991 Jan-Feb;10(1):1–14. doi: 10.1089/dna.1991.10.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song B. J., Gelboin H. V., Park S. S., Yang C. S., Gonzalez F. J. Complementary DNA and protein sequences of ethanol-inducible rat and human cytochrome P-450s. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of the rat enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 15;261(35):16689–16697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueno T., Gonzalez F. J. Transcriptional control of the rat hepatic CYP2E1 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4495–4505. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umeno M., Morris S., Matsunaga E., Gelboin H. V., Gonzalez F. J. Sequence of the 5' end of the developmentally regulated rat P450 PB1 (P450IIC6) gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 11;16(13):6249–6249. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.13.6249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman D. J., Azaroff L. Phenobarbital induction of cytochrome P-450 gene expression. Biochem J. 1992 Feb 1;281(Pt 3):577–592. doi: 10.1042/bj2810577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams S. C., Cantwell C. A., Johnson P. F. A family of C/EBP-related proteins capable of forming covalently linked leucine zipper dimers in vitro. Genes Dev. 1991 Sep;5(9):1553–1567. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.9.1553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuarin J., Schibler U. Expression of the liver-enriched transcriptional activator protein DBP follows a stringent circadian rhythm. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1257–1266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90421-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaphiropoulos P. G., Mode A., Norstedt G., Gustafsson J. A. Regulation of sexual differentiation in drug and steroid metabolism. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Apr;10(4):149–153. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90167-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet J. R., Wood K. V., DeLuca M., Helinski D. R., Subramani S. Firefly luciferase gene: structure and expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):725–737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]